Mono-allelic mutation analysis for identifying germline mutations
a technology of monoallelic mutations and germline mutations, applied in the field of monoallelic mutation analysis for identifying germline mutations, can solve the problems of presenting a continuing challenge in the sensitive and specific dissection of germline mutations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
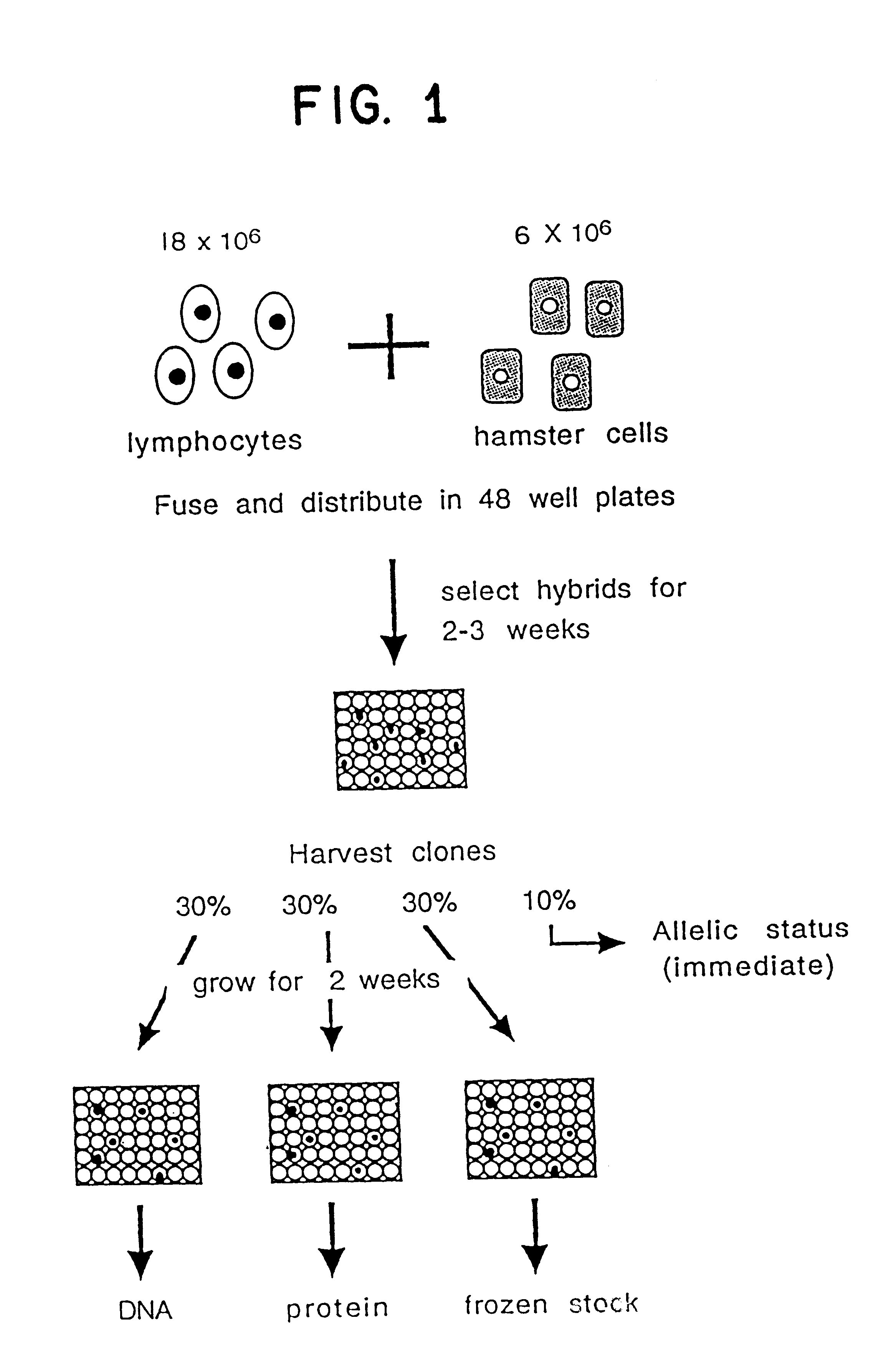
This example demonstrates the development of a simple scheme for producing somatic cell hybrids from routinely available clinical samples such as peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL).
Cells. The Urd-A cell line.sup.16 was grown in F-12 supplemented with 10%(v / v) dialyzed fetal calf serum and 30 mM uridine at 37.degree. C. The UCW56 cell line.sup.17 was grown in Dulbeco's Modified Eagles medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10%(v / v) fetal calf serum (FCS) at 32.degree. C. Lymphoblastoid lines were grown in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10%(v / v) FCS. Peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) were isolated with Histopaque 1077 (Sigma) according to the manufacturer's protocol. The cells were used immediately for fusions, or resuspended in RPMI 1640 / 10% FCS, with or without 10 mg / ml PHA and 50 U / ml IL2, and incubated at 37.degree. C. overnight. Alternatively, Histopaque isolated PBL were frozen at -80.degree. C. in RPMI 1640 / 10% FCS containing 10% DMSO.
