Molybdenum transporter and gene thereof
A transporter and base technology, applied in genetic engineering, angiosperms/flowering plants, plant peptides, etc., can solve problems such as unclear characteristics, low identity, and unknown functions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] (Materials and methods)
[0079] [cultivation of plant]
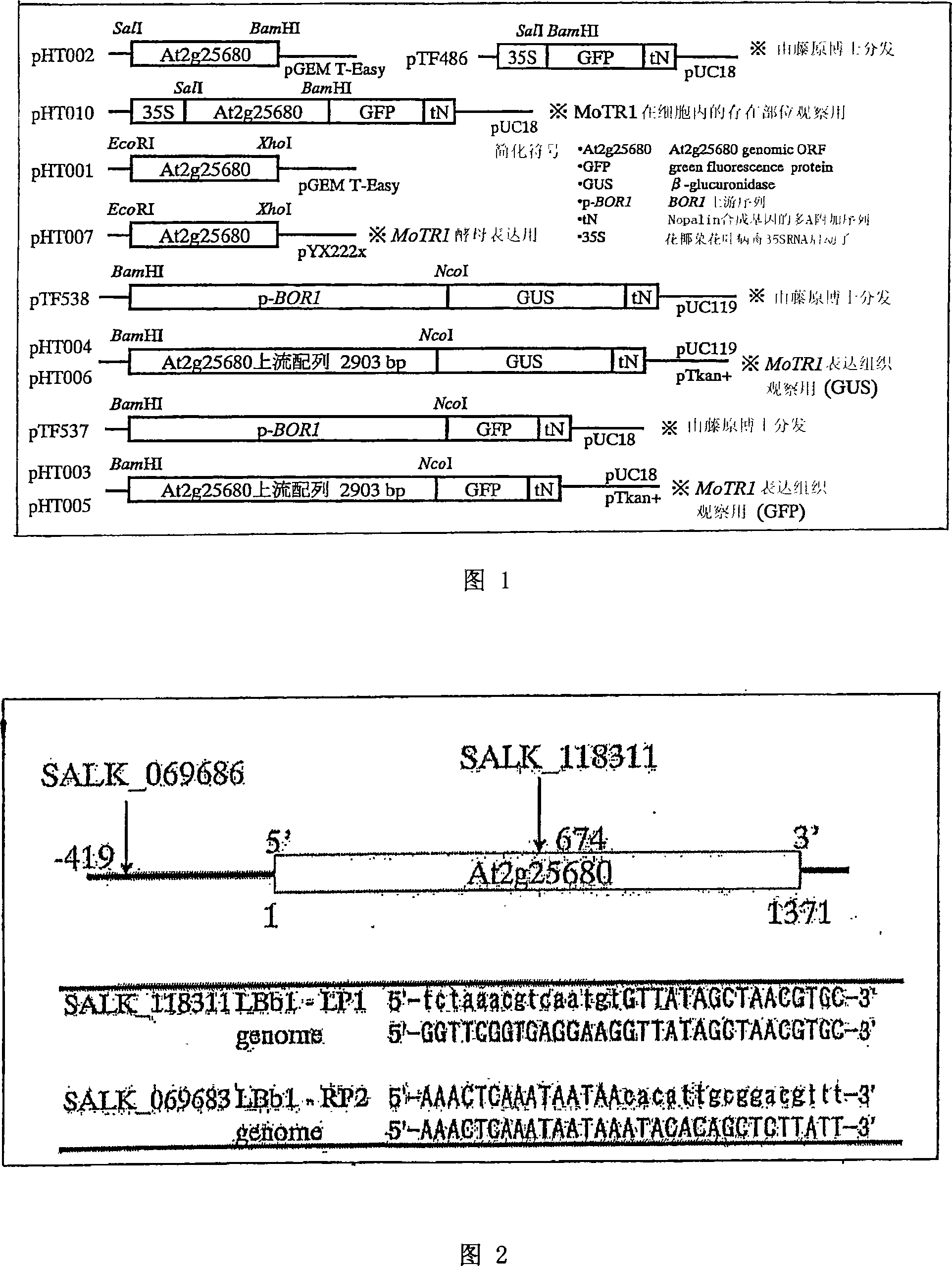
[0080] In this experiment, Arabidopsis lines Col-0, Ler and the recombinant inbred (RI) system (Lister and Dean, 1993) formed by mating them were used. Co1-0 and Ler used laboratory stock. The RI system was a distribution accepted from the Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre. In addition, foreign gene fragments (T-DNA) from the mutant strain SALK institute inserted into the gene-disrupting strains SALK_069683 and SALK_18311 were also accepted for distribution. The background of these mutants is Col-O.
