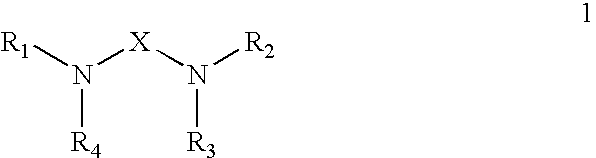
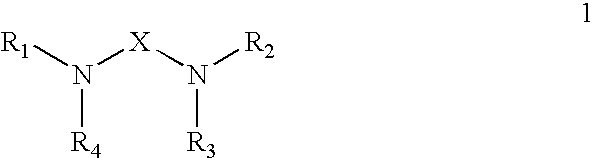
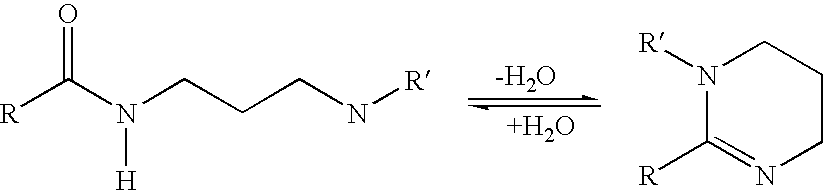Polyamide curative from substituted amine mixture and dimer fatty acid or ester
a technology of polyamide, which is applied in the field of polyamide curative from substituted amine mixture and dimer fatty acid or ester, can solve the problems of increasing teta price, and achieve the effect of fast drying speed and good coating appearan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Synthesis of 3-aminopropyl-1,3-diaminopropane
[0047]To a batch reactor was added 510.4 g of acrylonitrile and 6 g of water. The contents were heated to 60° C. To this mixture was added 85 g of ammonia over 5 hours. The reactor pressure was maintained at 2.4 MPa to keep the ammonia liquid. Once the ammonia addition was completed the reactor temperature was maintained for an additional two hours. The reactor was then cooled and the contents were emptied to yield 572.5 g of the intermediate product.
[0048]A 1 liter batch reactor was charged with 100 g of isopropanol and 3.9 g of Raney Co catalyst. The reactor was pressure cycled first with nitrogen and then with hydrogen to remove any traces of entrained air. After pressure cycling, the reactor was filled with 5.5 MPa hydrogen and heated to 120° C. Then 260 g of product from the previous step was added to the reactor over 4 hours. During this time reactor pressure was maintained at 5.5 MPa by supplying hydrogen to it from a one liter bal...
example 2
Synthesis of Polyamide from Example 1
[0050]To a one liter glass reactor, 380.6 g of dimer acid (Pripol 1012, Uniqema) was added while purging the system slowly with nitrogen. The stirrer was started after the addition of dimer acid and 47.3 g of TOFA (Sylfat FA-1, Arizona Chemical Co.) was added slowly to this system. Next 110.4 g of the product from Example 1 was added over ten minutes and the stirrer rate was increased to 100 rpm. The contents were then heated to 250° C. and 36.5 g of water was removed by distillation. The reactor was cooled down to 140° C. and at this point 263.3 g of xylene was added and the reactor was further cooled to less than 80° C. and finally 122.5 g of isobutyl alcohol was added. The final product was golden-brown in color. The product had an AHEW of 502.
example 3
Synthesis of Mixture of N-3-aminopropyl ethylenediamine, N,N′-bis(3-aminopropyl) ethylenediamine, and N,N,N′-tris(3-aminopropyl) ethylenediamine
[0051]To a 1 liter batch reactor was added 236 g of ethylenediamine and to that 5 g of water was added, and the contents were heated to 60° C. To this mixture 417 g of acrylonitrile was added over 5 hours. Once the acrylonitrile addition was completed the reactor temperature was maintained for an additional 1.5 hours.
[0052]A 1 liter batch reactor was charged with 100 g of isopropanol, 6.6 g of water and 7.5 g of Raney Co catalyst. The reactor was pressure cycled first with nitrogen and then with hydrogen to remove any traces of entrained air. After pressure cycling, the reactor was filled with 5.5 MPa hydrogen and then heated to 120° C. The 500 g of product from the previous step was the added to the reactor over 4 hours. During this time reactor pressure was maintained at 5.5 MPa by supplying hydrogen to it from a one liter ballast tank. On...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com