Nucleotide sequence, method and agent case for detecting bovine spongiform encephalitis specific risk substance in beef
A nucleotide sequence and mad cow disease technology, applied in the field of inspection and quarantine, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, sensitivity that cannot meet the needs of detection, high cost, etc., and achieve good stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] 1. Materials
[0073] 1. Test material
[0074] Pollution-free beef taken from the Yuxiangyuan slaughterhouse and some beef randomly bought from the supermarket.
[0075] 2. Test reagents
[0076] (1) Total RNA Extraction Kit
[0077] TRIzol Reagent Total RAN Isolation kit, a product of Invitrogen Life Technologies, was purchased from New Economics.
[0078] (2) Ready-To-Go TM RT-PCR Beads Amersham Biosciences products were purchased from Shenzhen Piji Biological Company.
[0079] (3) RT-PCR reaction solution
[0080] Taq TM PCR kit, product of TaKaRa Company, purchased from Liuhetong Economic and Trade Co., Ltd., including:
[0081] 10×PCR Buffer (Mg 2+ free)
[0082] dNTP Mixture (each 2.5mmol / L)
[0083] Taq DNA polymerase (5U / μl)
[0084] MgCl 2 (25mM)
[0085] (4) DEPC treated water
[0086] The products of TaKaRa Company were purchased from Liuhetong Economic and Trade Co., Ltd.
[0087] (5) Chloroform
[0088] Analytical pure grade, newly ope...
Embodiment 2
[0195] Embodiment 2, sensitivity test
[0196] 1. Method
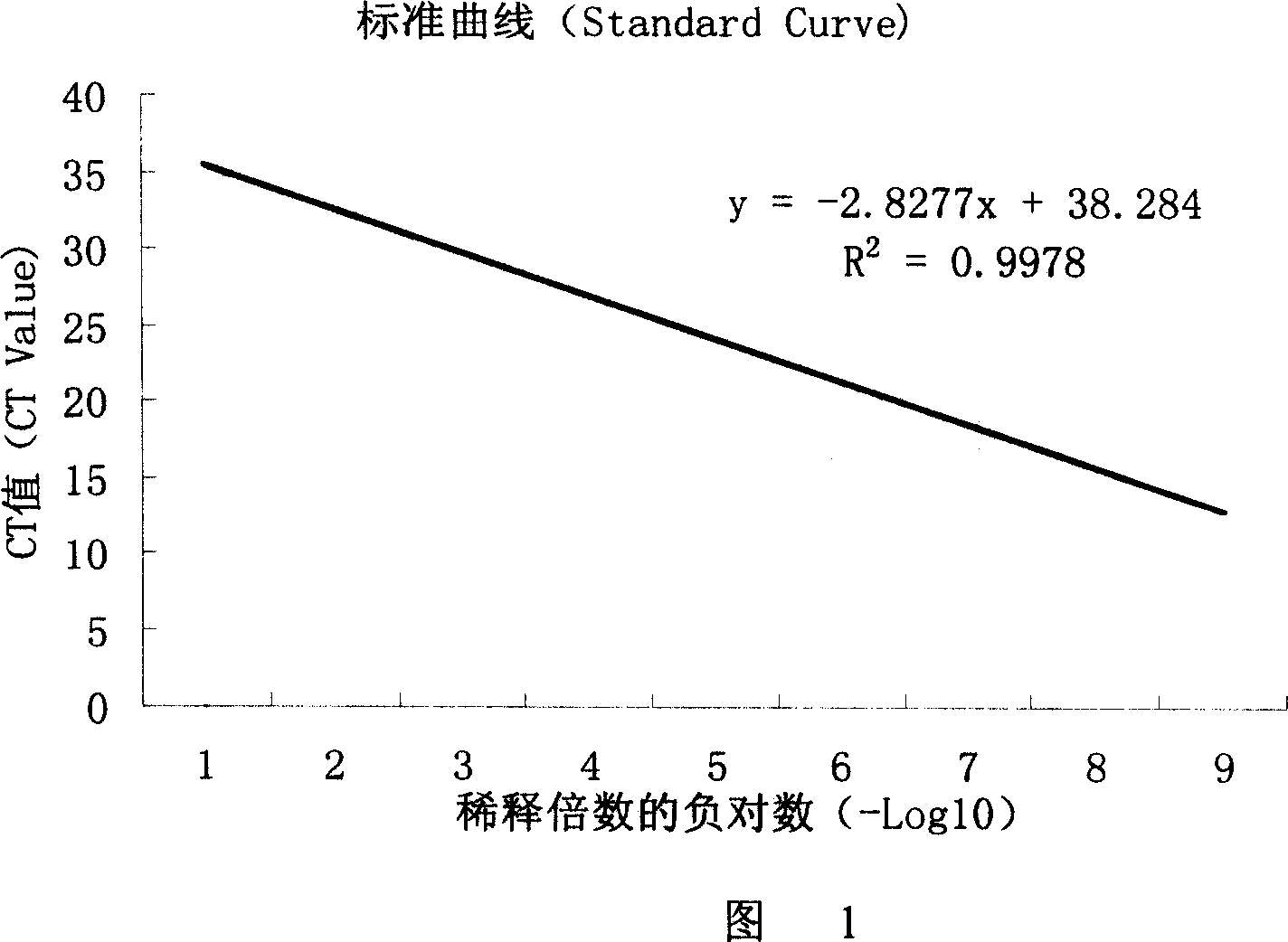
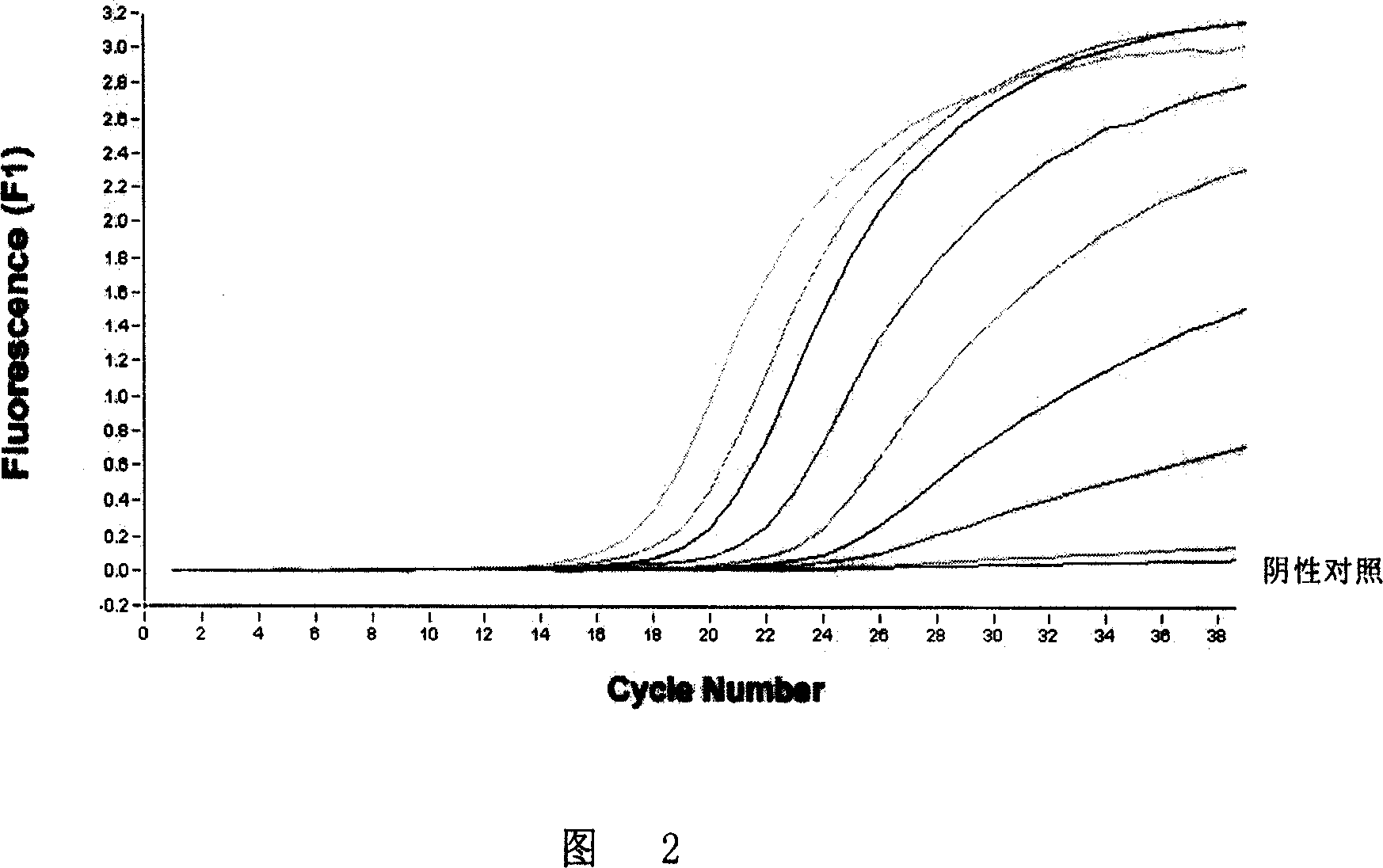
[0197] 1. Determination of the minimum detection concentration of RNA
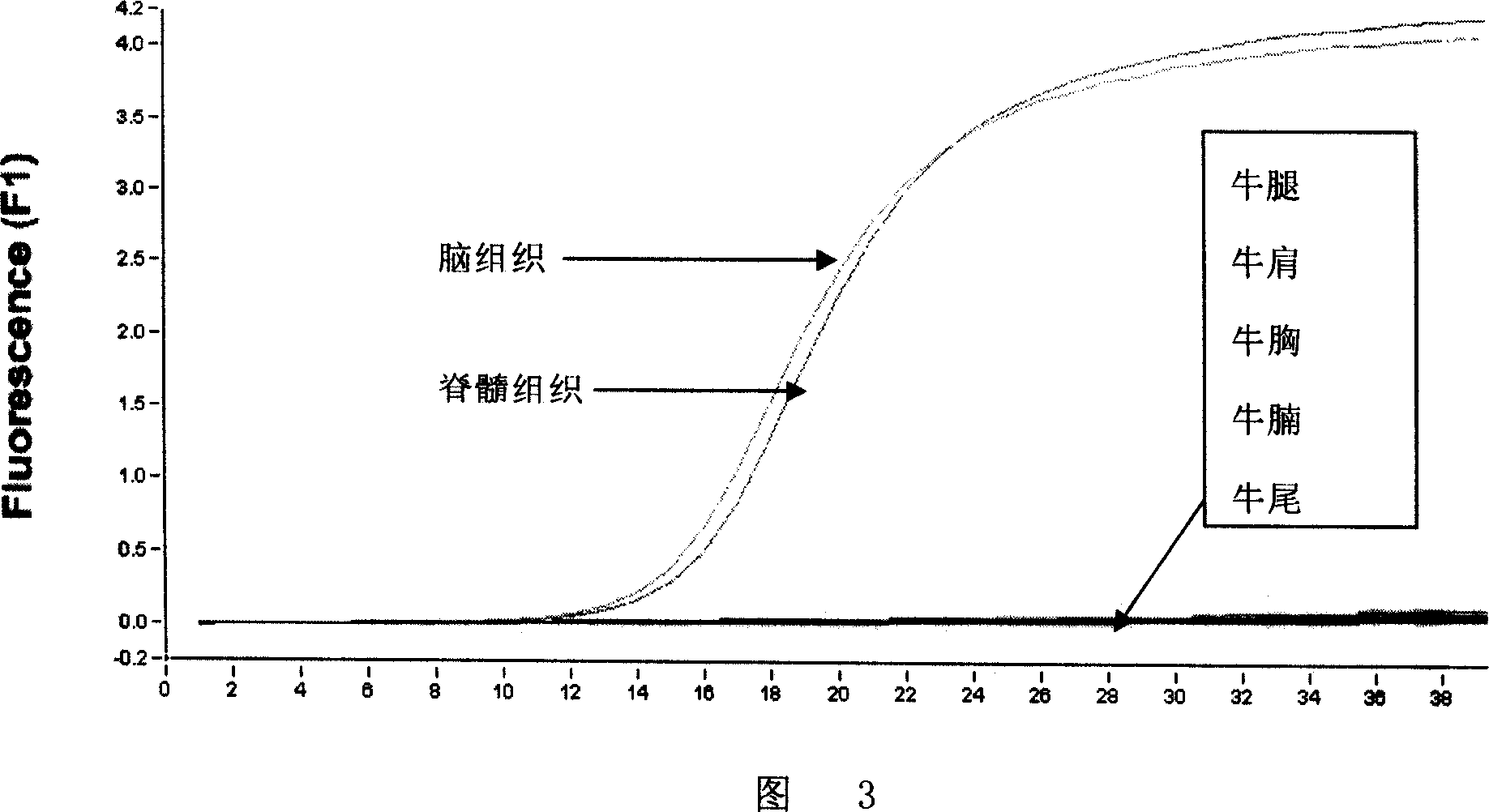
[0198] The RNA extracted from the brain tissue or the spinal cord was respectively infinitely diluted 10-fold to determine the lowest detection RNA concentration.
[0199] 2. Determination of the minimum detection limit of tissue homogenate
[0200] Make 10% homogenate of brain tissue or spinal cord with sterilized PBS, then perform 10-fold gradient dilution, and then extract RNA for fluorescent RT-PCR to determine the minimum detection limit of tissue homogenate.
[0201] 3. Determination of the minimum detection limit of experimental contaminated beef
[0202] Make 10% homogenate of brain tissue or spinal cord with sterilized PBS, then perform 10-fold gradient dilution, and then use cotton swabs to apply 500ul of tissue homogenate of each dilution evenly to the surface of a piece of non-polluted beef of 10×10cm, and then use A cotton swab was...
Embodiment 3
[0214] Embodiment 3, stability test
[0215] 1. Method
[0216] The brain or spinal cord tissues were subjected to the following different treatments for the stability test:
[0217] 1. Thermal stability test
[0218] The brain or spinal cord tissue stock solution, 20%, 10%, 1%, 0.1% and 0.01% dilutions were heated at 100°C for 30 minutes, and then RNA was extracted for fluorescent RT-PCR and thermal stability test.
[0219] 2. Storage stability test at room temperature
[0220] Different equal amounts of brain or spinal cord tissue were stored at room temperature for 1d, 2d, 3d, 4d, and 5d, respectively, and then RNA was extracted for fluorescent RT-PCR to conduct a room temperature stability test.
[0221] 3.4 ℃ cold storage stability test
[0222] Store the brain or spinal cord tissue stock solution, 20%, 10%, 1%, 0.1% and 0.01% dilutions at 4°C for 1d, 2d, 3d, 4d, 5d, 8d, 11d, and 15d, then extract RNA for fluorescent RT -PCR for cold storage stability test.
[0223]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com