Isolation of somatic cell hybrids. The following pro...
example 2
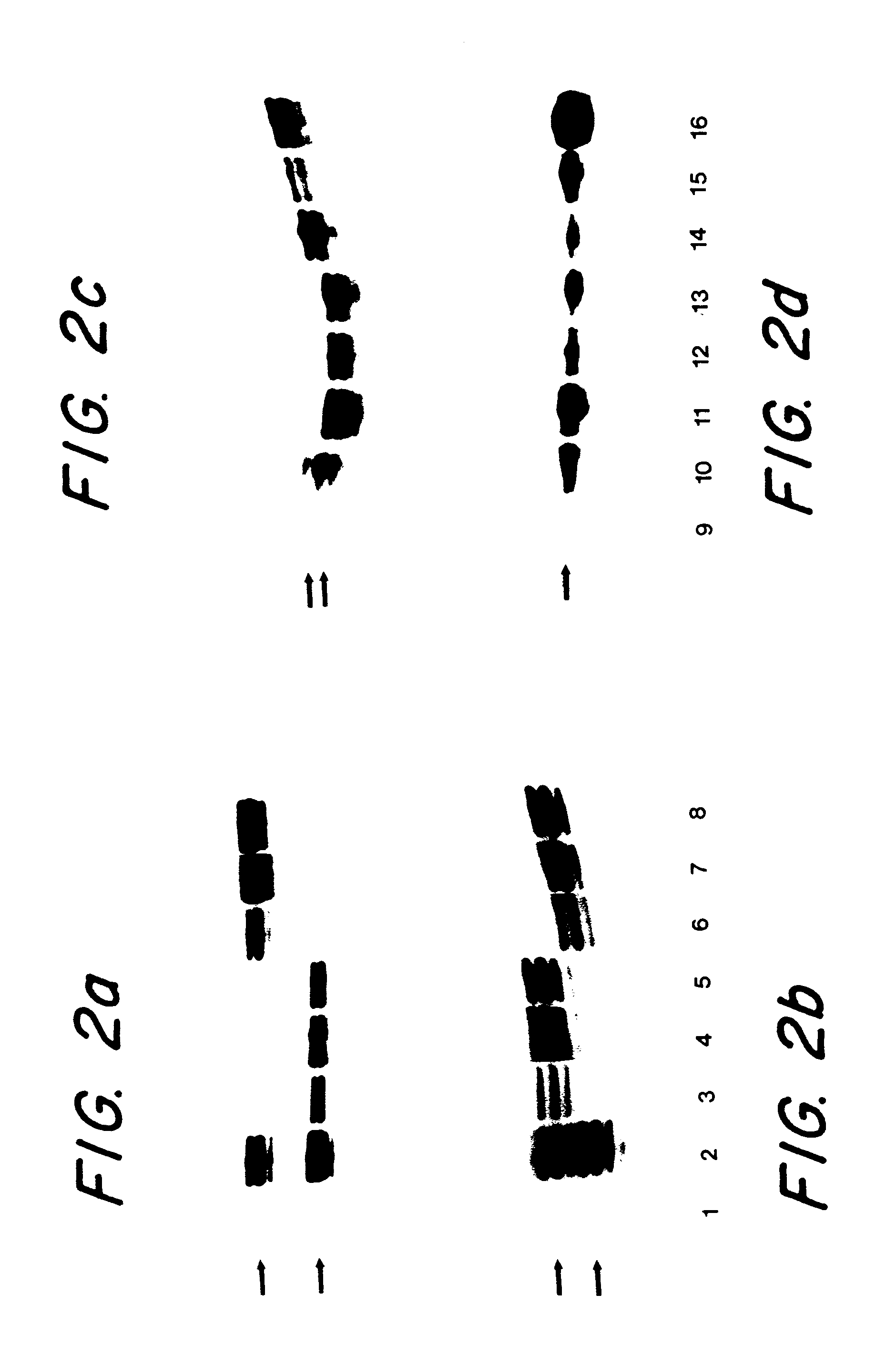
This example demonstrates that single alleles were isolated in the somatic cell hybrid clones.
DNA analysis. Confluent cells in 48 well plates were washed with Hank's balanced salt solution, and 100 ml of proteinase K (100 mg / ml) in TE 10 (10 mM Tris [pH 8.0], 1 mM EDTA) were added to each well. The plates were incubated for 2 hr at 58.degree. C. The liquid was transferred to 1.5 ml tubes and boiled for 5 minutes. Cells growing in suspension were collected by centrifugation, and DNA was prepared similarly, except that the 58.degree. C. incubation was performed in 1.5 ml tubes. Two ml of each DNA sample were used for each PCR reaction. The microsatellite markers used for chromosome 2 were YH5 and CA7.sup.4,18, and for chromosome 5 were D5S82.sup.19 and LSCA.sup.20. The PCR reactions were carried out in 96 well plates with end-labelled primers in 10 ml reactions in PCR Master Mix (Boehringer Mannheim), by heating to 95.degree. C. for 30 seconds, 50.degree. C for 1 minute, 70.degree. C....
