FORMULATION, USE AND METHOD FOR BROAD-SPECTRUM PROPHYLAXIS AND TREATMENT OF VIRAL INFECTIONS CAUSED BY SARS-CoV-2 AND OTHER EMERGING VIRUSES
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
EGCG Forms Complexes with Zinc at Physiological pH
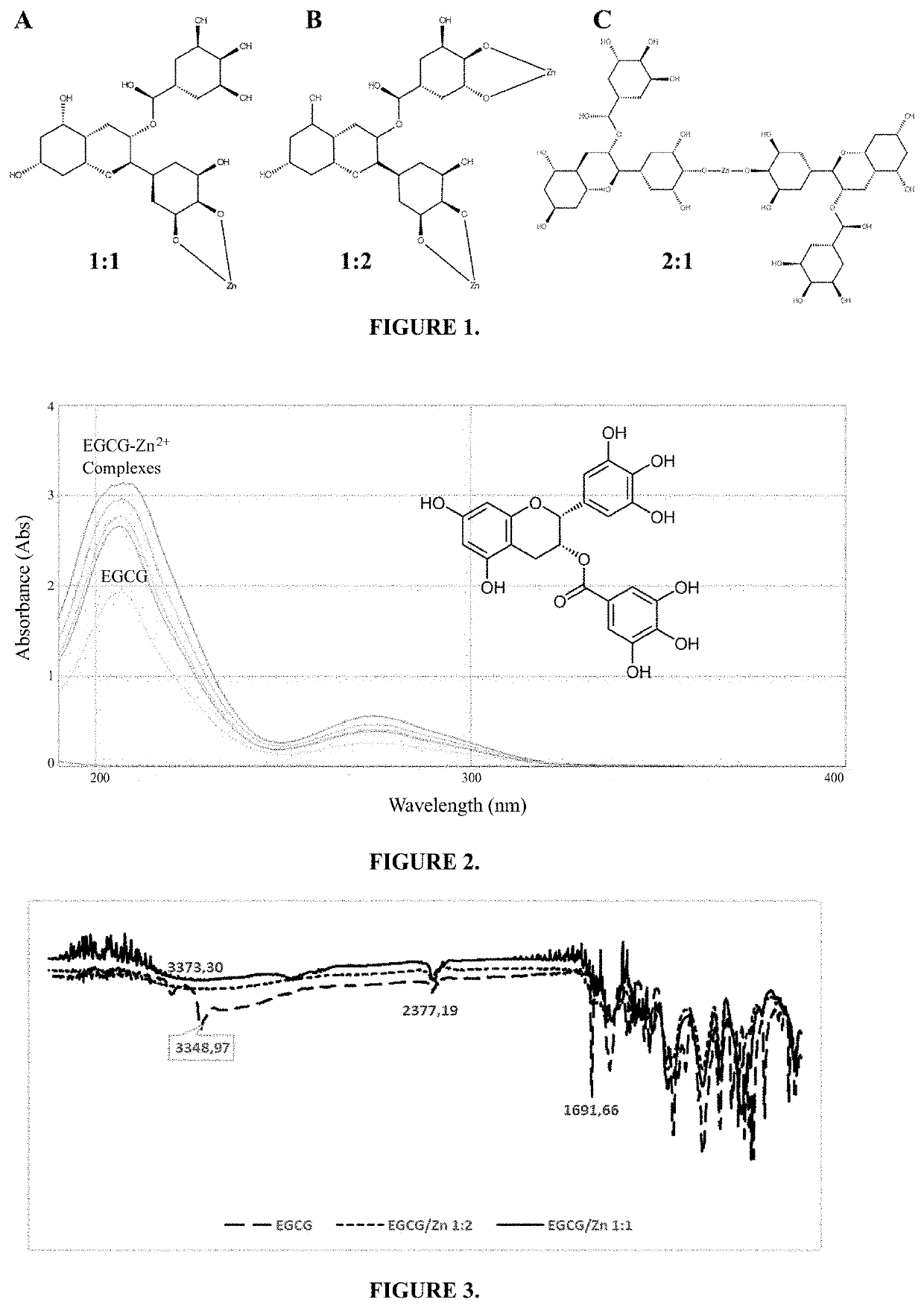
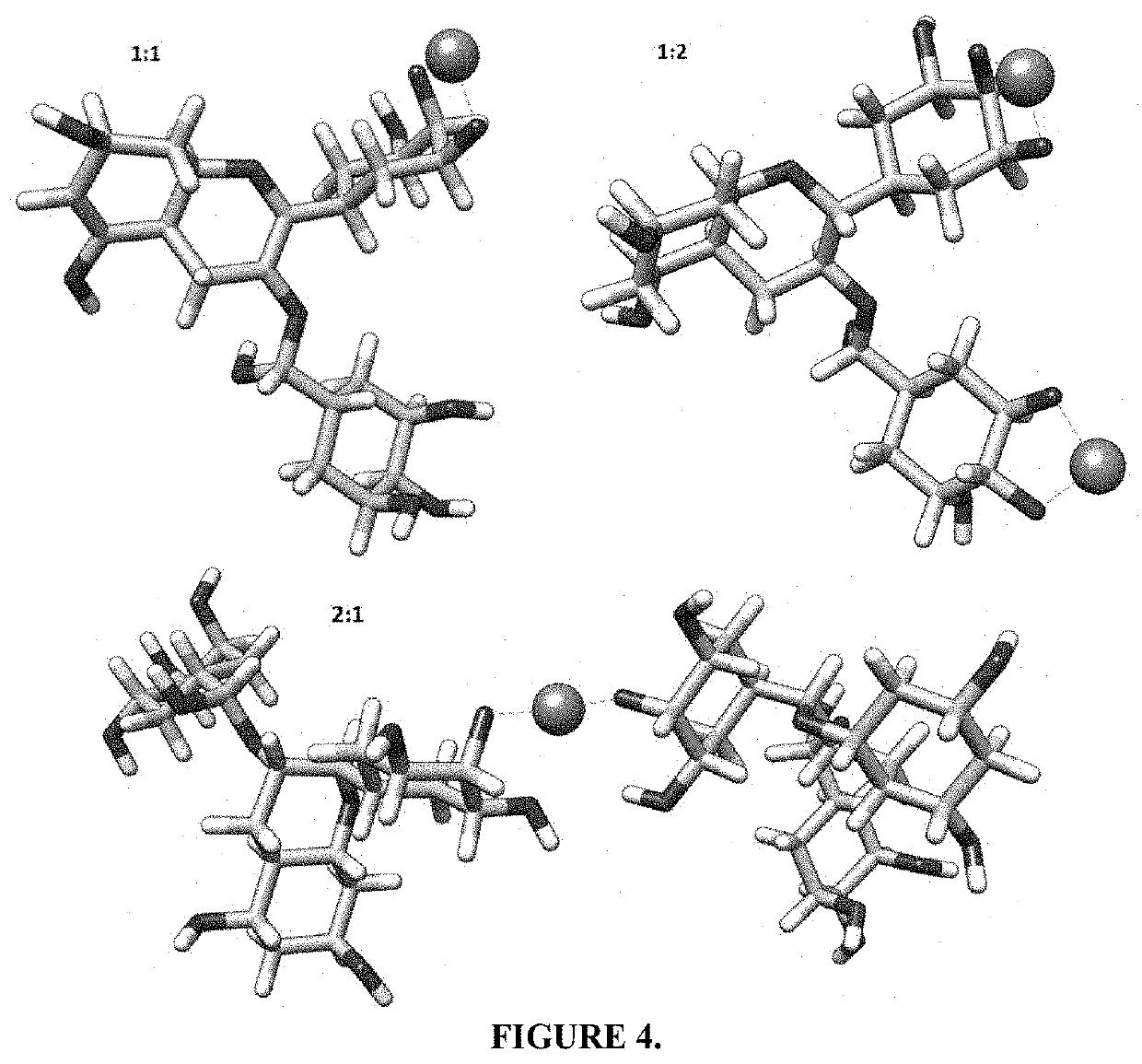
[0078]Briefly, a 10 mM EGCG solution was stirred at 750 rpm at 20° C. under the protection of nitrogen. Meanwhile, 10 mM zinc chloride was slowly added to the EGCG solution in a 2:1 molar ratio. The pH of the mixture was adjusted to 7.4 by adding 10 mM NaHCO3. Next, the products formed were collected by centrifugation, washed with deionized water, and lyophilized until the dry EGCG-Zn2+ complex was obtained. The resulting complex was analyzed by FT-IR, with ATR in the range of 800 to 4000 in transmittance, and the absorbance was measured with UV / Vis spectrophotometer, in the range of 190 to 900 nm. We have proposed the formation of at least 3 complex species between EGCG and Zn2+, which are outlined in FIG. 1 and FIG. 4. In addition, changes are observed in the UV-Vis absorption spectra of EGCG compared to the complexes formed, where changes are seen in the 216 nm which are increased in the complexes formed, as seen in FIG. 2. It was...
