Agents for preventing and treating disorders involving modulation of the ryanodine receptors
a technology of ryanodine receptor and agent, which is applied in the direction of biocide, drug composition, metabolic disorder, etc., can solve the problems of increased compensatory energy consumption, increased ryr1 channel closed state and intracellular casup>2+/sup> leakage, and significant acceleration of muscle fatigue. , to achieve the effect of enhancing binding of fkbp proteins and reducing affinity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
RyR2 PKA Phosphorylation and FKBP12.6 Binding
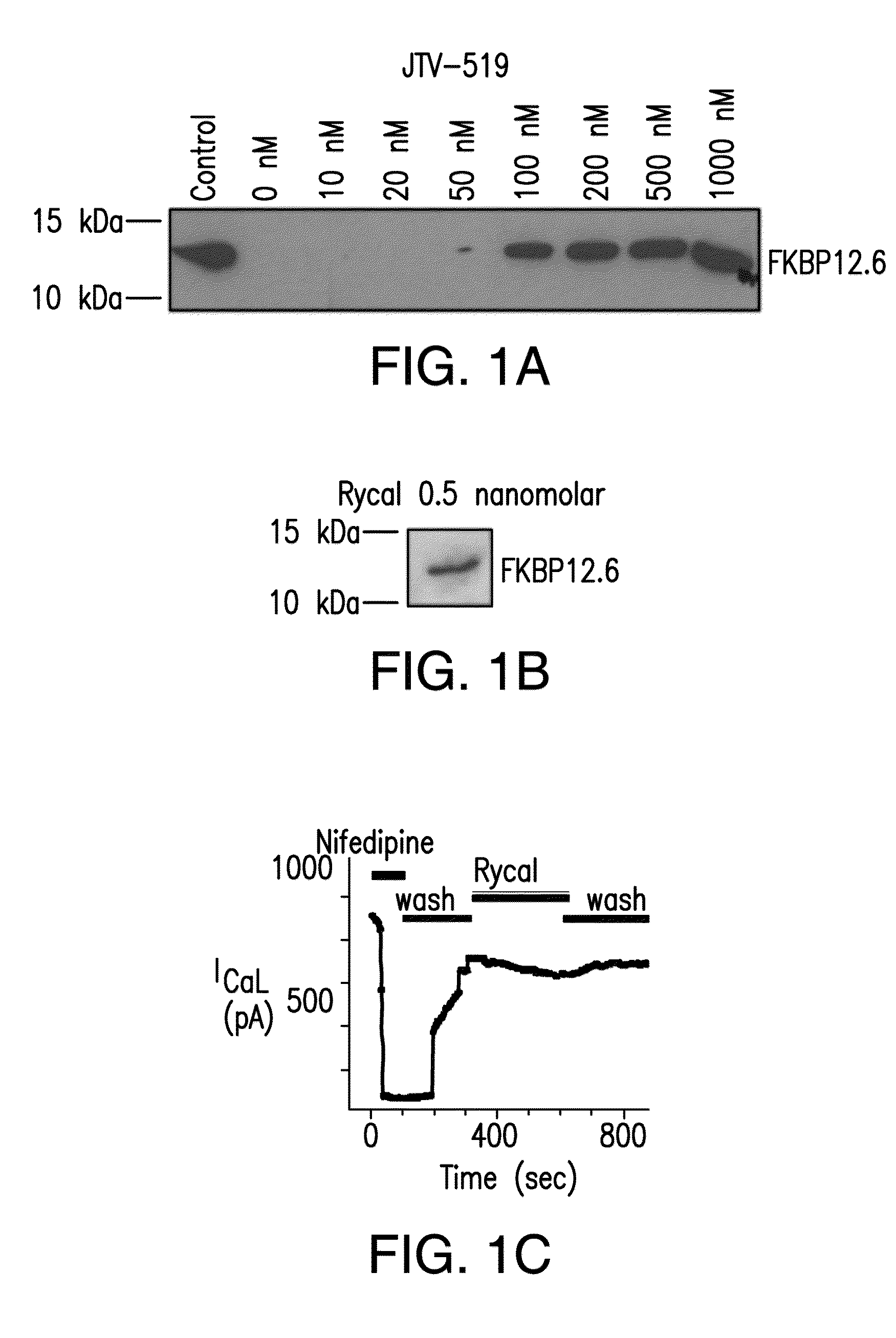
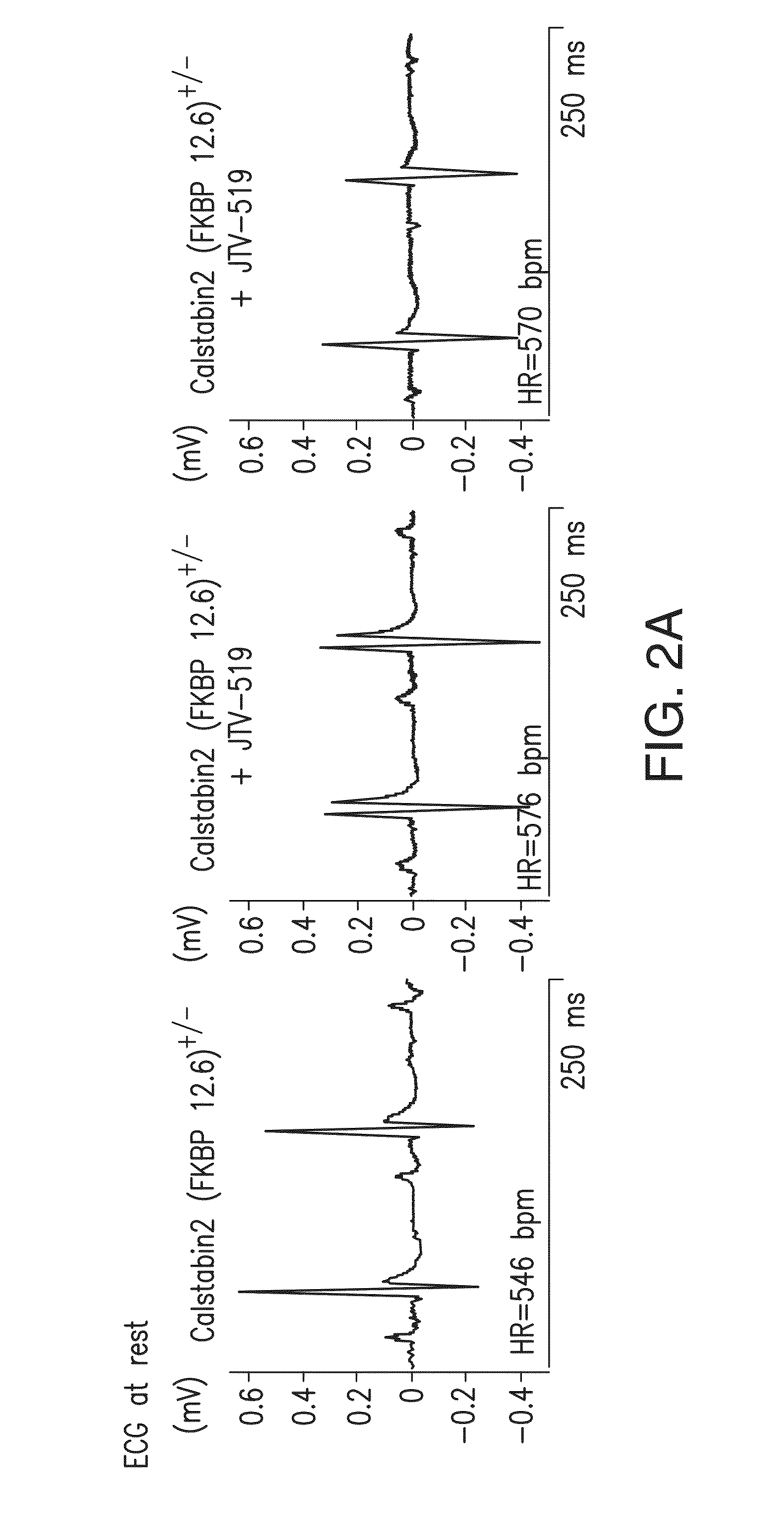
[0488]Cardiac SR membranes are prepared, as previously described (Marx, et al., PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell, 101:365-76, 2000; Kaftan, et al., Effects of rapamycin on ryanodine receptor / Ca(2+)-release channels from cardiac muscle. Circ. Res., 78:990-97, 1996). 35S-labelled FKBP12.6 was generated using the TNT™ Quick Coupled Transcription / Translation system from Promega (Madison, Wis.). [3H] ryanodine binding is used to quantify RyR2 levels. 