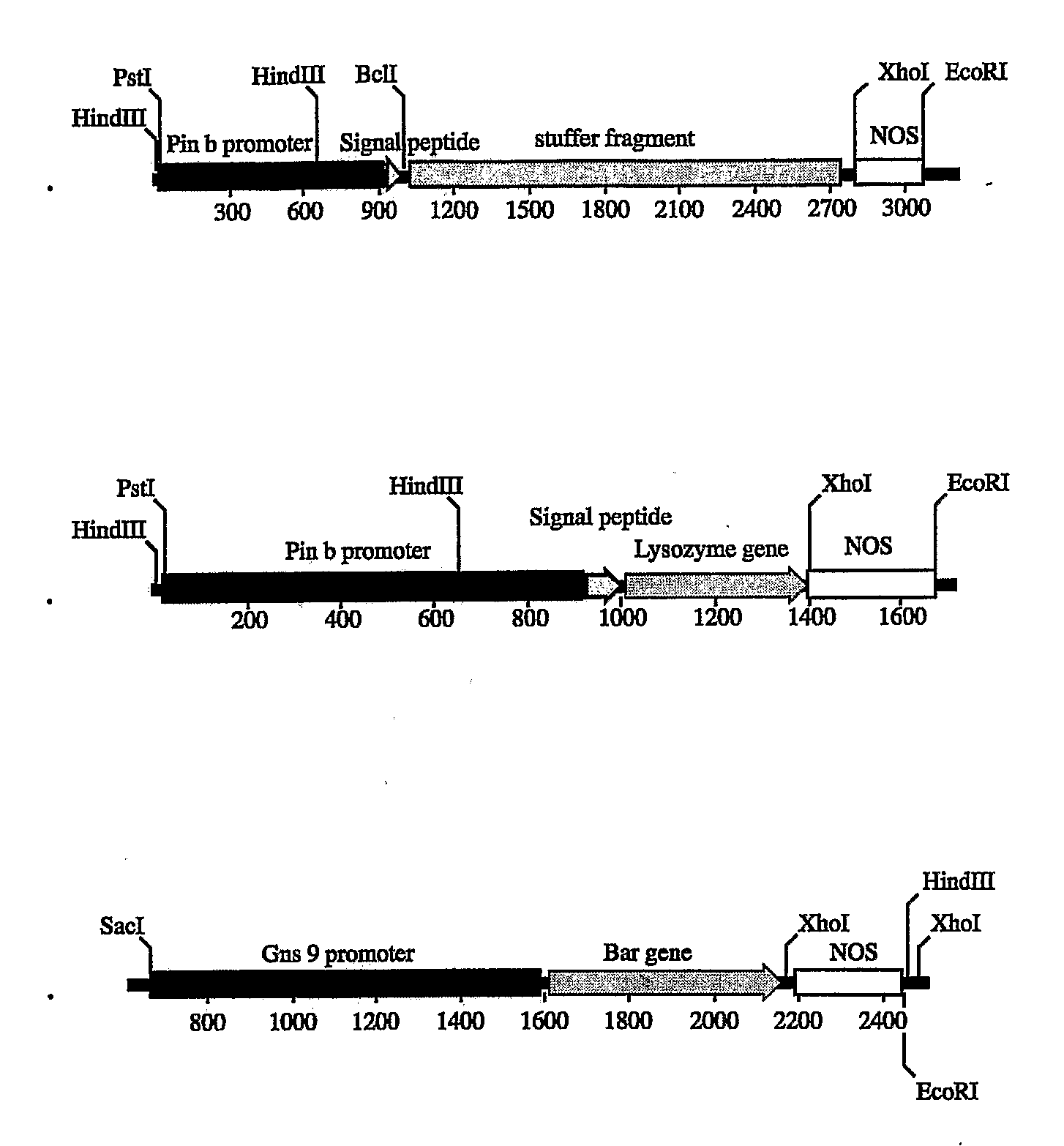
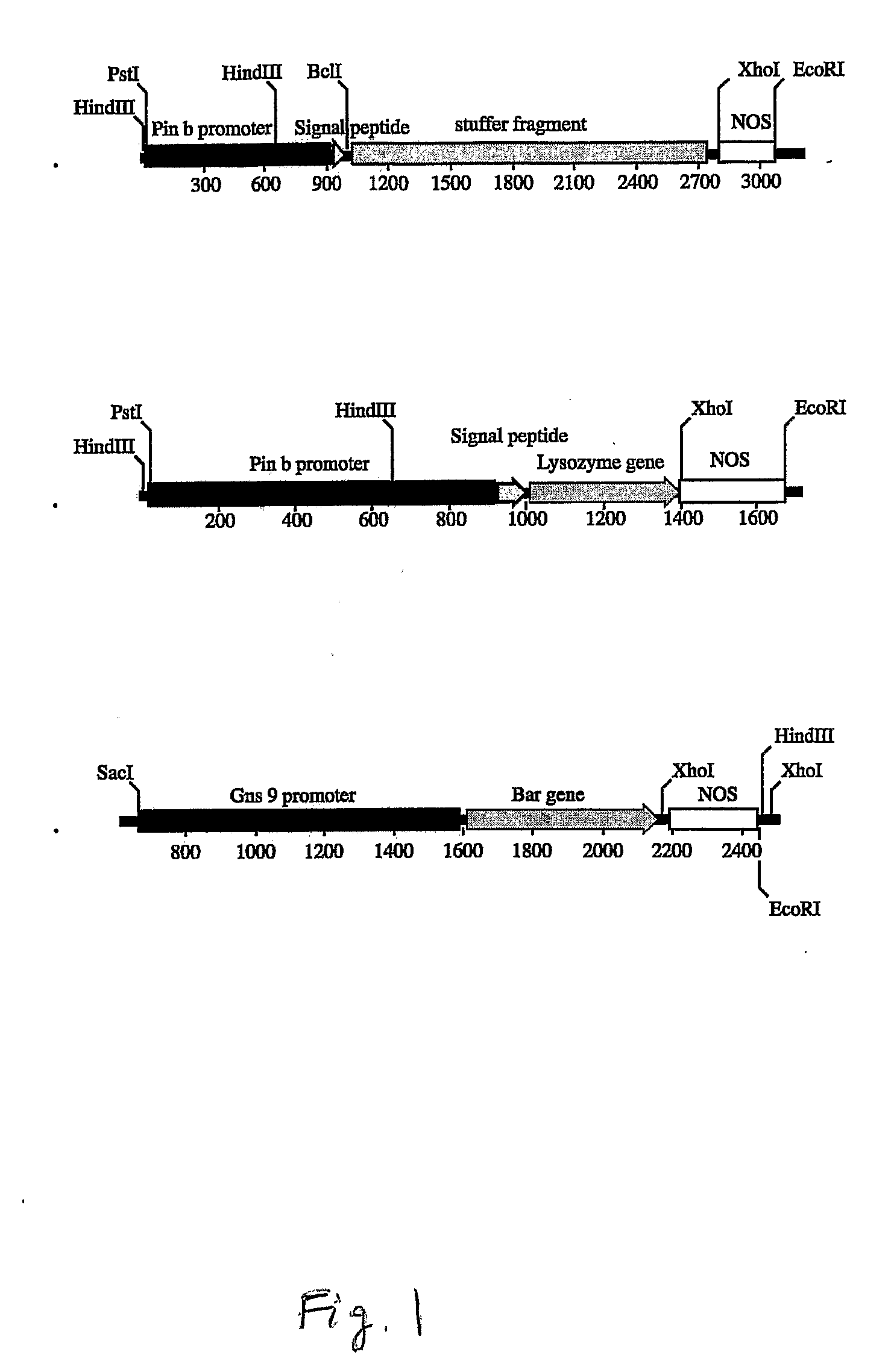
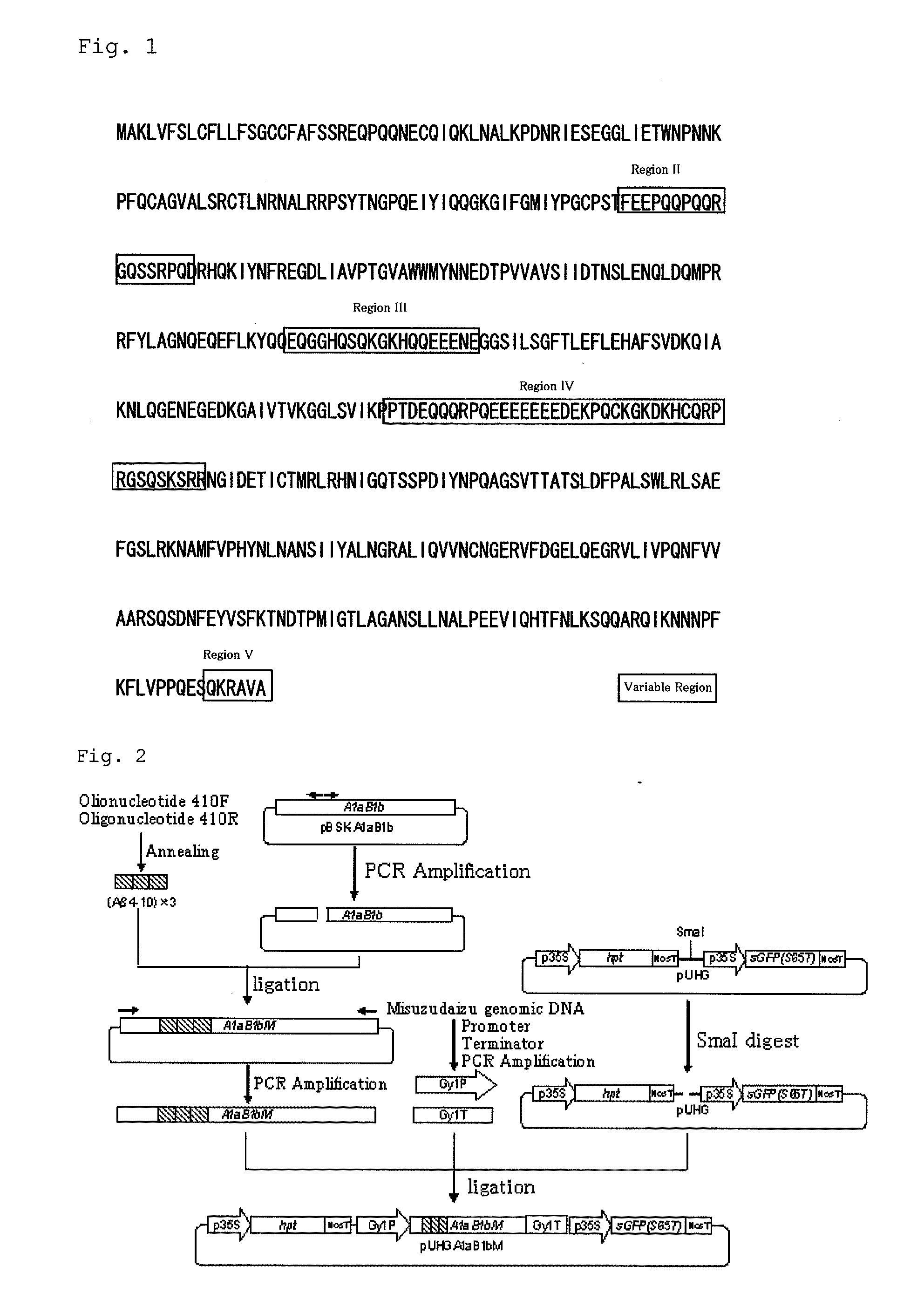
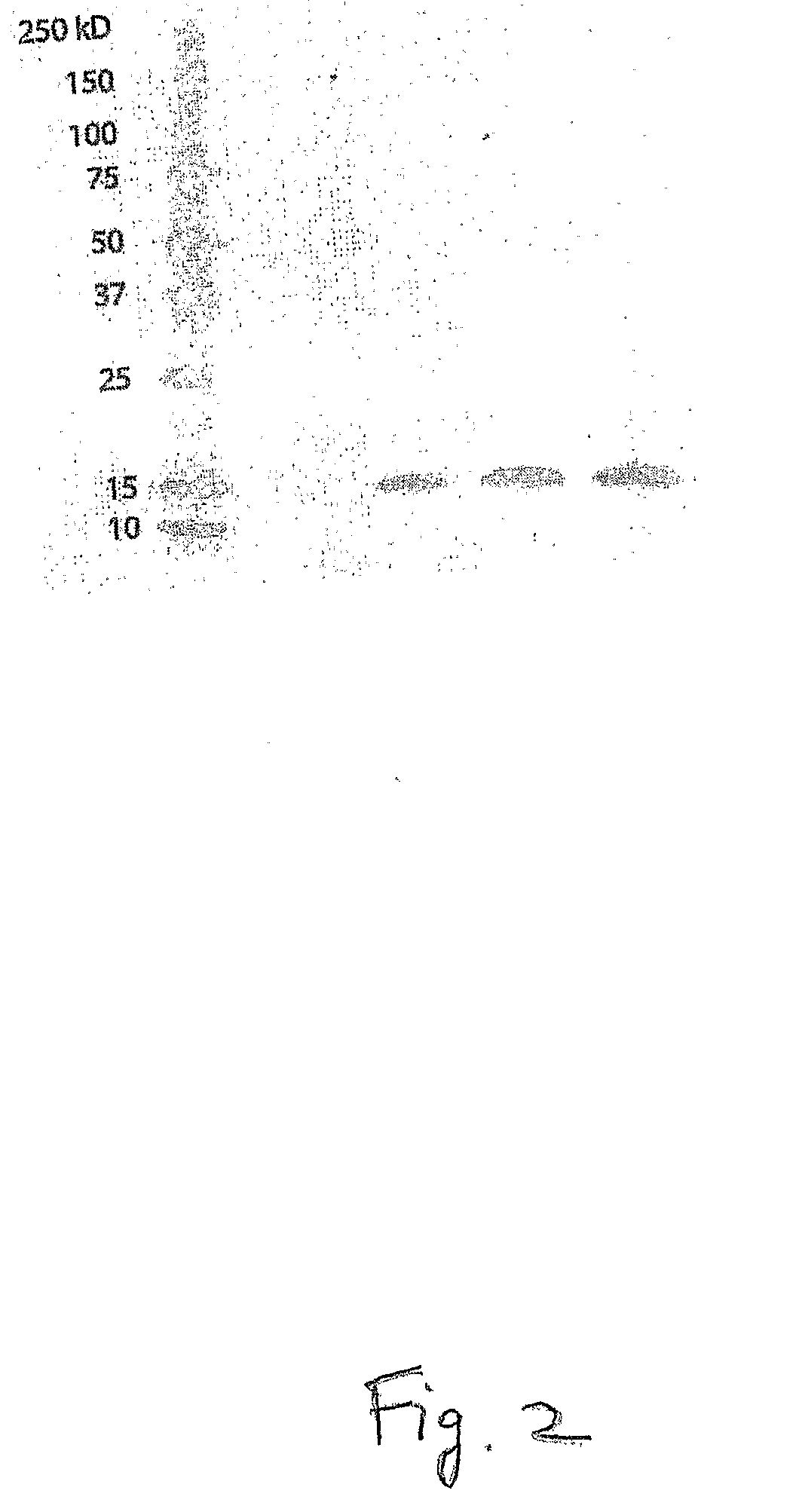Patents
Literature
100 results about "Storage protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Storage proteins serve as biological reserves of metal ions and amino acids, used by organisms. They are found in plant seeds, egg whites, and milk. Ferritin is an example of a storage protein that stores iron. Iron is a component of heme, which is contained in the transport protein, hemoglobin and in cytochromes.
Lipid metabolism regulators in plants
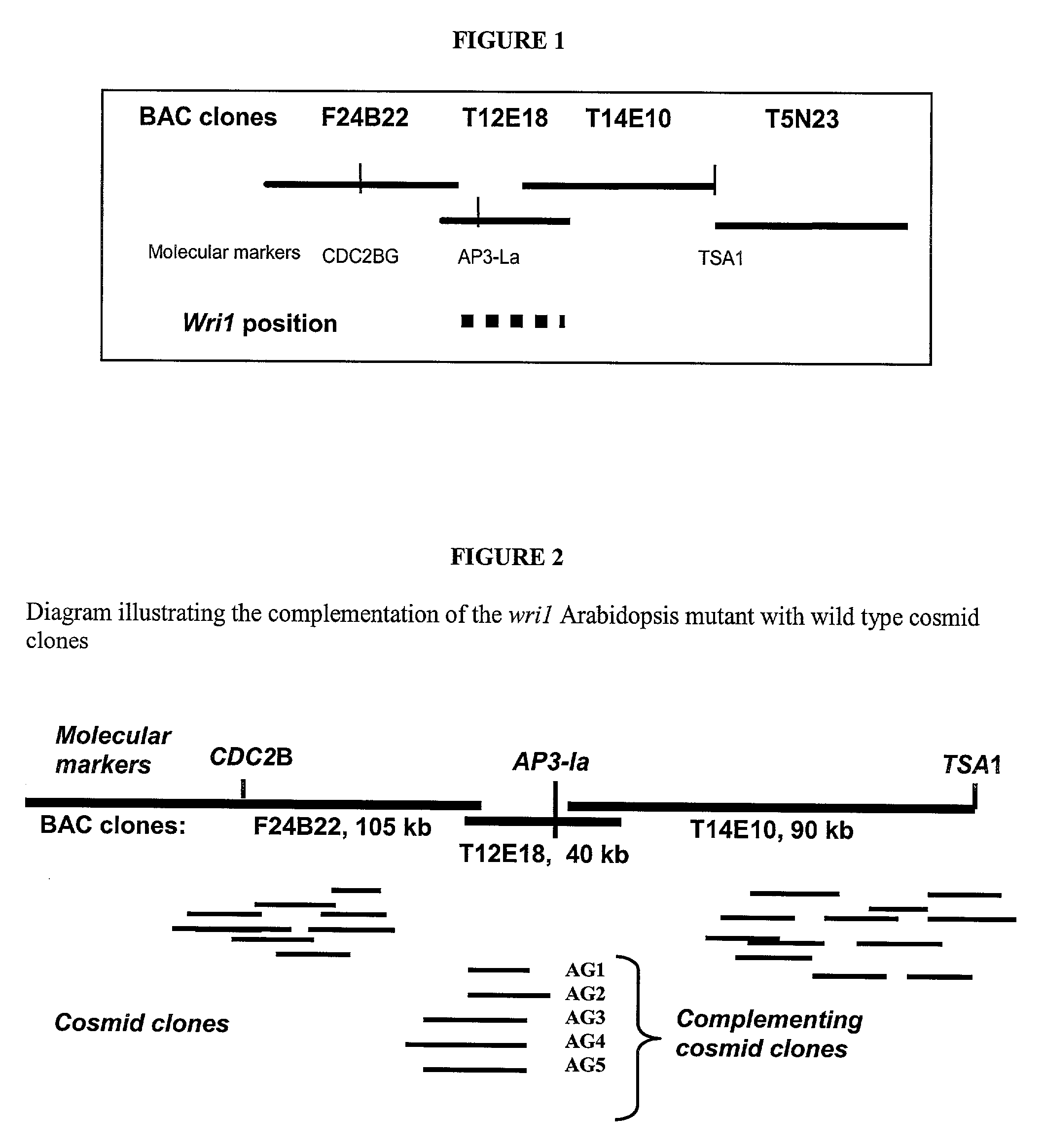
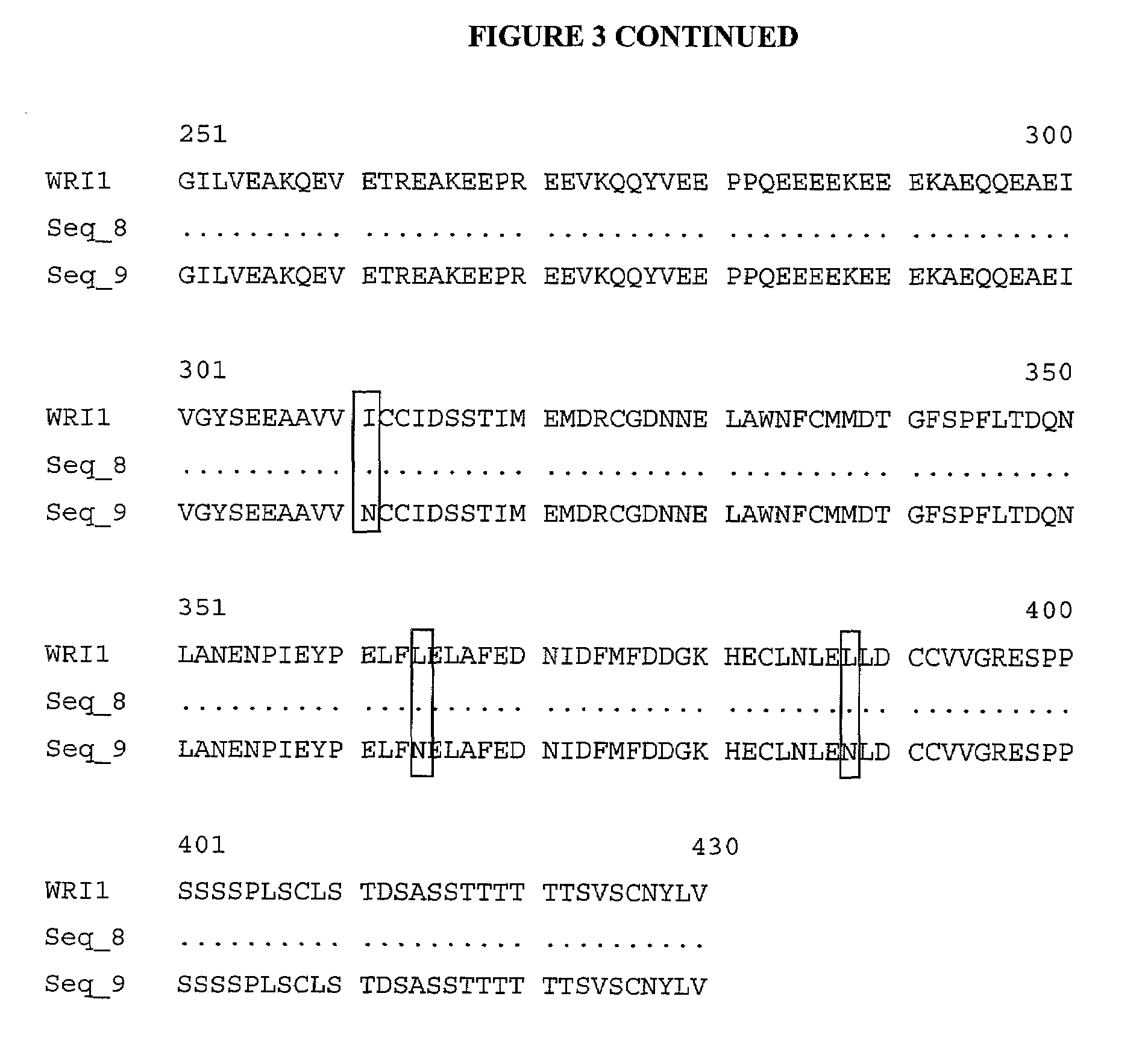
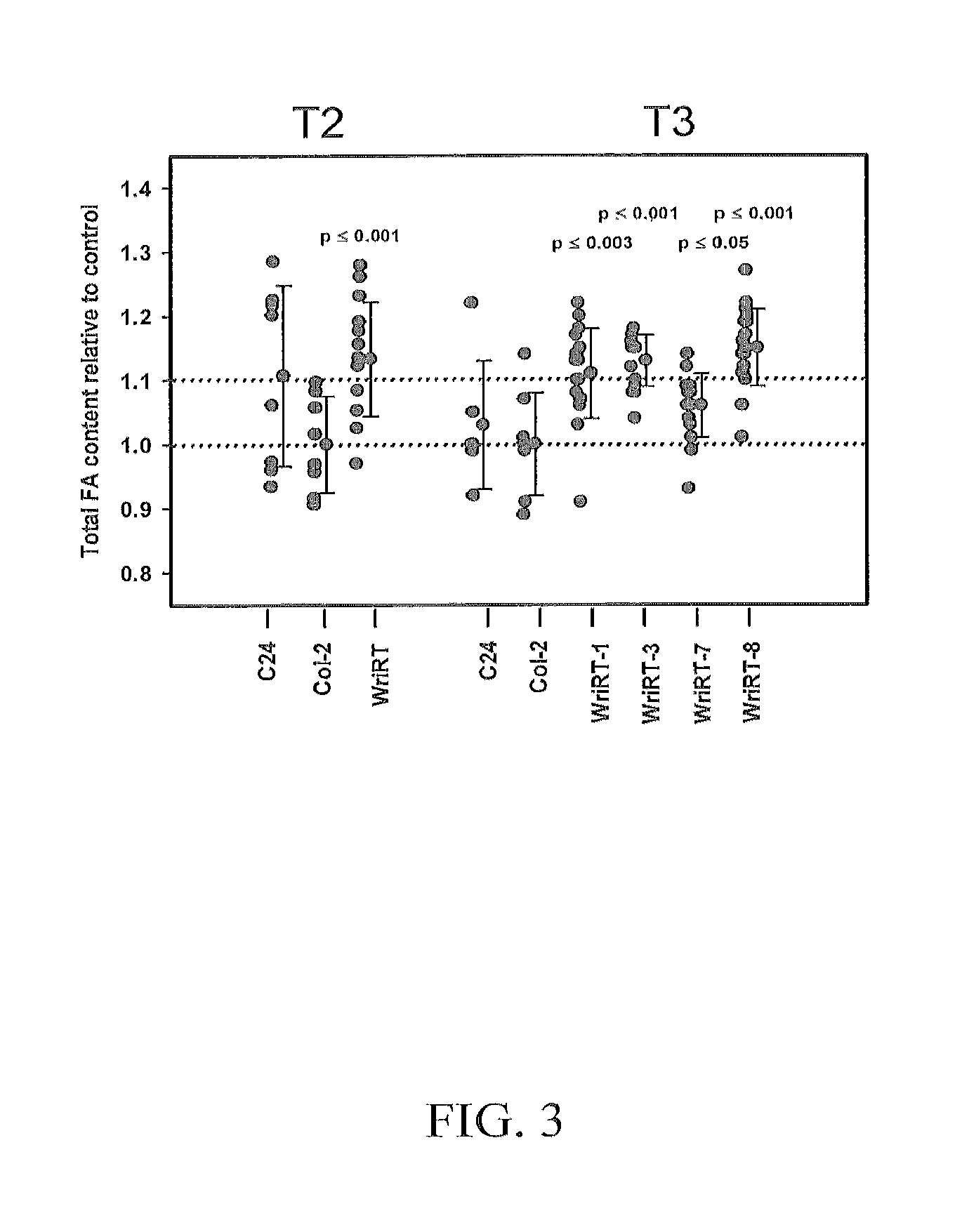
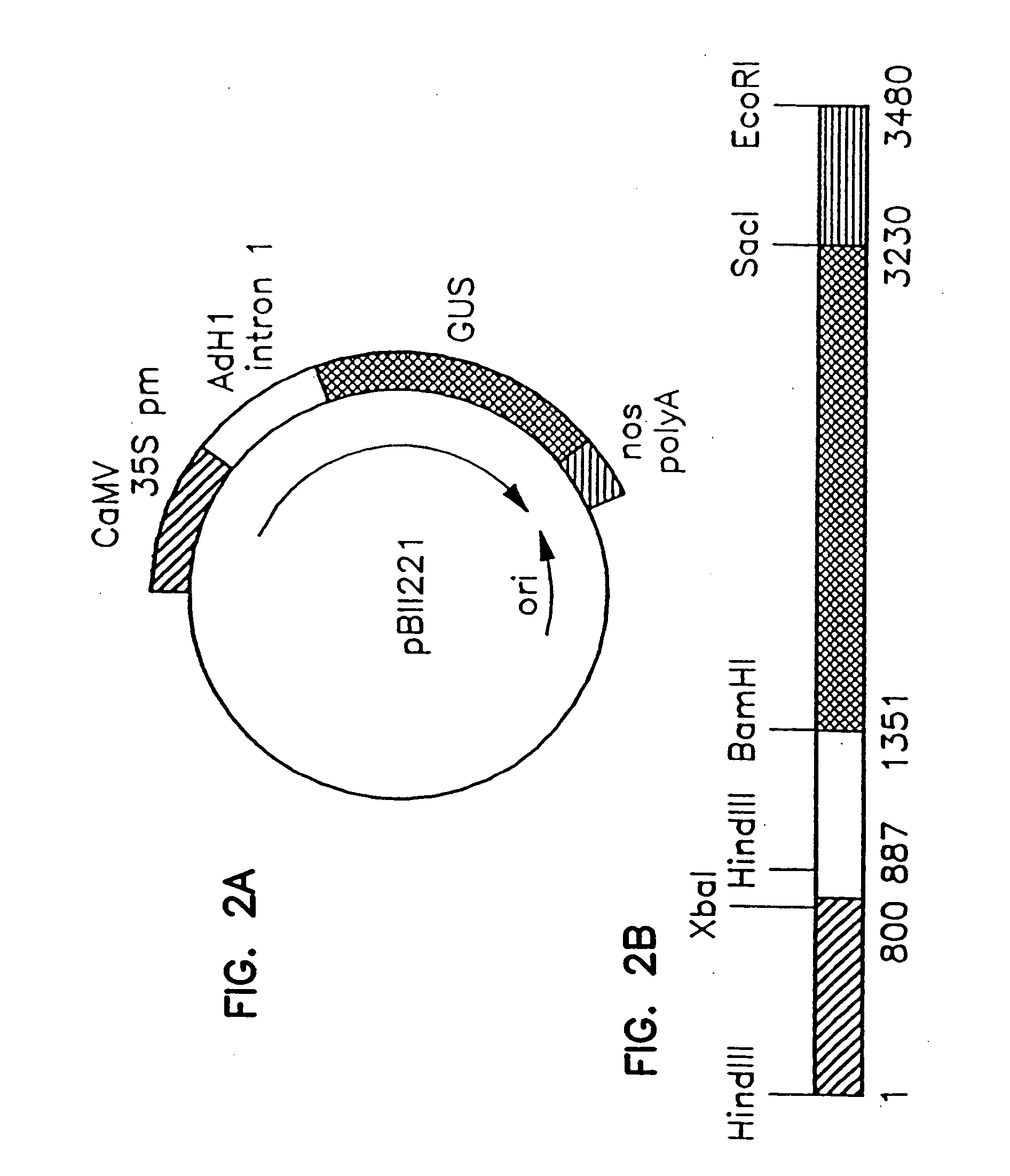
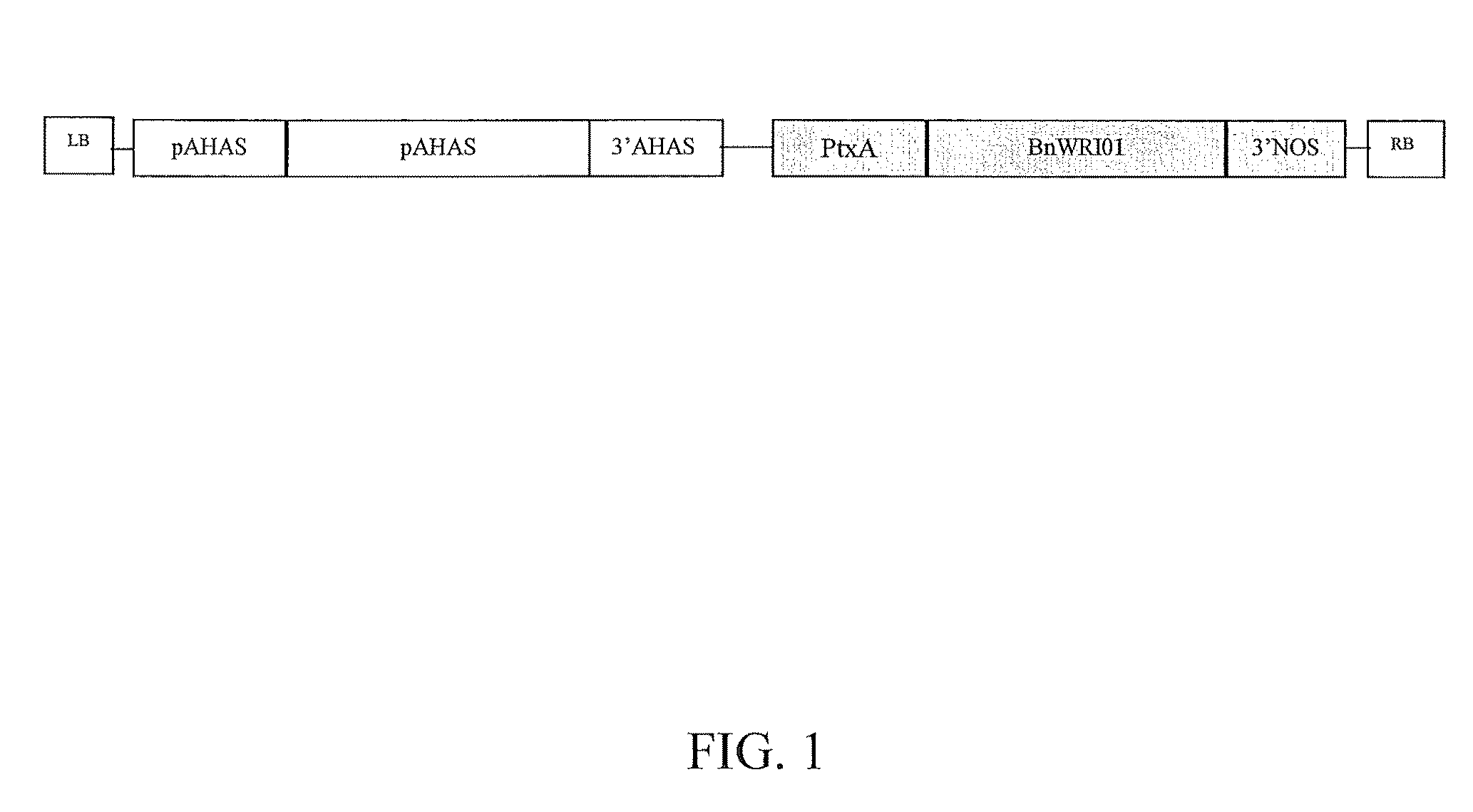
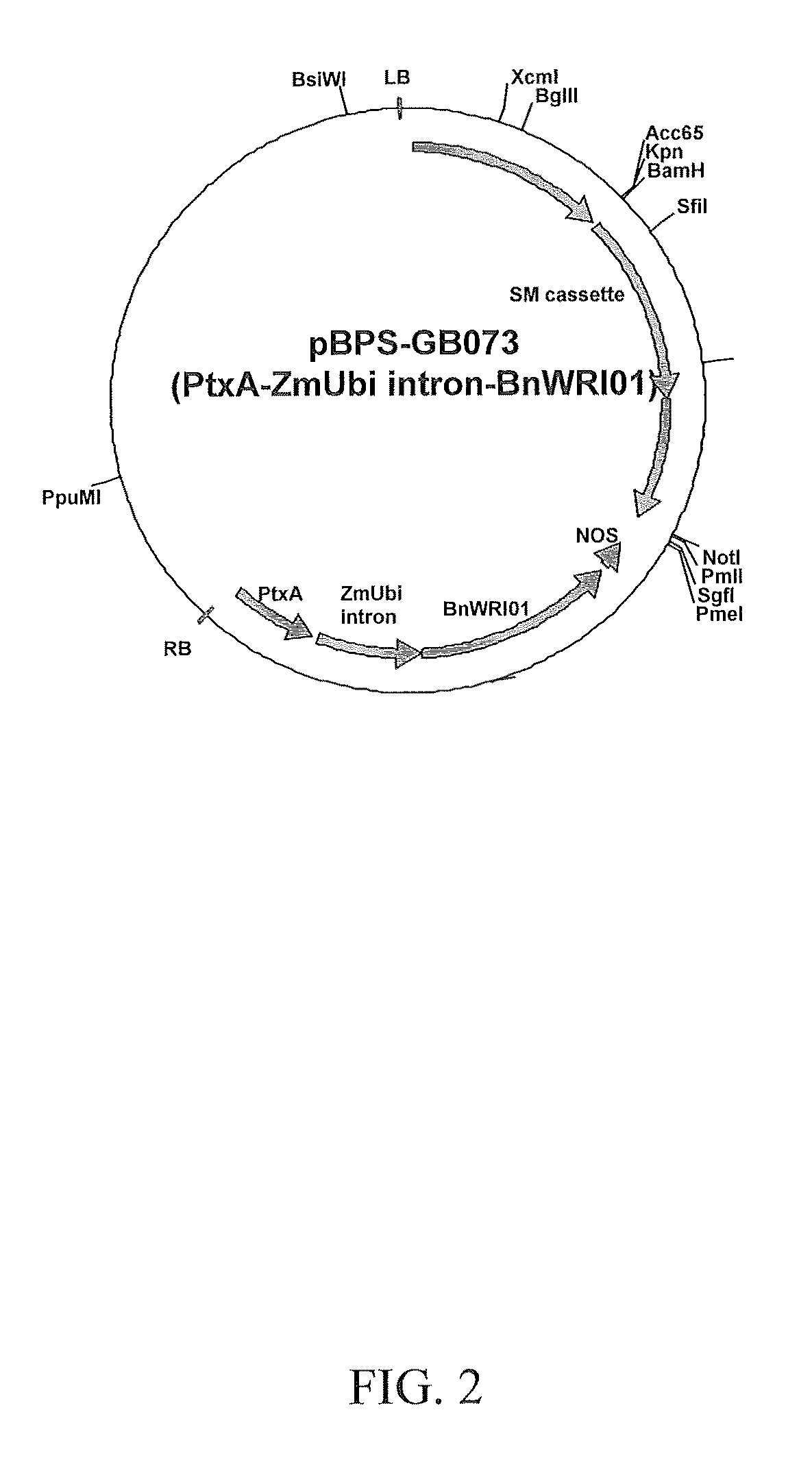
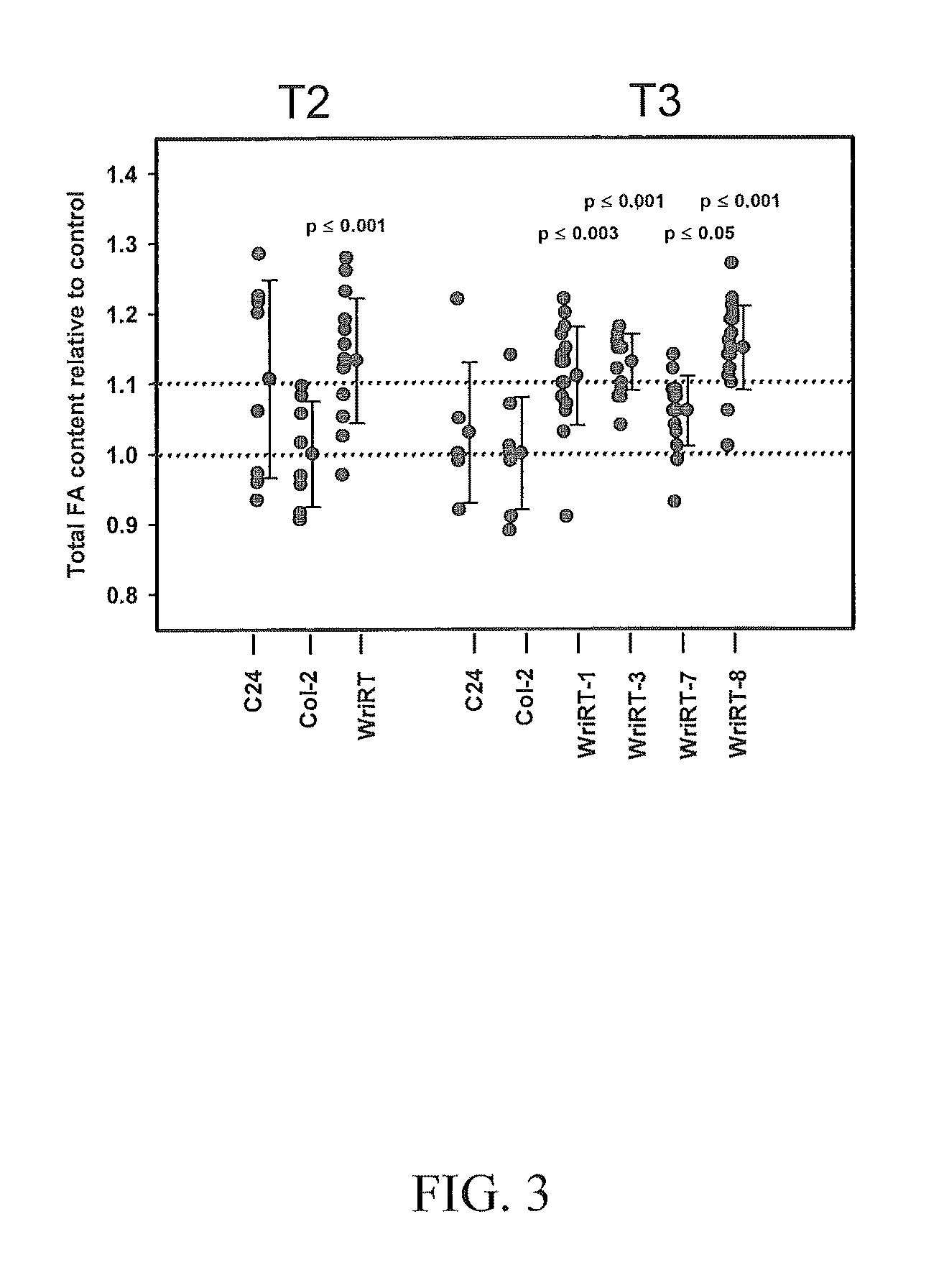
The present invention is directed to novel nucleic acid and amino acid sequences associated with the metabolism of seed storage compounds in plants. A novel discovery described herein lies in the identification of the nucleic acid sequences that encode the wri1 genetic locus in Arabidopsis thaliana, and lipid metabolism regulator (LMR) polynucleotide sequences contained therein. Preferably, the seed storage compounds are lipids, fatty acids, starches or seed storage proteins.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Nucleic acid molecules encoding WRINKLED1-like polypeptides and methods of use in plants
InactiveUS8217223B2High oil contentImprove the level ofBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyFatty acid
Isolated nucleic acids and proteins associated with lipid and sugar metabolism regulation are provided. In particular, lipid metabolism proteins (LMP) and encoding nucleic acids originating from Arabidopsis thaliana, Brassica napus, Glycine max, Oryza sativa, and Triticum aestivum are provided. The nucleic acids and proteins are used in methods of producing transgenic plants and modulating levels of seed storage compounds. Preferably, the seed storage compounds are lipids, fatty acids, starches, or seed storage proteins. The nucleic acids and proteins also are used in methods of modulating the seed size, seed number, seed weight, root length, and leaf size of plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
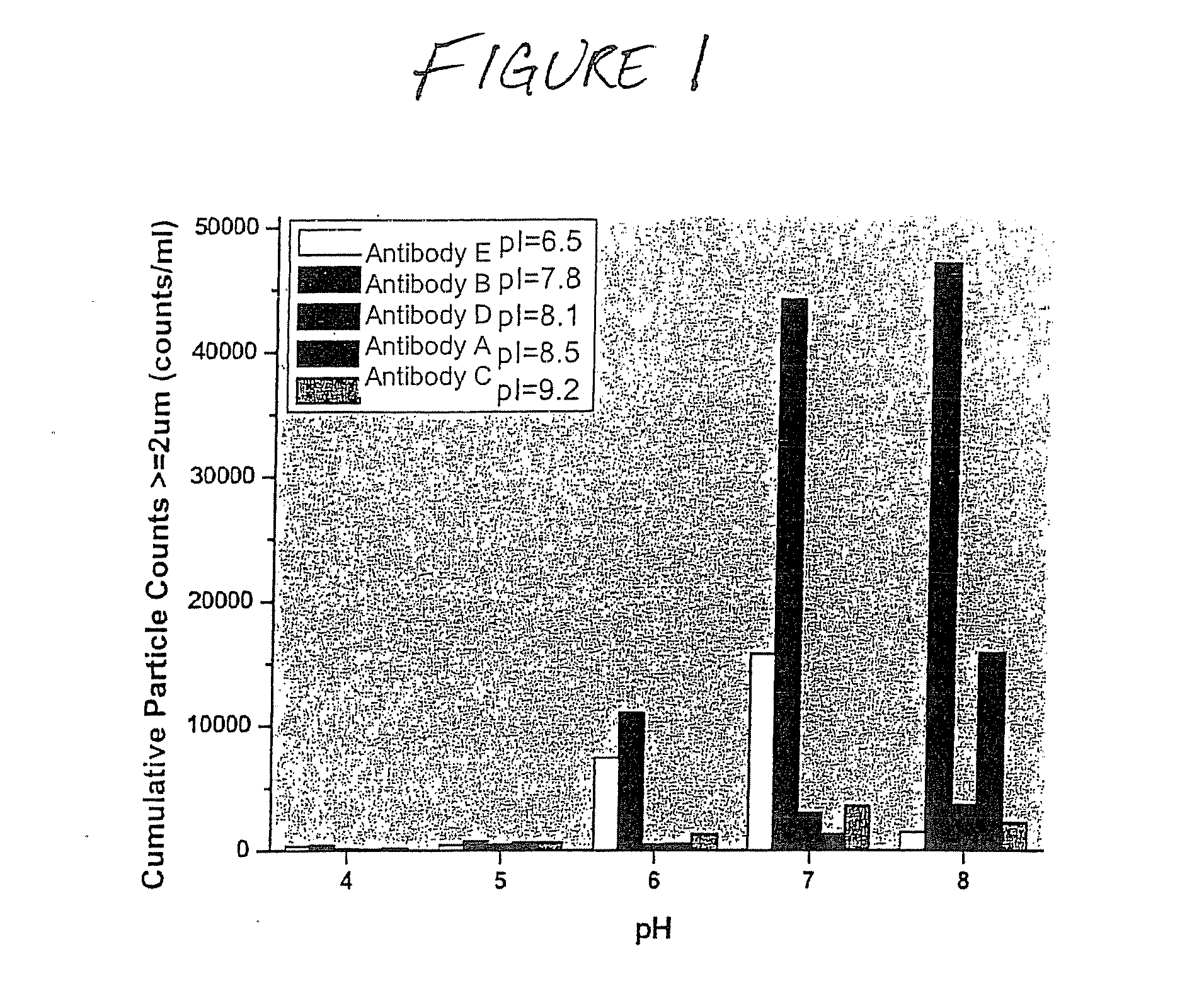
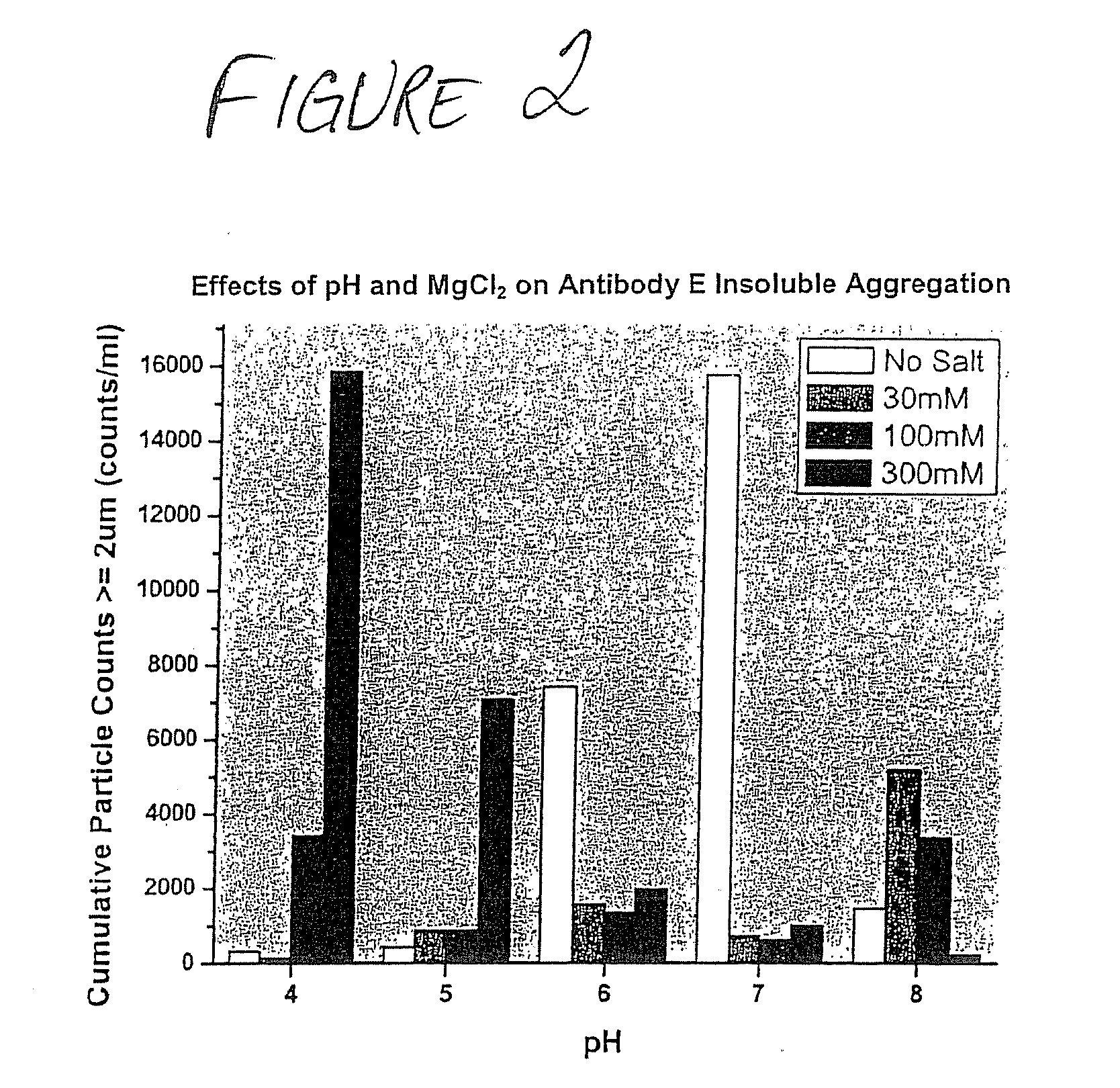
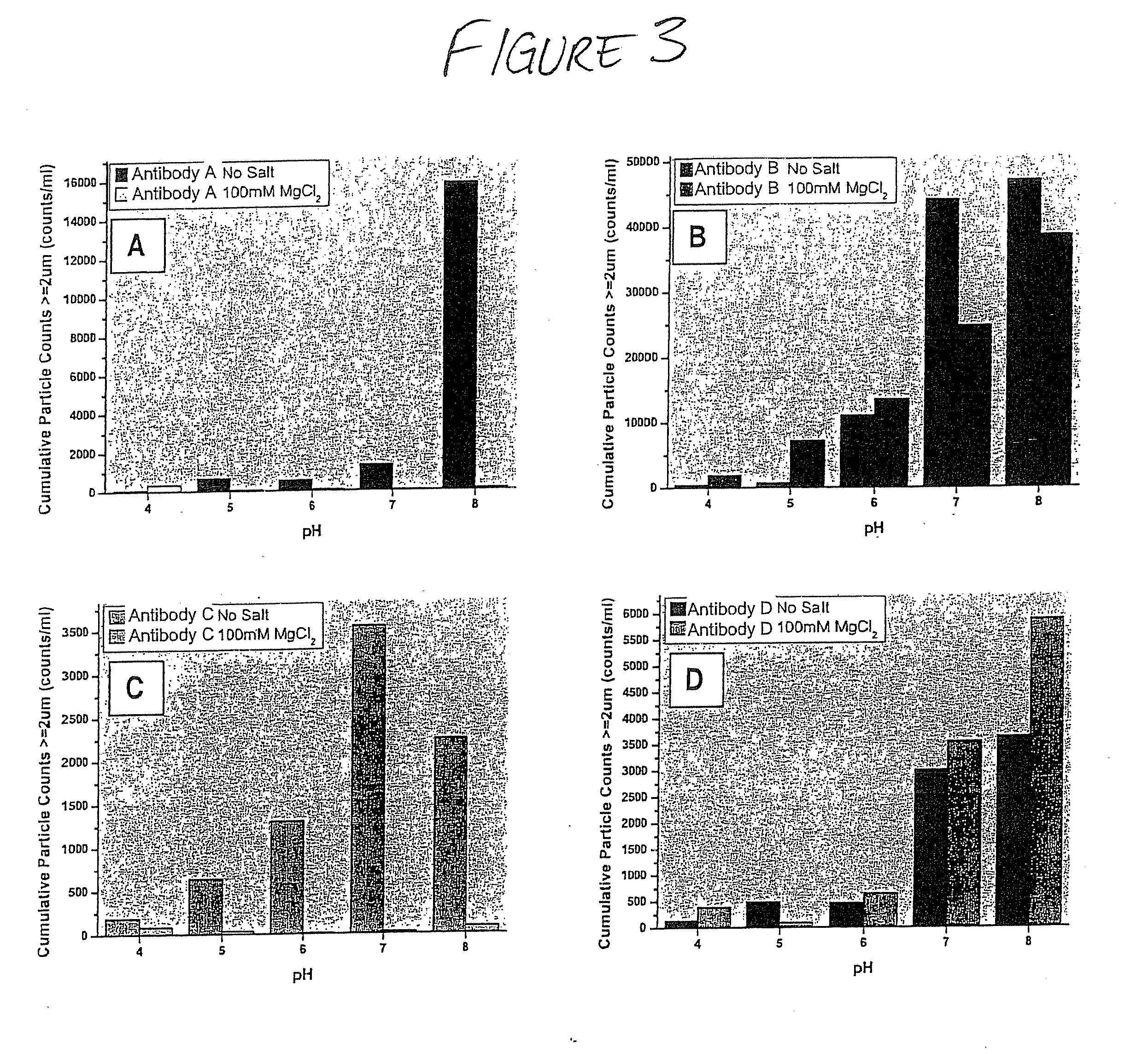
Formulations that inhibit protein aggregation
InactiveUS20070190047A1Inorganic non-active ingredientsAntibody ingredientsCell AggregationsProtein aggregation
