Composite microbial fodder additive
A feed additive and compound microorganism technology, applied in the field of compound microorganism feed additives, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory use effect, large investment, complicated process equipment, etc., and achieve the effects of enhancing body immunity, increasing economic benefits, and improving breeding environment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
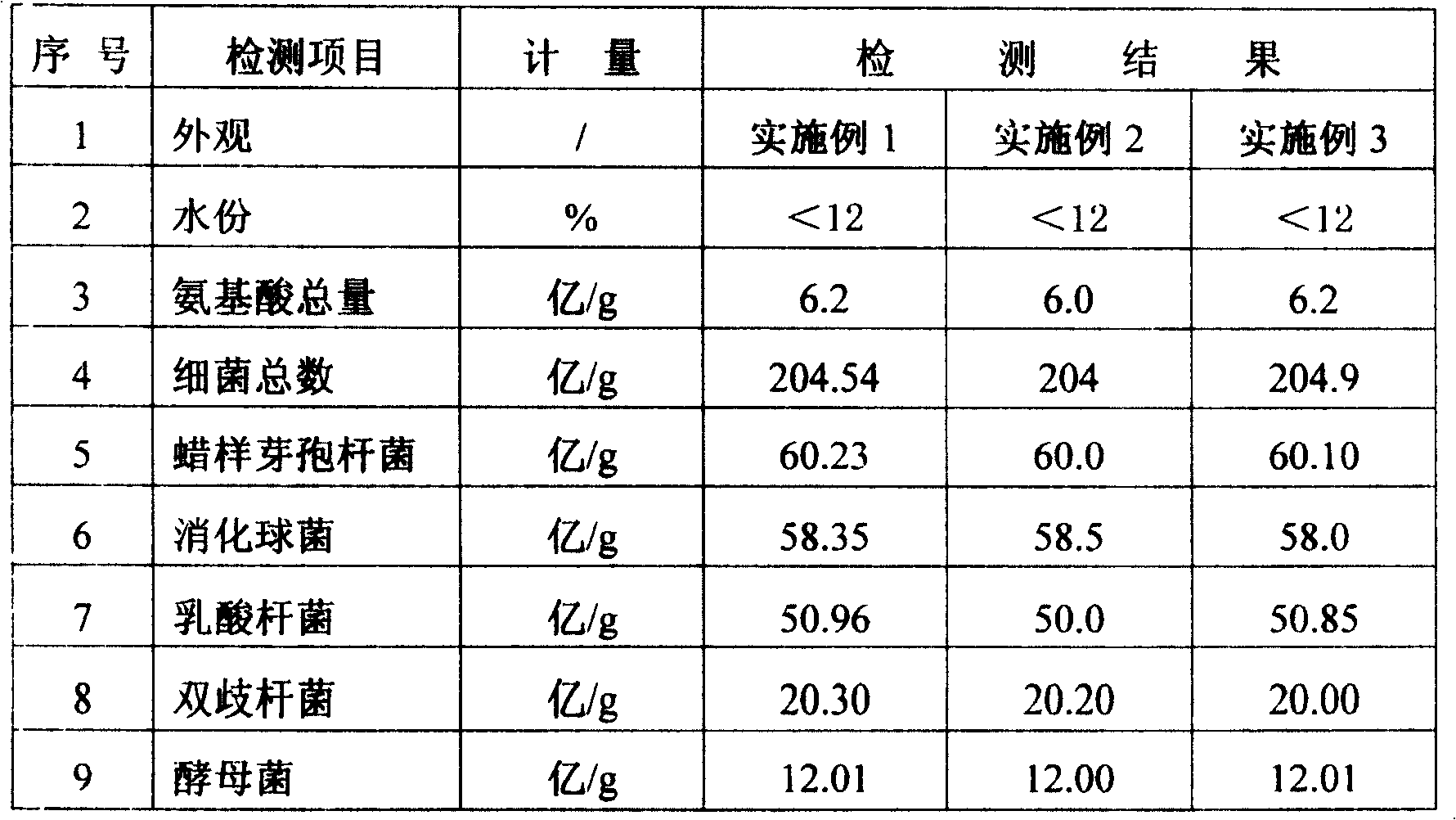
Embodiment 1
[0038] 1. The percentage of live bacteria of various microbial strains in liquid bacterial liquid:
[0039] Bacillus cereus 25.2% Peptococcus 23.4% Bifidobacterium 8%
[0040] Yeast 4.2%, sight bacteria 12%, photosynthetic bacteria 5%
[0041] Lactic acid bacteria 22.2%
[0042] 2. Solid medium:
[0043] Corn flour 25%, soybean meal 20%, rice flour 7%
[0044] Corn gluten meal 30% Bran 10% Apple pomace 5%
[0046] 3. Preparation method:
[0047] 1) taking various raw materials in proportion for subsequent use;
[0048] 2) Mix liquid lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria and photosynthetic bacteria in a weight ratio of 1:1:1 to obtain anaerobic liquid composite bacteria (1), and mix Bacillus cereus, Peptococcus, yeast and actinomycetes in a weight ratio After mixing in a ratio of 1:1:1, the aerobic compound liquid strain (2) is obtained, which is set aside;
[0049] 3) Mix 25% corn flour, 20% soybean meal, 7% rice flour, 30% corn gluten flou...
Embodiment 2
[0057] 1. The percentage of live bacteria of various microbial strains in liquid bacterial liquid:
[0058] Bacillus cereus 24% Peptococcus 25% Bifidobacterium 7%
[0059] Yeast 4% Sight bacteria 13% Photosynthetic bacteria 4%
[0060] Lactic acid bacteria 23%
[0061] 2. Solid medium:
[0062] Corn flour 20%, soybean meal 25%, rice flour 5%
[0063] Corn gluten meal 32% Bran 12% Apple pomace 4%
[0065] 3. Preparation method:
[0066] 1) taking various raw materials in proportion for subsequent use;
[0067] 2) Mix liquid lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria and photosynthetic bacteria by weight 1:1:1 to obtain anaerobic liquid composite bacteria (1), and mix Bacillus cereus, Peptococcus, yeast and actinomycetes by weight 1: After mixing in a ratio of 1:1, the aerobic composite liquid strain (2) is obtained, which is set aside;
[0068] 3) Mix 20% corn flour, 25% soybean meal, 5% rice flour, 32% corn gluten powder, 12% bran, 4% pomace and 2...
Embodiment 3
[0076] 1. The percentage of live bacteria of various microbial strains in liquid bacterial liquid:
[0077] Bacillus cereus 26% Peptococcus 21% Bifidobacterium 10%
[0078] Yeast 5% Sight bacteria 11% Photosynthetic bacteria 6%
[0079] Lactic acid bacteria 21%
[0080] 2. Solid medium:
[0081] Corn flour 30% soybean meal 15% rice flour 8%
[0082] Corn gluten meal 20% Bran 15% Apple pomace 7%
[0084] 3. Preparation method:
[0085] 1) taking various raw materials in proportion for subsequent use;
[0086] 2) Mix liquid lactic acid bacteria, bifidobacteria and photosynthetic bacteria by weight 1:1:1 to obtain anaerobic liquid composite bacteria (1), and mix Bacillus cereus, Peptococcus, yeast and actinomycetes by weight 1: After mixing in a ratio of 1:1, the aerobic composite liquid strain (2) is obtained, which is set aside;
[0087] 3) Mix 30% corn flour, 15% soybean meal, 8% rice flour, 20% corn gluten powder, 15% bran, 7% apple pomac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com