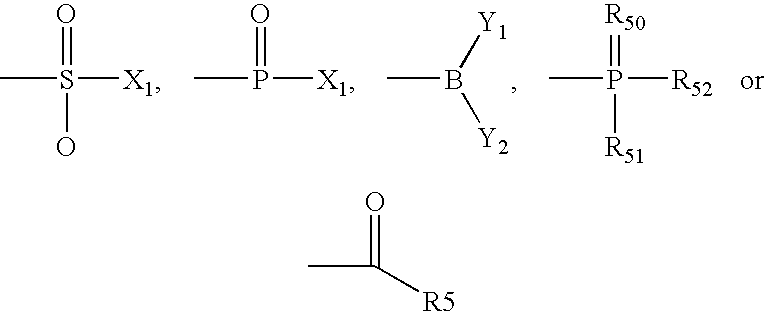
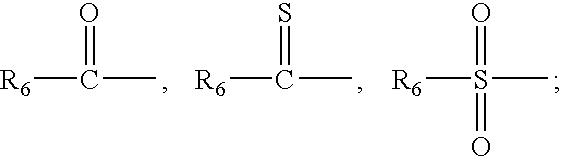
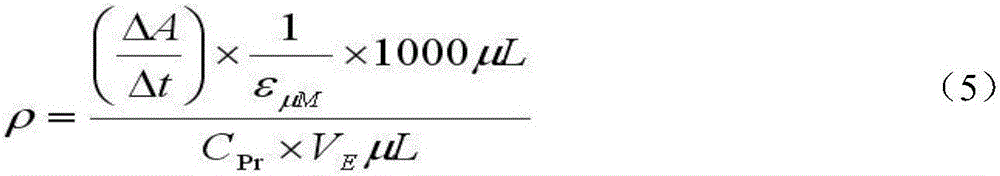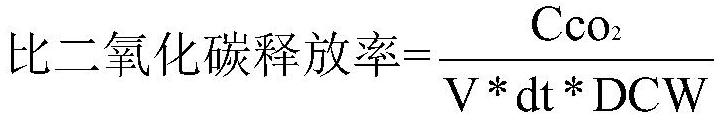Patents
Literature
94 results about "Glycan metabolism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
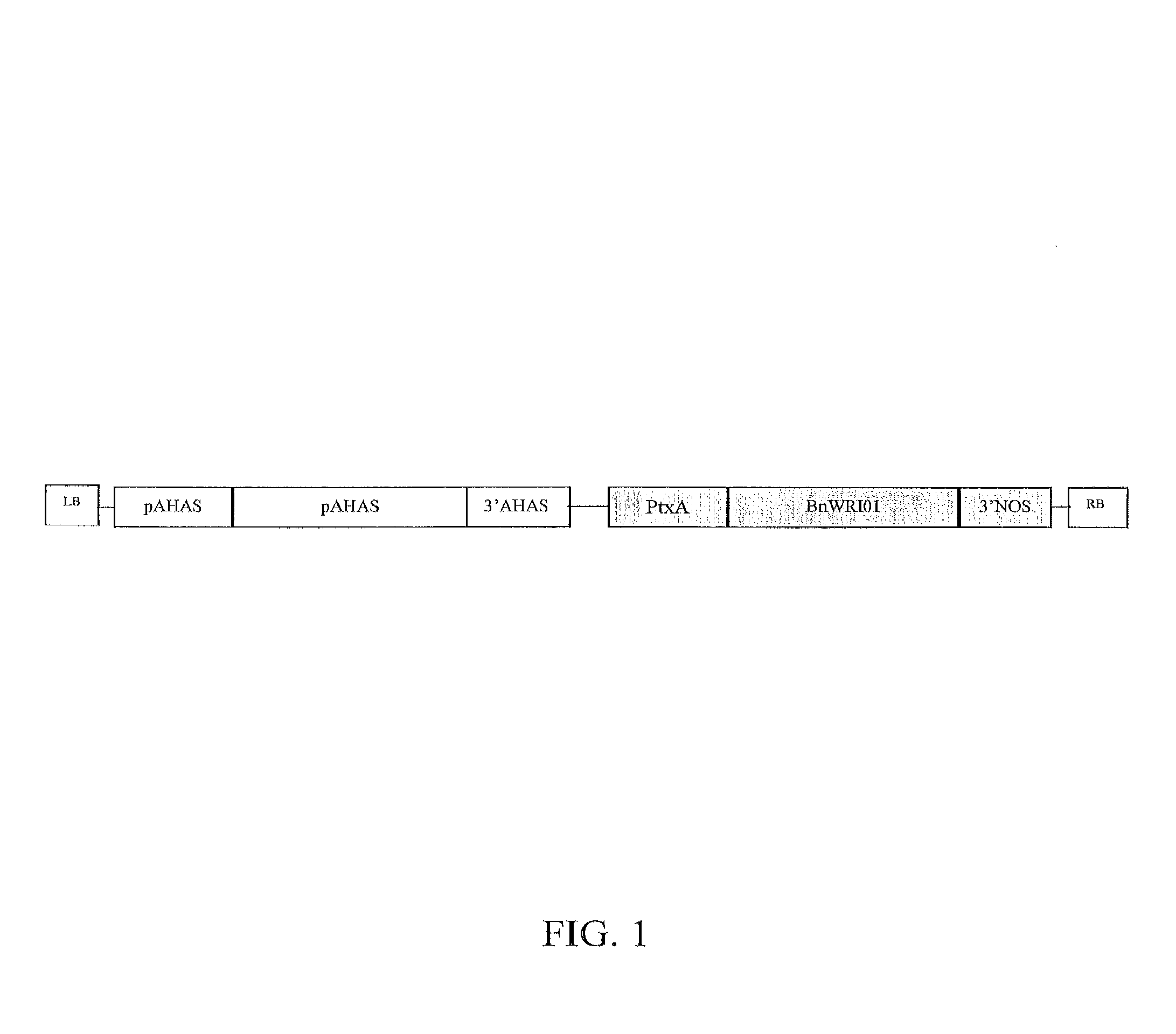
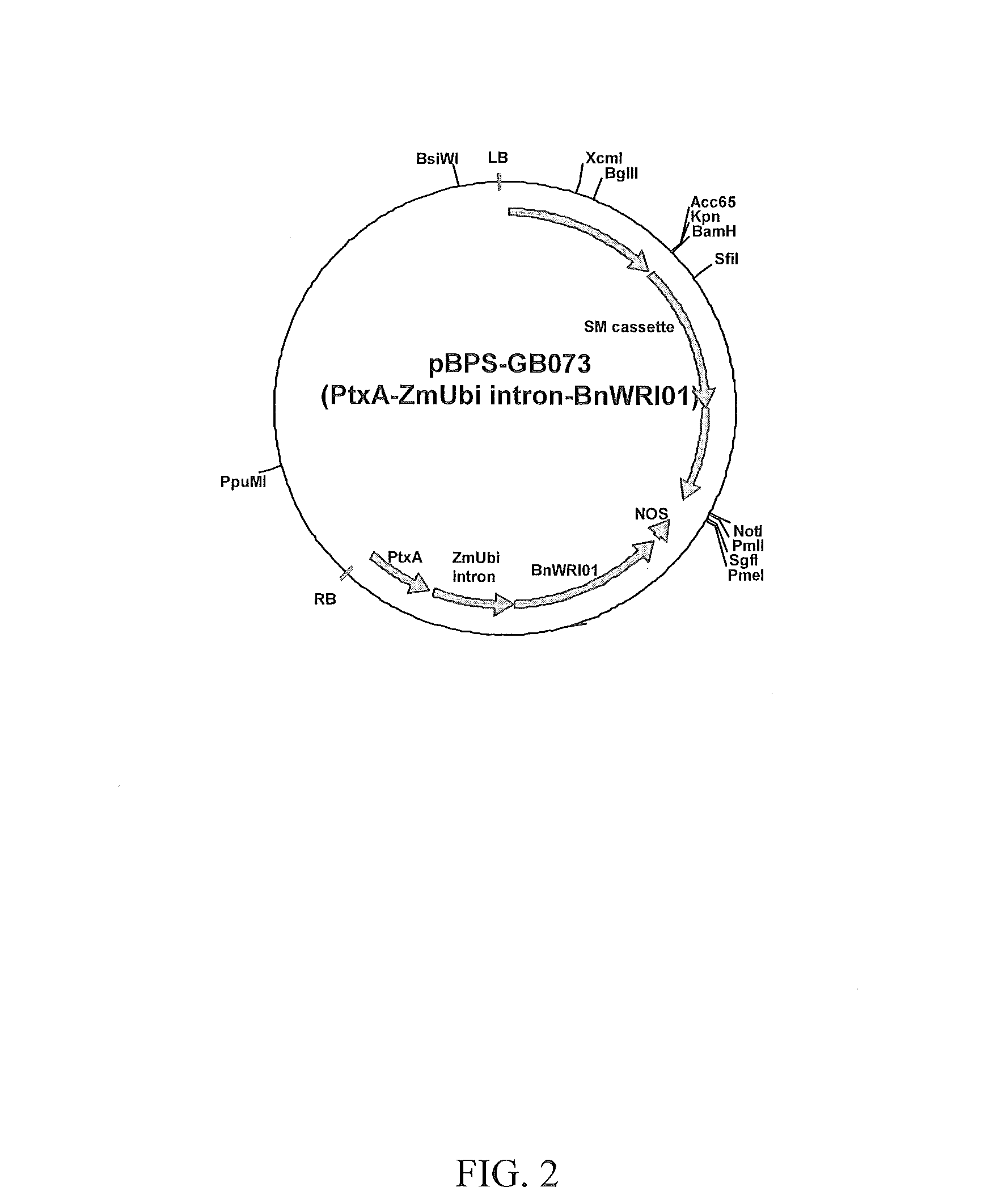
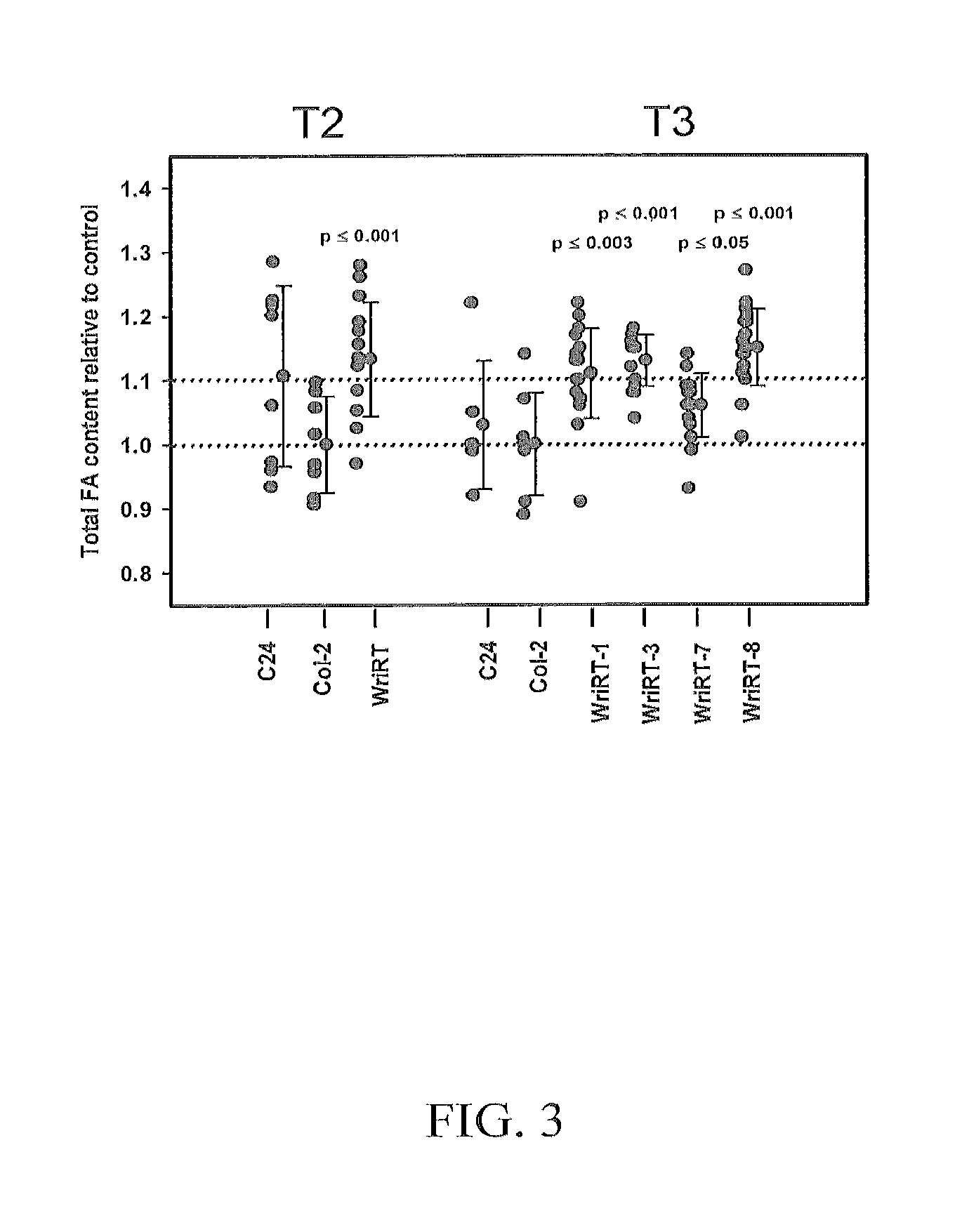
Nucleic acid molecules encoding WRINKLED1-like polypeptides and methods of use in plants
InactiveUS8217223B2High oil contentImprove the level ofBryophytesSugar derivativesBiotechnologyFatty acid
Isolated nucleic acids and proteins associated with lipid and sugar metabolism regulation are provided. In particular, lipid metabolism proteins (LMP) and encoding nucleic acids originating from Arabidopsis thaliana, Brassica napus, Glycine max, Oryza sativa, and Triticum aestivum are provided. The nucleic acids and proteins are used in methods of producing transgenic plants and modulating levels of seed storage compounds. Preferably, the seed storage compounds are lipids, fatty acids, starches, or seed storage proteins. The nucleic acids and proteins also are used in methods of modulating the seed size, seed number, seed weight, root length, and leaf size of plants.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method of regulating glucose metabolism, and reagents related thereto
InactiveUS20040176307A1Long-term abatementLong-term reductionBiocideDipeptide ingredientsLipid storageChylomicron