Disclosed is a stable pharmaceutically acceptable formulation containing a pharmaceutically acceptable amount of a protein. Also disclosed are methods for preparing such formulations and methods for inhibiting protein aggregate formation induced by physical stresses associated with processing, manufacture, shipping, and storing protein formulations, particularly freeze / thaw stress.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Thermostable proteases
InactiveUS7179630B2High nutritional valueIncrease the degree of hydrolysisFatty acid chemical modificationDough treatmentWild typeTrypsin inhibitor
The present invention relates to thermostable proteases having an amino acid sequence which homologous to the amino acid sequence of proteases derived from Nocardiopsis, and the production thereof by wild-type and recombinant host cells including transgenic plants and non-human transgenic animals. The proteases are effective in animal feed, in particular fish feed, and detergents. The proteases are capable of degrading the soybean Bowman-Birk inhibitor, and other antinutritional factors such as soybean agglutinin and the Kunitz trypsin inhibitor, as well as the isolated soy storage proteins glycinin and beta-conglycinin. Characteristic structural features of relevance for the thermostability of these proteases of peptidase family S2A or S1E are disclosed.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Plant With Reduced Protein Content in Seed, Method of Constructing the Same and Method of Using the Same
InactiveUS20080096277A1Reduce expressionReduced protein contentBryophytesSugar derivativesGMO PlantsProtein content
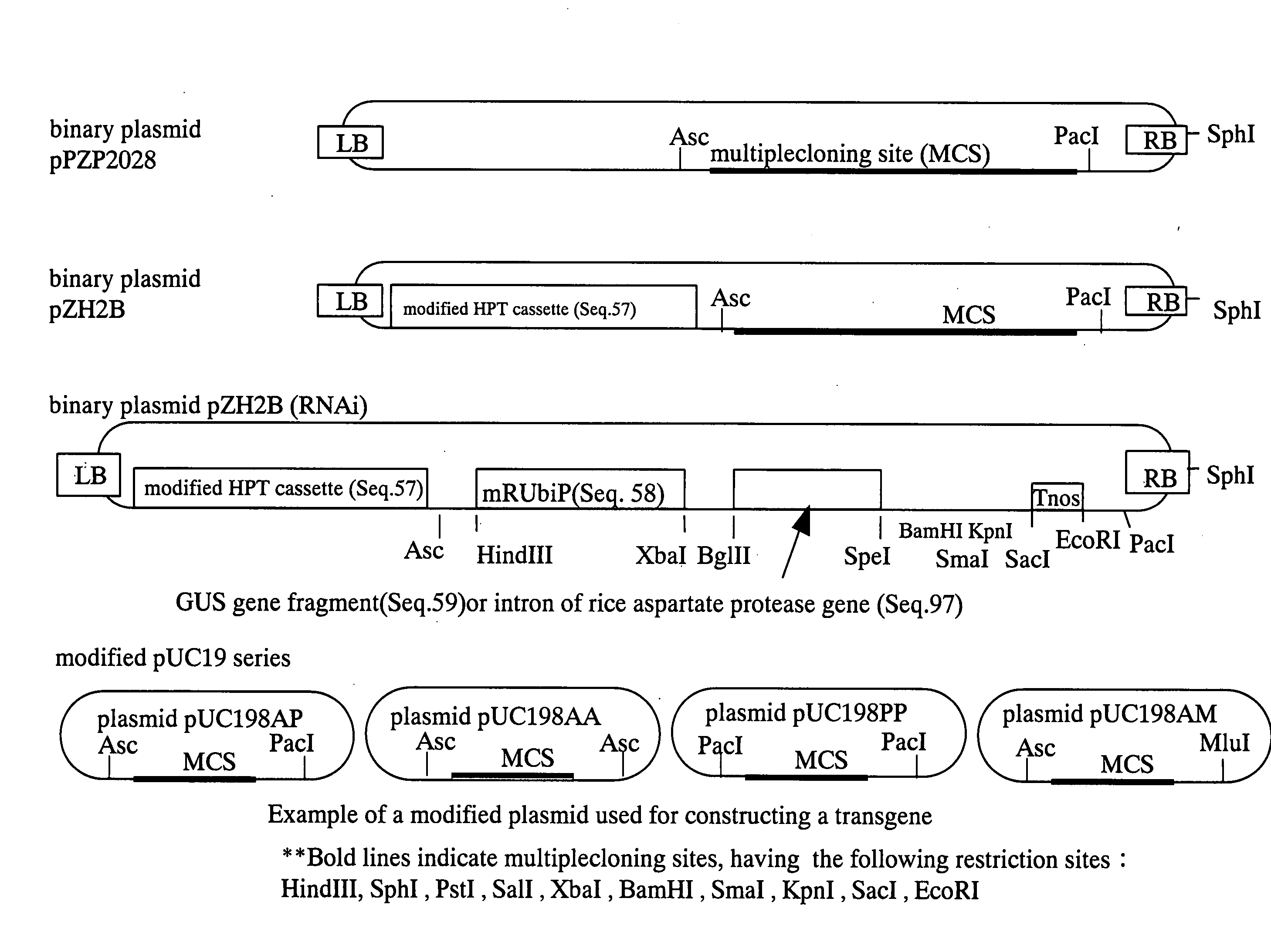
It is intended to provide a method of reducing the total amount of stored protein, to develop a technique required therefor, and to provide a plant and its seeds developed by the above method and a method of using such a plant and seeds. More specifically, a nucleic acid molecule containing a consecutive nucleic acid sequence of at least 15 in length which is complementary with a nucleic acid sequence encoding prolamine polypeptide or a nucleic acid sequence having a homology of at least about 70% to the complementary nucleic acid sequence having at least 15 nucleotide length. A method of reducing the expression dose of a protein in a seed of a plant which comprises: A) the step of providing the above-described nucleic acid molecule; B) the step of transferring the nucleic acid molecule into the cells of the plant; C) the step of re-differentiating the cells to construct a transgenic plant; and D) the step of obtaining seeds from the transgenic plant.
Owner:INC ADMINISTRATIVE AGENCY NAT AGRI & BIO ORIENTED RES ORG
Expression of human serum albumin (HSA) in monocot seeds
