Stratified gate dielectric stack for gate dielectric leakage reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
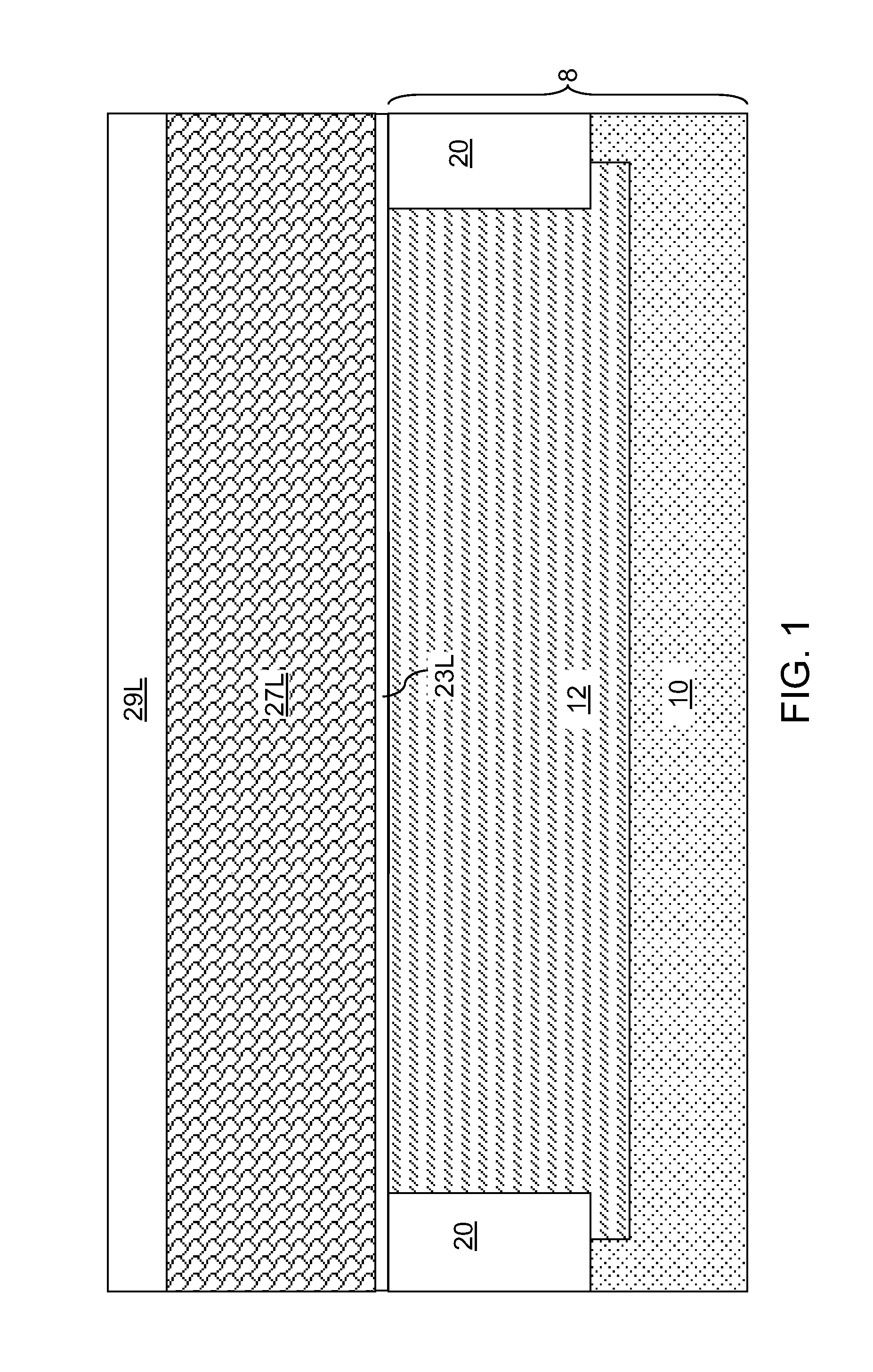
[0031]Referring to FIG. 1, a first exemplary semiconductor structure according to the present disclosure includes a semiconductor substrate 8, on which various components of field effect transistors are subsequently formed. The semiconductor substrate 8 can be a bulk substrate including a bulk semiconductor material throughout, or a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate (not shown) containing a top semiconductor layer, a buried insulator layer located under the top semiconductor layer, and a bottom semiconductor layer located under the buried insulator layer.