The present invention provides methods and compositions for modification and regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, generally to reduce insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, obesity, hyperlipidemia, hyperlipoprotein-emia (such as chylomicrons, VLDL and LDL), and to regulate body fat and more generally lipid stores, and, more generally, for the improvement of metabolism disorders, especially those associated with diabetes, obesity and / or atherosclerosis.
Owner:1149336 ONTARIO +2
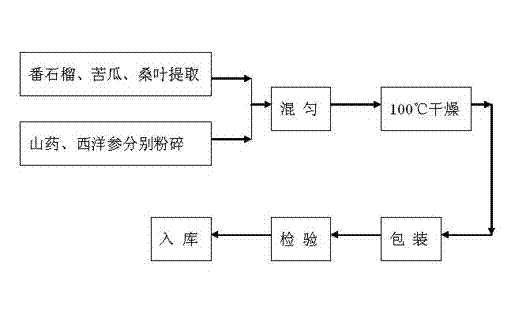
Health-care beverage of guava and making method of health-care beverage
InactiveCN102763884AGreat tastePleasant tea fragranceTea substituesFood preparationBitter gourdDiabetic care
The invention discloses a health-care beverage of guava. The health-care beverage is characterized by comprising the following substances and materials in parts by weight: 30-50 parts of guava, 20-40 parts of bitter gourd, 10-30 parts of Chinese yam, 20-40 parts of folium mori and 5-20 parts of American ginseng. The health-care beverage can be made into dosage forms of tablets, capsules, granules, tea bags and the like; the health-care beverage tastes good, has the original flavor, has the pleasant tea fragrance, is applicable for long-term drinking of glycosuria patients, has the functions of conditioning the insulin secretion and promoting the glycometabolism and fat metabolism, and is capable of conditioning the physiological functions of glycosuria patients, recovering the normal functions of the spleen and stomach and achieving the functions of blood sugar reduction, fat reduction, and glycosuria adjuvant therapy; and when being drunk or taken by ordinary people, the health-care beverage also has the functions of promoting the human body conditioning ability and ensuring the health.
