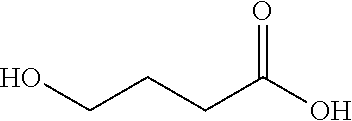
Production of salts of 4-hydroxybutyrate using biobased raw materials
a technology of gamma hydroxybutyrate and raw materials, applied in the field of gamma hydroxybutyrate, can solve the problems of affecting the effect of gamma hydroxybutyrate, and causing nausea, dizziness, drowsiness, etc., and achieves the effects of alcohol consumption, reducing the risk of ghb
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of Biobased Gamma-Butyrolactone (GBL) from the Pyrolysis of a Genetically Engineered Microbe Producing poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB)
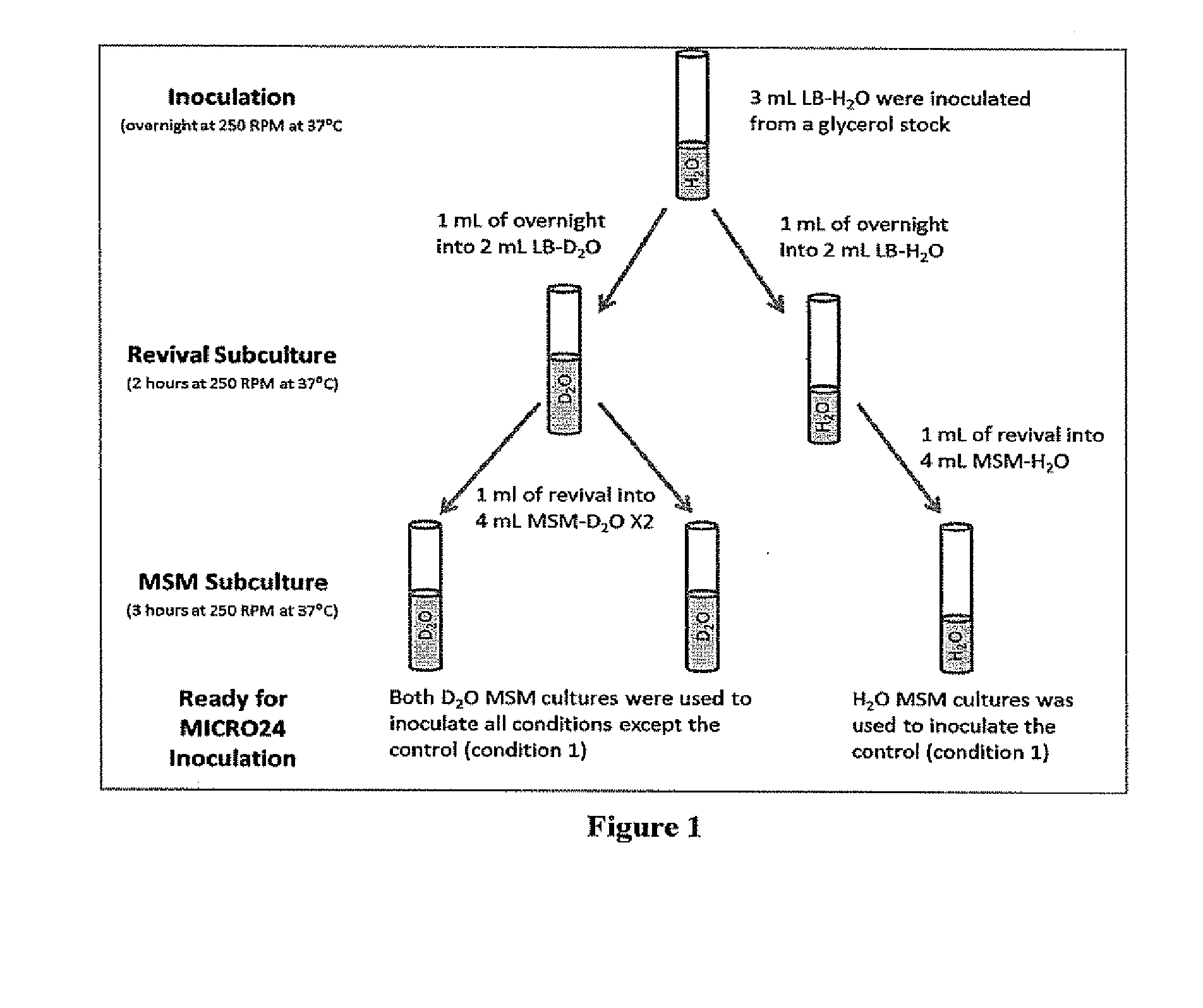
[0175]In this example biobased GBL is produced for the conversion to Biobased GHB for use in pharmaceutical applications with improved monitoring and safety. Biomass containing poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (poly-4HB) was produced in a 20 L New Brunswick Scientific fermentor (BioFlo 4500) using a genetically modified E. coli strain specifically designed for high yield production of poly-4HB from glucose syrup as the sole carbon feed source. The use of a renewable resource based feedstock such as glucose syrup as the sole carbon source enables the production of a biobased P4HB and hence the production of biobased GBL and derivatives including biobased gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB). Examples of the E. coli strains, fermentation conditions, media and feed conditions are described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,316,262; 6,689,589; 7,081,357; and 7,229,804. The E...
example 2
Post Purification of Biobased GBL by Distillation, Steam Stripping and Peroxide Treatment
[0180]This example outlines a procedure for the purification of biobased GBL liquid prepared from pyrolysis of a genetically engineered microbe producing poly-4-hydroxybutyrate polymer mixed with a catalyst as outlined previously in Example 1.
[0181]The GBL purification is a batch process whereby the “crude” GBL liquid recovered after pyrolysis is first filtered to remove any solid particulates (typically <1% of the total crude GBL weight) and then distilled twice to remove compounds contributing to odor and color.
[0182]Filtration of the crude GBL liquid was carried out on a lab scale using a Buchner fritted-glass funnel coupled to an Erlenmeyer receiving flask. Approximately 1 liter of crude GBL was filtered which resulted in approximately 0.99 liters of recovered GBL liquid.
[0183]The distillation of the filtered GBL liquid was carried out using a high vacuum 20 stage glass distillation column. ...
example 3
Production of Biobased-GBL from Purified P4HB Coupled with Thermolysis
[0188]In this example biomass containing P4HB is produced in a fermentation process using glucose as the sole carbon feed source as described above. Following the fermentation, the P4HB is extracted from the biomass and purified. Suitable methods for purifying P4HB from biomass are described in for example U.S. Pat. No. 6,610,764 to Tepha and Metabolix and U.S. Pat. Nos. 7,981,642 and 7,576,173 to Metabolix Inc. Purified P4HB is subjected to a thermolysis procedure essentially under the same conditions as in Example 1 and GBL is produced. GBL produced using this approach should have a biobased content of around 99% when tested according to the standard ASTM-D6866-11 testing protocol.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com