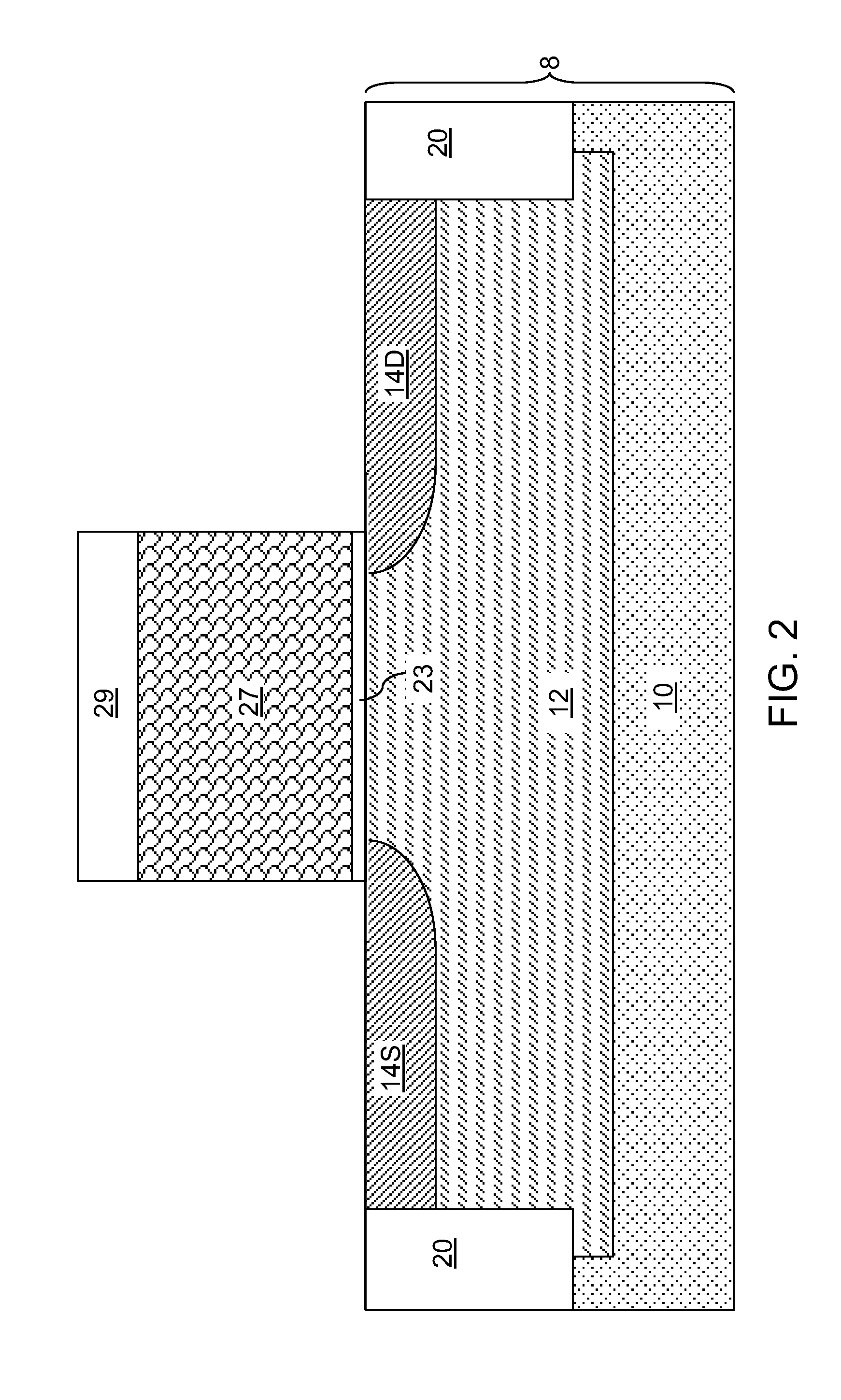
[0032]Various portions of the semiconductor material in the semiconductor substrate 8 can be doped with electrical dopants of n-type or p-type at different dopant concentration levels. For example, the semiconductor substrate 8 may include an underlying semiconductor layer 10 and an active region 12 having a doping different from the doping of the underlying semiconductor layer 10. The active region 12 can be a doped well. ...