Owner:GUANGXI JINSAI HEALTH PRODS
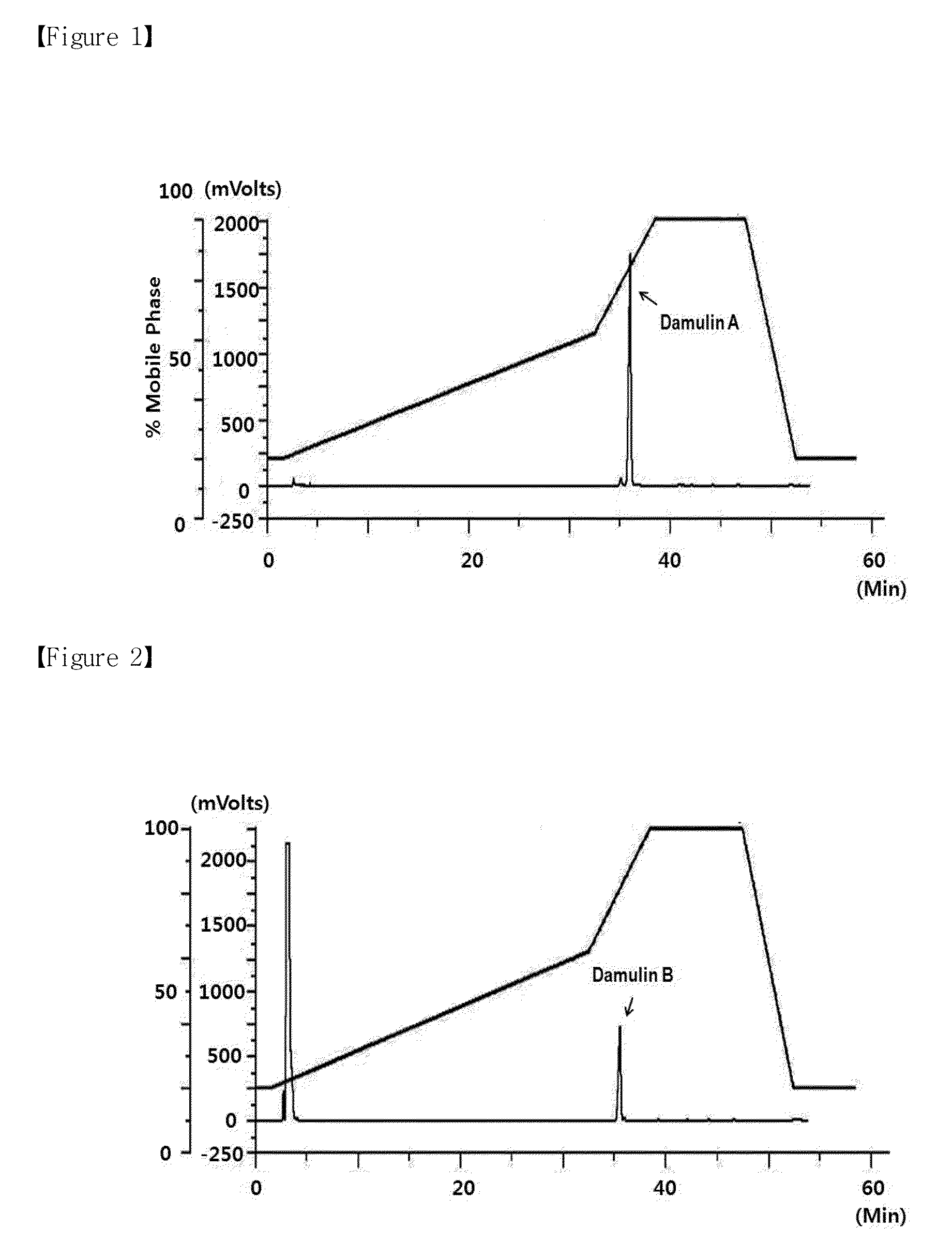
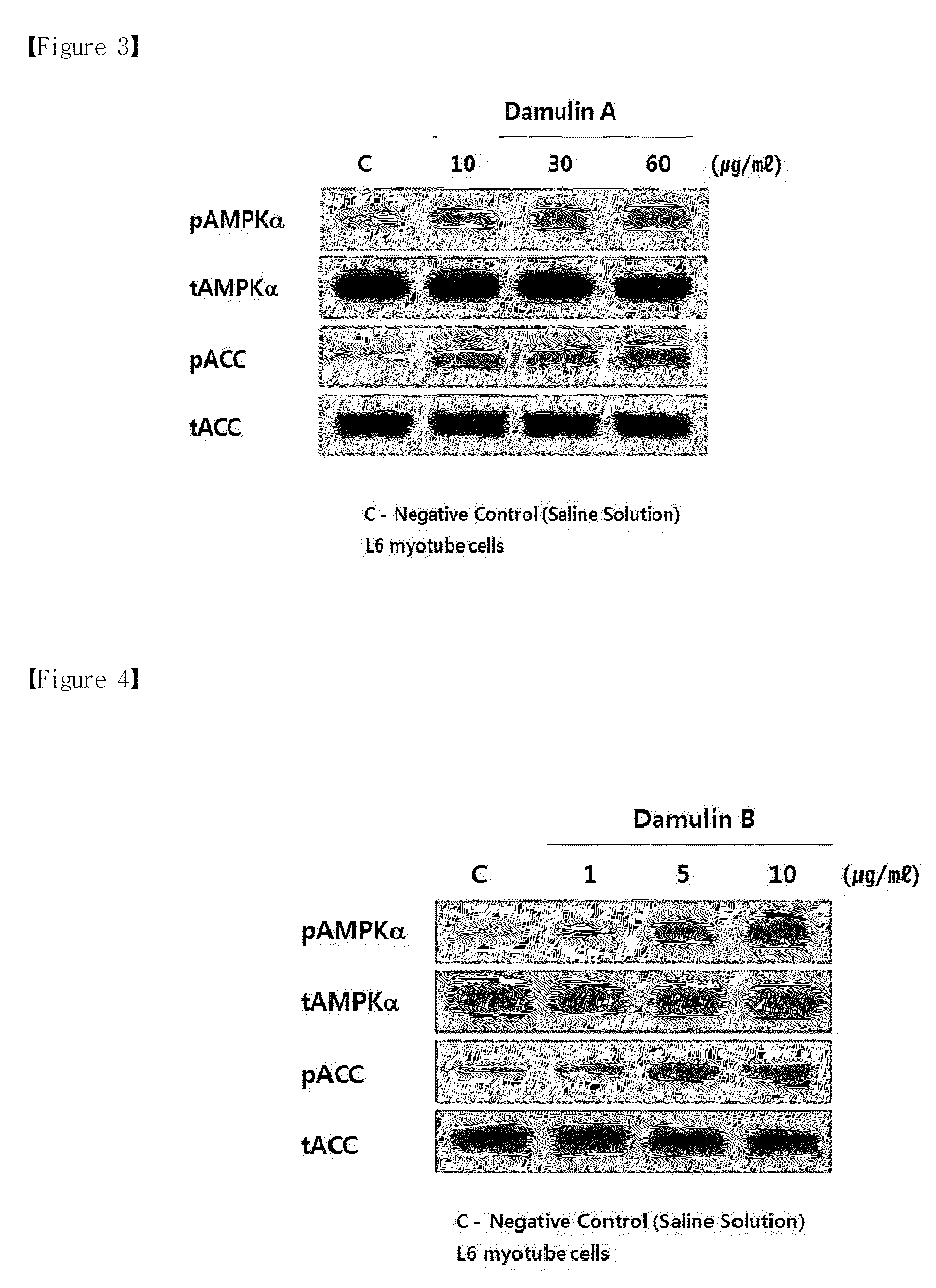
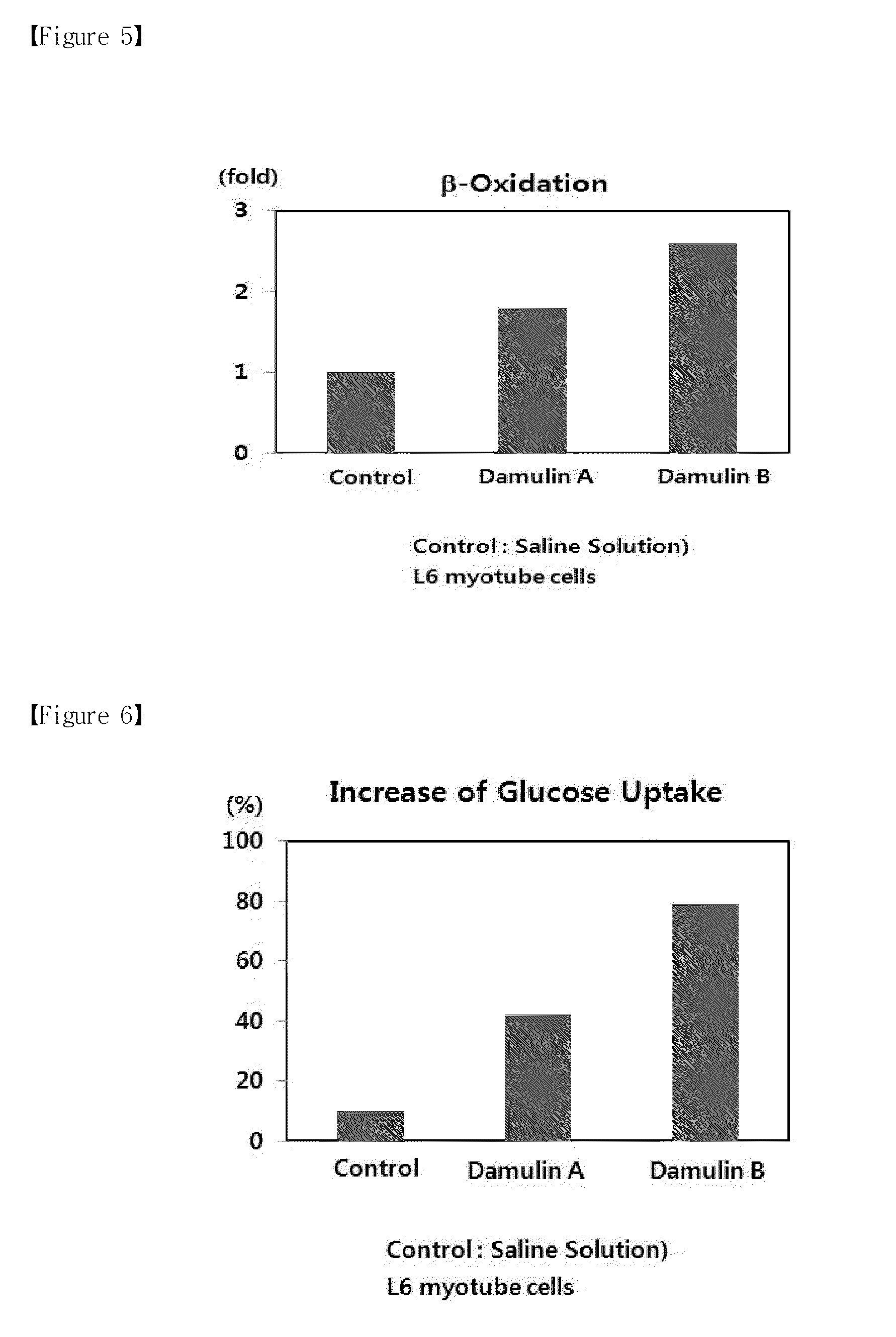
Method for preparing gynostemma pentaphyllum extract with increasing damulin a and damulin b contents, and pharmaceutical compositions of the same for treating metabolic disease
ActiveUS20110015142A1Improving/treating effect on metabolic syndromeIncrease temperatureOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCholesterolAdditive ingredient
Disclosed is an AMPK activating material used for improving and treating metabolic syndrome, in which AMPK (AMP-activated protein kinase) is a main enzyme for regulating an energy sensor and lipid / glucose metabolism in the body. The activation of AMPK inhibits the synthesis of fat and cholesterol, and accelerates the reduction of body fat and blood glucose, thereby improving obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipidaemia. The disclosed AMPK activating material contains, as active ingredients having an improving and treating effect on metabolic syndrome, including obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipidaemia, a novel compound 2α,3β,12β-trihydroxydammar-20(22)-E,24-diene-3-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→)-β-D-glucopyranoside], named Damulin A, and a novel compound 2α,3β,12β-trihydroxydammara-20,24-diene-3-O-[β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→)-β-D-glucopyranoside], named Damulin B. Herein, the contents of damulin A and damulin B (as active indicator ingredients for AMPK activation) can be increased by treating a Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract with high temperature / high pressure. Accordingly, the novel Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract with a significantly increased AMPK activating capability can be used for improving or treating metabolic syndrome, such as obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipidaemia.
