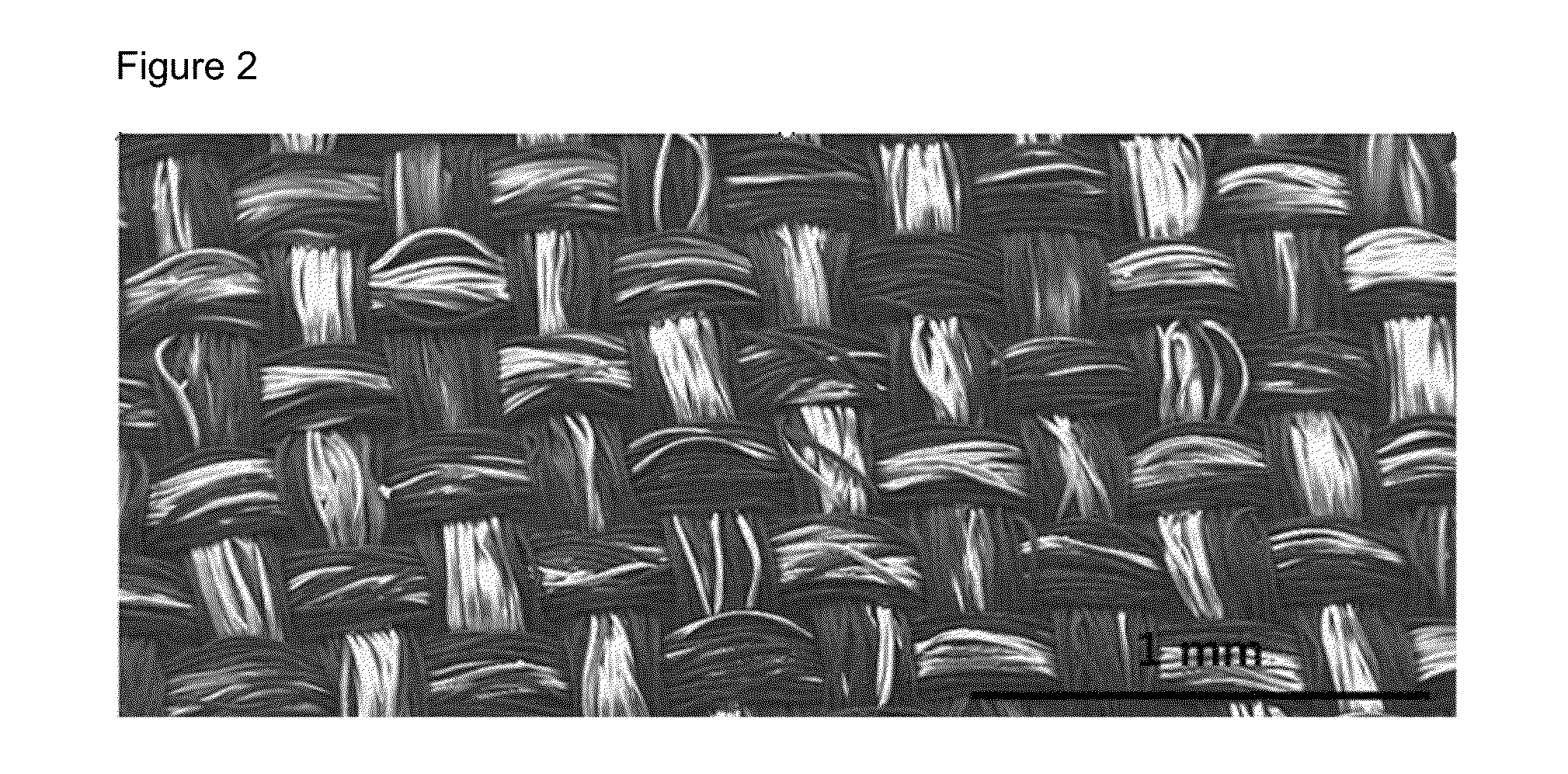Super-hydrophobic fiber having needle-shaped NANO structure on its surface, method for fabricating the same and fiber product comprising the same
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example 1
eedle Fiber
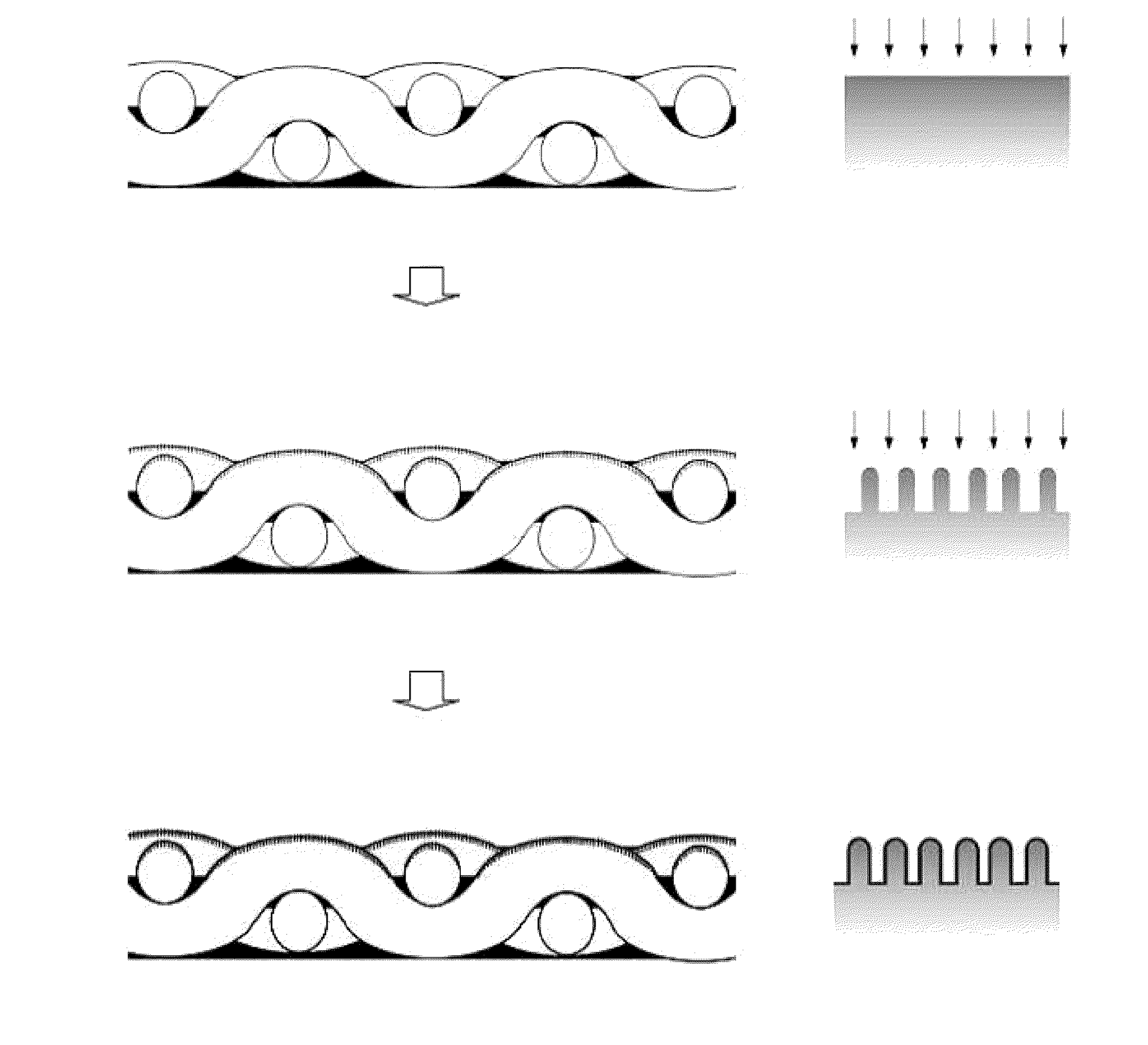
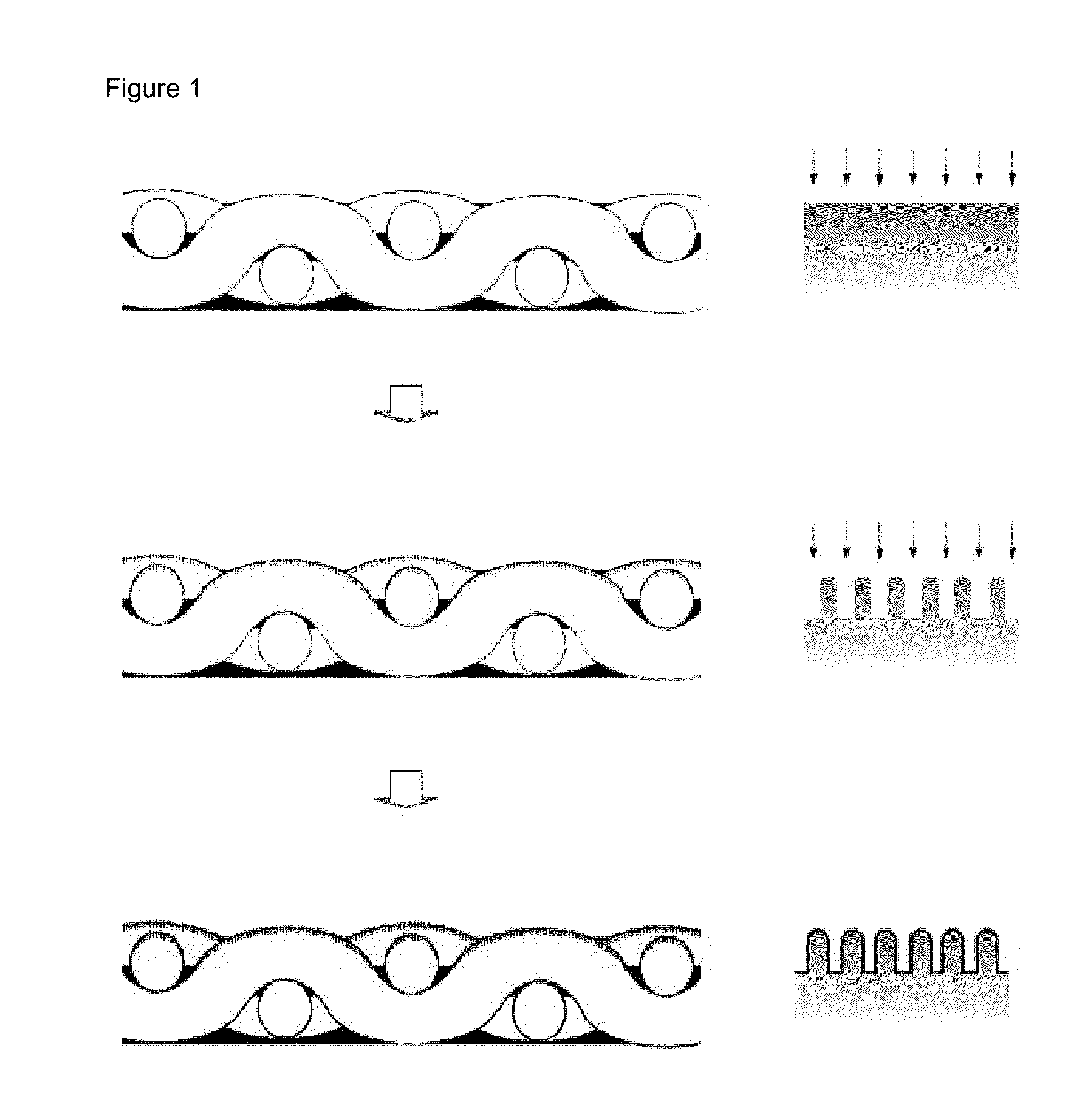
[0069]A polyester fabric was used as pre-treating fiber, and hexamethyldisiloxane was used as a hydrophobic material. First, the polyester fabric was etched for about 30 min using an ion-beam etching device by a plasma etching method (dry etching) using O2 as a reactive gas under conditions of a pressure of 20 mTorr, an oxygen flow rate of 10 sccm, an RF-power of 250 W, and a bias voltage of 400V, thereby fabricating a nano-needle fiber having a surface including needle-shaped nano structures, as illustrated in the middle of FIG. 1.
preparation example 2
Hydrophobic Fiber
[0070]Plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) was used to perform a plasma treatment on the surface (on the surface of the nano-needle fiber) of needle-shaped nano structures in Preparation Example 1 for about 15 sec while hexamethyldisiloxane was allowed to flow at 10 sccm under conditions of a pressure of 10 mTorr, an RF-power of 250 W, and a bias voltage of 400 V, and a coating layer including hexamethyldisiloxane as a hydrophobic material was formed as illustrated in the bottom of FIG. 1, thereby fabricating super-hydrophobic fiber.
[0071]FIGS. 2 and 3 are photographs of the surface of the pre-treating fiber before the etching step was performed, taken at various magnifications by using a scanning electron microscope. It can be seen that the pre-treating fiber before the etching step was performed had a significantly smooth surface. However, FIG. 4 is photographs of the surface of the nano-needle fiber after the etching step was performed, taken by scan...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com