example 3
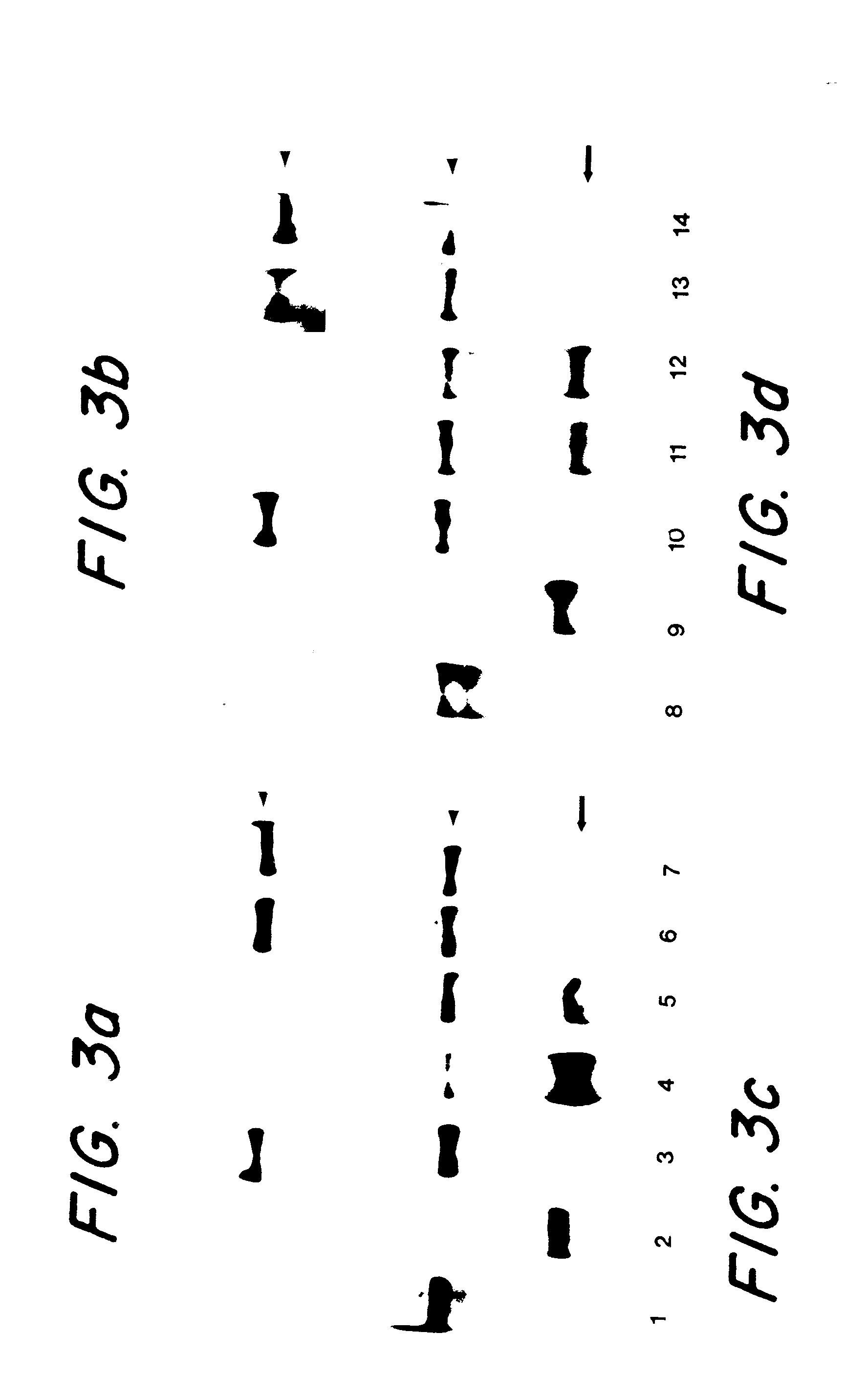
This example demonstrates that mutations that result in greatly reduced expression of the full length gene product are detectable by Western blotting of hybrid proteins using appropriate antibodies.
Western blot analysis. Cells were resuspended in buffer composed of 0.0625M Tris (pH 6.8), 5% beta-mercaptoethanol, 2% SDS, 10% glycerol, / 0.025% bromophenol blue, and quantitated according to previously published methods.sup.22. Western blot analysis for APC was carried out according to ref. 23. Briefly, proteins were separated by electrophoresis in 3% low melting point agarose gels and transferred to polyvinyldifluoride membranes (Immobilon; Millipore) by capillary action in TBS (100 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl) containing 0.05% SDS. These membranes were treated as described below. For hMSH2, proteins were separated on 10% polyacrylamide / SDS gels, and transferred to polyvinyldifluoride membranes for 1 hr in 40 mM glycine, 48 mM Tris, 0.0375% SDS buffer using a semi-dry electroblotter (ISS). Th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com