A method of producing human serum albumin (HSA) in monocot plant seeds, by transforming a monocot plant cell with a chimeric gene containing a promoter from the gene of a maturation-specific monocot plant storage protein, a first DNA sequence operably linked to the promoter and encoding a signal sequence, and a second DNA sequence linked in translation frame with the first DNA sequence and encoding HSA, where the first DNA sequence and the second DNA sequence together encode a fusion protein containing an N-terminal signal sequence and the HSA; growing a monocot plant from the transformed monocot plant cell for a time sufficient to produce seeds containing the HSA; and harvesting the seeds from the plant.
Owner:VENTRIA BIOSCIENCE
Preparation of heterologous proteins on oil bodies
The present invention relates to the use of a class of genes called oil body protein genes that have unique features. The discovery of these features allowed the invention of methods for the production of recombinant proteins wherein a protein of interest can be easily separated from other host cell components. The invention is further exemplified by methods for exploitation of the unique characteristics of the oil body proteins and oil body genes for expression of polypeptides of interest in many organisms, particularly plant seeds. Said polypeptides may include but are not limited to: seed storage proteins, enzymes, bioactive peptides, antibodies and the like. The invention can also be modified to recover recombinant polypeptides fused to oil body proteins from non-plant host cells. Additionally the invention provides a method of using recombinant proteins associated with seed oil bodies released during seed germination for expression of polypeptides that afford protection to seedlings from pathogens. Finally, the persistent association of oil body proteins with the oil body can be further utilized to develop a biological means to create novel immobilized enzymes useful for bioconversion of substrates.
Owner:SEMBIOSYS GENETICS INC
High-level expression of fusion polypeptides in plant seeds utilizing seed-storage proteins as fusion carriers
InactiveUS20070150976A1High expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesHeterologousHigh level expression
The expression of heterologous peptides or polypeptides in the seeds of monocot plants is optimized by generating fusion protein constructs in which monocot plant seed storage proteins are used as fusion protein carriers for the heterologous peptides or polypeptides. The heterologous peptides or polypeptides are preferably small, about 10 kDa or less and / or between 5 and 100 amino acids in length. These heterologous peptides or polypeptides may be used in human and animal nutritional and therapeutic compositions.