Owner:TG BIOTECH CO LTD
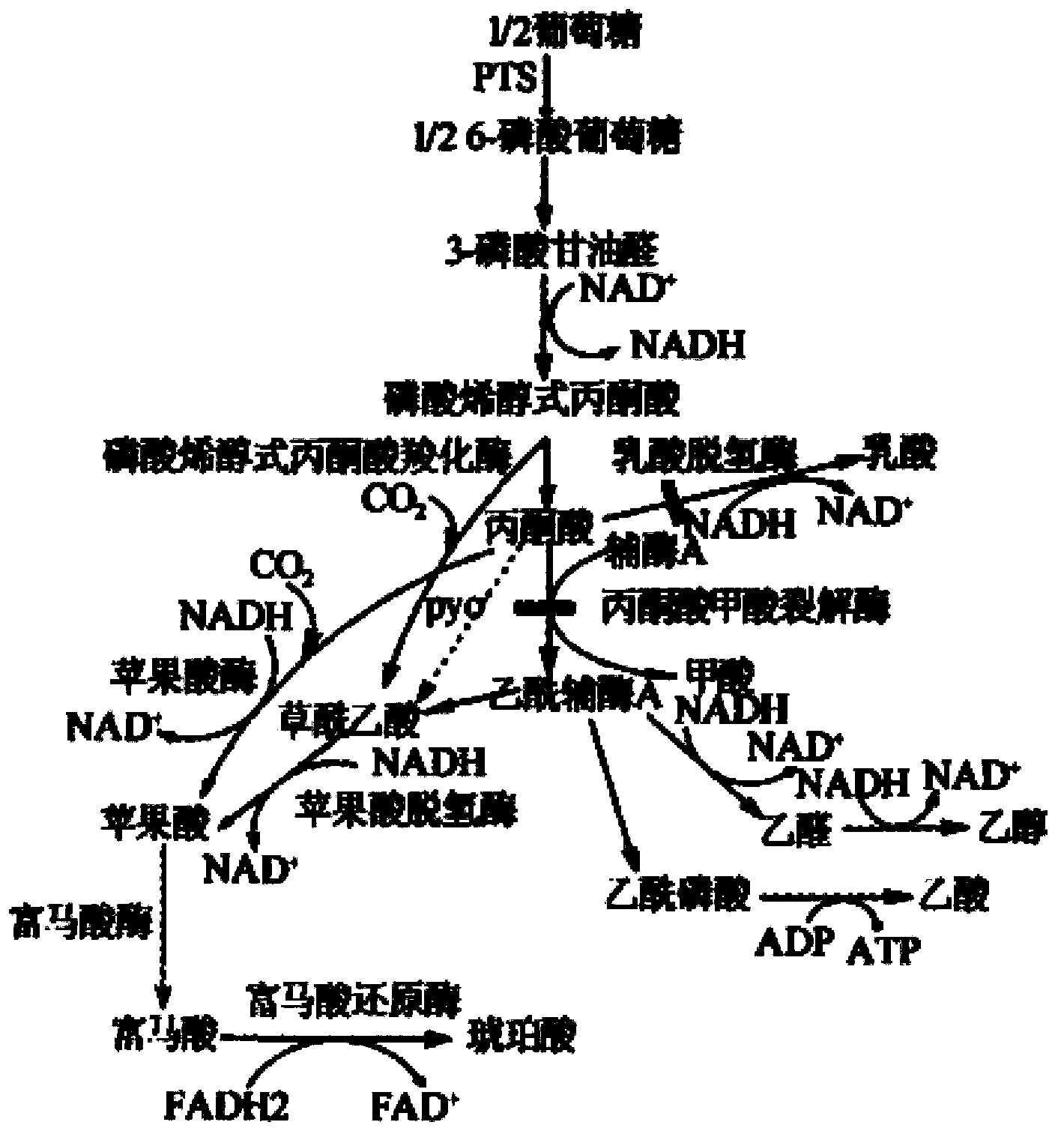
Method for constructing genetically engineered Escherichia coli using xylose metabolism to produce succinate
InactiveCN102296082AIncrease biomassTo achieve the purpose of isolating bacteriaOxidoreductasesLigasesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
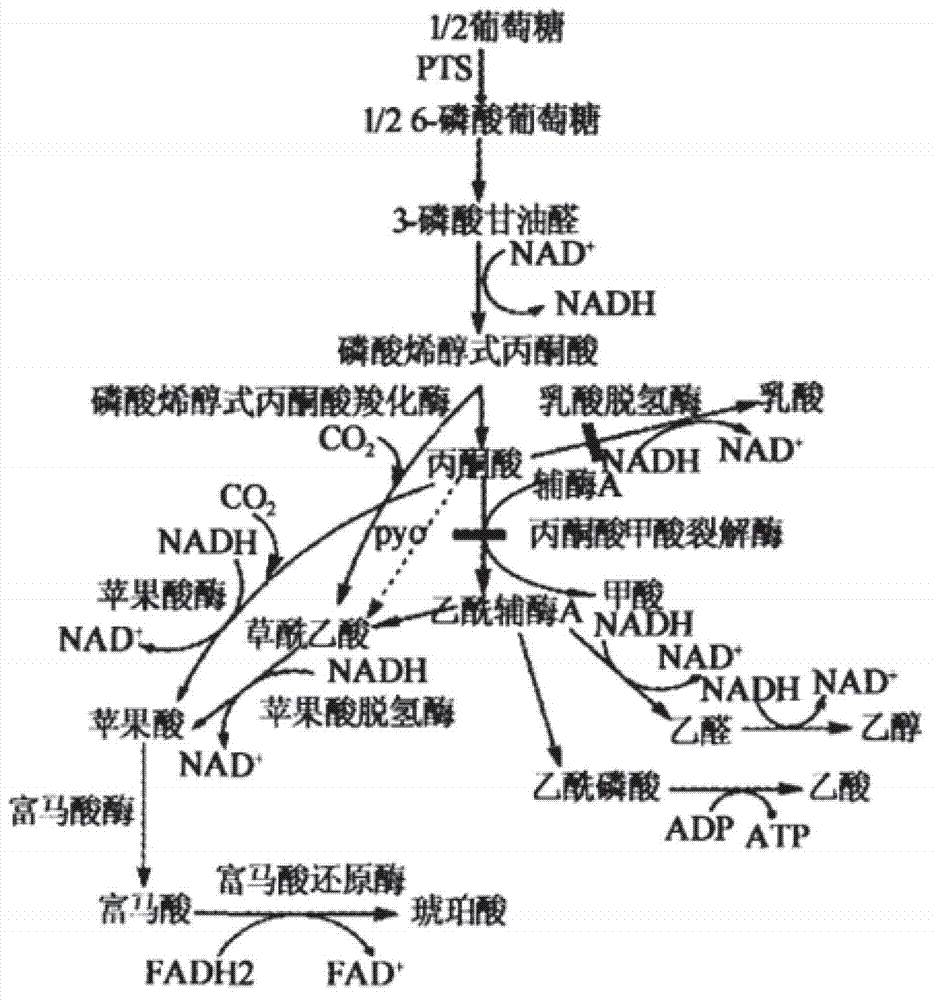
Provided is a construction method of an escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria producing succinic acid by xylose metabolism and the method for producing succinic acid by fermentation using the bacteria. The ATP biosynthesis pathway of escherichia coli is modified by means of molecular biology and the enzyme activity related to the pathway is over-expressed; thus the total ATP amount within escherichia coli cells is effectively increased such that the recombinant escherichia coli is able to grow using xylose metabolism, and the succinic acid synthesis efficiency is thereby significantly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and construction and application thereof
