Aromatization Catalyst Preparation with Alkali Metal Present During a Washing Step
a technology of aromatization catalyst and alkali metal, which is applied in the direction of physical/chemical process catalyst, bulk chemical production, hydrocarbon oil treatment product, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to perform an ion exchange process, and achieve the effect of reducing catalyst micropore volume, reducing catalyst surface area, and increasing product selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples
[0092]The invention is further illustrated by the following examples, which are not to be construed in any way as imposing limitations to the scope of this invention. Various other aspects, modifications, and equivalents thereof which, after reading the description herein, may suggest themselves to one of ordinary skill in the art without departing from the spirit of the present invention or the scope of the appended claims.
[0093]Supported catalysts were tested for their performance in aromatization reactions using the following general procedure. The supported aromatization catalysts were ground and sieved to about 25-45 mesh, and 1 cc of the sieved catalyst was placed in a ⅜-inch OD stainless steel reactor vessel in a temperature controlled furnace. After reducing the catalyst under flowing molecular hydrogen, a feed stream of aliphatic hydrocarbons and molecular hydrogen was introduced to the reactor vessel at a pressure of 100 psig, a H2:hydrocarbon molar ratio of 1.3, and a liq...
examples 1-5
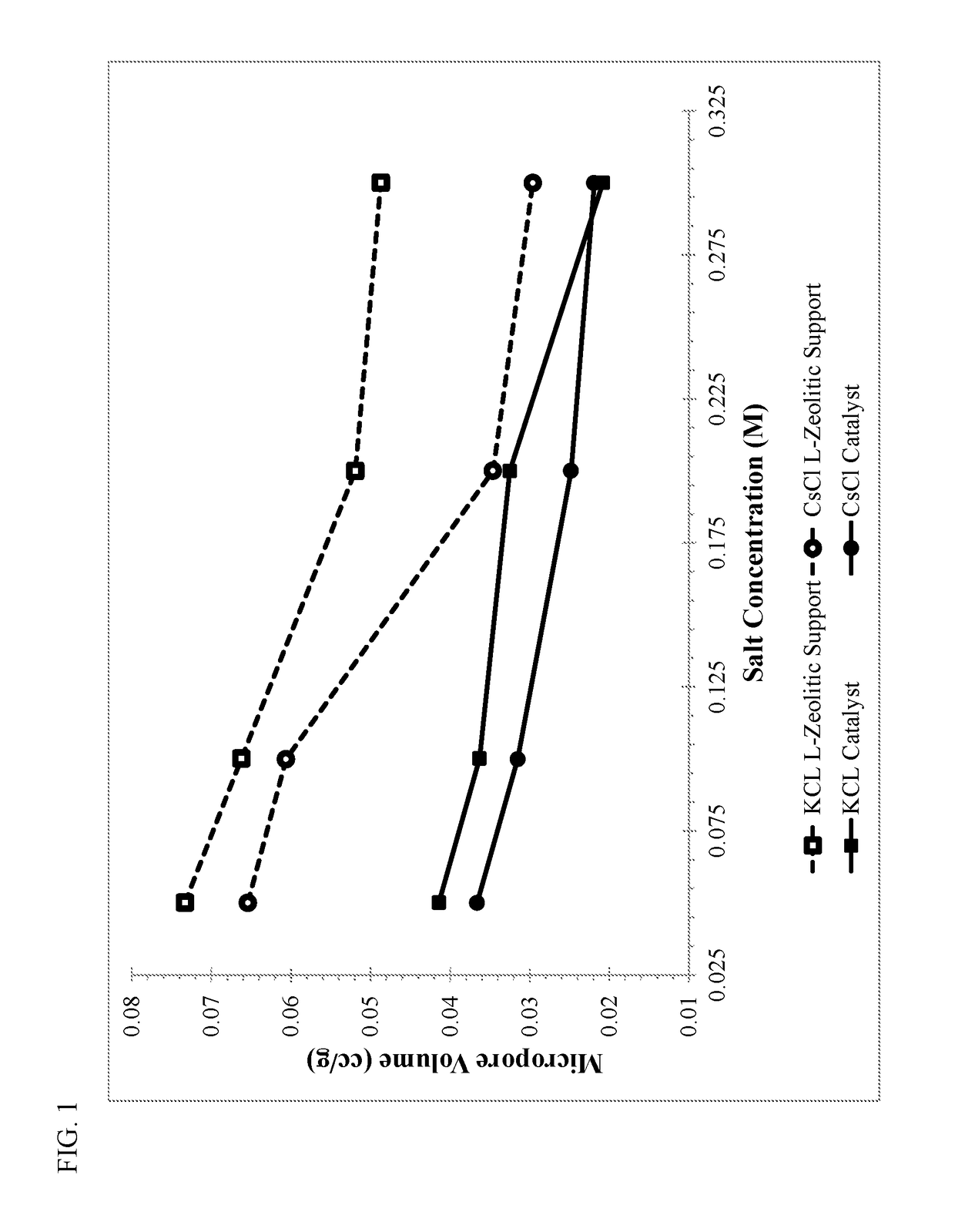
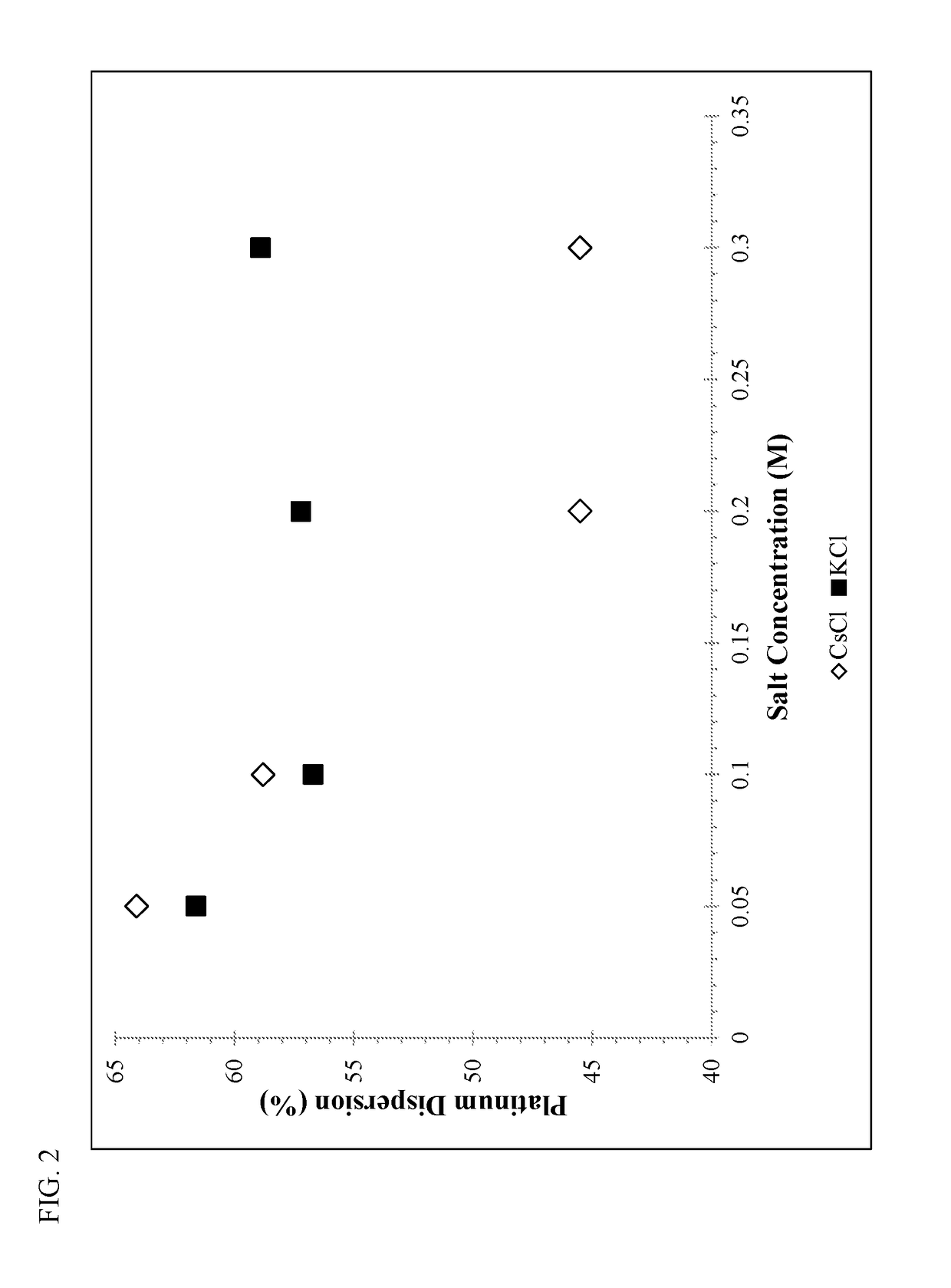
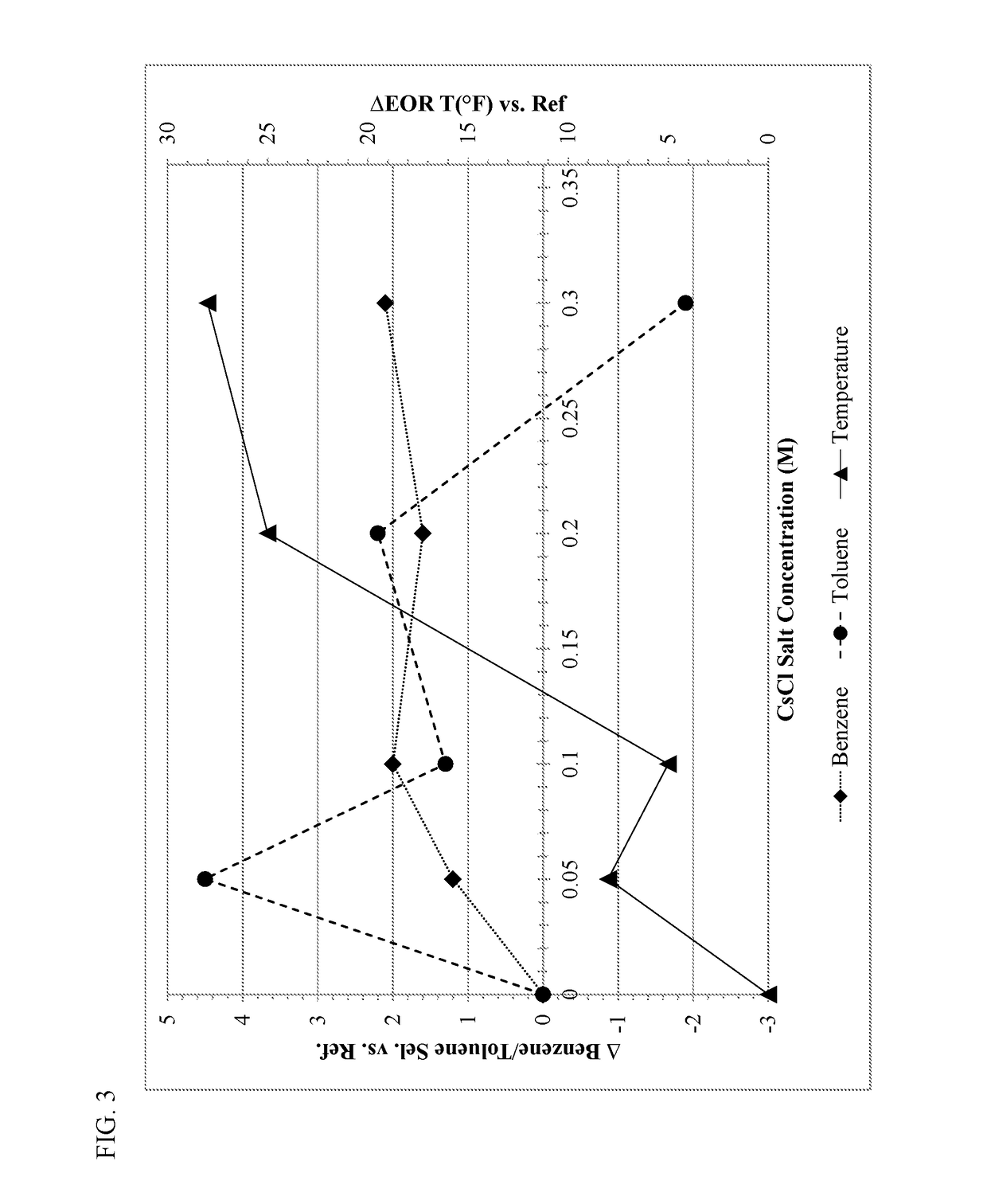
[0096]A standard bound KL-zeolite consisting of approximately 17 wt. % silica binder was used as the starting material for Examples 1-5. The bound zeolite base was washed either with water (Example 1) or with water containing 0.1 M of an alkali metal salt (NaCl, KCl, RbCl, or CsCl—Examples 2-5). The washing conditions consisted of 3 wash cycles, each conducted at 100° F. for 20 minutes with the weight of the wash water (with or without alkali metal) being 2.5 times the weight of the bound zeolite base. The washing was performed batchwise with N2 bubbling to agitate the mixture.
[0097]Table I summarizes the metals analysis of the alkali metal enriched zeolite supports after drying and calcining in air at 250° F. and 900° F., respectively. The alkali metal washing steps with rubidium or cesium (Examples 4-5) significantly reduced the amount of sodium in the support, and resulted in about 0.5 moles of the respective alkali metal (per kg) in the alkali metal enriched zeolite support. Alk...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molar concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com