Owner:VENTRIA BIOSCIENCE
Method and uses for expressing polypeptide in endosperm using cereal non-storage protein as fusion vector
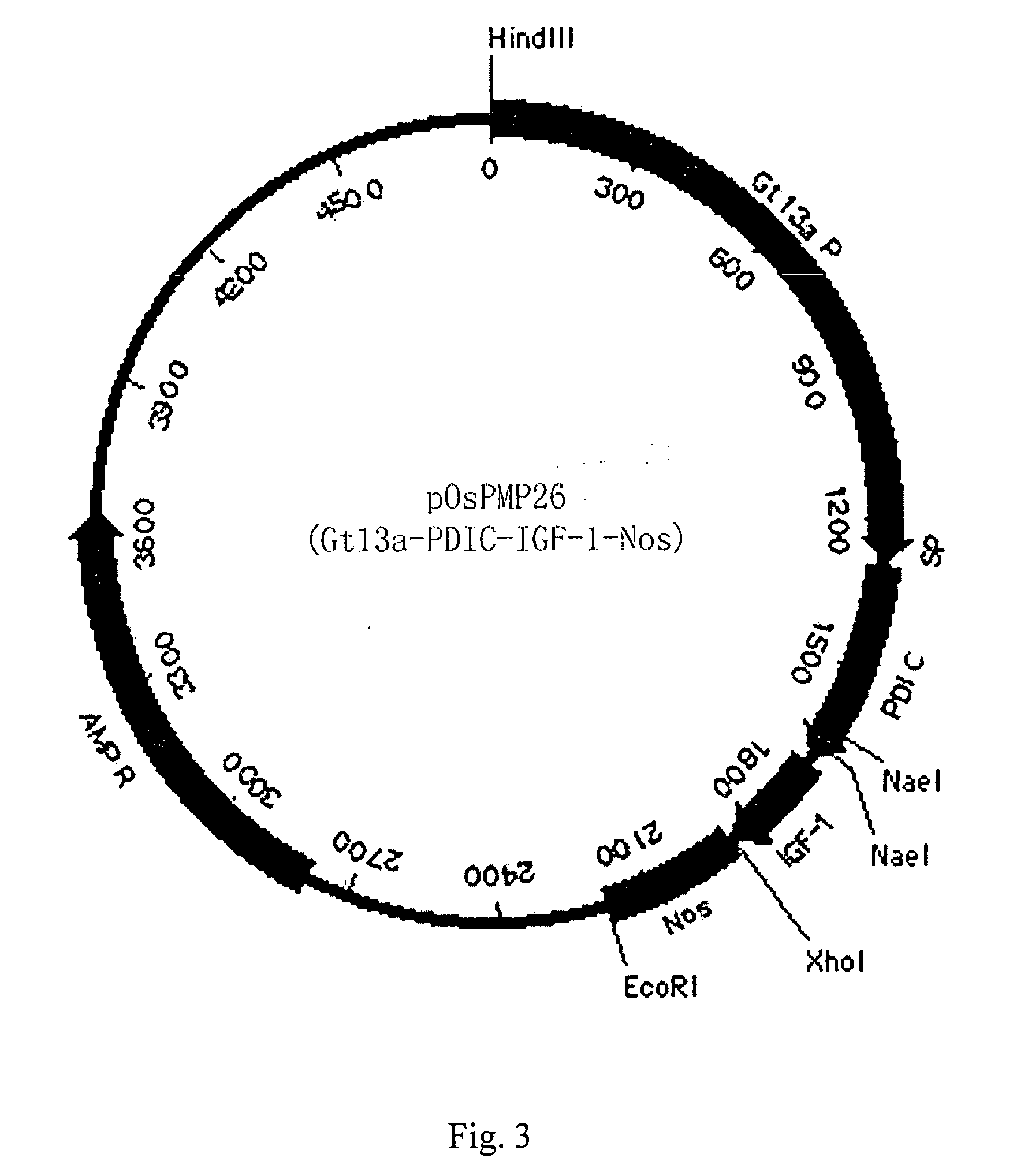
ActiveCN1884517AImprove solubilityBiologically activeInsulin-like growth factorsFermentationGenetically modified riceFusion Protein Expression
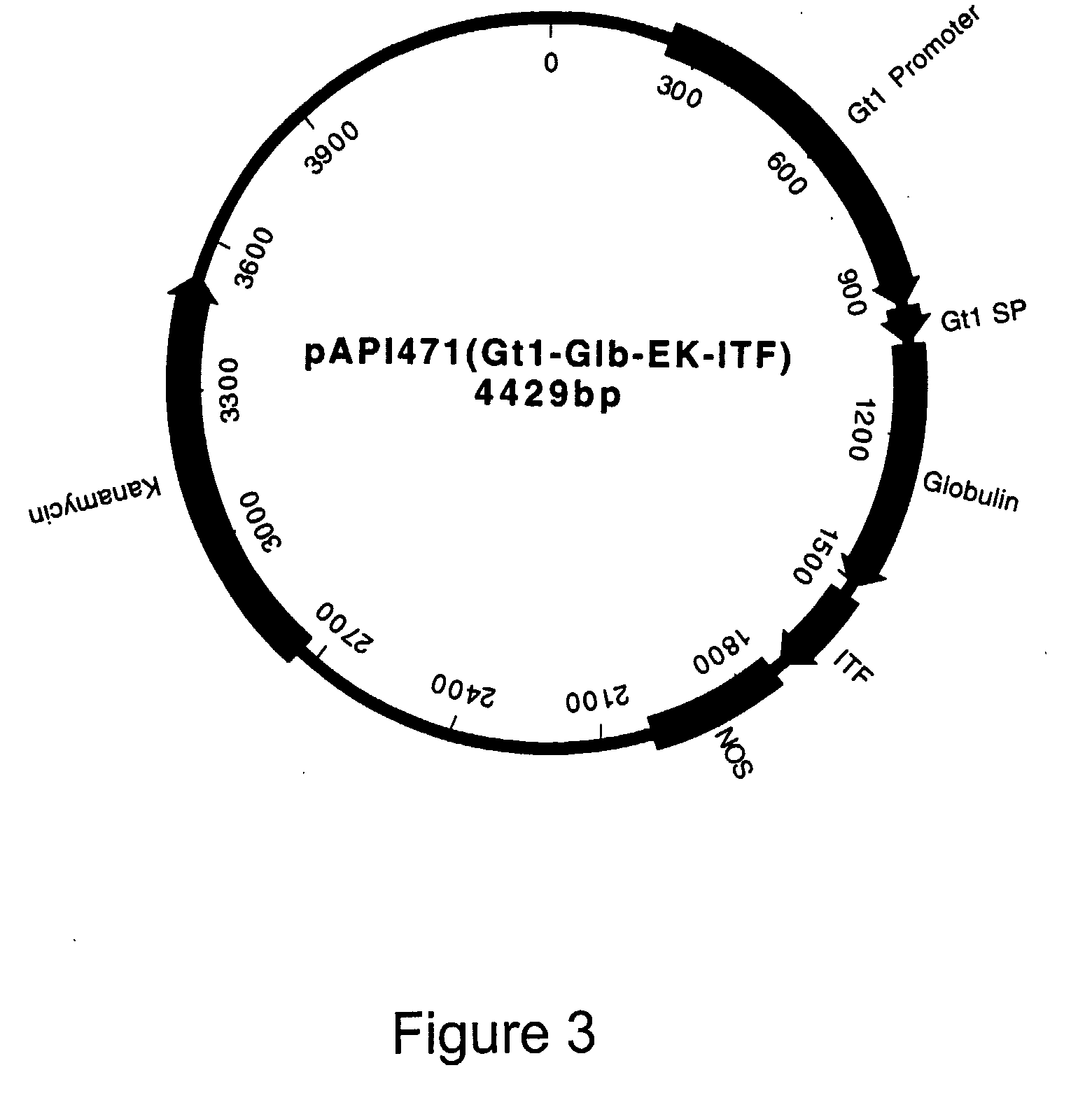
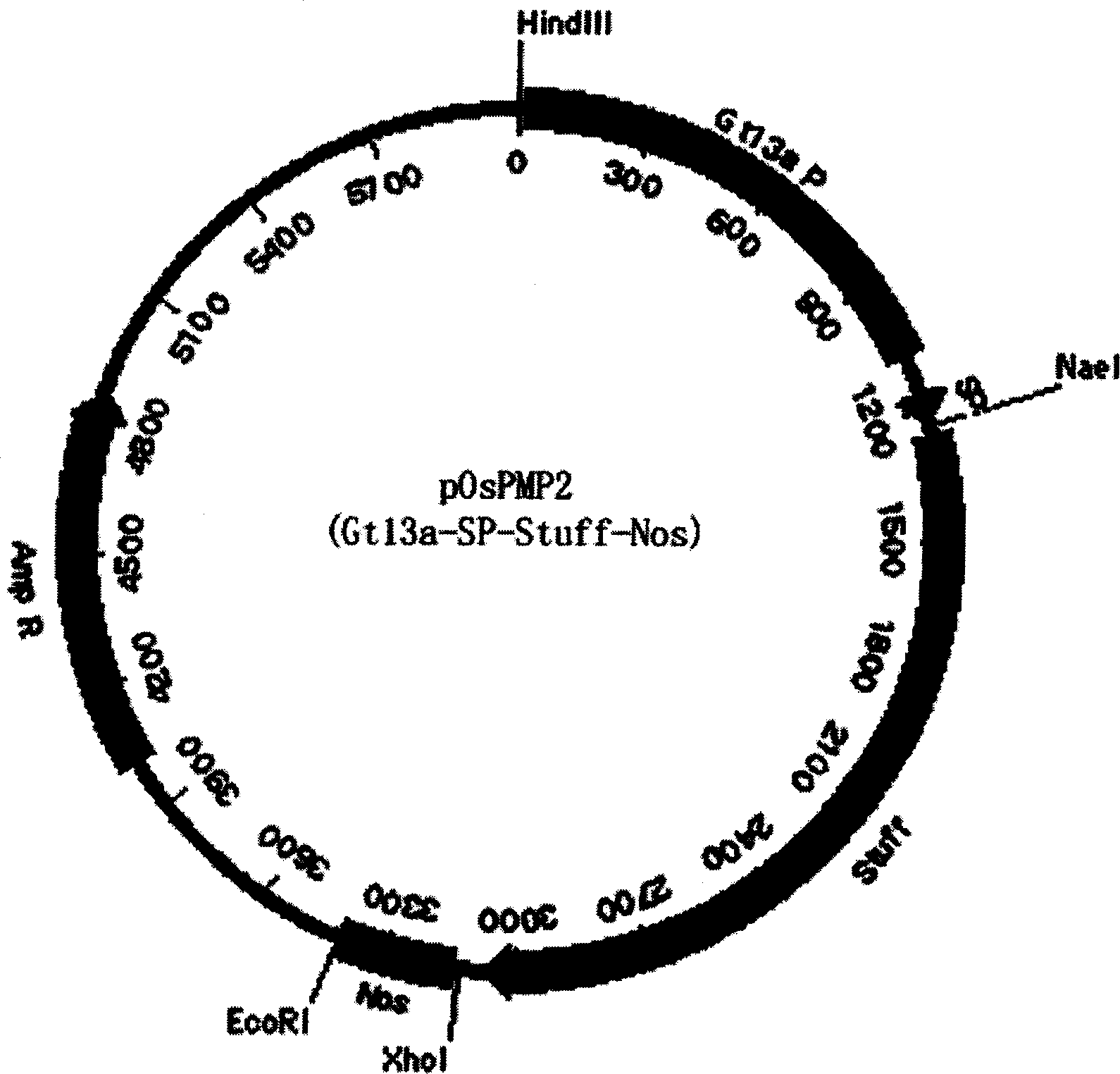
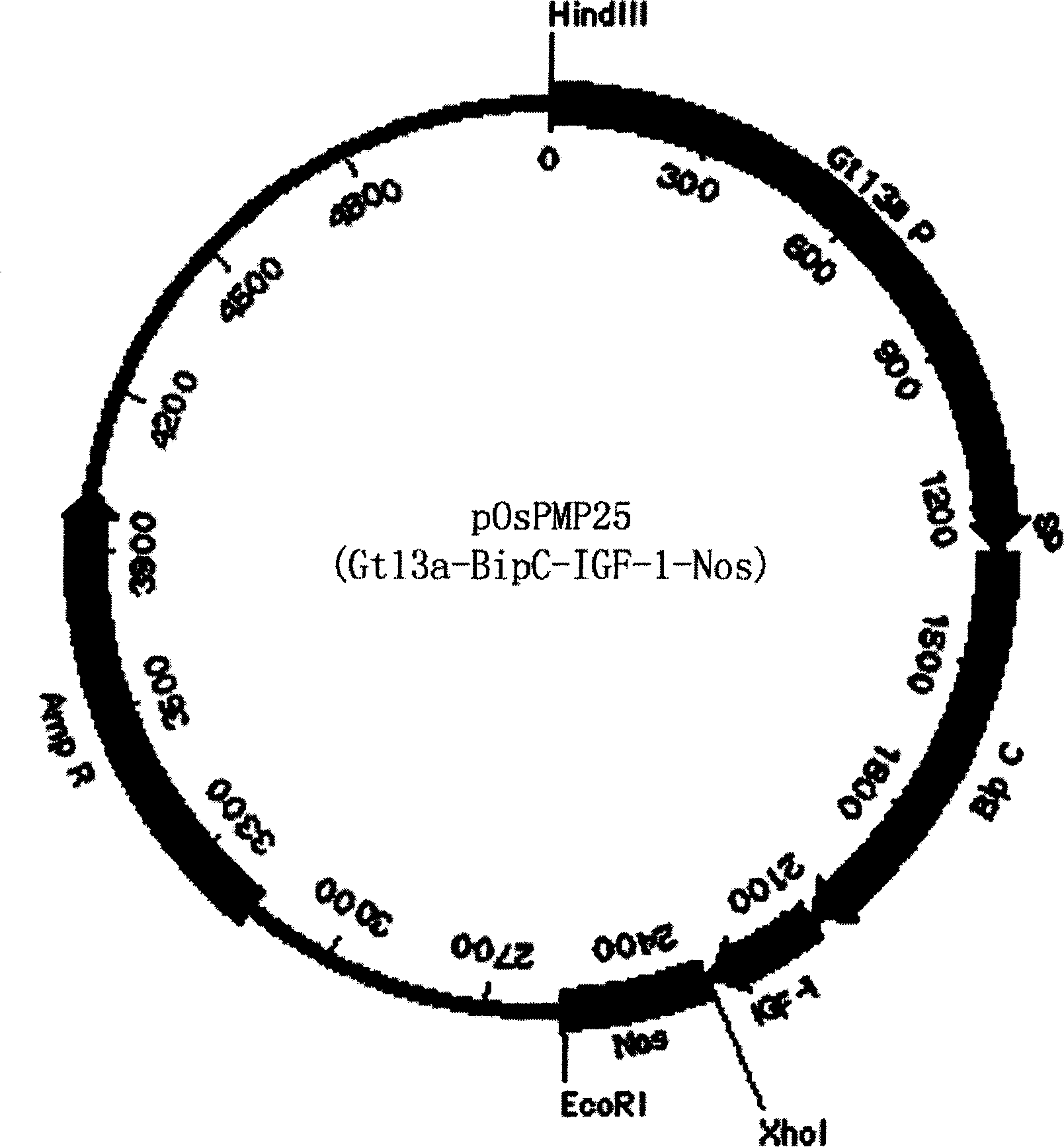
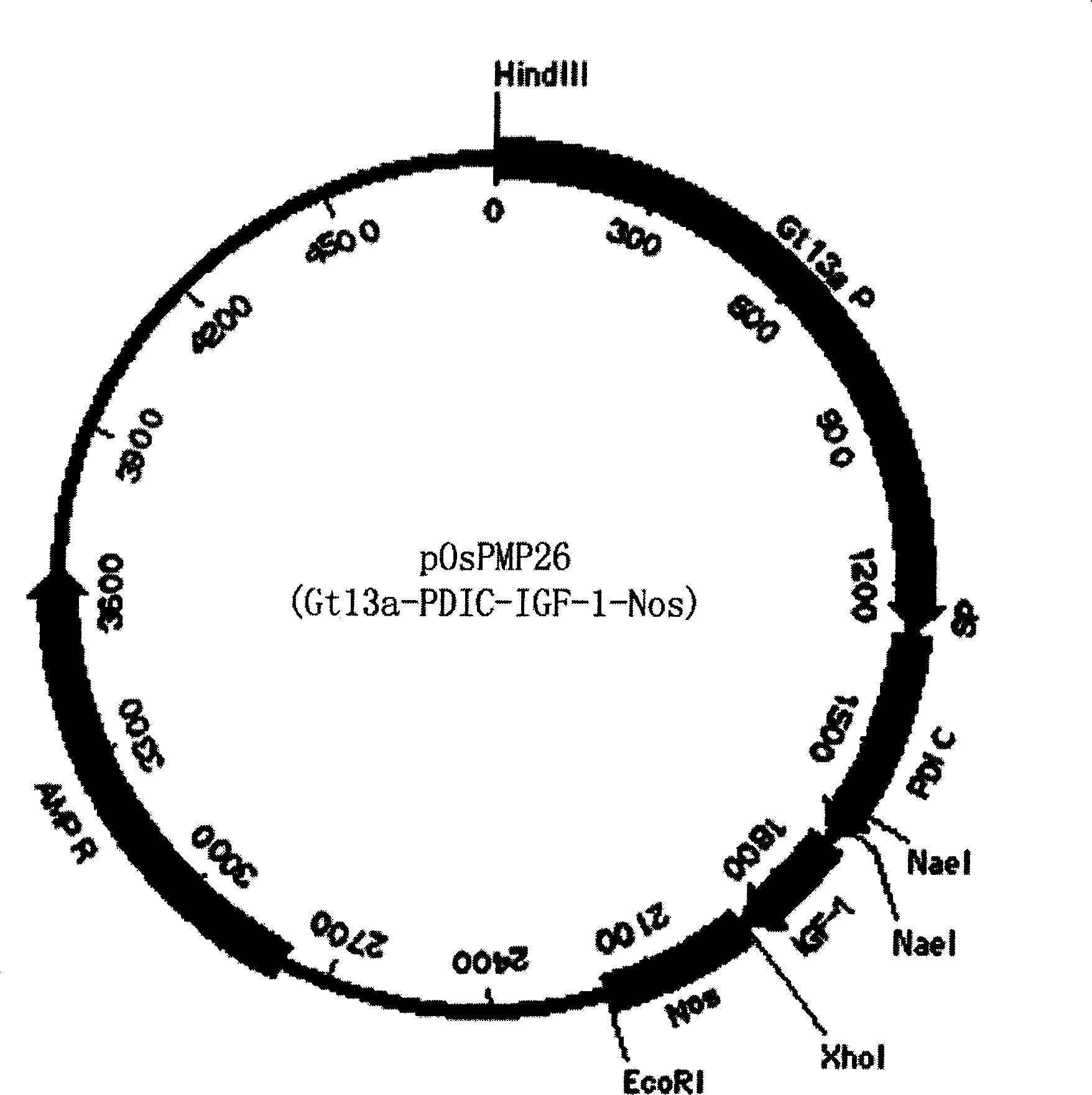
The invention discloses a method of using corn non-storage protein as molten carrier in endosperm expression polypeptide and its application, which includes: first obtaining rice astopic promoter and signal peptide; secondarily constructing rice albuminous cell specific expression carrier; thirdly using rice preference codon to prepare rice non-storage protein Bip gene C-end which is used as molten carrier, wheat PD1 gene C end and para-insulin growth factor-1 gene; fourthly constructing expression fusion protein carrier; fifthly obtaining genetically modified rice and barley plant with more than 0.3 % seed dry weight of their fusion protein expression. The invention is of simple process, convenient operation and low cost, and can be used in corn endosperm to express various polypeptides.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP
Methods of Expressing Heterologous Protein in Plant Seeds Using Monocot Non Seed-Storage Protein Promoters
InactiveUS20080010697A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesRice plantsPlanting seed
The invention is directed to expression of non-plant proteins in rice plants. Expression is optimized by use of a non-rice promoter of a monocot protein gene and its corresponding signal peptide for expression of the non-plant protein in rice plant at high yields. The invention is useful for making human proteins, polypeptides and peptides in rice seeds. The expressed protein product can be isolated from the rice seed for administration to humans or other animals.
Owner:VENTRIA BIOSCIENCE
Transformed soybean plant which accumulates vaccine, and use thereof
ActiveUS20110243975A1Efficient productionAccelerate the accumulation processNervous disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseWild type
A transformed soybean plant having a gene encoding a modified seed storage protein introduced therein, obtained by inserting a gene encoding an Alzheimer's disease vaccine to a variable region(s) of a gene encoding a wild-type seed storage protein, is produced, and said vaccine is produced and accumulated in the seeds thereof.
Owner:HOKKO CHEM IND CO LTD (JP)
Method of expressing small peptides using cereal non-storage proteins as fusion carrier in endosperm and the use thereof
ActiveUS20070289033A1Reduce solubilityPoor bioactivitiesSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesSmall peptideA-DNA
The present invention provides a method of using cereal non-storage protein as fusion carrier to highly express small peptides in host endosperm cells. The method includes the steps of providing an endosperm-specific promoter and a DNA leading sequence encoding an endosperm-specific signal peptide; providing the gene of a non-storage protein as fusion carrier and an target gene; constructing a expression vector containing the promoter and DNA leading sequence, the gene of the fusion carrier, and a target gene; and expressing the expression vector in a host endosperm cell. Also provided in the invention are a vector constructed there from and the use thereof.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP
Leavened products made from non-wheat cereal proteins
InactiveUS20090304861A1Stress resistantProtein composition from fishDough treatmentAdditive ingredientProtein-protein complex
Gluten-free baked products, particularly gluten-free bread products, which exhibit properties comparable those made with wheat flour. Compositions and methods for preparation of gluten-free baked products. A conditioned protein or protein composite which functions to replace gluten in gluten-free flour. The conditioned protein comprises one more non-wheat cereal storage proteins, particularly prolamins, optionally, but preferably in combination with one or more co-proteins which function to facilitate formation and stabilize formation of a protein network, e.g., β-sheet network, that facilitates retention of CO2 for leavening. More specifically, protein composites of zein and or other non-wheat prolamins with co-proteins including casein, elastin or mixtures thereof conditioned at temperatures above the glass transition temperature of the protein mixture provide improved ingredients for preparation of gluten-free breads and other baked products. Sorghum or maize mutant flours with prolamins available for viscoelastic protein formation may also be used.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
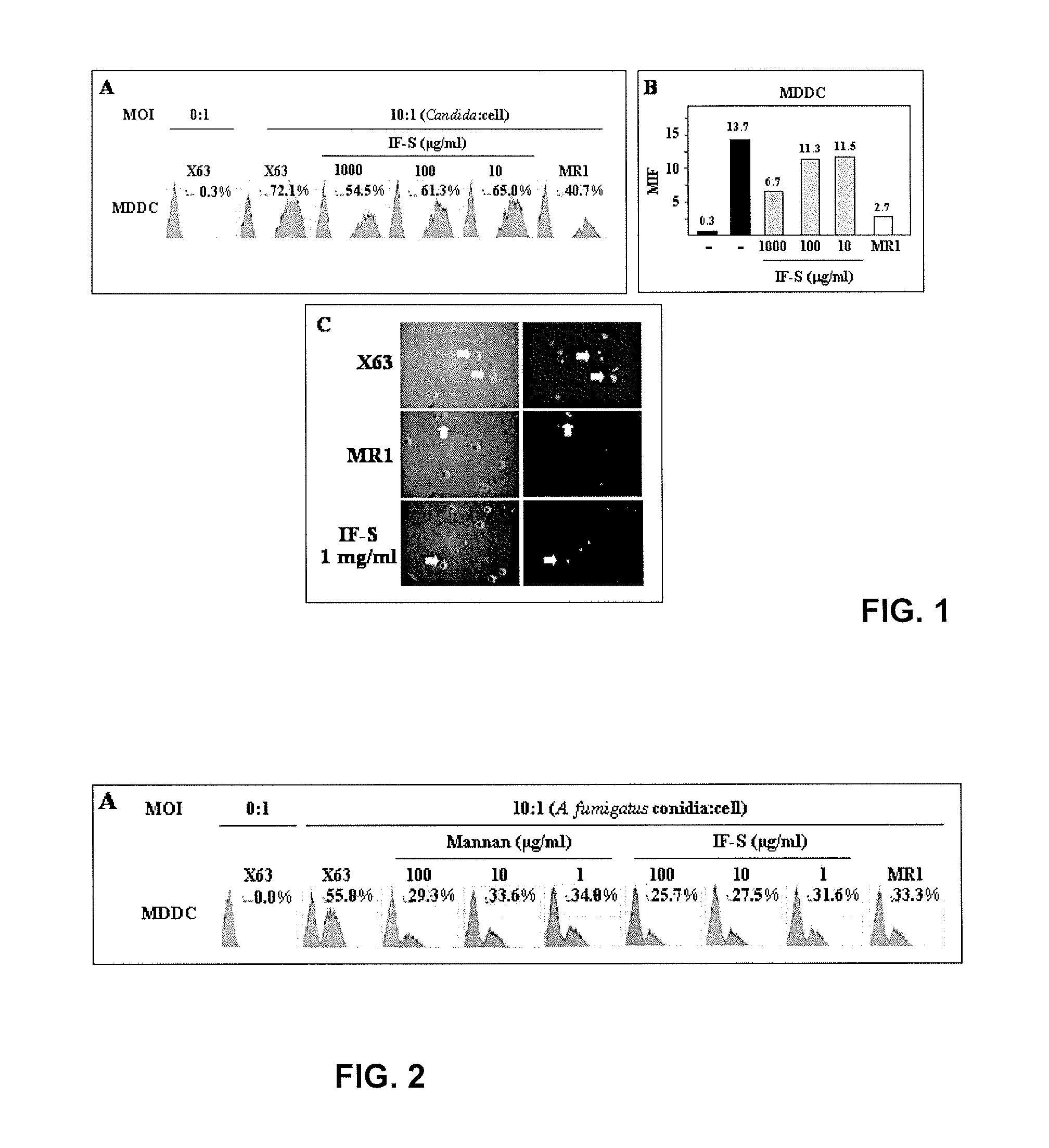
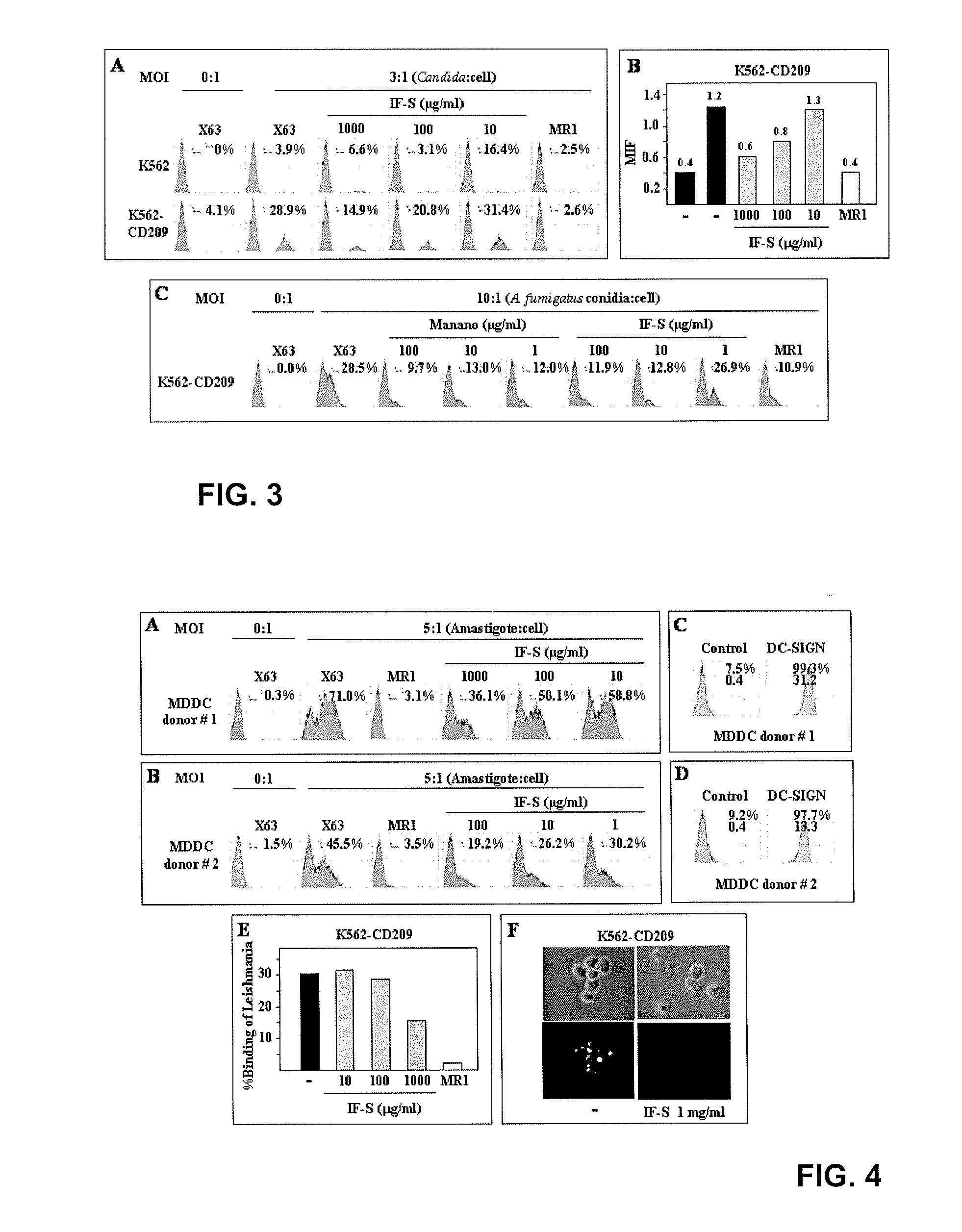
Products For Receptor Mediated Activation And Maturation Of Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cells By A Phosphorylated Glucomannane Polysaccharide
InactiveUS20080171002A1Easy to identifyOvercome problemsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDendritic cellPhosphorylation
Phosphorylated glucomannan polysaccharide compositions are shown to effectively enhance healthy immune function. Dosage forms including pills, sprays, functional foods and cosmetics may achieve this benefit while being essentially free of storage protein from nongerminated seeds of Ricinus communis.