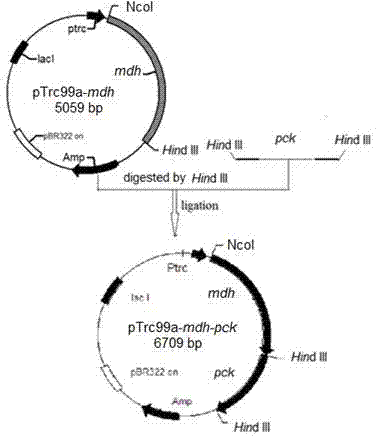
ActiveCN102864116AEasy to buildThe fermentation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
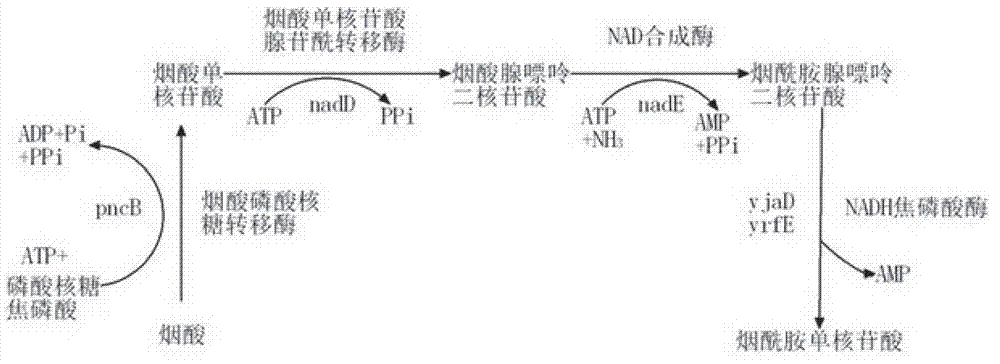
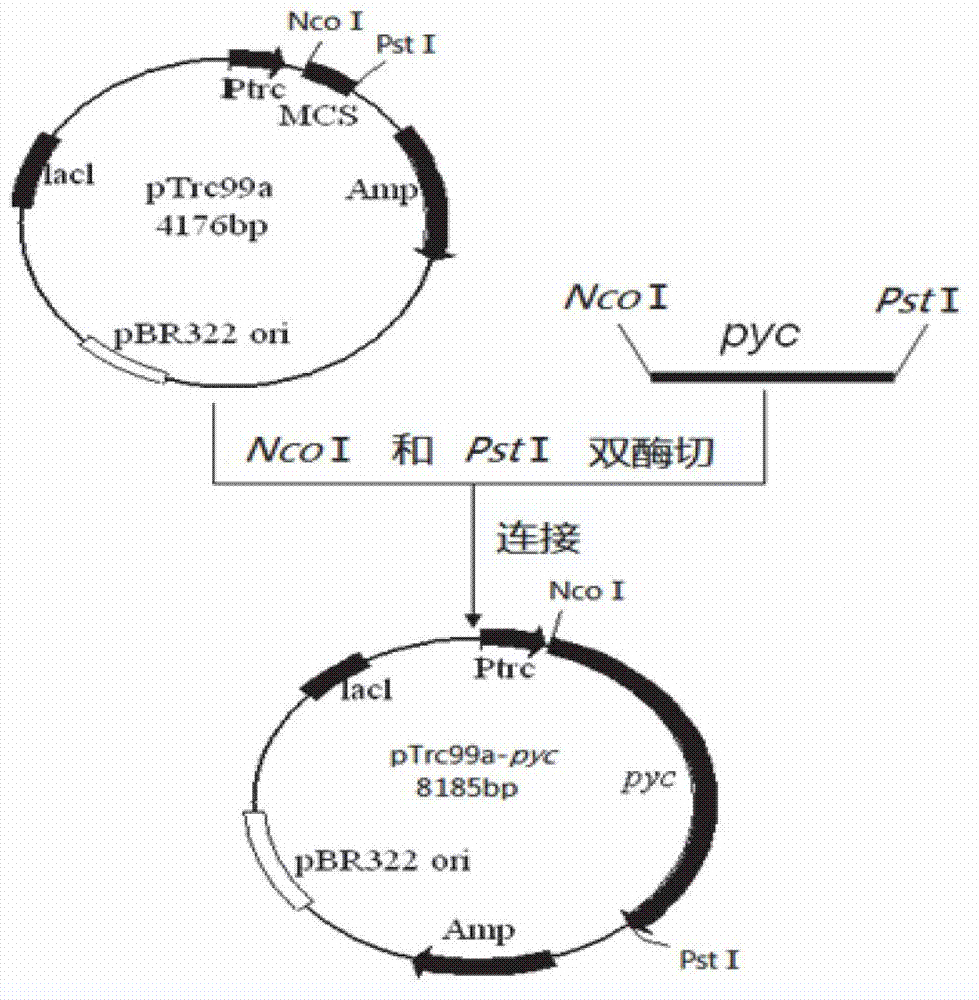
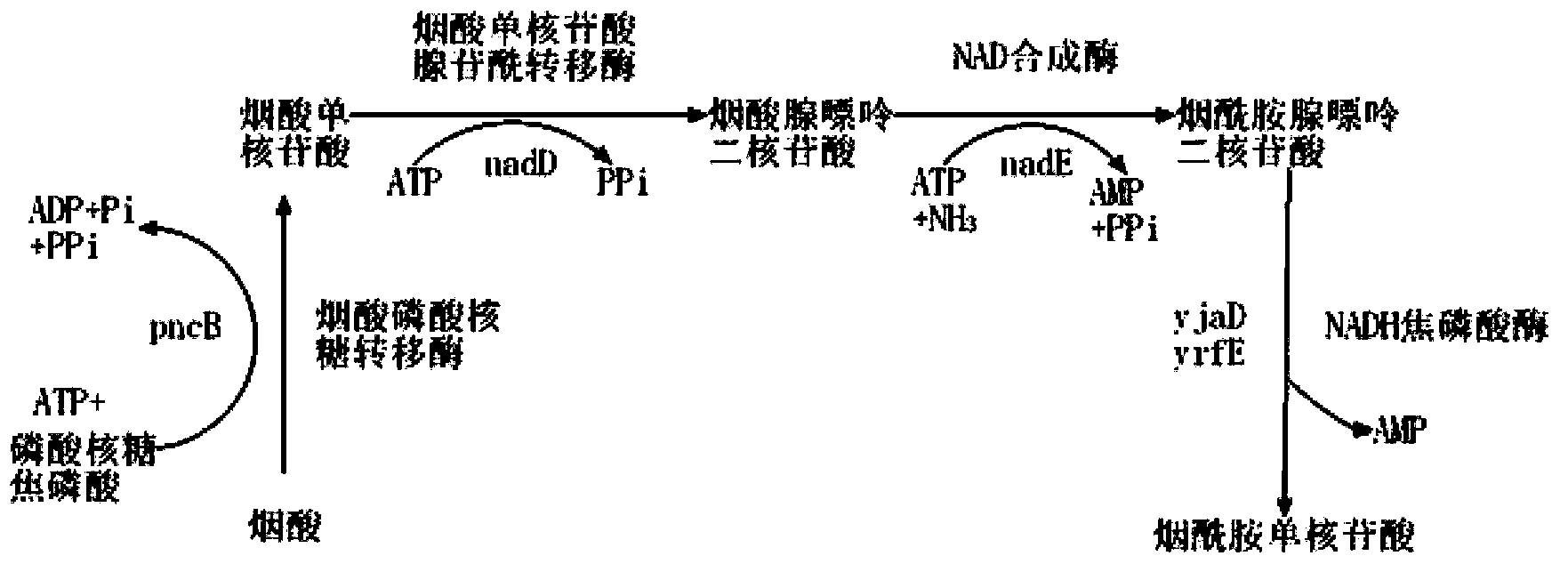
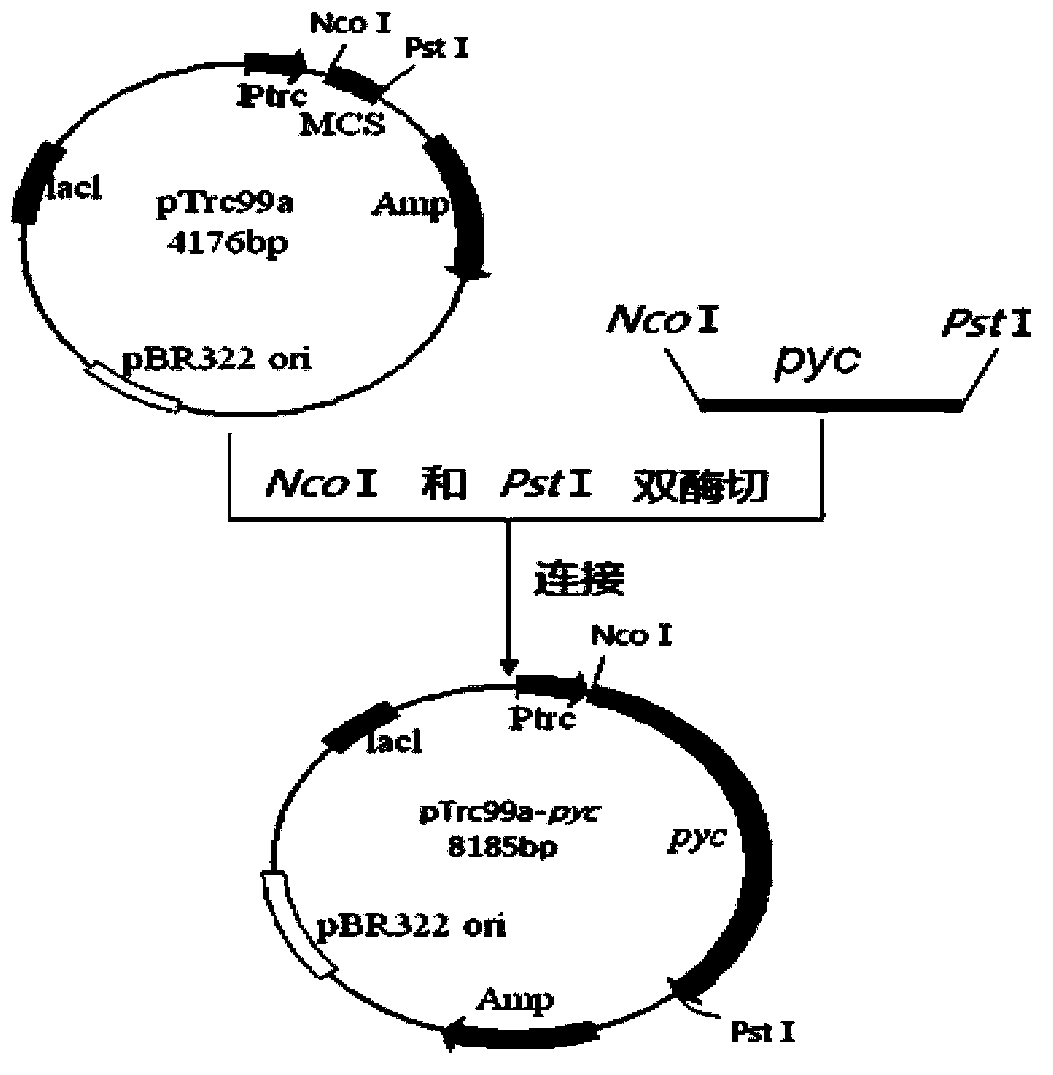
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid. The genetic engineering bacterium strain is named as Escherichia coli BA016, the preserving number registration number CCTCC NO is M 2012350. The invention further provides a construction method of the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation, recombinant escherichia coli can grow by glucose metabolism through joint excessive expression of exogenous pyruvic carboxylase and nicotinic acid ribose phosphate transferase, generation of by-product pyruvic acid is reduced, and accordingly the yield and production intensity of succinic acid are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Fluorescent dye-labeled glucose bioprobe, synthesis method and usage thereof
