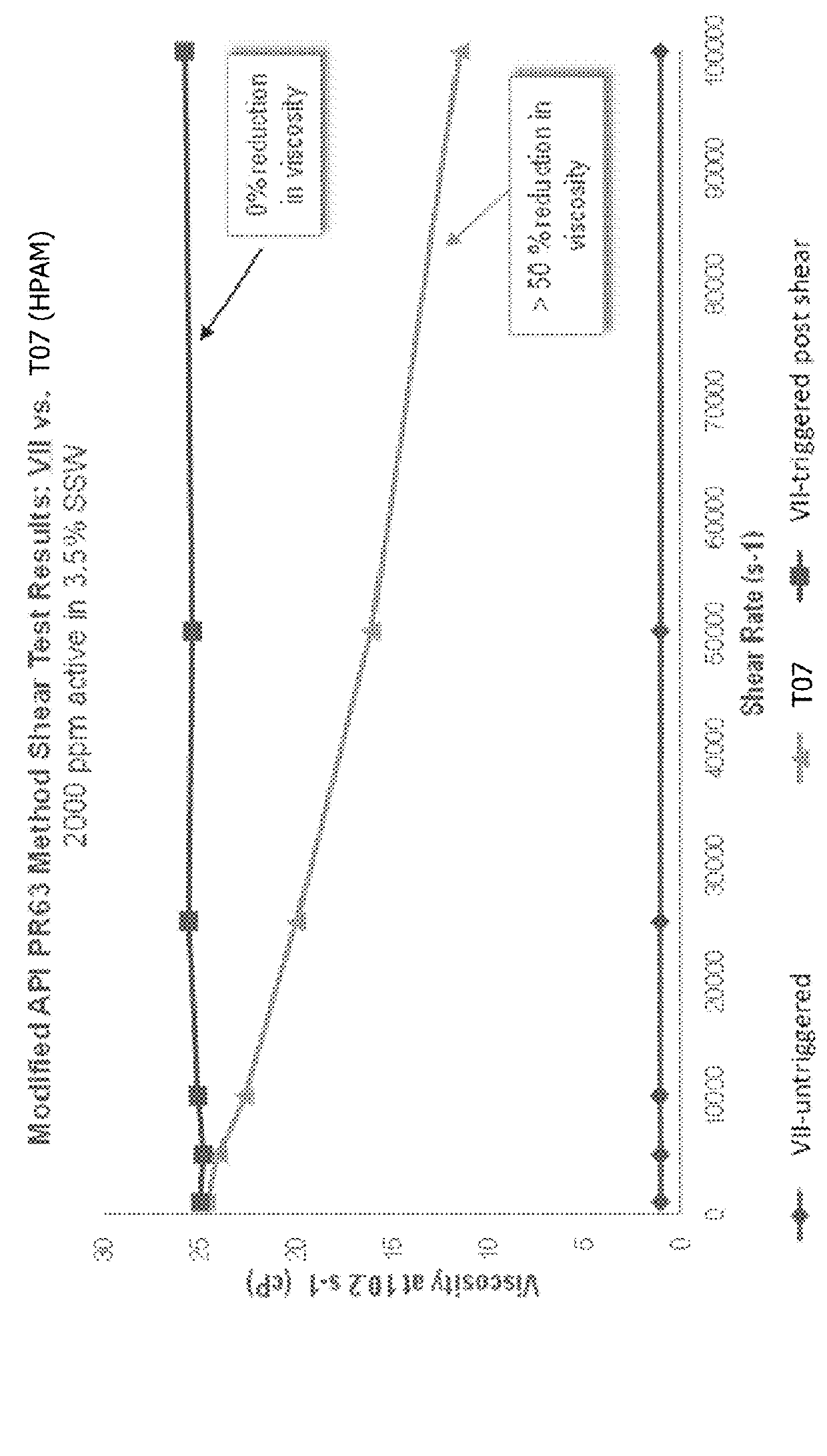
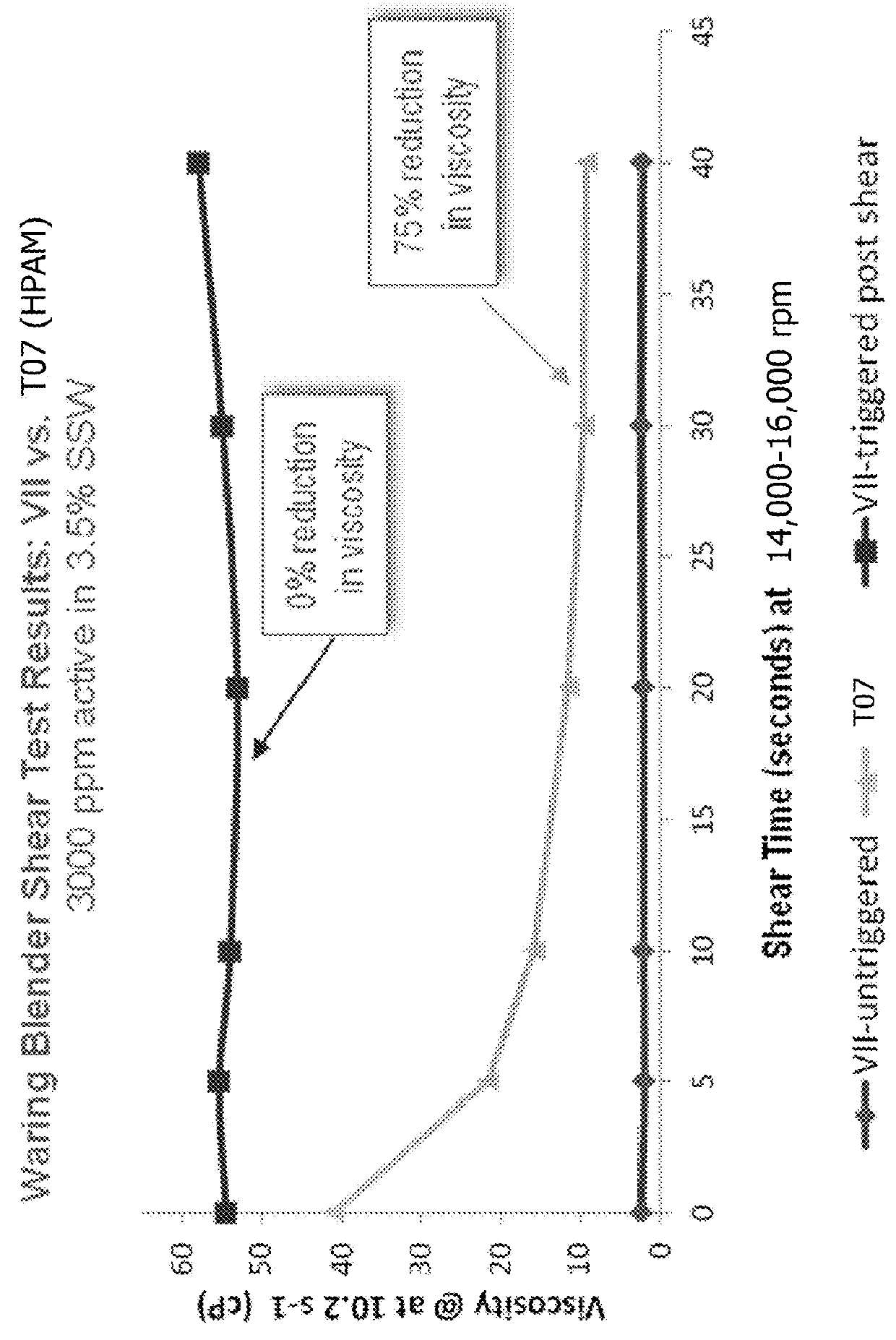
Polymer emulsions for use in crude oil recovery
a technology of polymer emulsions and crude oil, which is applied in the direction of fluid removal, chemistry apparatus and processes, and wellbore/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of poor sweep efficiency, and low molecular weight recovery, so as to increase improve the recovery of crude oil. , the effect of increasing the recovery of crude oil
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
General Procedure for Preparation of Poly(Acrylic Acid-Acrylamide)
[0207]A poly(acrylic acid-acrylamide) product was produced by polymerizing a water-in-oil emulsion including an aqueous monomer phase and an external hydrocarbon oil phase. The monomer phase included an aqueous mixture of about 29 mole % of acrylic acid and 71 mole % of acrylamide, neutralized in an ice bath with a sodium hydroxide solution to pH 7-8.5. In addition, a cross-linker of glyoxal bisacrylamide containing solution, a chain transfer agent of sodium formate, and a chelant of tetrasodium diethylenediaminetetraacetate were added to the monomer phase. The glyoxal bisacrylamide-containing solution was prepared by adding glyoxal into an acrylamide aqueous solution neutralized with a sodium hydroxide solution to pH 8 to 8.5 and stirring the mixture at 37° C. for 2 to 3 hours. The oil phase included a hydrocarbon oil and one or more surfactants.
[0208]The emulsion was formed by adding the monomer phase to the oil pha...
example 2
Product I