100 μg of microsomes are diluted in 100 μl of 10-mM imidazole buffer (pH 6.8), incubated with 250-nM (final concentration) [35S]-FKBP12.6 at 37° C. for 60 min, then quenched with 500 μl of ice-cold imidazole buffer. Samples are centrifuged at 100,000 g for 10 min and washed three times in imidazole buffer. The amount of bound [35S]-FKBP12.6 is determined by liquid scintillation counting of t...
example 2
Immunoblots
[0489]Immunoblotting of microsomes (50 μg) is performed as described, with anti-FKBP12 / 12.6 (1:1,000), anti-RyR-5029 (1:3,000) (Jayaraman, et al., FK506 binding protein associated with the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor). J. Biol. Chem., 267:9474-77, 1992), or anti-phosphoRyR2-P2809 (1:5,000) for 1 h at room temperature (Reiken, et al., Beta-blockers restore calcium release channel function and improve cardiac muscle performance in human heart failure. Circulation, 107:2459-66, 2003). The P2809-phosphoepitope-specific anti-RyR2 antibody is an affinity-purified polyclonal rabbit antibody, custom-made by Zymed Laboratories (San Francisco, Calif.) using the peptide, CRTRRI-(pS)-QTSQ, which corresponds to RyR2 PKA-phosphorylated at Ser2809. After incubation with HRP-labeled anti-rabbit IgG (1:5,000 dilution; Transduction Laboratories, Lexington, Ky.), the blots are developed using ECL (Amersham Pharmacia, Piscataway, N.J.).