ActiveUS20100105149A1Improve performanceSugar derivativesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceDiseaseSynthesis methods
The present invention relates to a fluorescent dye-labeled glucose analog, and a synthesis method and usage of the same, and more particularly, to novel glucose α and β anomers in which a fluorescent dye is labeled by O-1-glycosylation, an asymmetric synthesis method of the anomers, a molecular bioimaging method of the anomers, and a screening method of curing or preventing drugs for diseases related to glucose metabolism.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
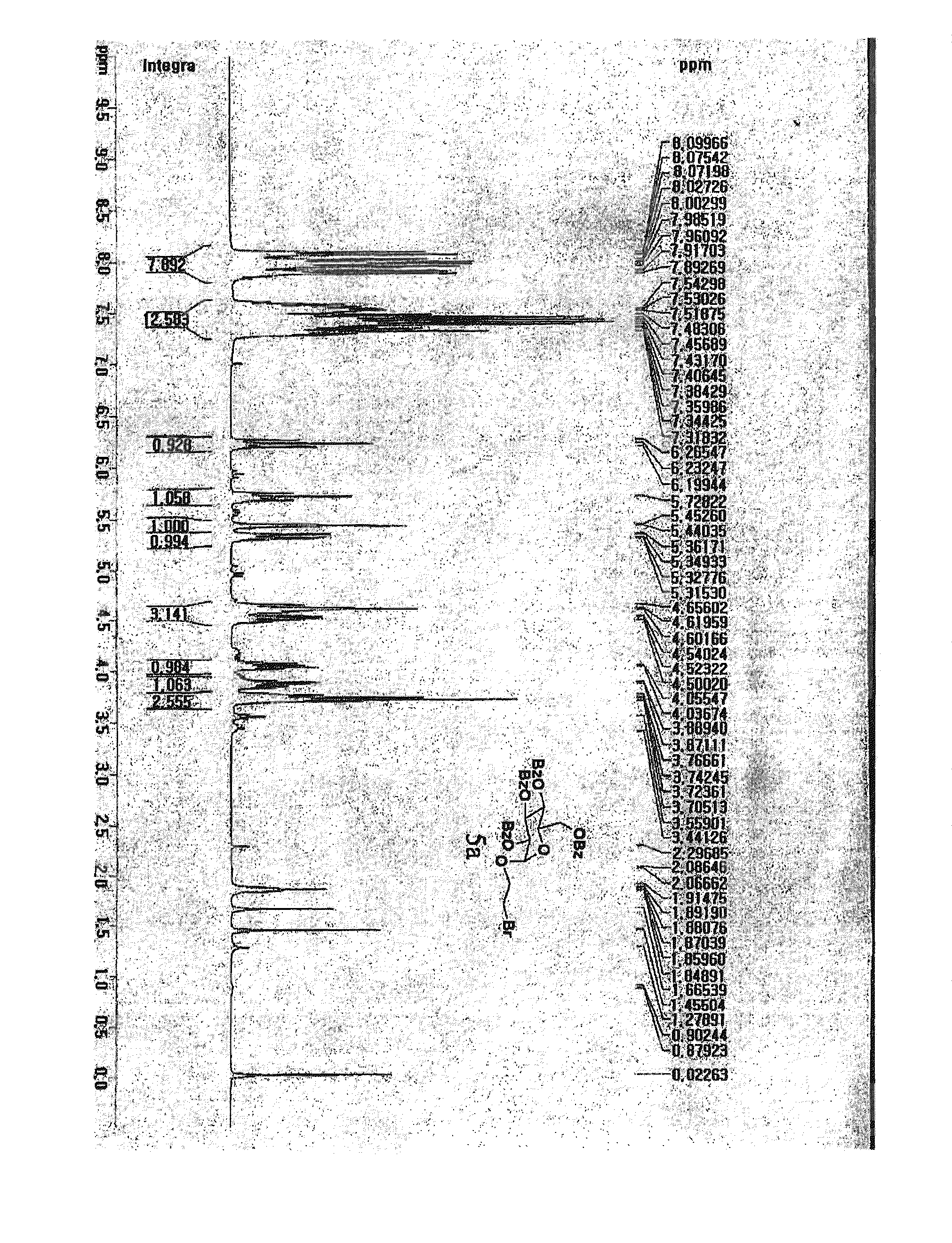
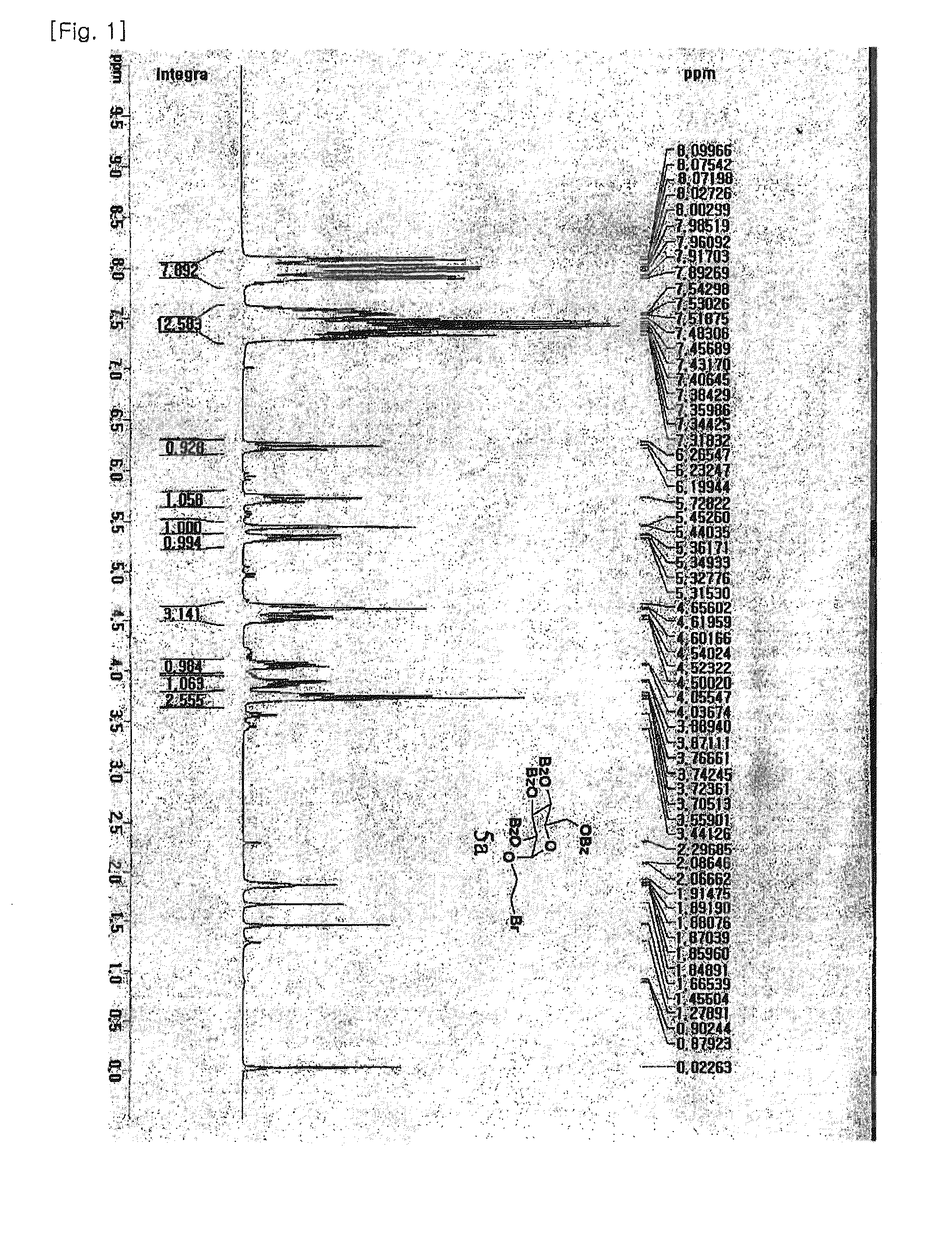
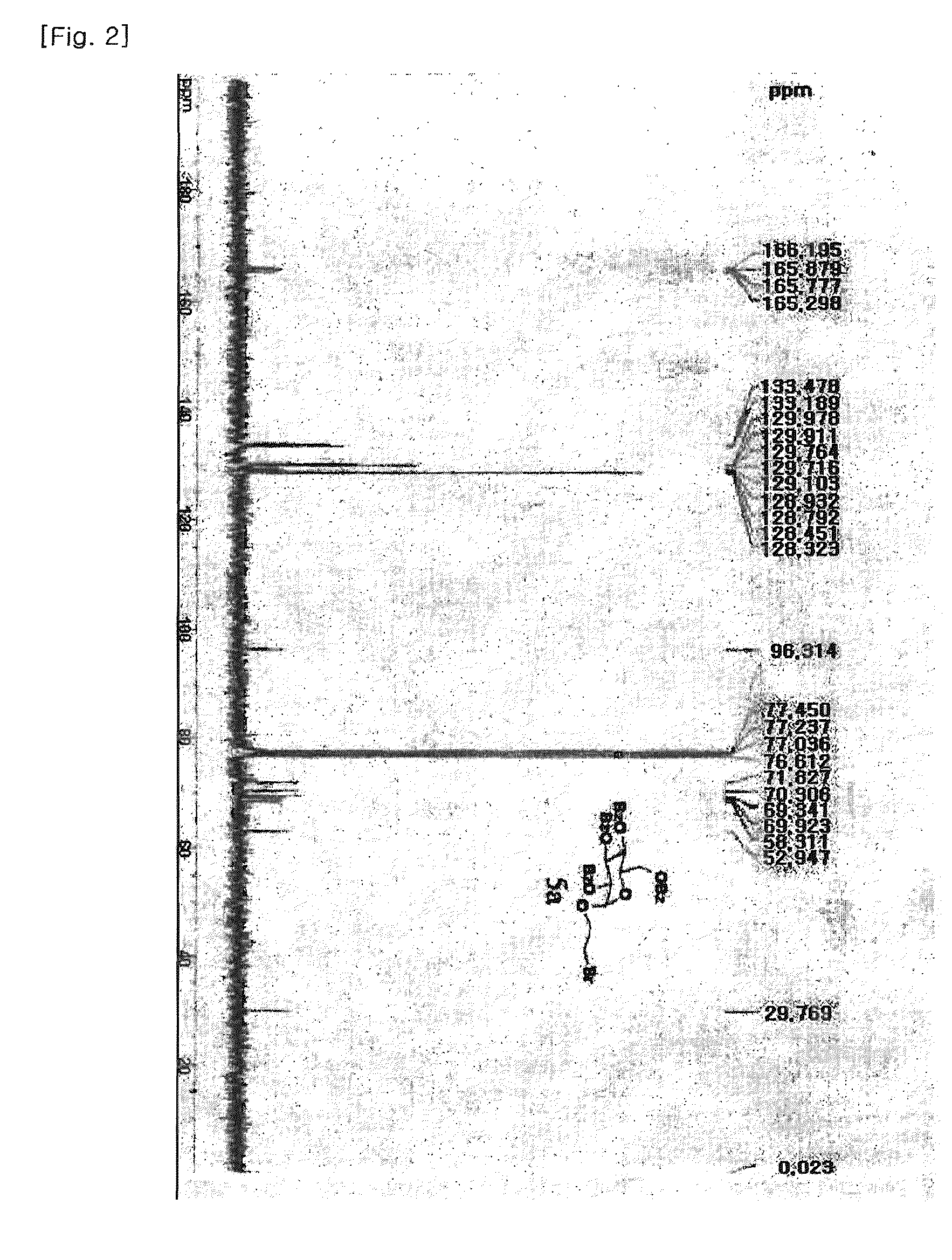
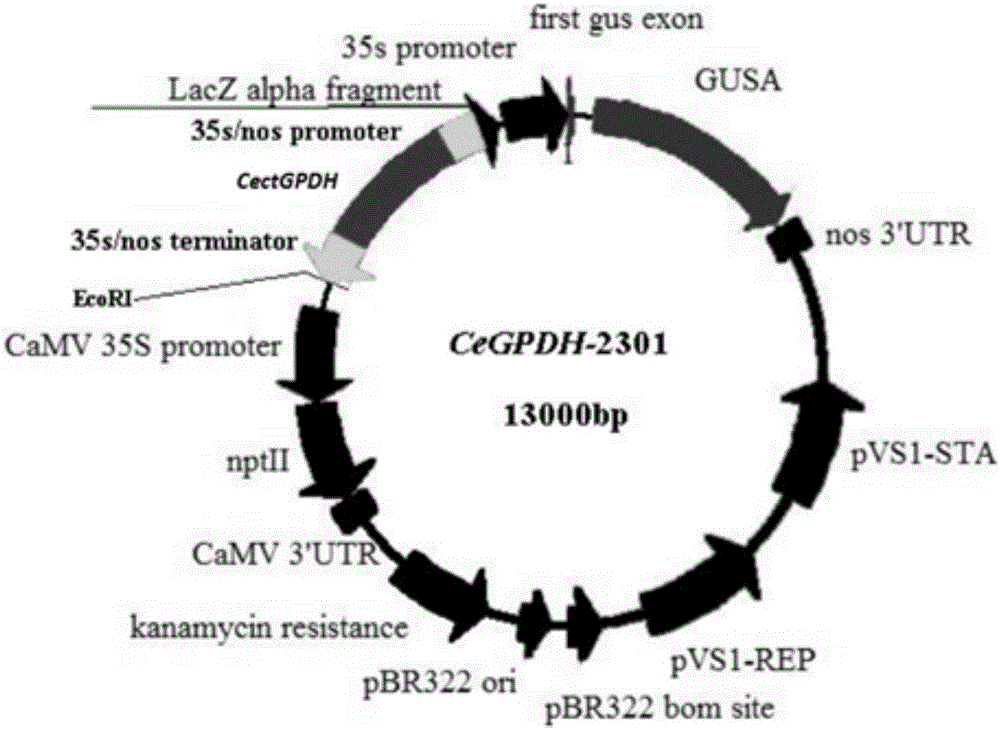
CectGPDH2 (cytosolic glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase 2) gene and application thereof
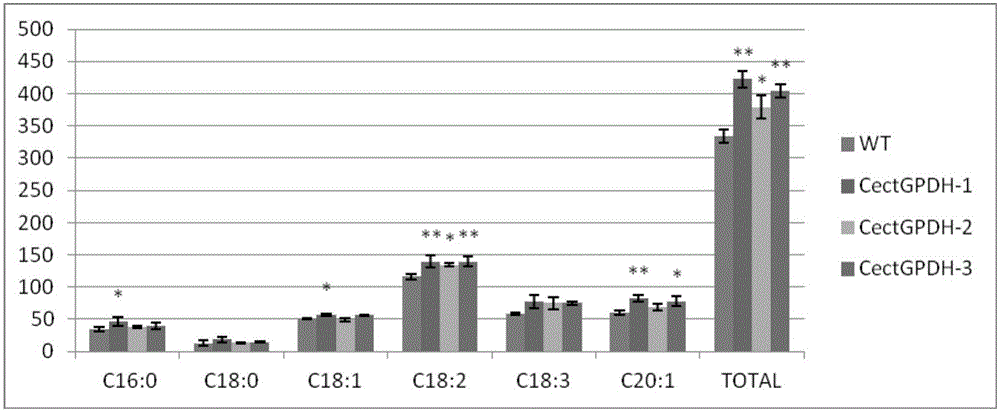
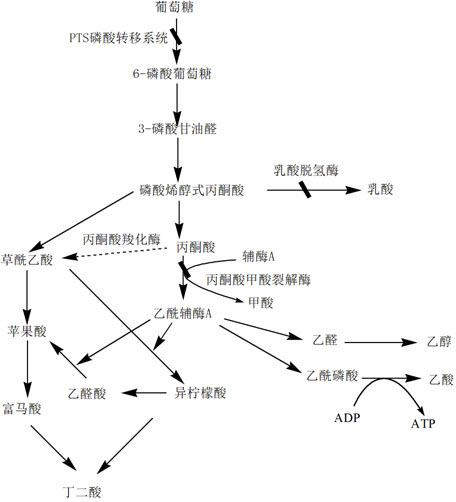
The invention provides a CectGPDH2 gene and an application thereof in increase of fatty acid content. The nucleotide sequence of the CectGPDH2 gene is shown as SEQ NO.1. The gene