[0211]Product I was produced by following the general procedure of Example 1. The monomer phase consisted of 370.676 g of 50.30 wt. % acrylamide, 137.082 g of deionized water and 78.730 g of acrylic acid, neutralized in an ice-bath with 84.000 g of 50 wt. % aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. In addition, a glyoxal bisacrylamide-containing solution comprising of 0.120 g of 1 wt. % glyoxal solution, 9.940 g of 50.3 wt. % acrylamide and 0.80 g of 1 wt. % sodium hydroxide solution, 0.350 g of sodium formate and 0.090 g of tetrasodium diethylenediaminetetraacetate were added to the monomer phase. The oil phase consisted of 280.000 g of a parrafinic solvent (Exxsol D80), 13.060 g of sorbitan monooleate (Span® 80) and 21.940 g of polyoxyethylene sorbitan trioleate (Tween® 85). For the polymerization, 0.528 g of 2,2′-azobisisobutryonitrile was used.
example 3
Product II
[0212]Product II was produced by following the general procedure of Example 1. The monomer phase consisted of 370.676 g of 50.30 wt. % acrylamide, 137.257 g of deionized water and 78.730 g of acrylic acid, neutralized in an ice bath with 84.000 g of 50 wt. % aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. In addition, a glyoxal bisacrylamide containing solution comprising of 0.120 g of 1 wt. % glyoxal solution, 9.940 g of 50.3 wt. % acylamide and 0.80 g of 1 wt. % sodium hydroxide solution, 0.175 g of sodium formate and 0.090 g of tetrasodium diethylenediaminetetraacetate were added to the monomer phase. The oil phase consisted of 280.000 g of parrafinic solvent (Exxsol D80), 13.060 g of sorbitan monooleate (Span® 80) and 21.940 g of polyoxyethylene sorbitan trioleate (Tween® 85). For the polymerization, 0.528 g of 2,2′-azobisisobutryonitrile was used.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com