Owner:CANTABRIA GROUP LCC
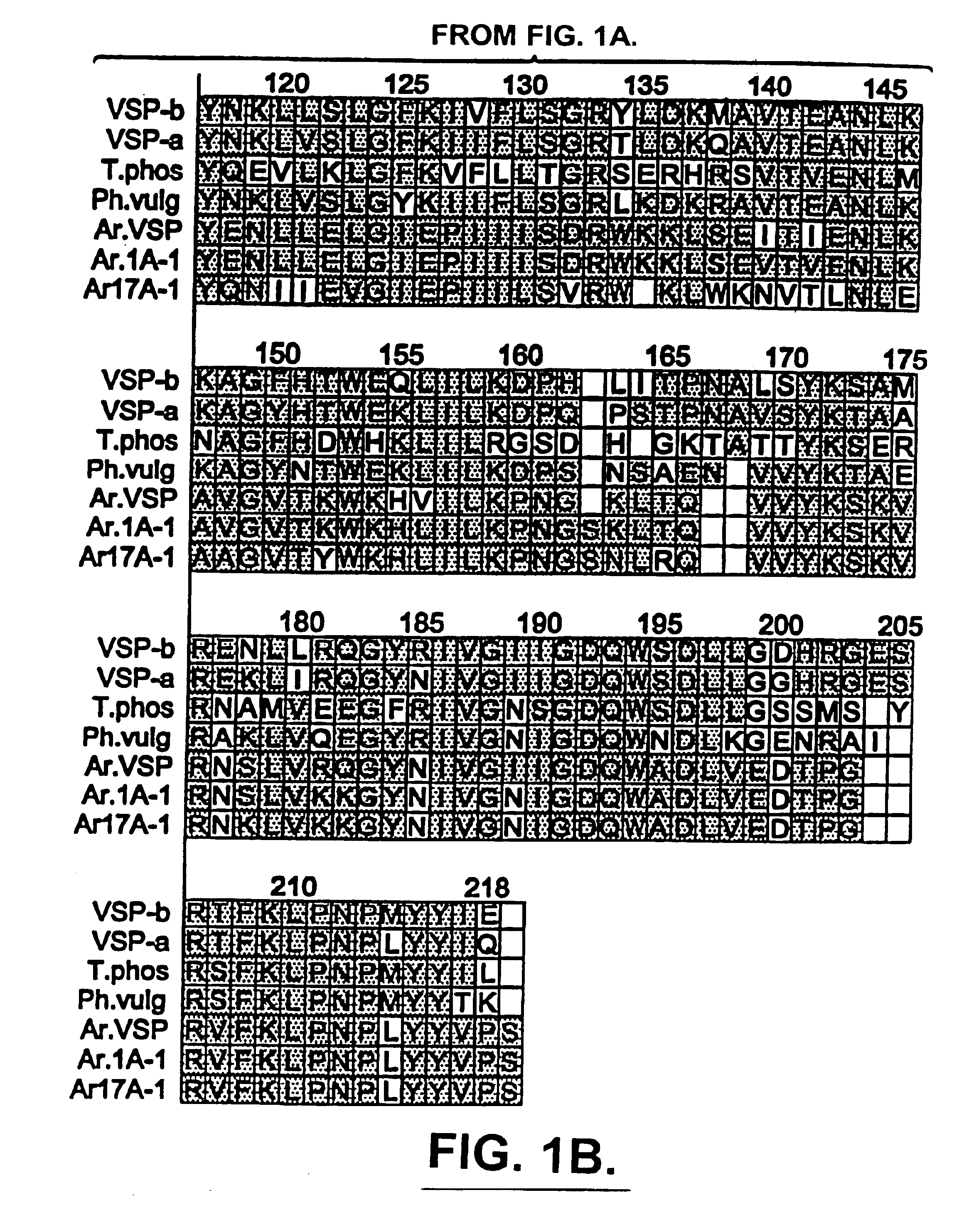
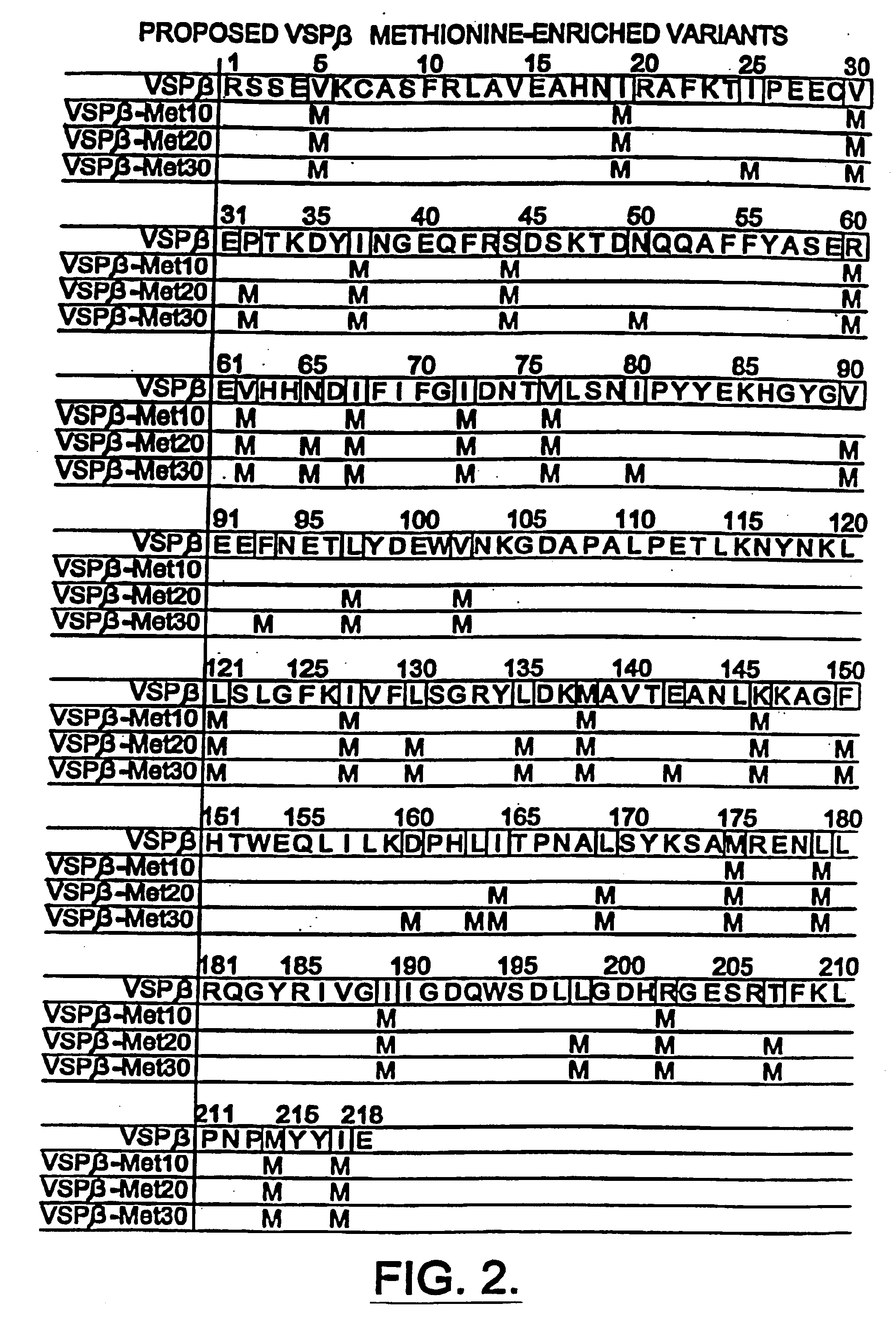
Compositions and methods for altering amino acid content of proteins
InactiveUS6905877B1Increased methionine levelImprove the level ofMicroorganism librariesPlant peptidesAmino acid compositionDrug biological activity
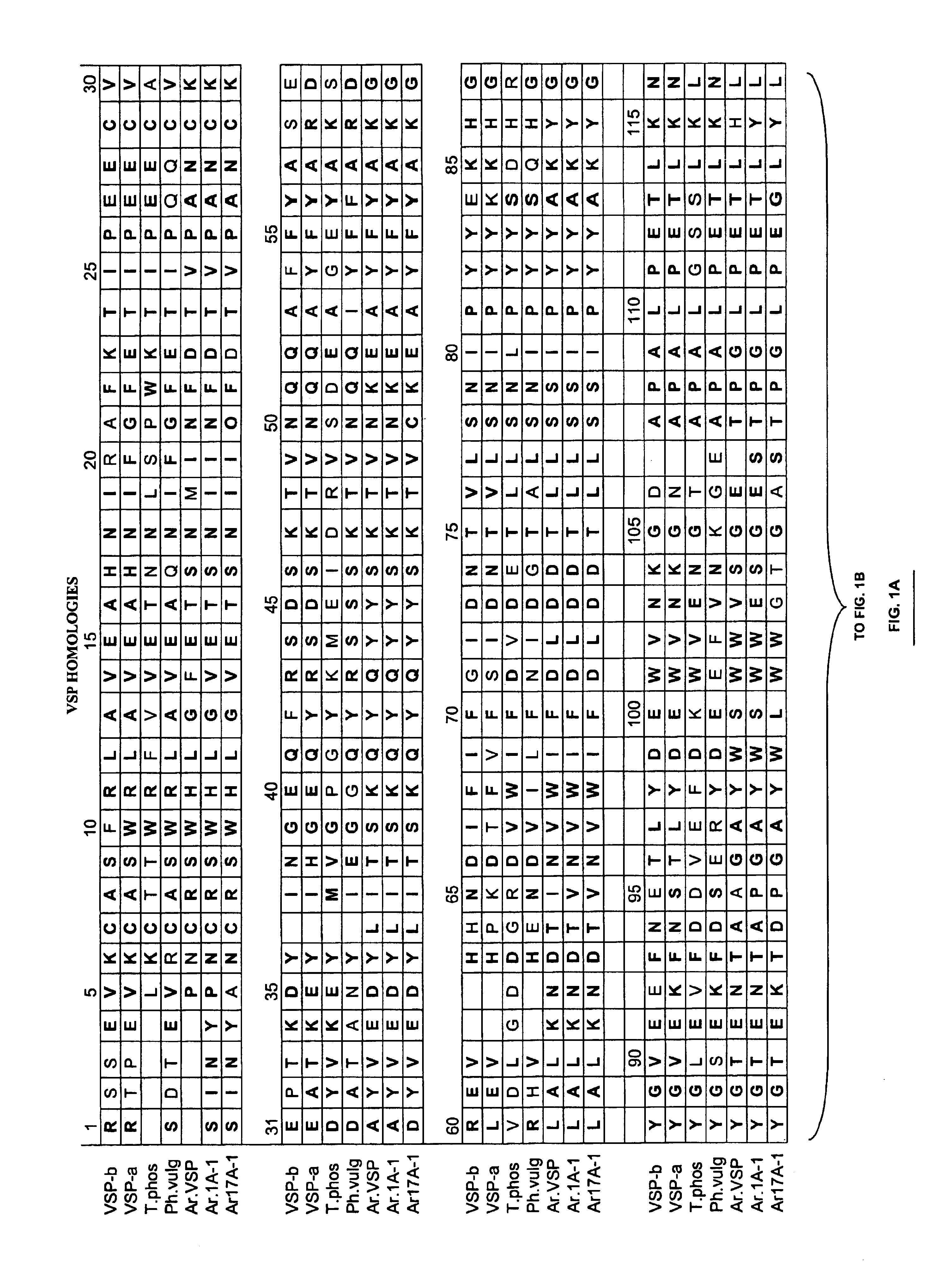
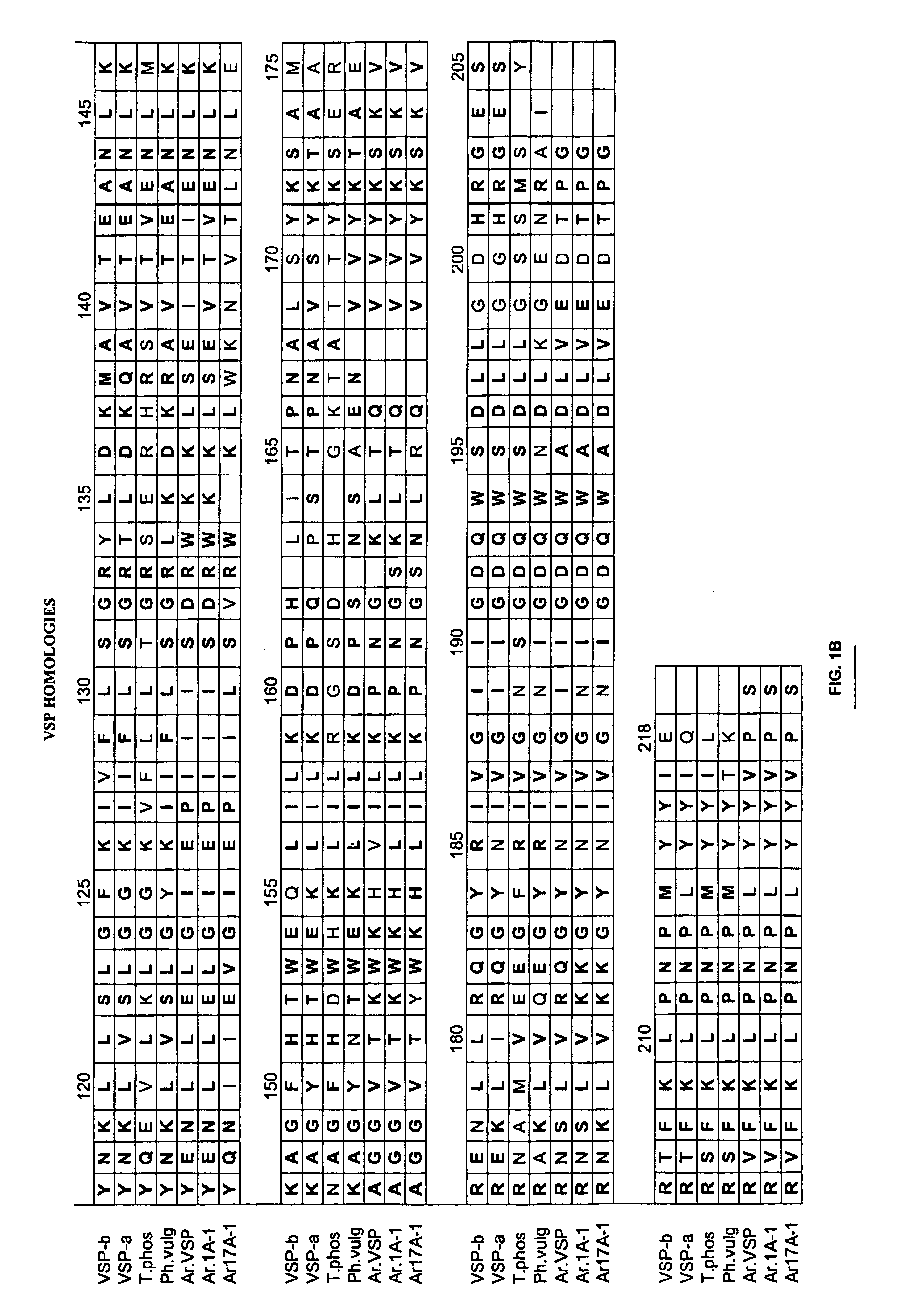
Methods and compositions for altering amino acid composition of a protein of interest are provided, particularly proteins whose three-dimensional structure is unknown. The method comprises creating interacting molecules to the native protein and selecting for engineered proteins which retain the native conformation by antibody binding. In this manner, the levels of essential amino acids in a protein can be increased yet the biological activity of the protein maintained. Also provided is an exemplary plant protein—Glycine max vegetative storage protein (VSP)—in which methionine levels have been increased.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Compositions and methods for altering amino acid content of proteins
InactiveUS6946589B1Sugar derivativesMicroorganism librariesAmino acid compositionDrug biological activity
Methods and compositions for altering amino acid composition of a protein of interest are provided, particularly proteins whose three-dimensional structure is unknown. The method comprises creating interacting molecules to the native protein and selecting for engineered proteins which retain the native conformation by antibody binding. In this manner, the levels of essential amino acids in a protein can be increased yet the biological activity of the protein maintained. Also provided is an exemplary plant protein—Glycine max vegetative storage protein (VSP)—in which methionine levels have been increased.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Fertile transgenic corn plants
InactiveUS20070022493A1Increase whole kernel levelClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesAdemetionineGenetically modified maize
Fertile transgenic Zea mays (corn) plants which stably express recombinant DNA which is heritable are provided wherein said DNA preferably comprises a recombinant gene which encodes a seed storage protein, so that the amino acid profile of the corn is improved.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Transgenic rice PA110-15 foreign insert flanking sequence and application
ActiveCN103966208AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStrain specificityAgricultural science
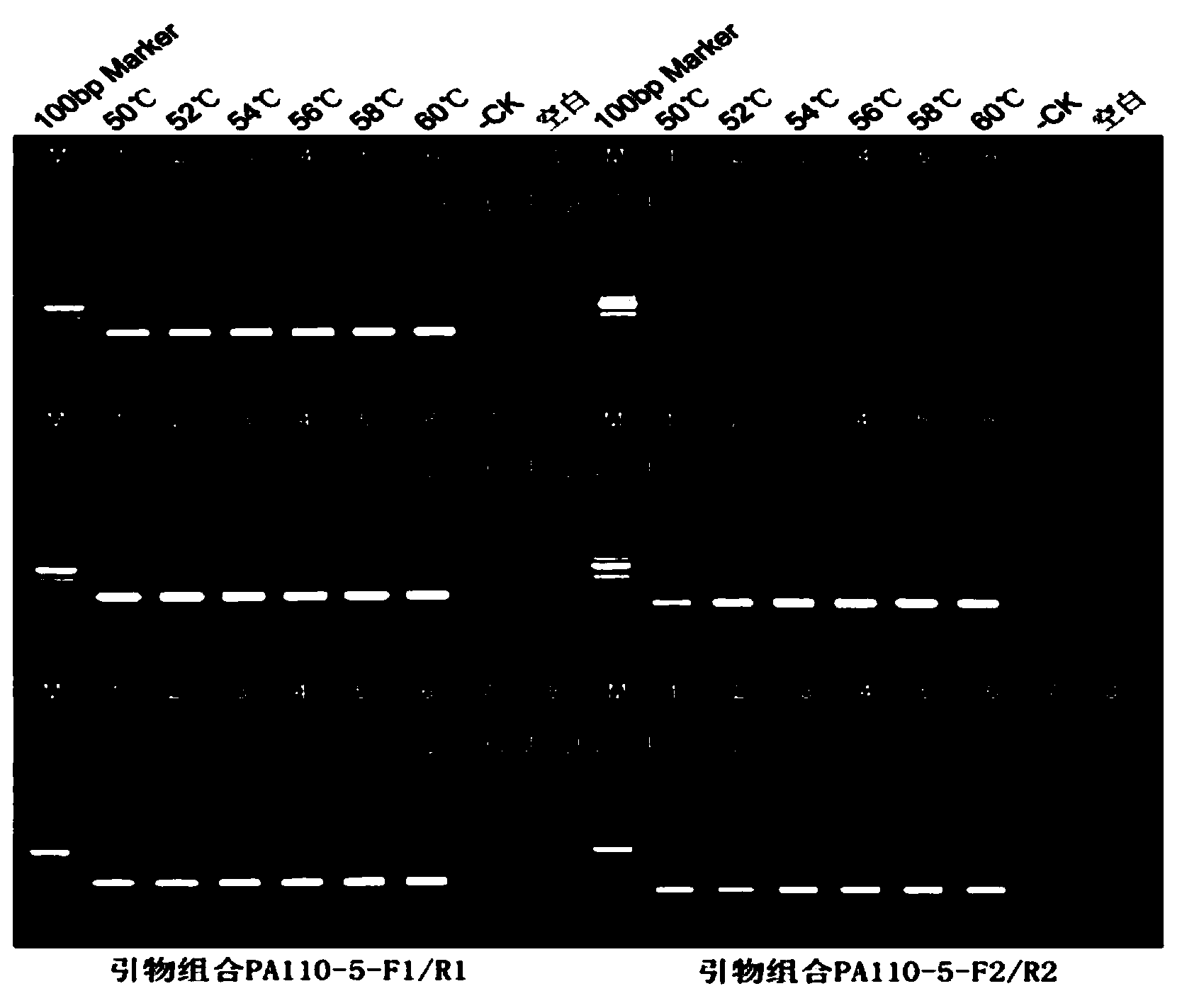
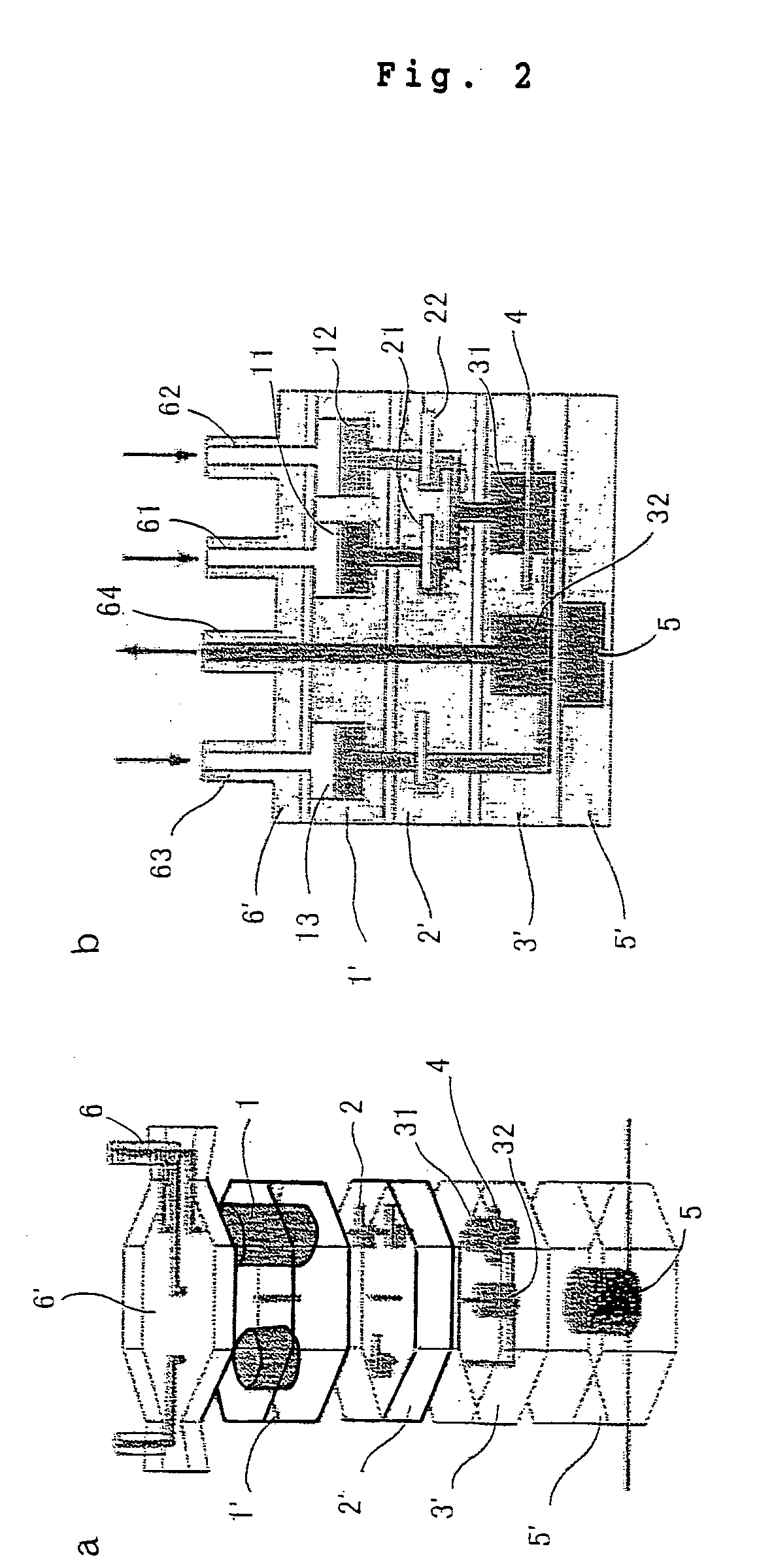
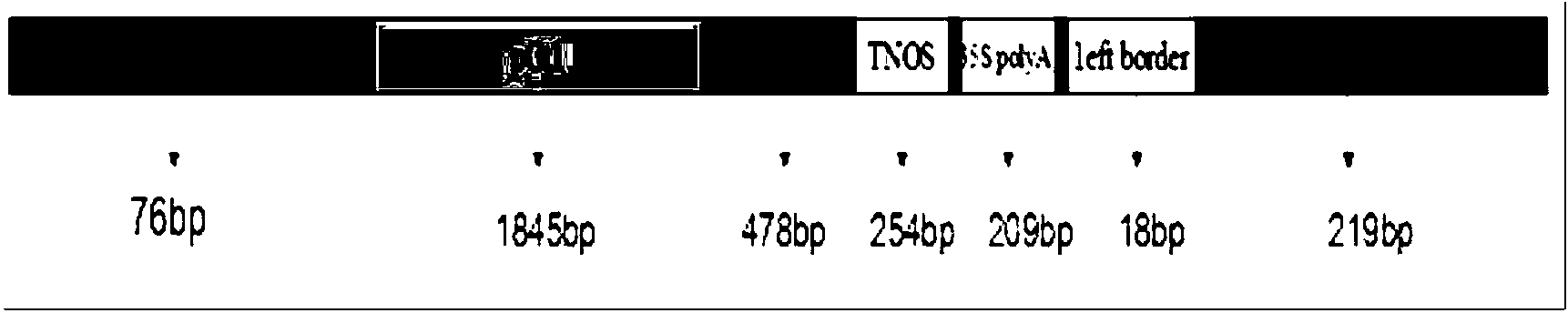
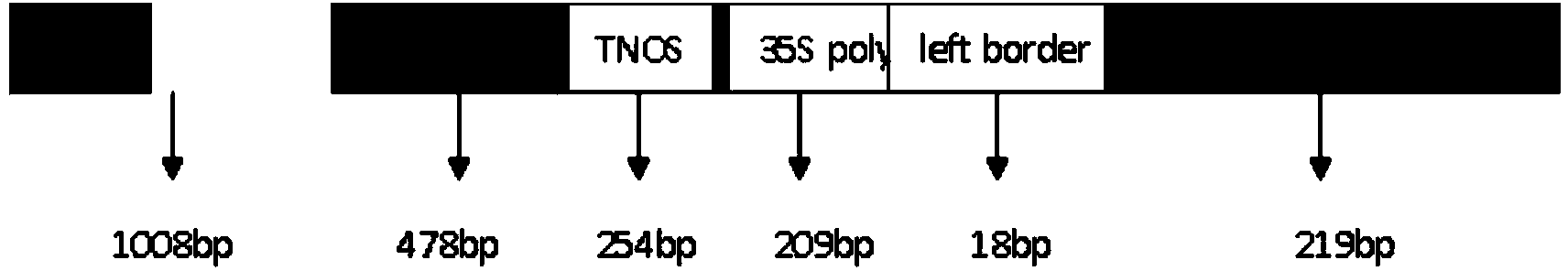
The invention discloses a transgenic rice PA110-15 foreign insert flanking sequence and an application. According to the transgenic rice PA110-15 foreign insert flanking sequence, firstly, a 5' end sequence and a 3'flanking sequence of a transgenic rice PA110-15 strain foreign inserted gene are provided, and nucleotide sequences of the 5' end sequence and the 3'flanking sequence are represented by SEQID NO.1 and SEQID NO.2.The invention provides aPCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection primer for transgenic ricePA110-15(expressing lysine-rich storage protein gene)strain specificity and a strain specificityqualitative detection method with the flanking sequence used as a target gene. Specificityexperiments indicate that the establishedtransgenic rice PA110-15 strain specificityqualitative PCR detection method has the high specificity. Sensitivity test results indicate thatthe sensitivity of the established detection method reaches 0.1%.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for developing a dairy protein cake
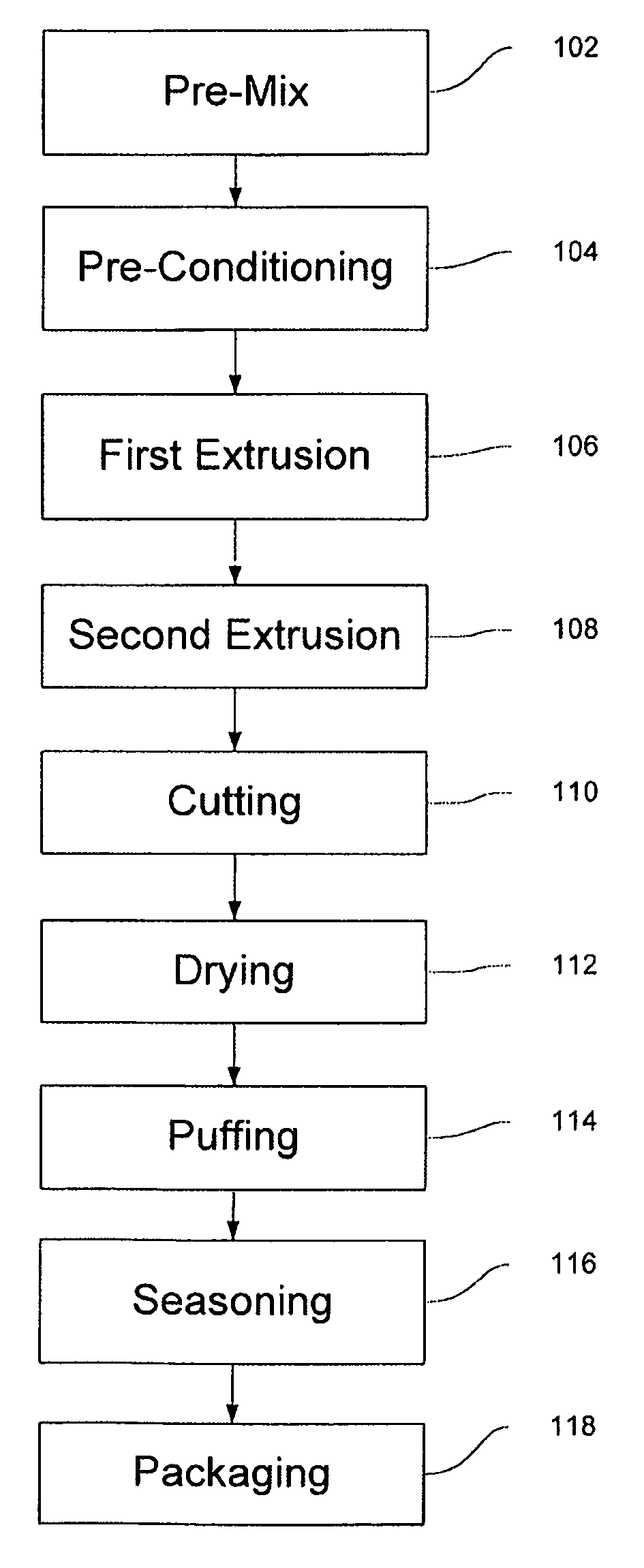
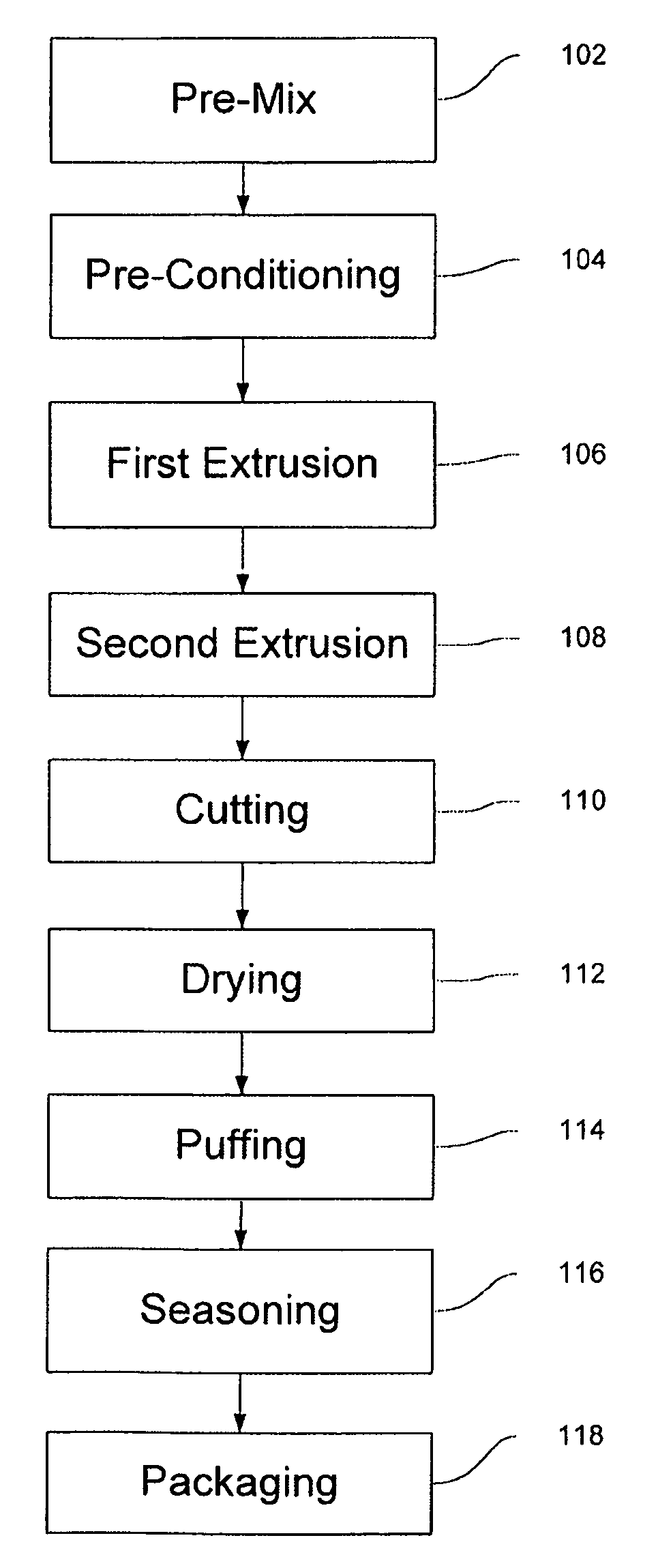
ActiveUS8313788B2Reduce the amount of solutionReduce resultDough treatmentFood ingredientsPotato starchBRAF Protein
