Drug delivery systems and methods for treatment of bladder cancer with gemcitabine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Gemcitabine Prostate Uptake from Bladder
[0064]A study was conducted on male Sprague Dawley rats administering 14C gemcitabine by intra-urinary bladder cannula, over a 6- or 24-hour continuous perfusion, or by a single IV bolus. The 6- and 24-hour continuous perfusions perfused 6.9 and 26.6 mg, respectively, of gemcitabine into the bladder. The single IV bolus included 5.0 mg of gemcitabine.
[0065]Blood (FIG. 8), urine, and tissue samples (e.g., bladder, prostate)(FIGS. 7 and 9) were collected and analyzed for gemcitabine content. The results are illustrated in FIGS. 7-9. The results show that sustained gemcitabine urine concentrations have been found to produce significant gemcitabine levels in bladder tissue, which are at or exceed therapeutic concentrations based on in vitro bladder cancer cell experiments. The gemcitabine levels in the bladder are shown in FIG. 9, which also depicts a significantly lower concentration of gemcitabine in the bladder 24 hours after a clinically relev...
example 2
Gemcitabine Study in Large Mixed Breed Hounds
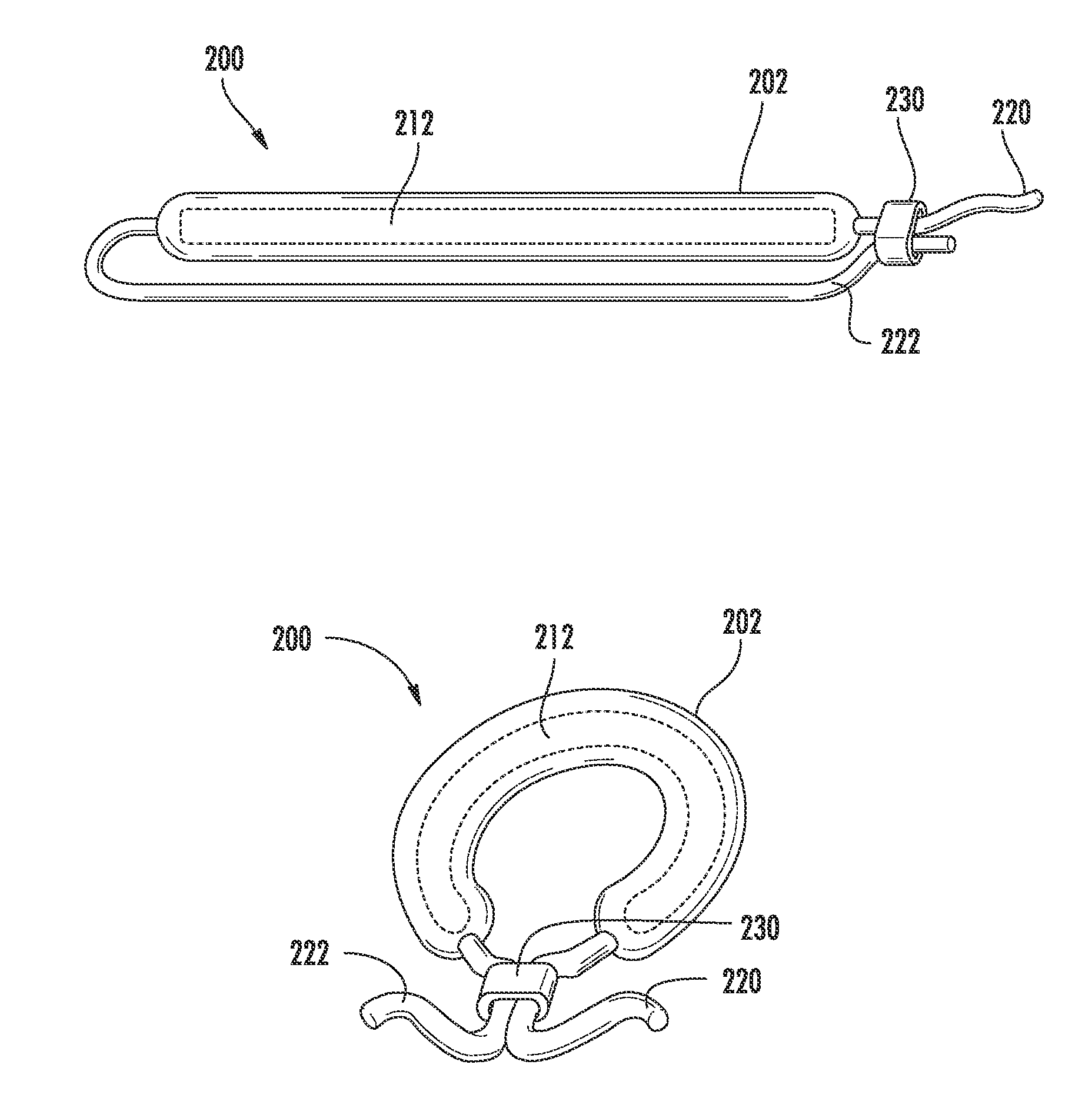
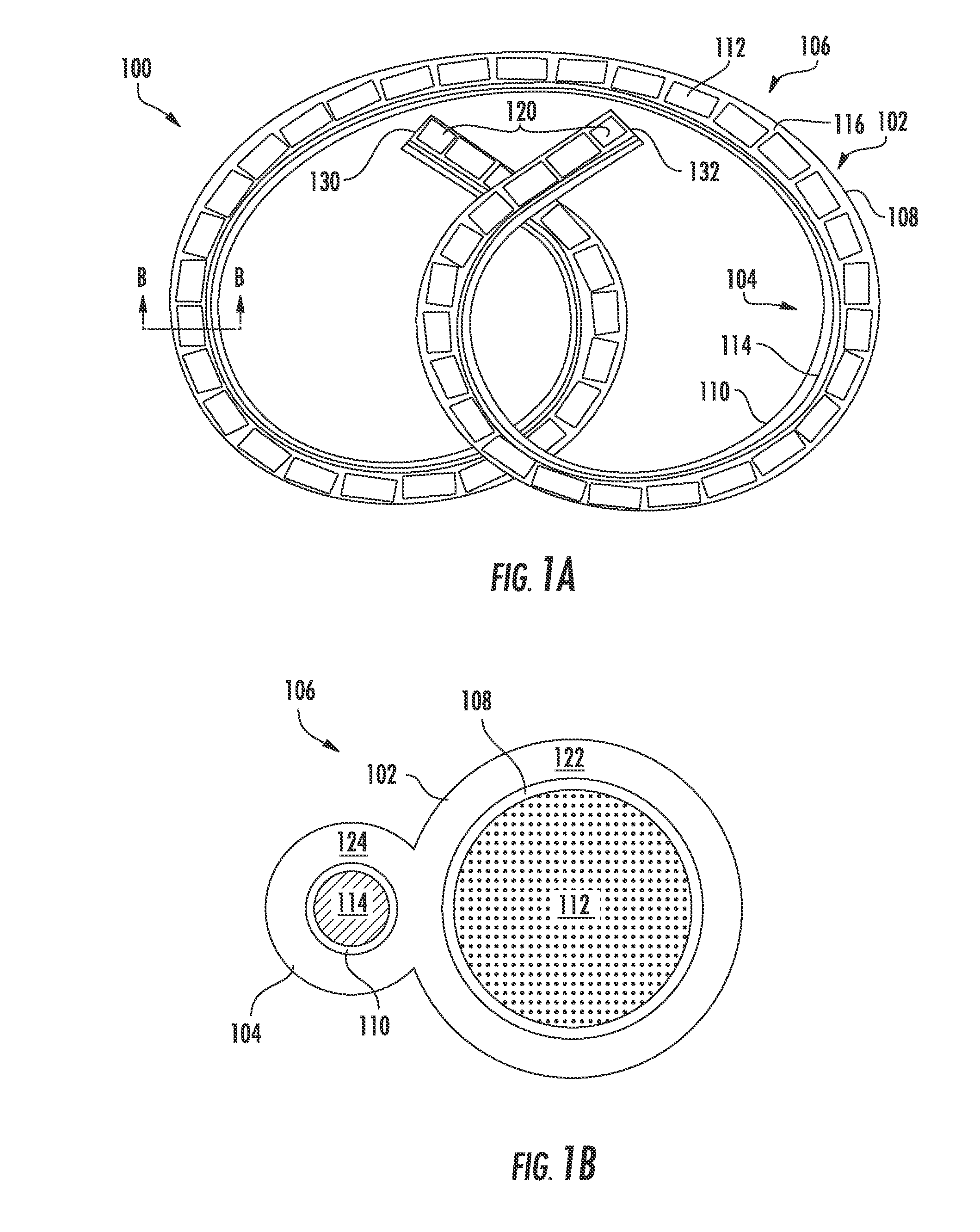
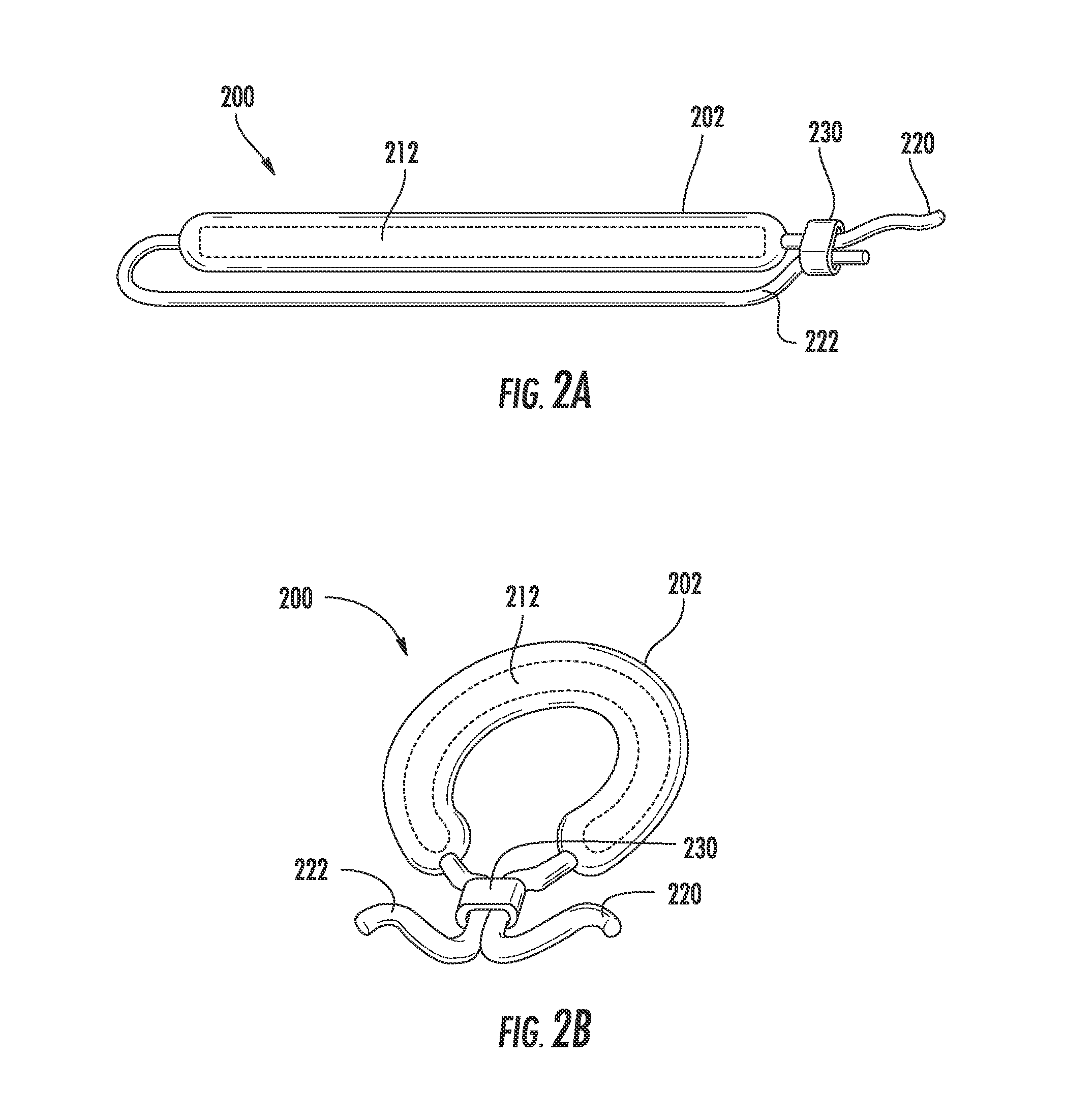
[0066]Two gemcitabine release systems (devices as shown in FIGS. 1A-1B) designed to release therapeutic levels (4 mg / day and 40 mg / day) into the urine were screened. The devices used either laser-drilled orifices or punched orifices for release of the gemcitabine. The systems tested were compared to intravesical instillations which were designed to mimic the standard intravesical doses used clinically. The test animals were large mixed breed hounds, with N=3 for each group.
[0067]Each system in vitro exhibited different release rates of gemcitabine. In vivo, one system yielded very low urine and tissue concentrations but was well tolerated by the test animal. The other system produced target urine concentration levels but was poorly tolerated by the test animal. Urine profiles were also variable and the duration of drug release was unacceptably short. It was also observed that intravesical administration produced significant urothelial les...
example 3
Gemcitabine Bladder Perfusion Study in Minipigs
[0069]Varying concentrations of gemcitabine were perfused into pigs for 7 days, N=5 (2 males and 3 females per treatment group). The perfusion animals were dosed at concentrations selected to bracket the target doses for bladder cancer in humans. For comparison, a gemcitabine releasing device (as shown in FIGS. 1A-1B) with large bore end caps (restraining plugs with a large aperture therethrough for drug release) with an intermediate in vitro release rate was deployed in a separate group of animals. All perfusion groups tolerated gemcitabine well, including the highest perfusion dose. In contrast, the gemcitabine-releasing devices produced intermediate urine concentrations but were not well tolerated.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com