Stem cell-derived hepatocytes in co-culture and uses thereof
a technology of stem cells and hepatocytes, which is applied in the field of in vitro cultures of human hepatic cells (hepatocytes), can solve the problems of severely limited resources of phhs and substantially limit their use in toxicology screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Micropatterned Pure iHep Cultures
[0099]Micropatterned cultures of primary iHeps (Cellular Dynamics International) were first prepared to confirm the ability of iHeps to exhibit characteristics of human hepatocytes. Initial iHep processing proceeded as follows. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived human hepatocytes were provided fresh in suspension by Cellular Dynamics International (CDI). Using a published protocol, CDI generates ˜95% pure iHeps (via α1-antitrypsin). Upon arrival, iHeps were processed according to manufacturer-supplied protocols. Briefly, iHep cell aggregates were rinsed with divalent cation-free Hank's Balanced Saline Solution (HBSS, Hyclone), dissociated with 0.5% trypsin-EDTA (Life Technologies), neutralized with a 1:1 solution of Roswell Park Memorial Institute 1640 (RPMI, Life Technologies) media and fetal bovine serum (FBS, Life Technologies), and pelleted via centrifugation. iHeps were re-suspended in Kryothaw (SciKon Innovation, Inc.) and further centrifuge...
example 2
Micropatterned Co-Cultures of iHeps and iMPHs
[0103]Micropatterned co-cultures (iMPCCs) of iHeps and iMPHs were established using the following methods.
[0104]Murine embryonic 3T3-J2 fibroblasts were the gift of Howard Green (Harvard Medical School). Cells were cultured at 37° C., 10% CO2 in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) with high glucose, 10% (v / v) calf serum, and 1% (v / v) penicillin-streptomycin.
[0105]Tissue culture polystyrene 24-well and 96-well plates (BD Falcon) were homogeneously coated with 25 μg / mL rat tail collagen I (BD Biosciences) and subjected to soft lithography-based methods to micropattern circular collagenous islands (500 μm diameter with 1200 μm center-to-center spacing). To establish iMPCCs, iHeps were seeded at a density of 6.66×105 cells / mL into micropatterned wells (300 μL and 50 μL per well in 24-well and 96-well plates, respectively) and agitated every 20 minutes to distribute cells for selective binding to collagen islands. Following 4-5 h for com...