A method for producing a shelf-stable protein-based pellet that is capable of expansion into a light, crispy snack cake, while providing a good source of protein and calcium. The method, in preferred embodiments, involves making dough from tapioca and potato starches and a milk protein derivative consisting of whey protein isolate, milk protein isolate or calcium caseinate. The mixture is extruded, sliced and dried in a series of dyers. The method produces a shelf-stable pellet having a moisture level of approximately 9-13% by weight which is further processed to produce a puffed dairy protein snack product, having a moisture level typically less than 2%.
Owner:FRITO LAY NORTH AMERICA INC
Proteases
Disclosed is a thermostable protease congenetic with the protease from Nocardiopsis and the preparation in the wild type reconstructed host-cells which contain the transgenic plant and the no-human transgenic animal cells. The protease is effective in animal feed, in particular to fish feed and washing agent. The protease can degrade soybean Bowman-Birk stayer, other anti-nutritional factors such as soybean agglutinin and Kunitz trypsinase stayer, and separated soybean storage protein, glycinin and beta-conglycinin. The structural characteristics related to the thermostability of the proteases of the peptidase family S2A or S1E.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Chemical reaction circuit for cell-free protein synthesis
InactiveUS20040147014A1Prevent backflowEasy to embedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroreactorChemical reaction
A chemical reaction circuit for cell-free protein synthesis characterized by, as a chemical reaction circuit for synthesizing a protein, having at least one reagent tank for storing a reagent for the protein synthesis and / or a reagent for detecting a product, a unidirectional valve for preventing the reverse-flow of the reagent(s), and a reaction tank connected to the reagent tank(s) via the unidirectional valve. This circuit is usable as a micro reactor whereby cell-free protein synthesis can be carried out.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection primer and qualitative detection method and kit for specificity of transgenic rice PA110-15 strain
ActiveCN103834646AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceBase sequence
The invention discloses a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) qualitative detection primer and a qualitative detection method and a kit for specificity of a transgenic rice PA110-15 strain. The invention firstly provides a connection area sequence inserted with a carrier gene and flanking rice sequence in a high-lysine storage protein transgenic rice PA110-15 strain, and the base sequence is shown as SEQ ID No.2. The invention further provides the PCR primer and the qualitative detection method for the specificity of the high-lysine storage protein transgenic rice PA110-15 strain. The specificity verification experiment shows that the PCR qualitative detection method for the specificity of the high-lysine storage protein transgenic rice PA110-15 strain is high in specificity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Nucleic acid molecules encoding wrinkled1-like polypeptides and methods of use in plants
InactiveUS20110162103A1High oil contentImprove the level ofBryophytesSugar derivativesGlycineBrassica
Isolated nucleic acids and proteins associated with lipid and sugar metabolism regulation are provided. In particular, lipid metabolism proteins (LMP) and encoding nucleic acids originating from Arabidopsis thaliana, Brassica napus, Glycine max, Oryza sativa, and Triticum aestivum are provided. The nucleic acids and proteins are used in methods of producing transgenic plants and modulating levels of seed storage compounds. Preferably, the seed storage compounds are lipids, fatty acids, starches, or seed storage proteins. The nucleic acids and proteins also are used in methods of modulating the seed size, seed number, seed weight, root length, and leaf size of plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method of accumulating foreign gene product in plant seed at high level