second embodiment
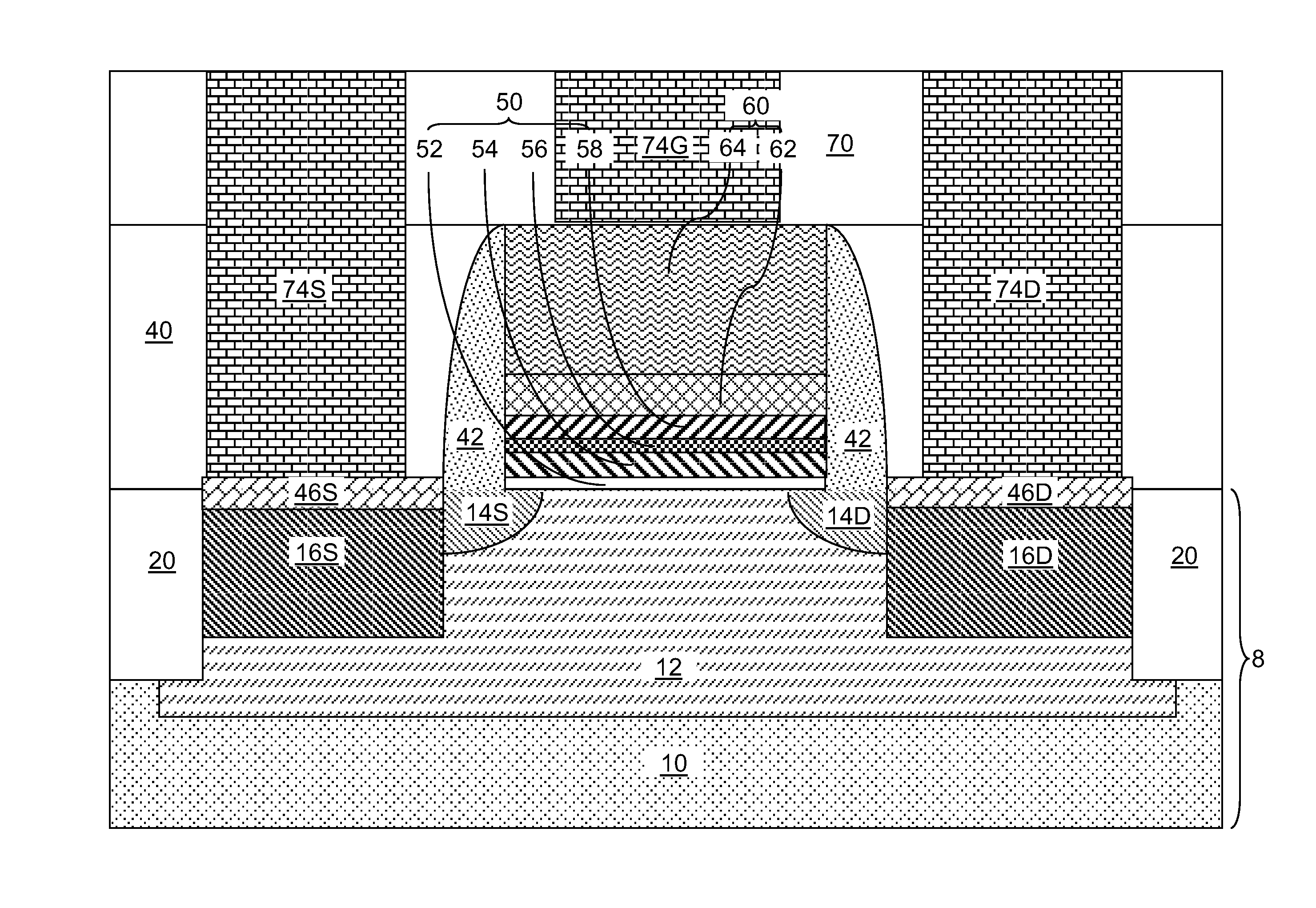
[0086]Referring to FIG. 13, a second exemplary semiconductor structure including a finFET having a gate dielectric 50 including a stratified gate dielectric stack is shown according to the present disclosure. A semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate including a handle substrate 110, a buried insulator layer 112, and a top semiconductor layer can be employed to form a semiconductor fin 9 on a substrate 8′ including the stack of the handle substrate 110 and the buried insulator layer 112. A body region 12′, a source extension region 14S, a drain extension region 14D can be formed within the semiconductor fin 9 prior to formation of a disposable gate structure straddling over the semiconductor fin 9. In the second exemplary semiconductor structure, the semiconductor fin 9 formed on a stack, from bottom to top, of a handle substrate 110 and a buried insulator layer 112 constitutes a semiconductor substrate.
[0087]The processing steps of FIGS. 1-7, one of 8 and 8A, 9-11, and one of 12...
third embodiment
[0090]Referring to FIG. 14, a third exemplary semiconductor structure according to the present disclosure is shown. In the third exemplary semiconductor structure, after formation of an interfacial dielectric layer, each of the first high-k gate dielectric layer 54L, the band-gap-disrupting dielectric layer 56L, the second high-k gate dielectric layer 58L, the work function material layer 62L, and the conductive material layer 64L, the work function material layer, and the conductive material layer 64L is deposited as planar layers below a temperature above which inter-atomic diffusion occurs at a detectable level across the first atomic interface or across the second atomic interface in lieu of deposition of the disposable gate level layers (23L, 27L, 29L) illustrated in FIG. 1. The temperature above which the inter-atomic diffusion occurs across the first atomic interface or across the second atomic interface is less than 800 degrees Celsius, and is typically in a range between 70...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com