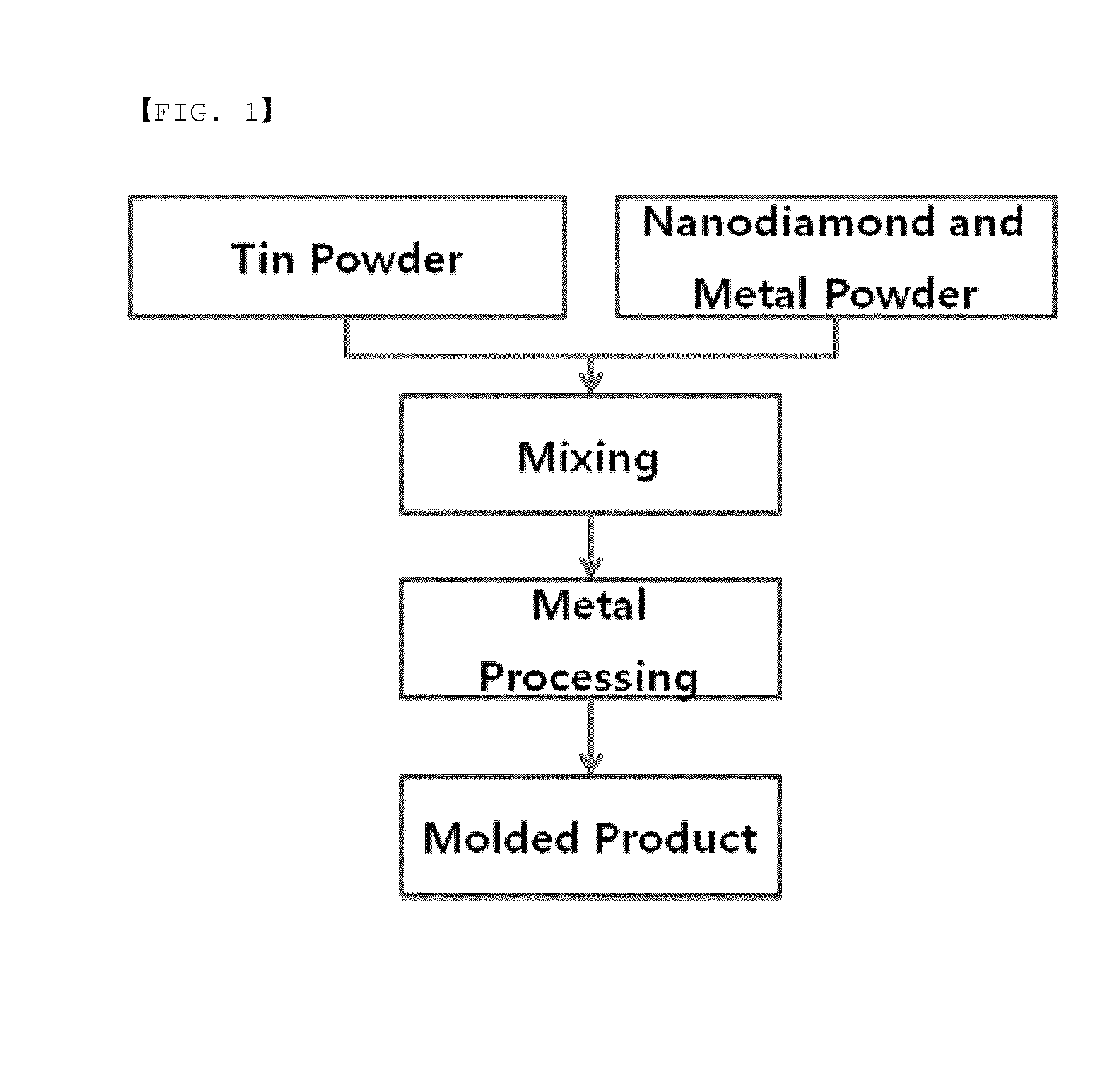
Low heat capacity composite for thermal cycler
a composite and thermal cycler technology, applied in biochemical apparatus and processes, specific use of bioreactors/fermenters, biomass after-treatment, etc., can solve the problems of low heat capacity of heat block, difficult use of aluminum in high-speed pcr, and high heat conductivity of heat block. , to achieve the effect of low heat capacity, excellent heat property and reduced raw material cos
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 7 to 12
Manufacture of Molded product from Tin-Nanodiamond-Silver Composite Powder
[0033]Molding was performed to prepare tin-nanodiamond-silver mixturecompositespecimensbyusingahigh-temperaturepressunder the same conditions as Example 1, except that a mixture of tin, nanodiamond, and silver at aratio of 90:5:5 (Example 7), amixture of tin, nanodiamond, and silver at a ratio of 85:5:10 (Example 8), a mixture of tin, nanodiamond, and silver at a ratio of 75:5:20 (Example 9), a mixture of tin, nanodiamond, and silver at a ratio of 46:5:49 (Example 10), a mixture of tin, nanodiamond, and silver at a ratio of 94:1:5 (Example 11), and a mixture of tin, nanodiamond, and silver at a ratio of 89:1:10 (Example 12) were used. The prepared specimens were subjected to calorimetry under the same condition as Example 1, and the calorimetric results were tabulated in Table 2.
TABLE 2Calorimetric results of tin-nanodiamond-silver mixture compositesHeatHeatvolumetricTinNanodiamondSilverDensityconductivitycapa...
examples 13 and 14
Manufacture of Molded Product from Tin-Copper Composite Powder
[0035]Moldingwasperformedtopreparetin-coppermixturecomposite specimens by using a high-temperature press under the same conditions as Example 1, except that a mixture of tin powder and copper powder at a ratio of 95:5 (Example 13) and a mixture of tin powder and copper powder at a ratio of 90:10 (Example 14) were used.
[0036]The prepared specimens were subjected to calorimetry under the same condition as Example 1, and the calorimetric results were tabulated in Table 3.
TABLE 3Calorimetric results of tin-copper mixture compositesHeatHeatvolumetricTinCopperdensityconductivitycapacityheat capacitySpecimencontentcontent(g / ml)W / (m K)J / (g K)J / (cm3 K)Example 1395% 5%7.17330.1320.2231.600Example 1490%10%7.21823.0660.2151.552Comparative 0%Al 100%2.696179.0000.9142.464example 1
[0037]It can be confirmed from Table 3 that each of the present examples has excellent heat capacity and volumetric heat capacity, as compared with Comparati...
example 15
Manufacture of Molded Product from Tin-Copper-Antimony Composite Powder
[0038]Molding was performed to prepare a tin-copper-antimony mixture composite specimen by using a high-temperature press under the same conditions as Example 1, except that a mixture of tin powder, copper powder, and antimony powder at a ratio of 90:4:6 was used.
[0039]The prepared specimen was subjected to calorimetry under the same condition as Example 1. The results confirmed that that the present example has a heat conductivity of 37.443 W / (m K), heat capacity of 0.238 J / (g K) , and volumetric heat capacity of 1.748 J / (cm3 K) , which were excellent, as compared with Compared example 1 case where the existing aluminum powder was used alone.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volumetric heat capacity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com