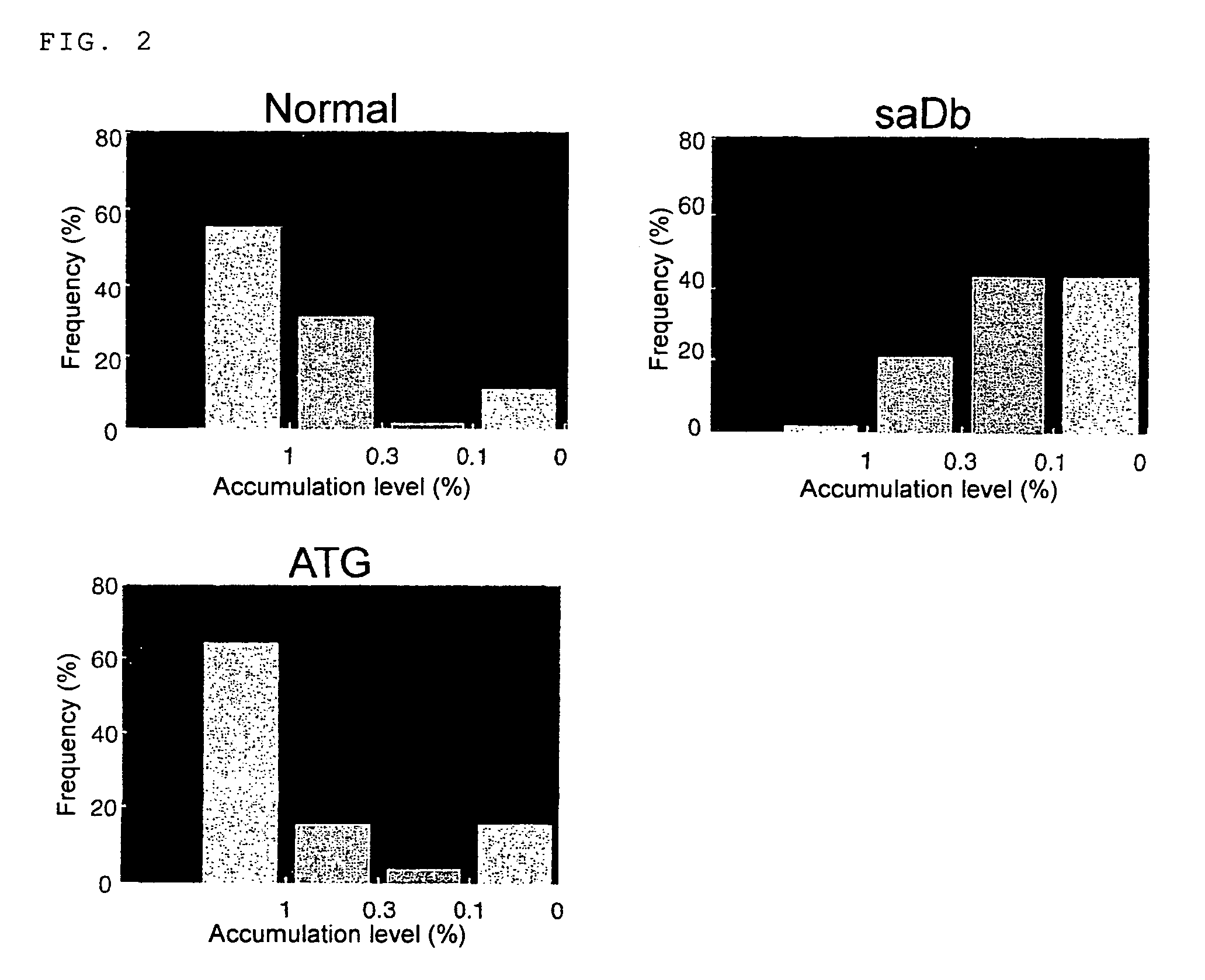
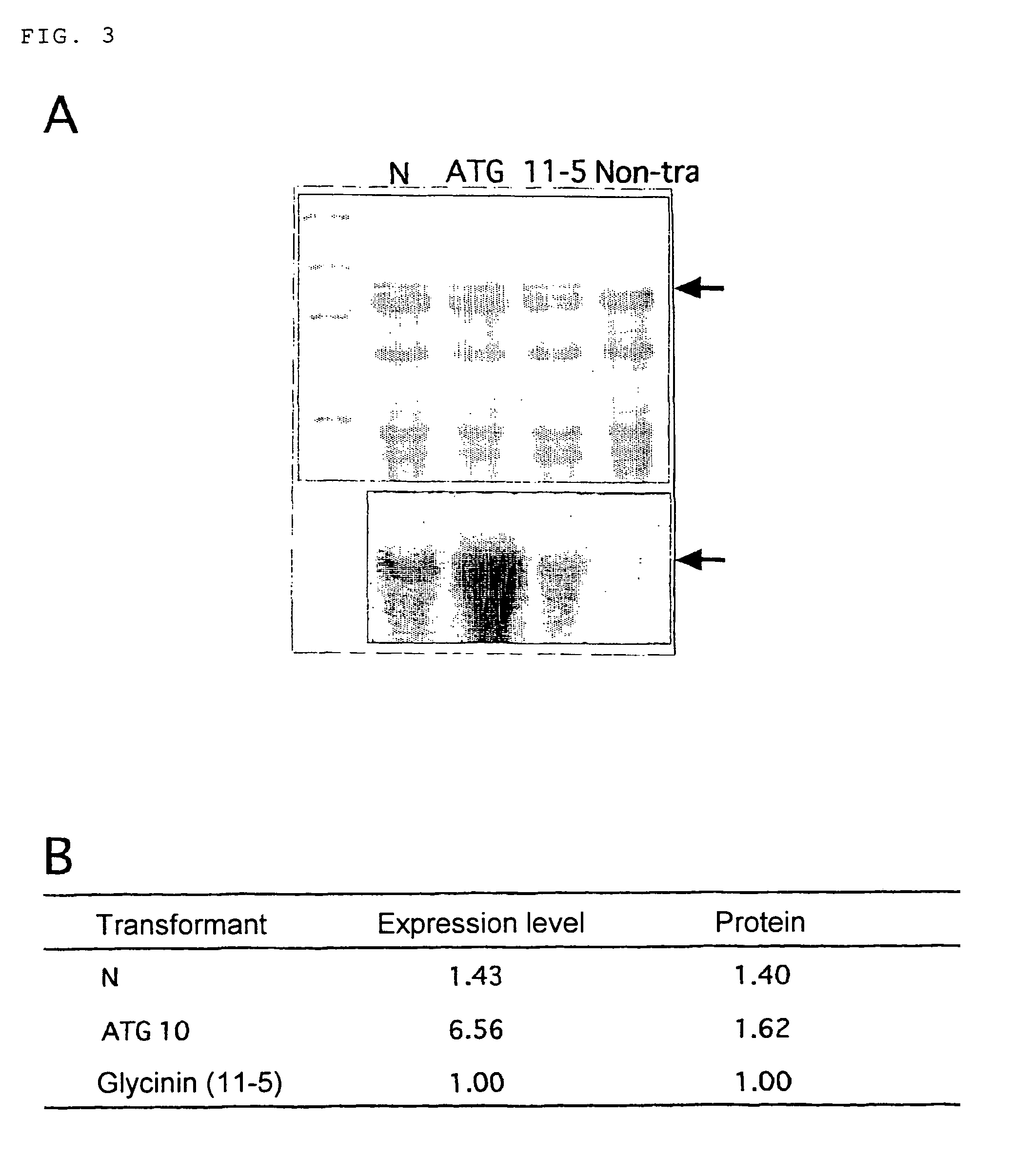
InactiveUS7473825B2Improve accumulation level of mRNANo improvement in expression levelHybrid cell preparationOther foreign material introduction processesDefective mutantPlanting seed
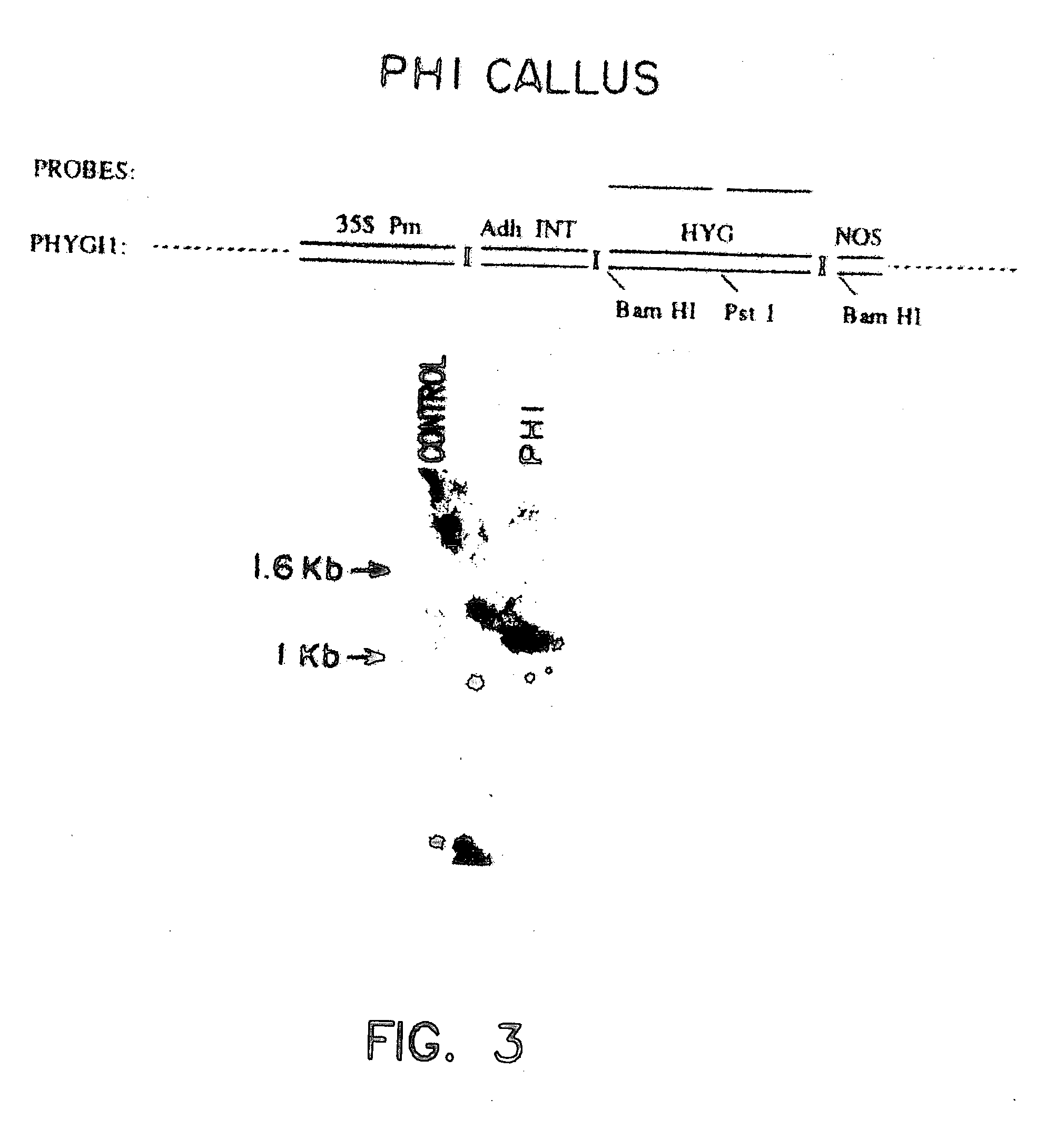
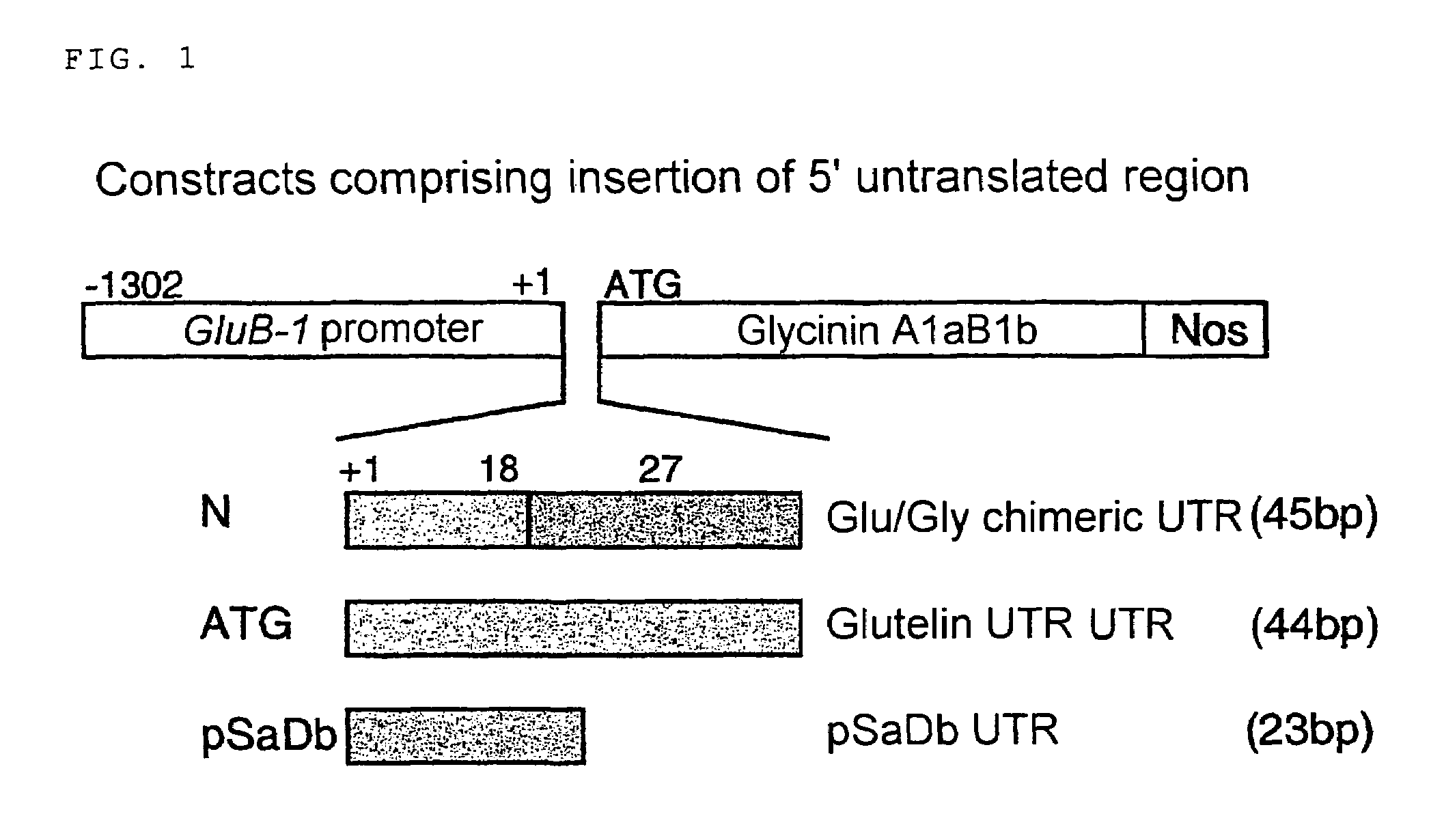
The present inventors succeeded in developing a vector that expresses high levels of a foreign gene in plant seeds by utilizing a 5′-untranslated region of a gene encoding a seed storage protein. The inventors also succeeded in accumulating high levels of a foreign gene product in plant seeds by utilizing a seed storage protein defective mutant as a target for foreign gene transfer.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Expression vector changing distribution of rice storage protein as well as preparation and use thereof
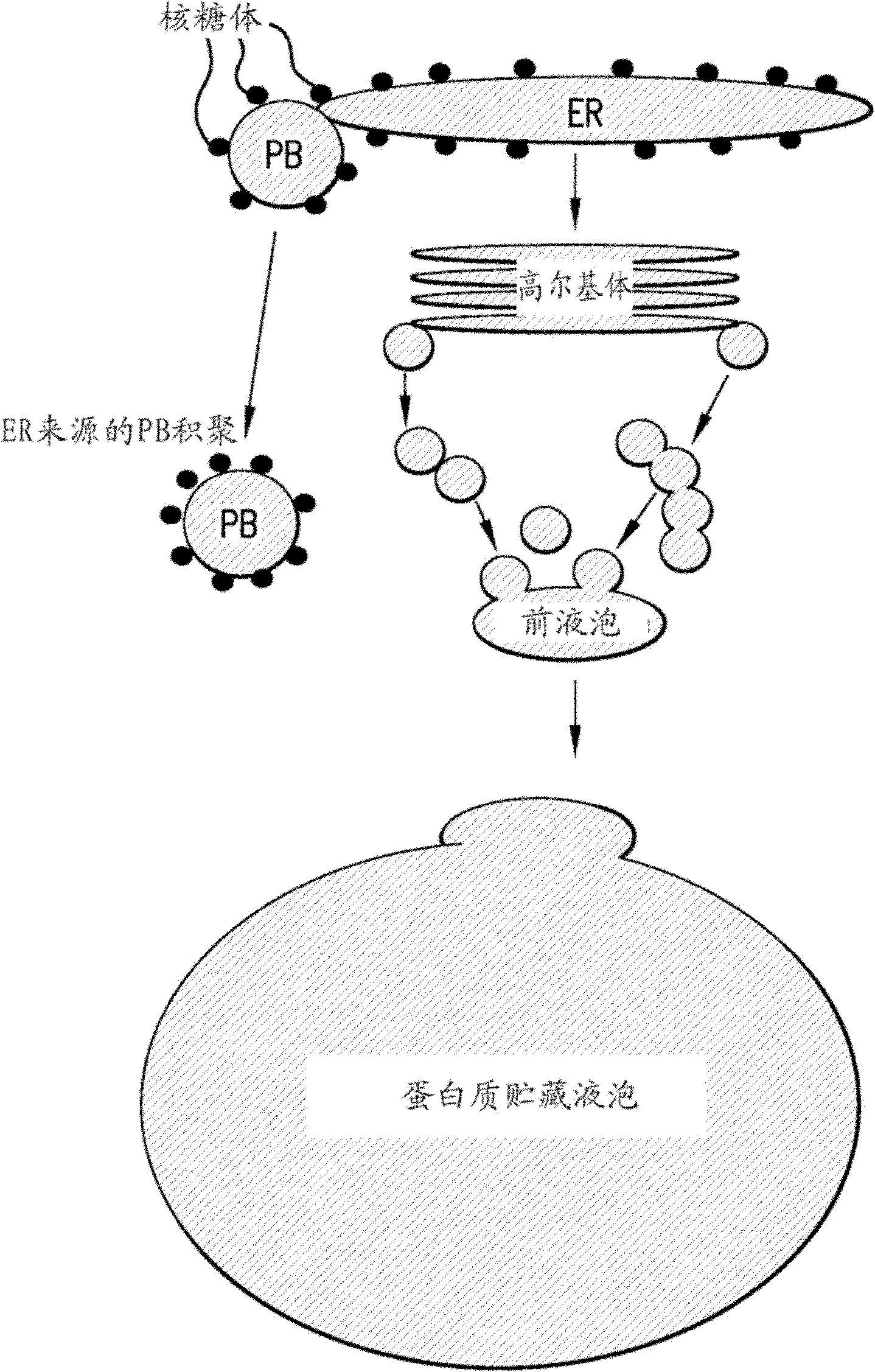
InactiveCN101250550AAvoid defects that impact yield lossHigh in proteinFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceAleurone
The invention discloses an expression vector which changes the distribution of rice storage protein, a method for preparing the expression vector and the application. The expression vector comprises a gene promoter, a storage protein gene fragment, a terminator and an endonuclease sensitive sequence, wherein the gene promoter is the gene promoter which is located on the central position of the rice and can be expressed. The expression vector can be applied to transform the rice to obtain new varieties whose content and quality of storage protein are changed on the central position of the rice. The expression vector of the invention overcomes the defect that an existing technique only can increase the content and the quality of the protein which is near and around an aleurone layer of the rice, obtains the special effect that rice protein is expressed in the center of granules, and avoids the defect which is existed in an existing technique that the quality improvement affects the decline of production, and since the expression vector of the invention is transformed to obtain new rice quality, the protein content of progeny polished rice is increased by at least 10% on the basis of the protein content of control polished rice which is not transformed.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
BZIP type transcripton factors regulating expression of rice storage protein
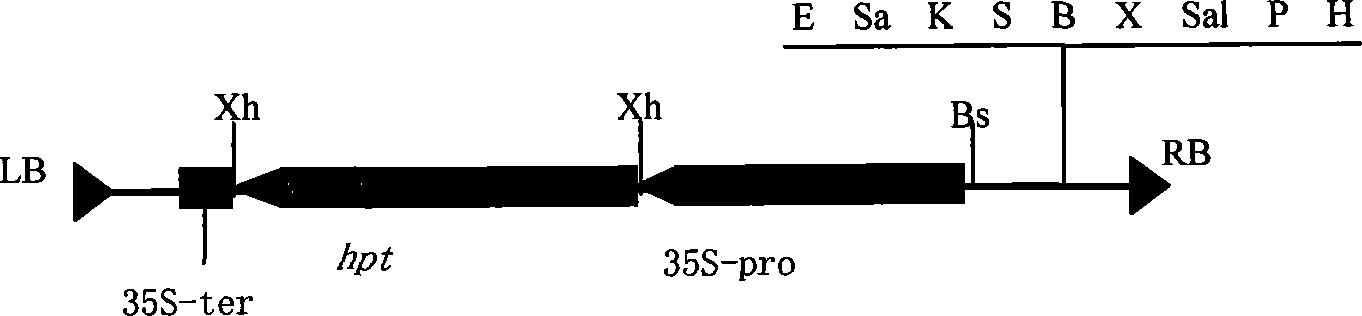
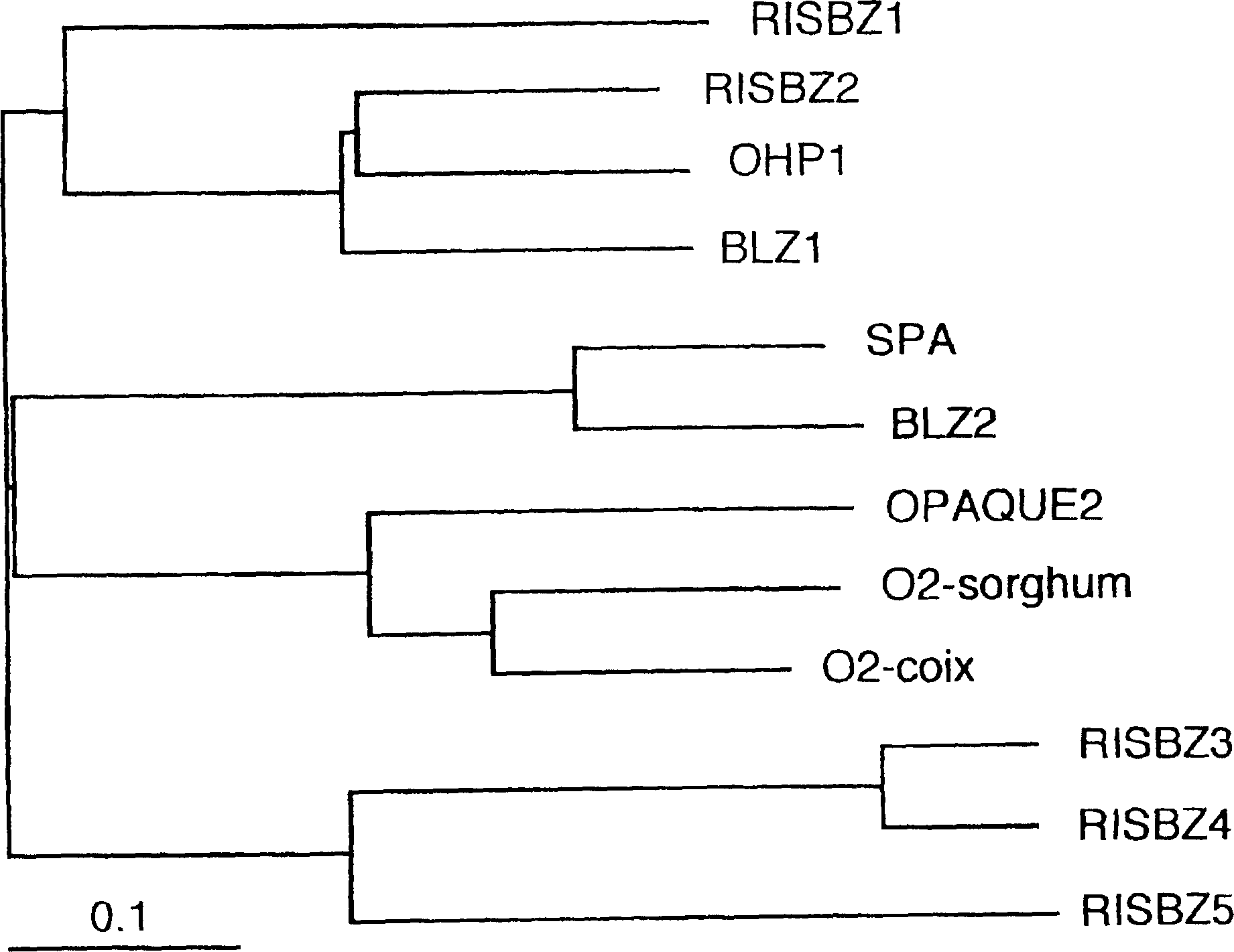
cDNAs (RISBZ1, RISBZ4, and RISBZ5) encoding bZIP transcription factors were isolated from a cDNA library originating in rice plant seed. The cDNAs encode novel proteins and have binding activity to the GCN4 motif. Among them, RISBZ1 activated transcription mediated by the GCN4 motif by 100-fold or more. Since the expression of RISBZ1 precedes the expression of a seed storage protein gene and is expressed only in maturing seeds, it is suggested that RISBZ1 controls the expression of rice seed storage proteins. In addition, by linking the recognition sequence of the transcription factor, the GCN4 motif, in tandem and introducing it into the promoter for a gene encoding seed storage protein to facilitate its binding to the transcription factor RISBZ1, expression of a foreign gene under the control of the modified promoters is greatly enhanced.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
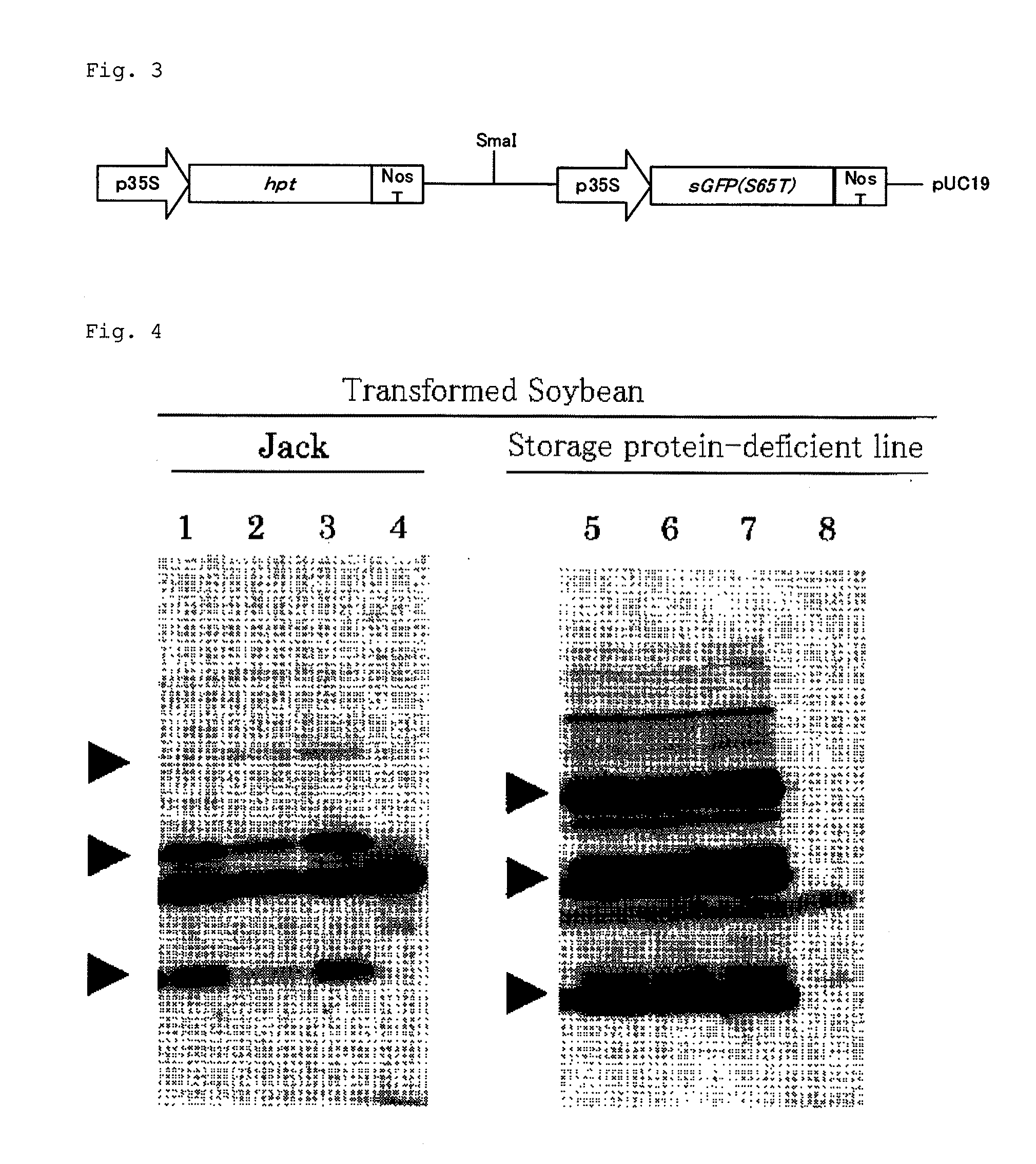
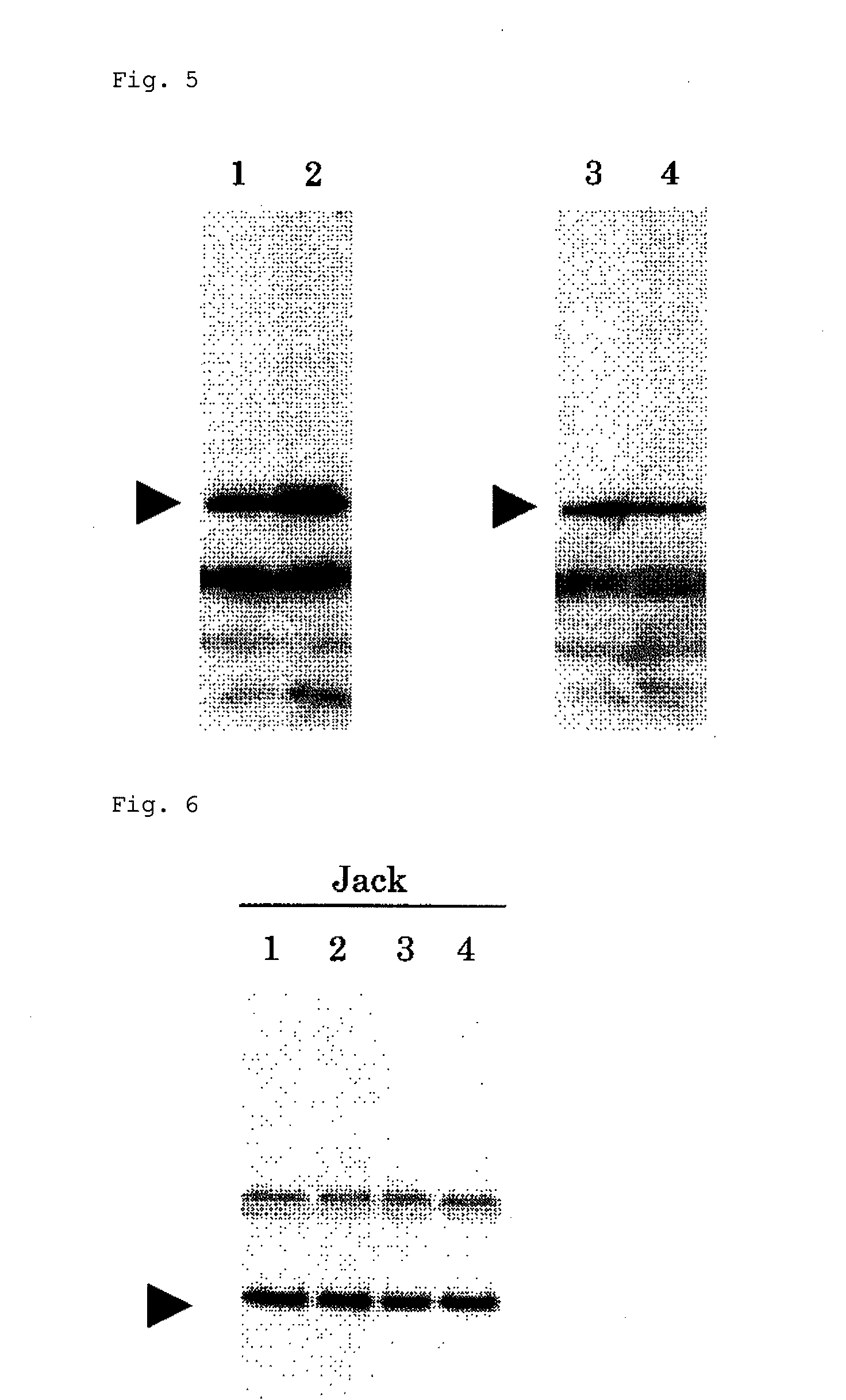
Improved protein production and storage in plants
A transgenic dicotyledonous plant has a deficiency of one or more plant seed storage proteins, further has a transgenic polynucleotide construct comprising an open reading frame operably linked to a storage protein promoter and an ER signal sequence. The polynucleotide construct encodes a protein product that can accumulate at high levels in the seed. Also provided are methods of producing a heterologous protein in a plant seed.