example 2
EGCG-Zn2+ Complexes Interact with Papain-Like Protease (PLP) of SARS-CoV-2 with more Favorable Energies than EGCG Molecule Alone or Zn Molecule Alone
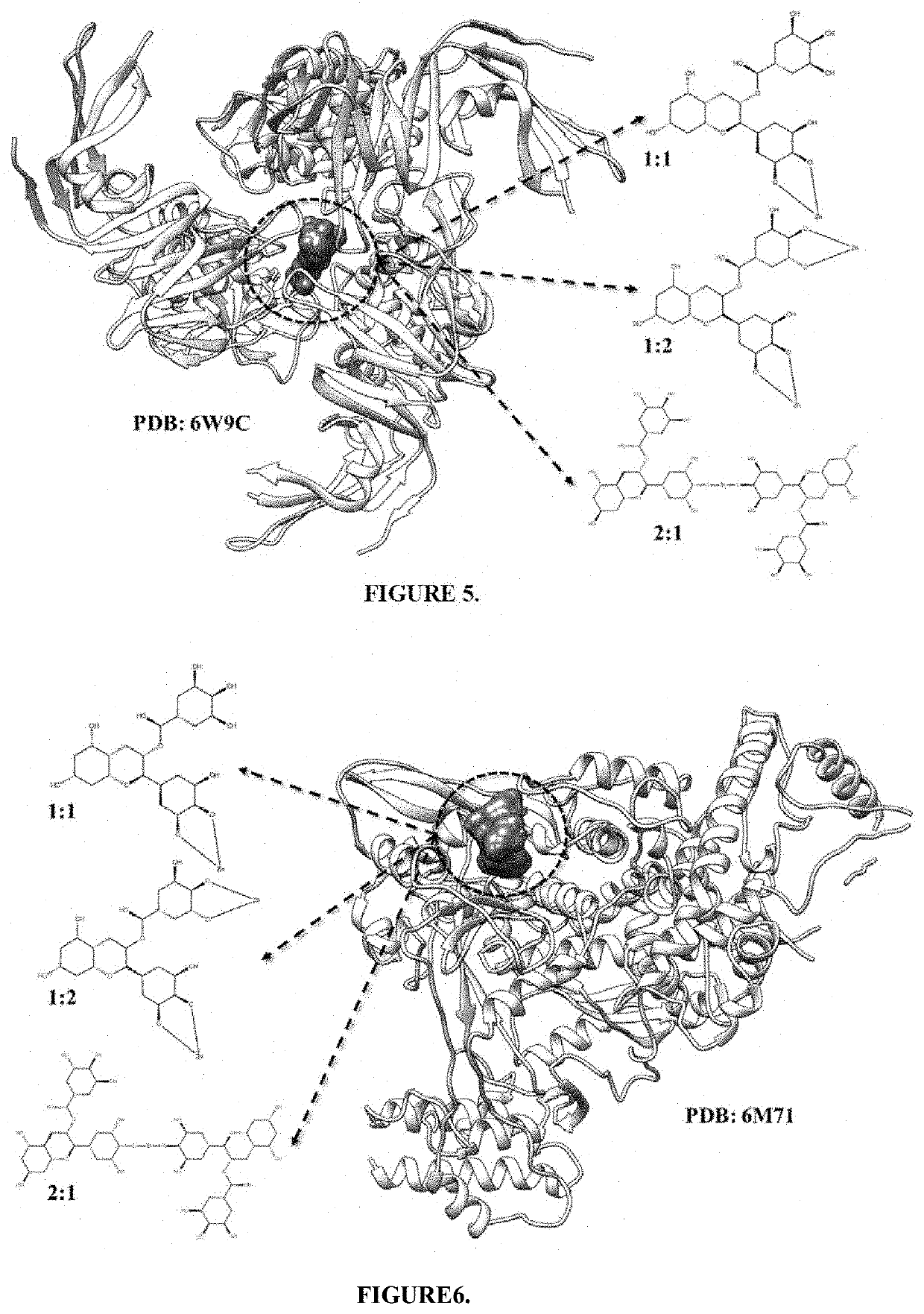
[0083]Multiple molecular docking analyzes, using 3 conformations of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes and the Papain-like protease of SARS-CoV-2, indicate that the binding energy is favorable (FIG. 5). Considering the conformation of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes 1:1 (1 EGCG: 1 Zn2+), the binding energies obtained was −9.3 Kcal / mol. For the conformation of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes 2:1 (2 EGCG: 1 Zn2+), the binding energies with PLP were −10.1 Kcal / mol. For the conformation of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes 1:2 (1 EGCG: 2 Zn2+), the binding energies with PLP were −9.6 Kcal / mol. Using the same methodology, for the EGCG molecule alone and Zinc gluconate alone, the binding energy with PLP were −8.6 Kcal / mol and −6.0 Kcal / mol, respectively. The binding energies obtained reflect the in-silico feasibility of forming the PLP-EGCG-Zn2+ complexes protein complex (Table 2), producing hy...
example 3
EGCG-Zn2+ Complexes Interact with RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase Protein (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2 with more Favorable Energies than EGCG Molecule Alone or Zn Molecule Alone
[0084]New molecular docking analyzes, using 3 conformations of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes and the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV-2, indicate that the binding energy is favorable (FIG. 6). Considering the conformation of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes 1:1 (1 EGCG: 1 Zn2+), the binding energies obtained were −7.5 Kcal / mol. For the conformation of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes 2:1 (2 EGCG: 1 Zn+2), the binding energies obtained were −9.6 Kcal / mol. For the conformation of EGCG-Zn2+ complexes 1:2 (1 EGCG: 2 Zn2+), the binding energies obtained were −8.3 Kcal / mol. Using the same methodology, for the EGCG molecule alone and Zinc gluconate alone, the binding energy obtained were −7.3 Kcal / mol and −6.5 Kcal / mol, respectively. The binding energies obtained reflect the in-silico feasibility of forming the RdRp-EGCG-Zn2+ complexes protein com...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Substance count | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com