example 3
Qualitative Assessment of iMPCC Stability
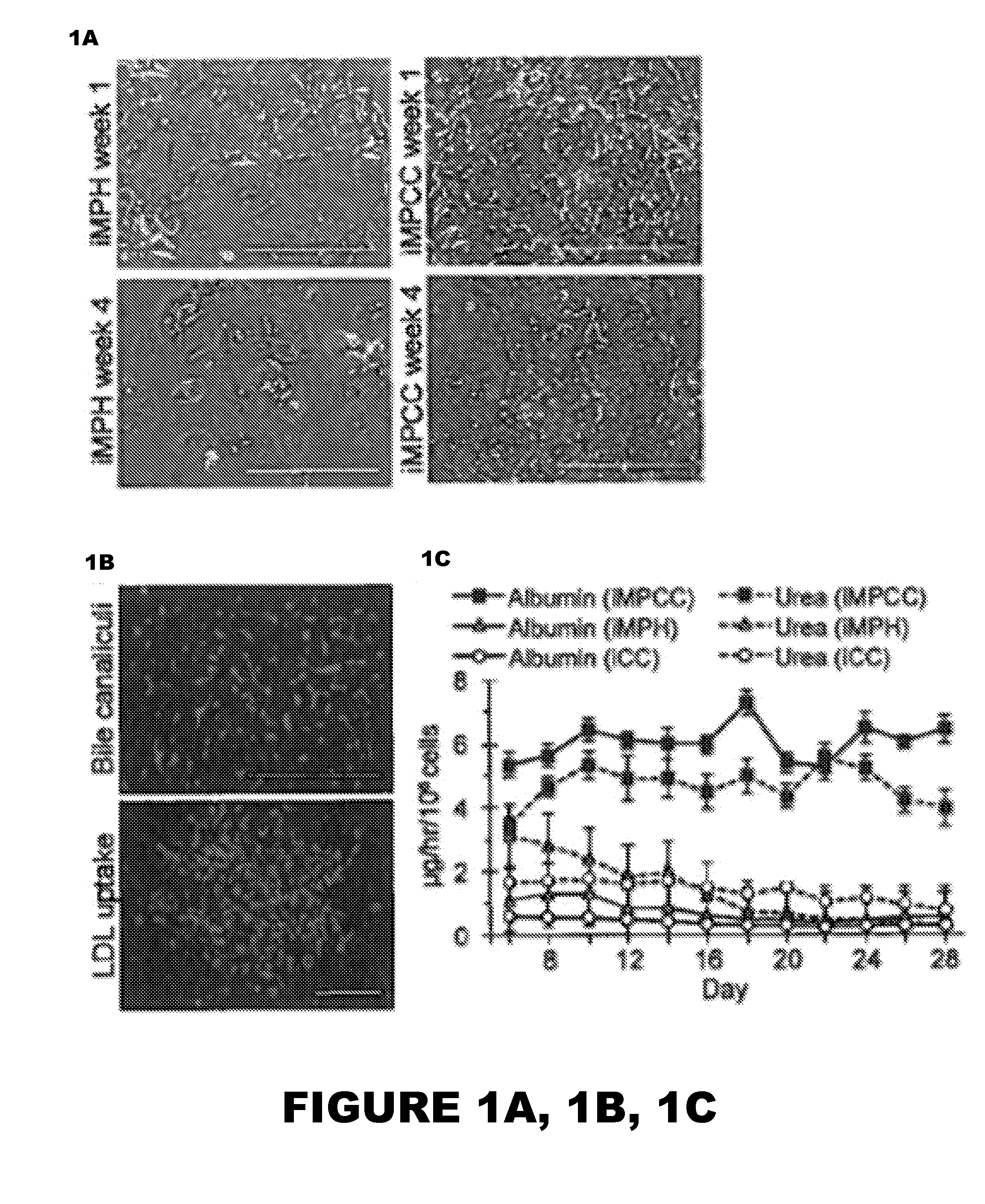
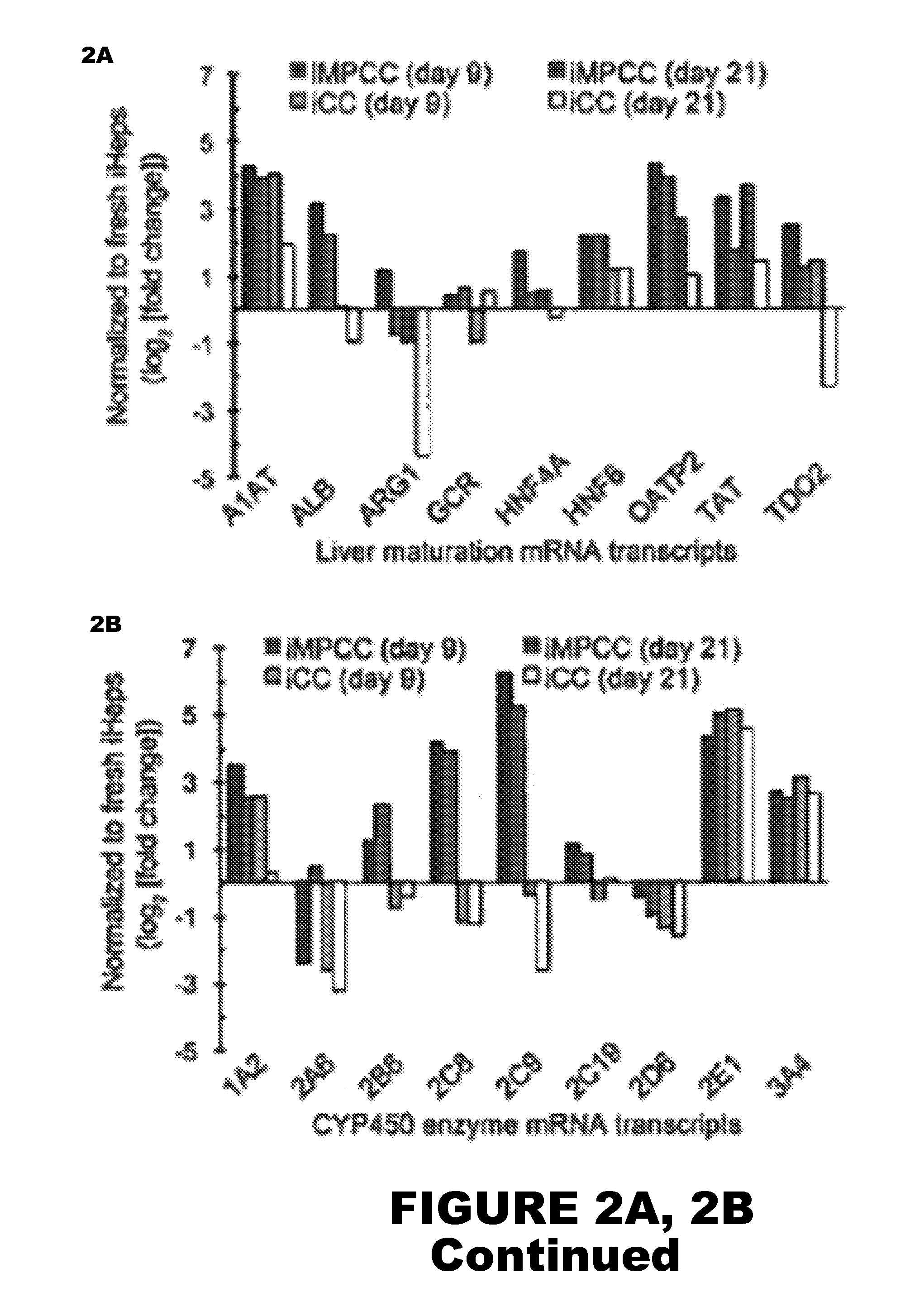
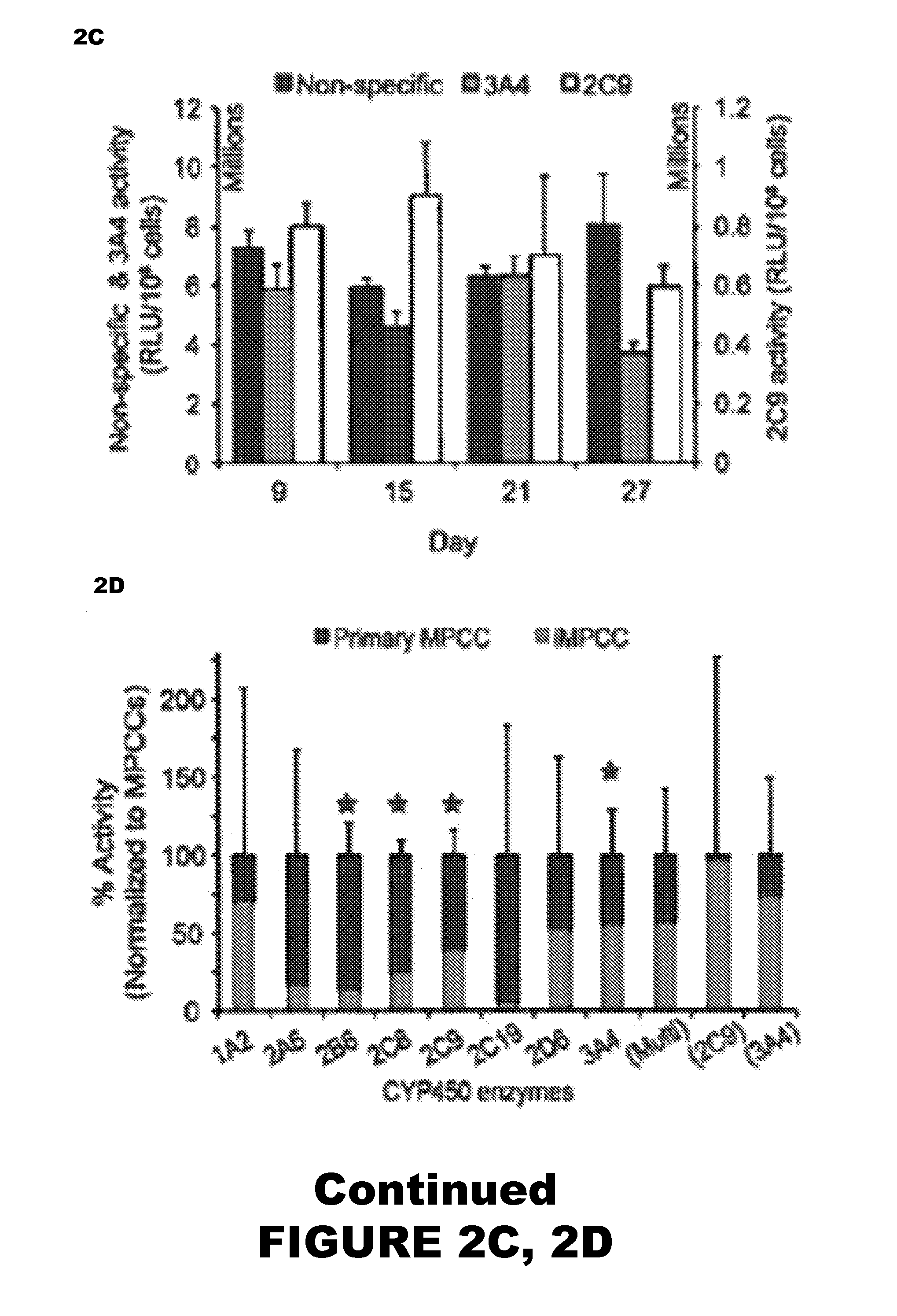
[0107]To qualitatively assess iMPCC stability, iHep morphology was monitored using an EVOS®FL cell imaging system with standard 10× or 20× objectives and phase contrast. For immunofluorescence, DAPI (357 / 44 Ex, 447 / 60 Em), GFP (470 / 22 Ex, 510 / 42 Em), and RFP (531 / 40 Ex, 593 / 40 Em) LED light cubes were used.
[0108]For albumin immunofluorescence, live cultures were washed once in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (Alfa Aesar) for 15 minutes, and followed with 3×PBS rinses (5 minutes each). Fixed cells were permeabilized using 0.1% triton X-100 (Amresco) for 10 minutes followed by another 3×PBS rinses (5 minutes each). Samples were incubated at 37° C. for 30 minutes in blocking solution, consisting of 20% goat serum (Thermo Scientific) in PBS. Primary rabbit anti-human intracellular albumin antibody (Rockland) was added to blocking solution 1:100 and incubated for 1 hour at 37° C. After incubation, cultures were washed...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com