[0081] The cultivation of Arabidopsis is based on the literature (Hirai, M.Y., fujiwara, T., Chino, M. and Naito, S. (1995) Effects of sulfate concentrations on the expression of a soybean seed storage protein gene and its reversibility in transgenic Arabidopsis Thaliana.Plant Cell Physi ol.36: 1 / 33 1-1 / 339) carried out with some modifications. Seeds were sown in asbestos (Nittobo Co., Tokyo, Japan) placed in...
Embodiment 2
[0151] (result)
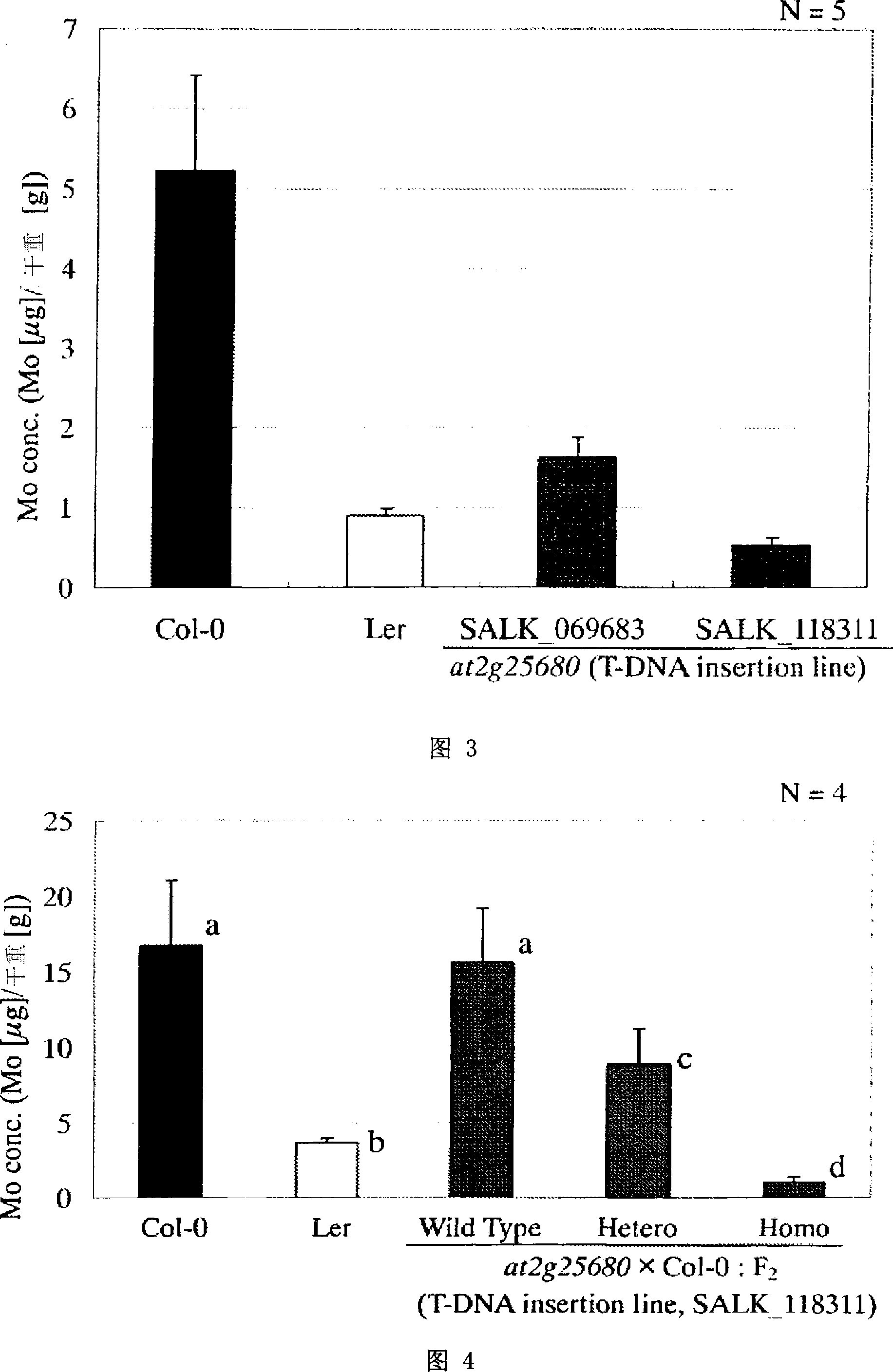
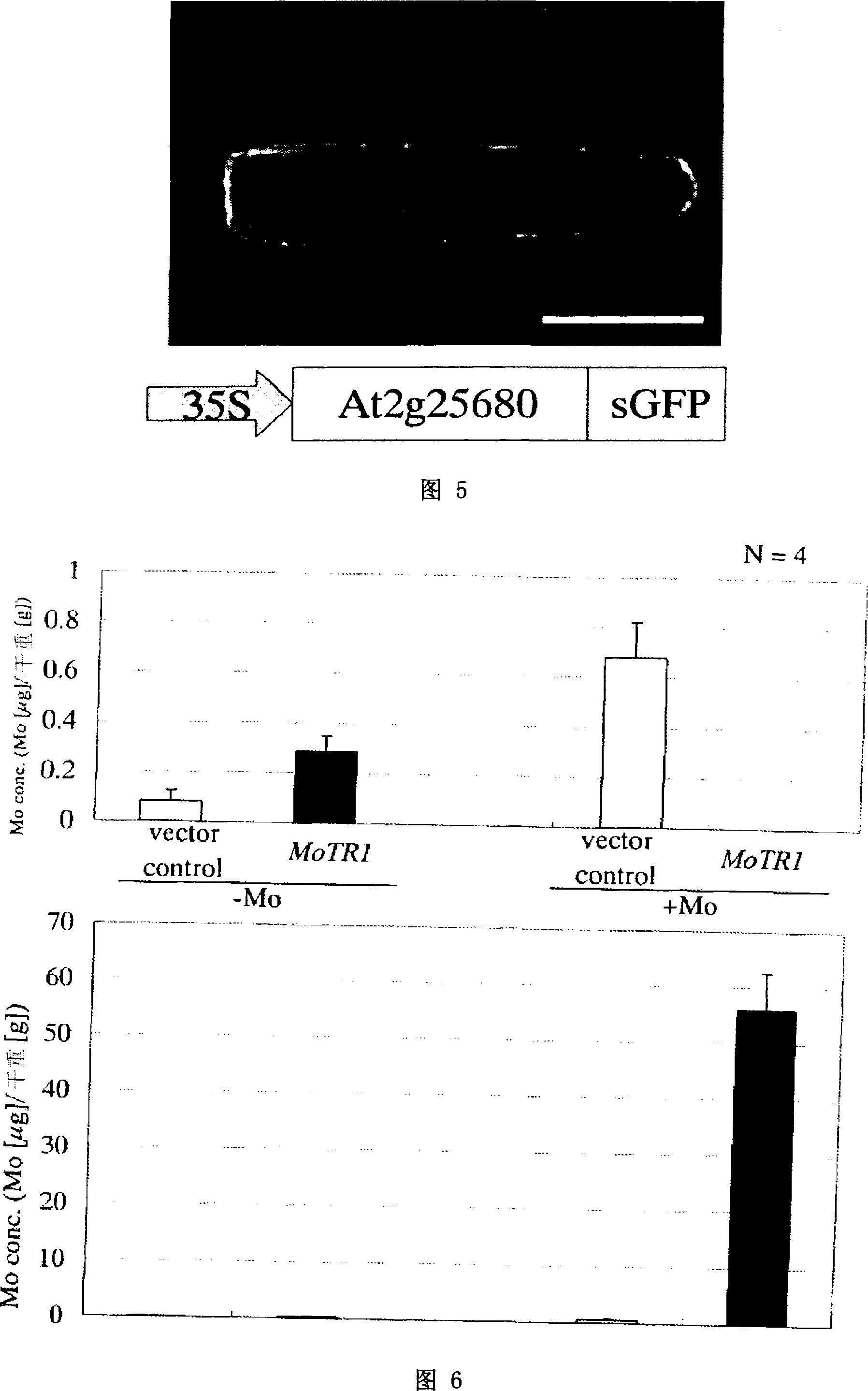
[0152] The present inventors compared the elemental composition of the leaves of Arabidopsis lines Col-0 and Ler, and found that the Mo concentration of the leaves of Col-0 was about three times that of Ler. In addition, by using the QTL analysis of the RI line 18 system formed by the mating of Col-0 and Ler, it was found that the QTL that dominates the Mo concentration in leaves exists in the two genetic markers mi238 and er located on the upper arm of the second chromosome. area.
[0153] Therefore, in order to identify genes that determine Mo concentrations in leaves, the RI line16 system (CL 36, 59, 84, 90, 160, 177, 179, 191, 194, 237, 253, 295, 303, 358, 370, 395; Lister, C. and Dean, C. (1993) Recombinant inbred lines for mapping RfLP and Phenotypic markers in Arabidopsis-thaliana. Plant J.4: 745-750), study its genotype and Mo concentrations in leaves. The results are shown in Table 2. Each RI system is represented by a CL number. Also, based on ...
Embodiment 3
[0186] (Discussion)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com