example 3
Single-Channel Recordings
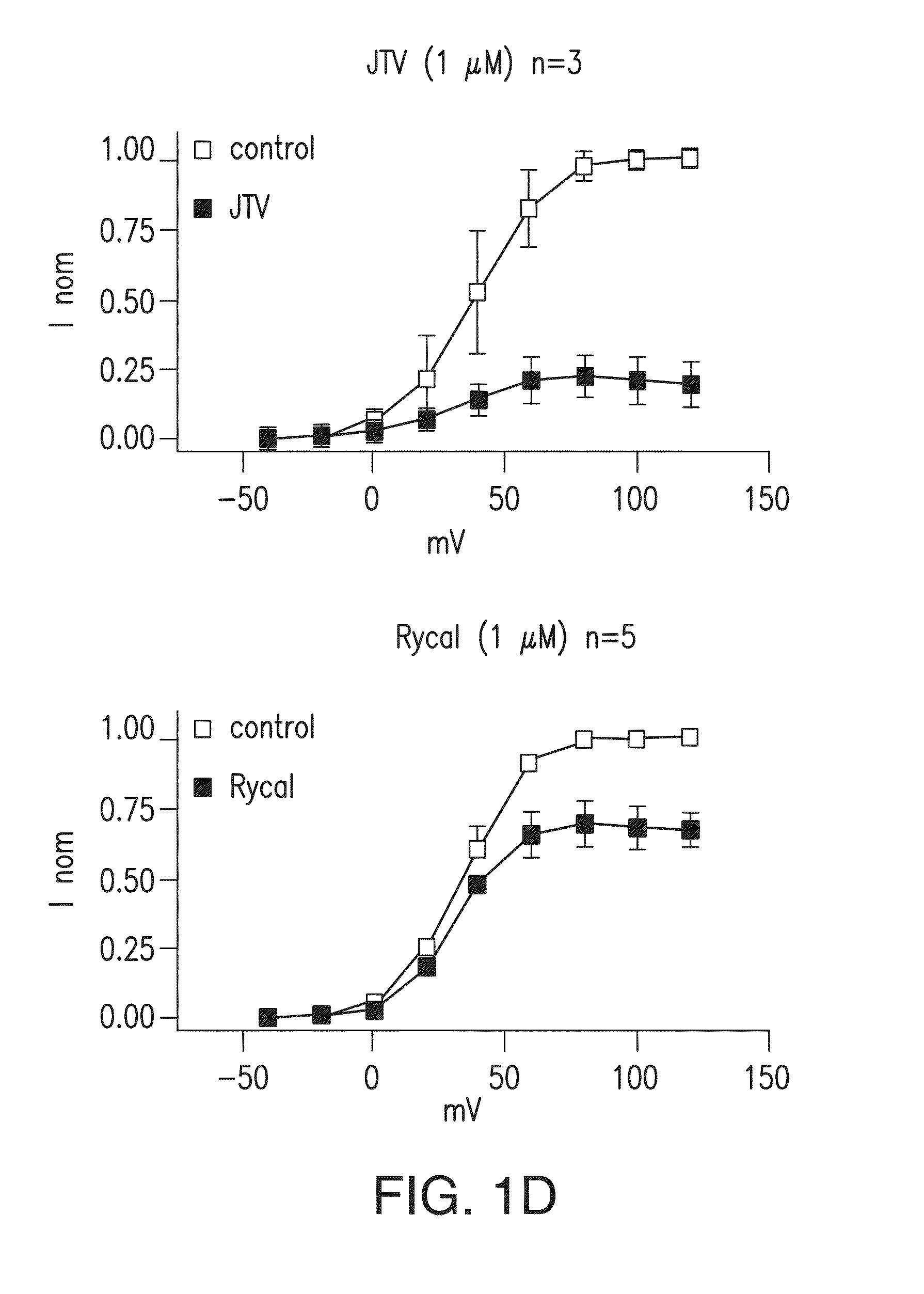
[0490]Single-channel recordings of native RyR2 from mouse hearts, or recombinant RyR2, are acquired under voltage-clamp conditions at 0 mV, as previously described (Marx, et al., PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell, 101:365-76, 2000). Symmetric solutions used for channel recordings are: trans compartment—HEPES, 250 mmol / L; Ba(OH)2, 53 mmol / L (in some experiments, Ba(OH)2 is replaced by Ca(OH)2); pH 7.35; and cis compartment—HEPES, 250 mmol / L; Tris-base, 125 mmol / L; EGTA, 1.0 mmol / L; and CaCl2, 0.5 mmol / L; pH 7.35. Unless otherwise indicated, single-channels recordings are made in the presence of 150-nM [Ca2+] and 1.0-mM [Mg2+] in the cis compartment. Ryanodine (5 mM) is applied to the cis compartment to confirm identity of all channels. Data is analyzed from digitized current recordings using Fetchan software (Axon Instruments, Union City, Calif.). All da...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com