Owner:DONALD DANFORTH PLANT SCI CENT +1
Methods and compositions for altering the functional properties of seed storage proteins in soybean
InactiveUS20050155102A1Altering functional propertyReducing and eliminating activityHydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesVacuolar processing enzymeLowering plants
The present invention provides methods and compositions useful for altering the functional properties of soybean seed storage proteins. It is the novel finding of the present invention that the functional properties of seed storage proteins can be altered by reducing the expression of one or more vacuolar processing enzymes in plant seed. Accordingly, in one embodiment, the invention provides a method for altering the functional properties of one or more soybean seed storage proteins. The method comprises transforming a soybean plant cell with at least one expression cassette capable of expressing a polynucleotide that reduces the activity of a vacuolar processing enzyme in the seed of said soybean plant, regenerating a transformed plant from the transformed plant cell, and collecting seed from the regenerated transformed plant. Plants that are genetically modified or mutagenized to alter the functional properties of one or more seed storage proteins, and the transgenic seed of such plants are also provided.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for checking purity of hybridized pepper seeds
ActiveCN103293212AThe method is simple and fastAccurate methodMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSweet PeppersHot peppers
The invention discloses a method for checking the purity of hybridized pepper seeds. The method is technically characterized by comprising the following steps of: soaking seeds into an acetone solution for 5-6 hours so that the seeds are degreased; taking out the seeds and airing; cutting one seed into three blocks and placing the seeds into a centrifugal tube; adding 90 microliters of extraction liquid; placing at 5 DEG C for 12 hours; extracting liquid supernatant to obtain seed storage protein extraction liquid; placing the liquid on a plate, filling glue, carrying out sample application and electrophoresis, taking the glue, dyeing and manufacturing a wafer to obtain a sample electrophoresis spectrum band; carrying out the method to respectively obtain a standard electrophoresis spectrum band and a detected sample electrophoresis spectrum band; and comparing the detected sample electrophoresis spectrum band with the standard electrophoresis spectrum band to obtain the purity of seed samples to be detected. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient, rapid and accurate; and the process is easy to master and control. The method is particularly suitable for checking the purity of a hot pepper*sweet pepper type hot pepper breed combination.
Owner:ANHUI HUIDA AGRO
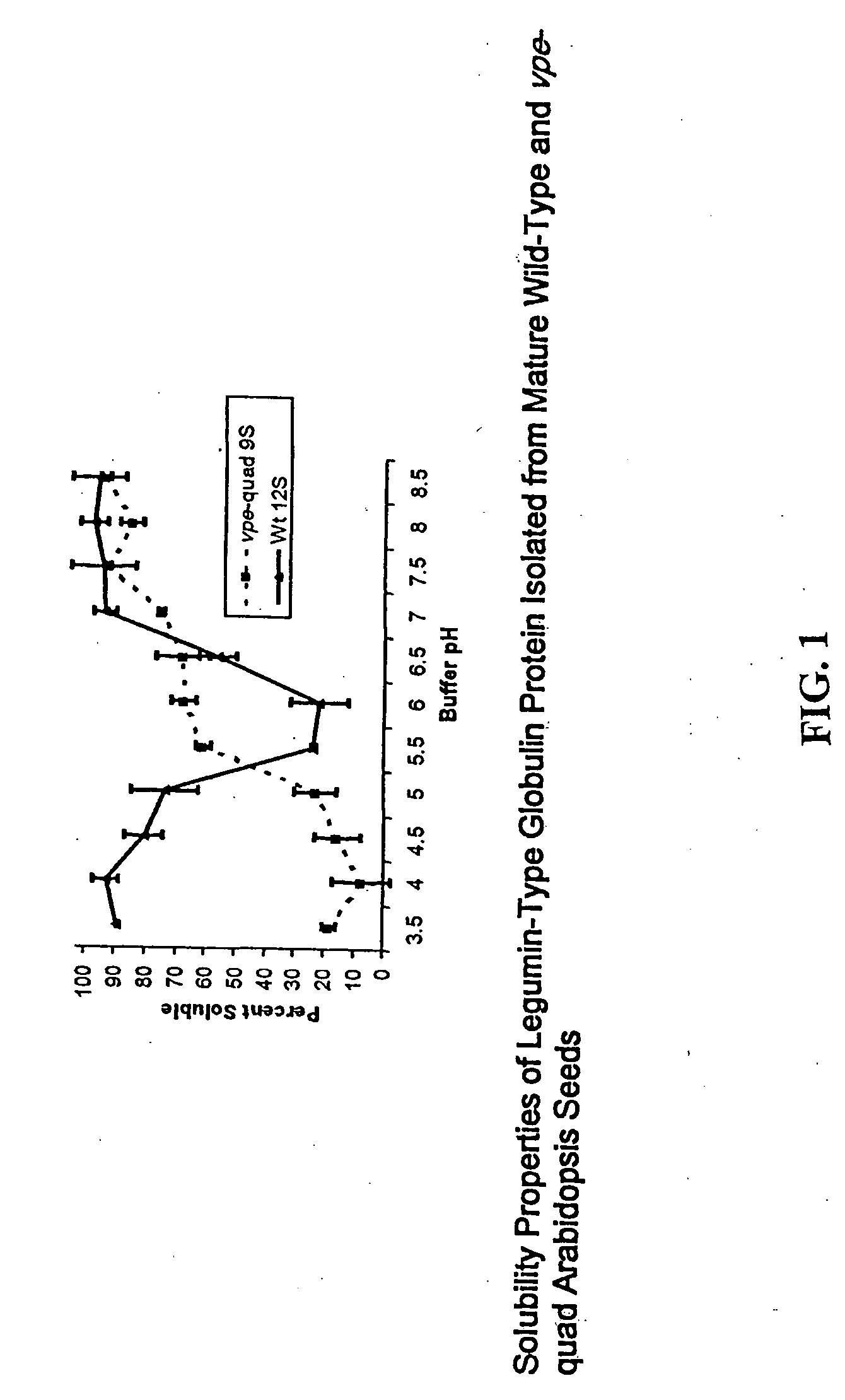
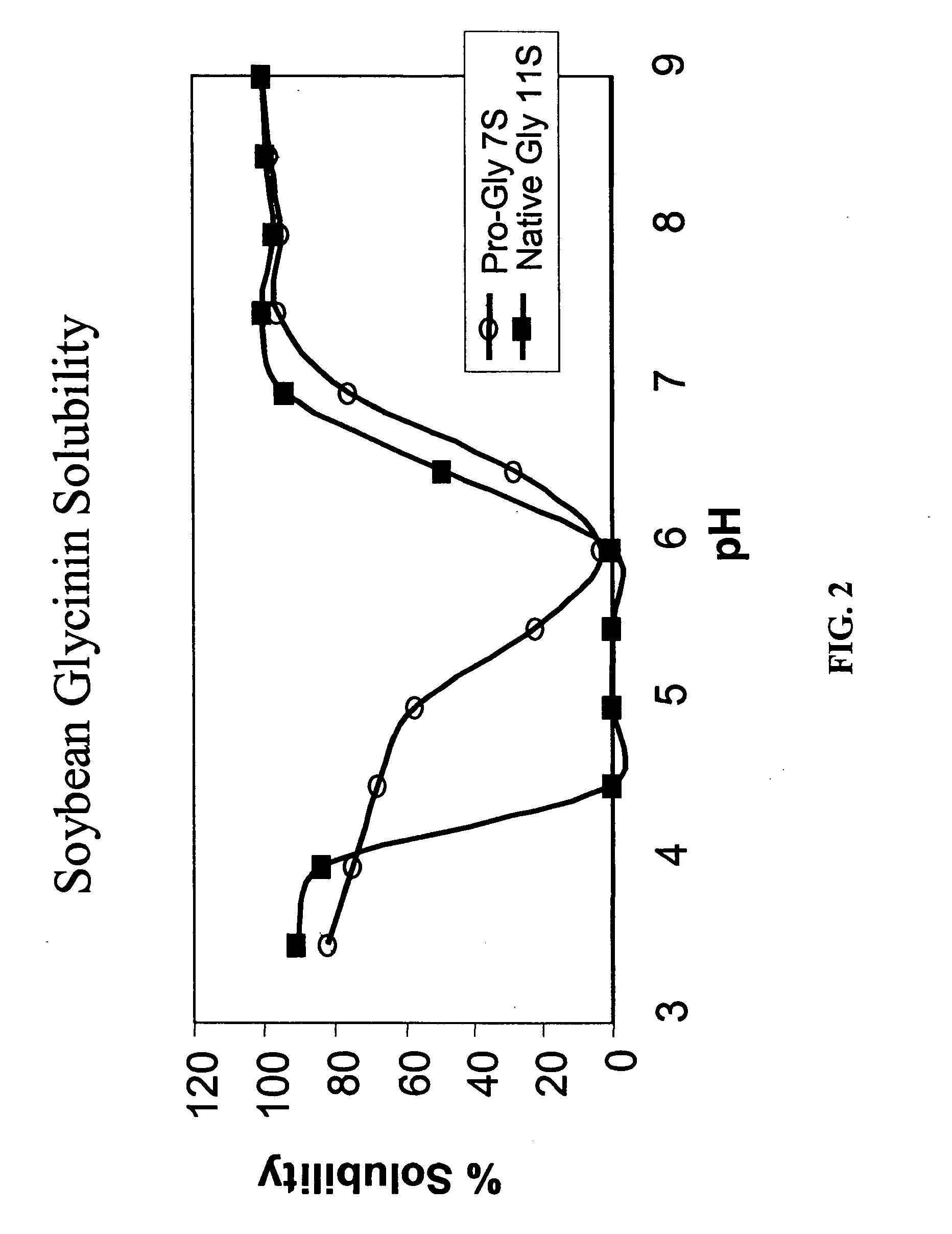
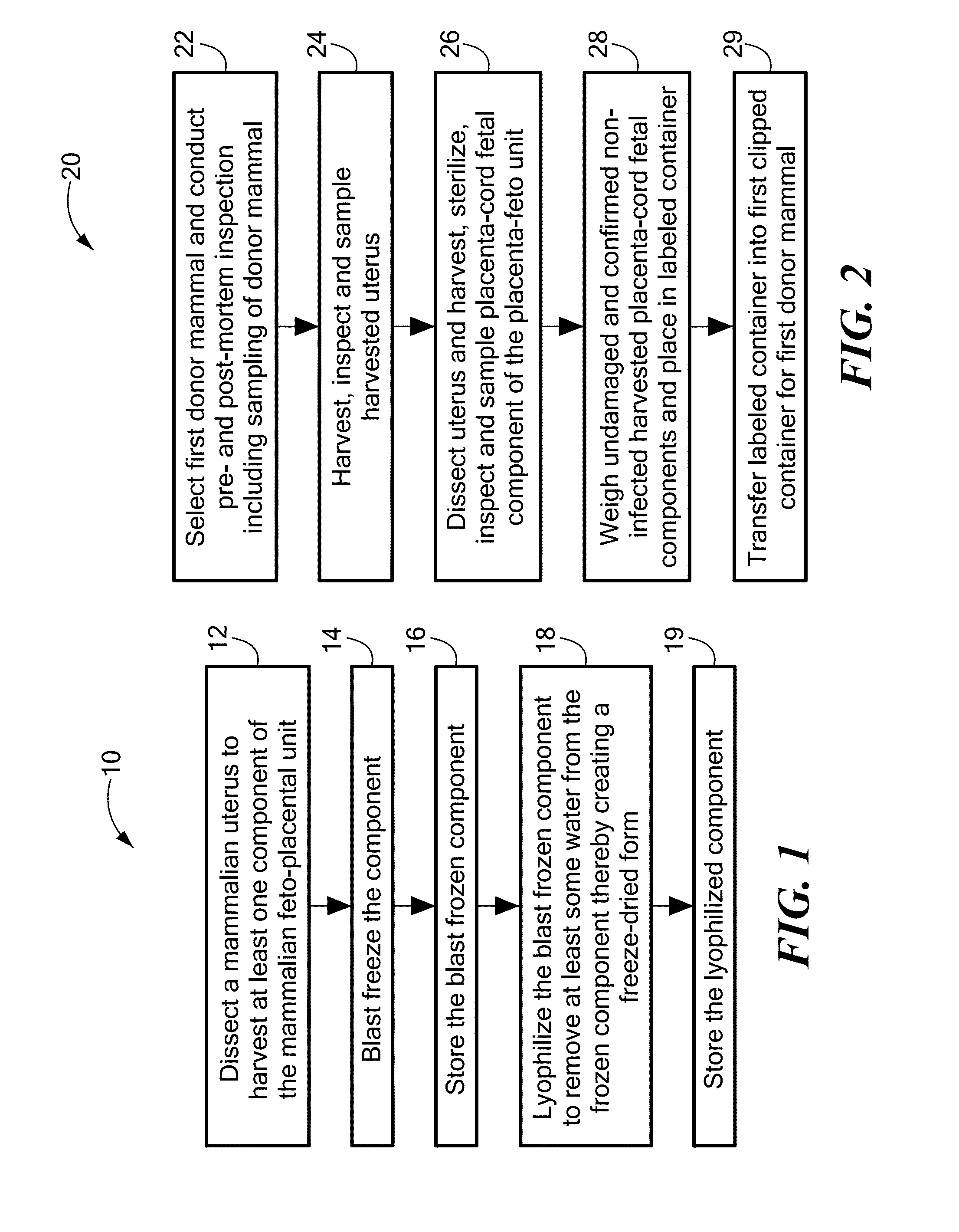
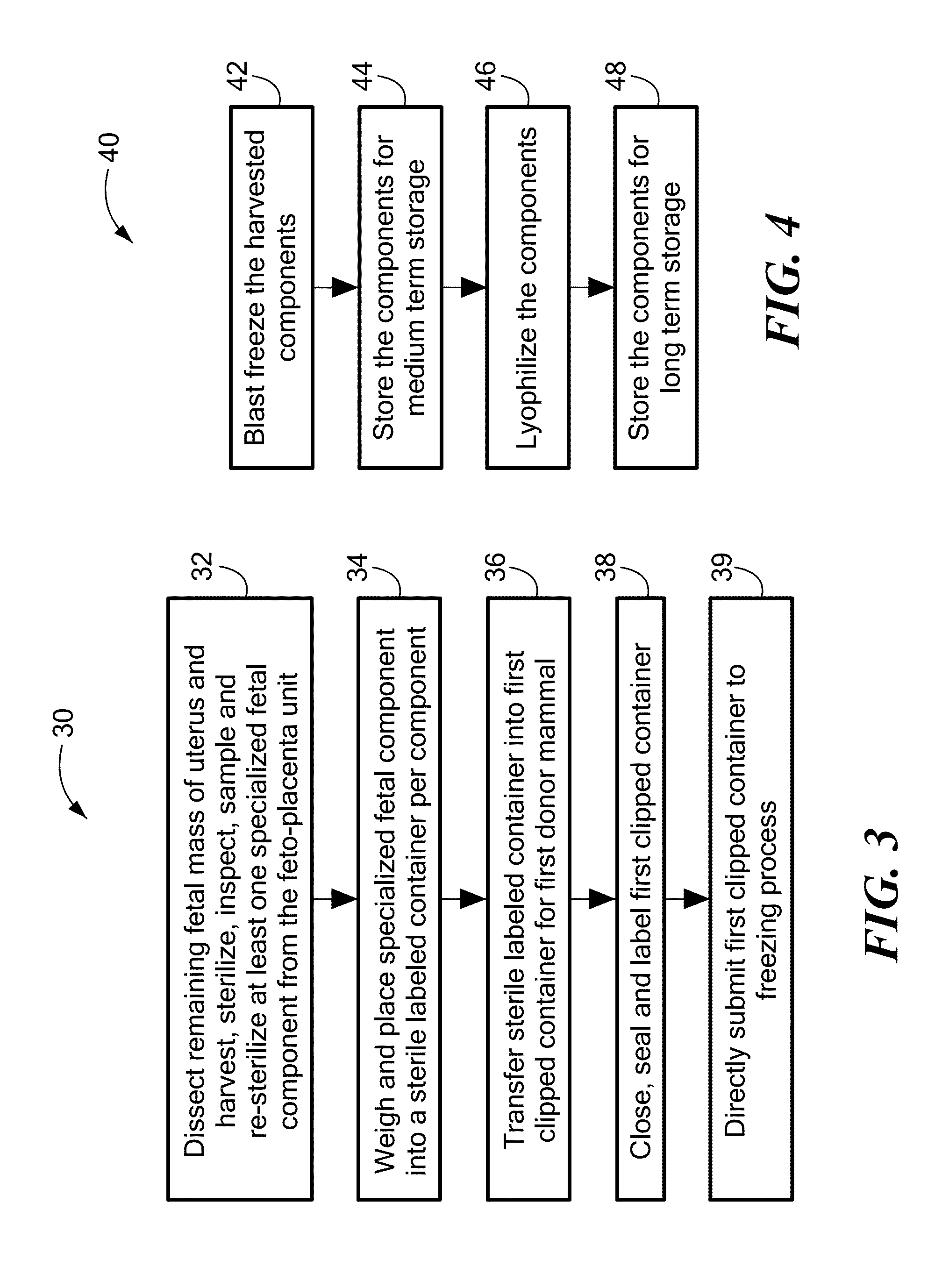
Method for the harvesting, processing, and storage of proteins from the mammalian feto-placental unit and use of such proteins in compositions and medical treatment
The invention provides a method of harvesting, processing and storing a plurality of proteins from a mammalian feto-placental unit. The method includes dissecting a mammalian uterus to harvest at least one component of the mammalian feto-placental unit; blast freezing the component; and storing the blast frozen component; wherein the blast frozen component includes the proteins. In one embodiment, the method includes lyophilizing the blast frozen component to remove at least some water from the blast frozen component thereby creating a freeze-dried form; and storing the lyophilized component; wherein the lyophilized component includes the proteins. The invention also provides a composition including proteins from at least one lyophilized, blast frozen component of a harvested mammalian feto-placental unit reconstituted with a fluid. The invention further provides method of treatment of a disease or aging in a mammalian subject including administering to the mammalian subject a plurality of proteins from at least one blast frozen component harvested from a mammalian feto-placental unit; and reducing an accumulation of at least one intracellular protein in the subject.
Owner:CASEY PATRICK J +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com