comes from Chlorella ellipsoidea and encodes GPDH, wherein the GPDH participates in shuttle of the mitochondrion G3P (glycerol-3-phosphate), provides electrons for respiratory chains, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of the key enzymes for connecting glucose metabolism with lipid metabolism and plays an important role in lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants. The total fatty acid content of seeds of Arabidopsis thaliana and rape genetically modified with the gene can be increased obviously, and the gene can be used for increasing the oil content of plant cells and the content of linoleic acid (C18:2) and eicosenoic acid (C20:1) in the plants and has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene engineering bacterial strain generating succinic acid and method of producing succinic acid by fermentation of the gene engineering bacterial strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, relates to a gene engineering bacterial strain generating succinic acid and a method of producing succinic acid by fermentation of the gene engineering bacterial strain, particularly to a gene engineering bacterial strain generating succinic acid, namely Escherichia coli BA103, by high-efficiency use of glucose, a construction method of Escherichia coli BA103 and a method of producing succinic acid by Escherichia coli BA103. By expression of an exogenous pyruvate carboxylase, recombinant Escherichia coli can grow by use of glucose metabolism, so that the yield of succinic acid is greatly increased, the generation intensity is greatly improved, and the generation of pyruvic acid as a by-product is reduced.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
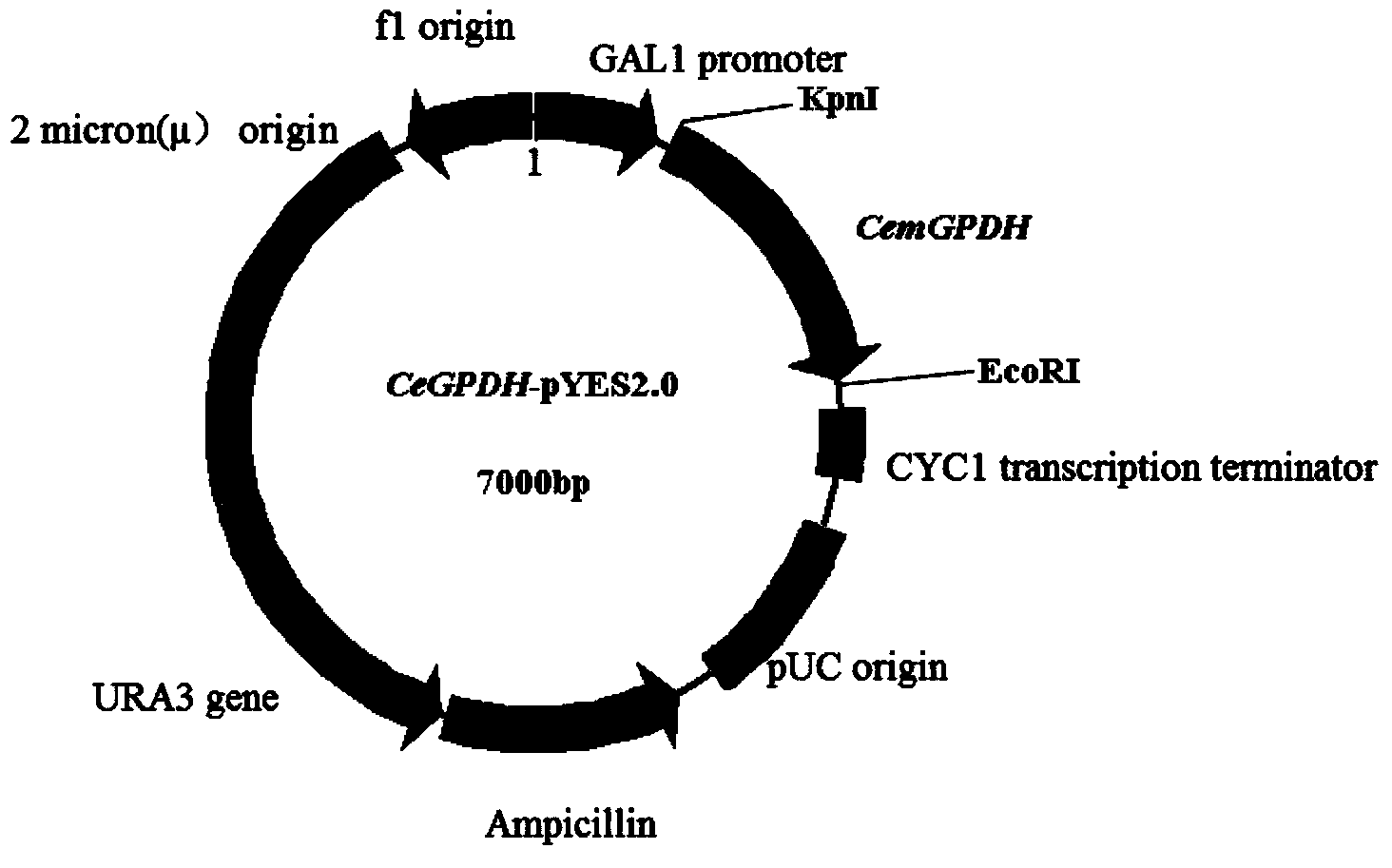
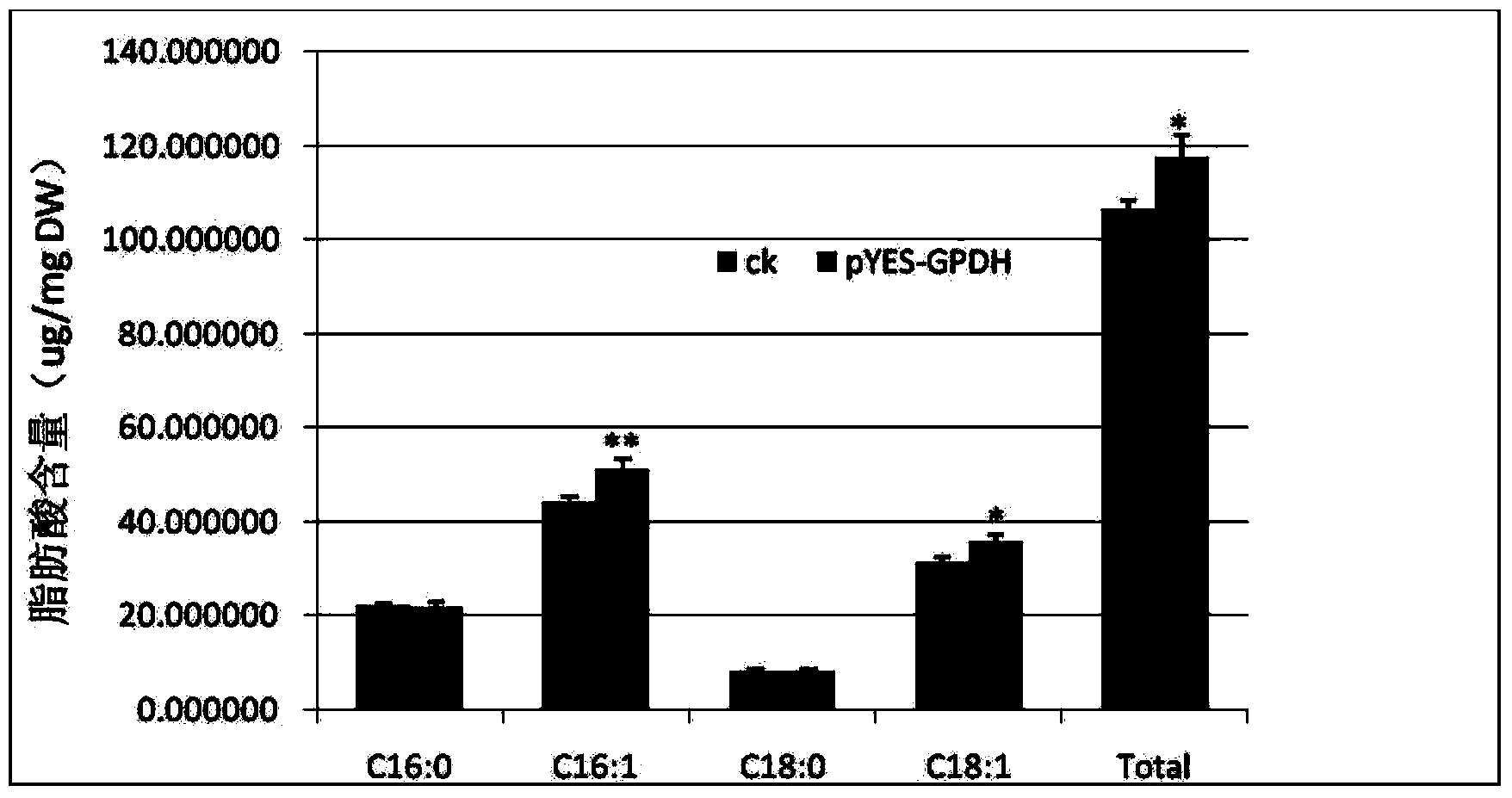
Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and application thereof
The invention provides a Cem GPDH (Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) gene and an application of the Cem GPDH gene in the aspect of increase of cellular fatty acid content. A nucleotide sequence of the Cem GPDH gene is represented as SEQ ID NO: 1. The gene is derived from Chlorella ellipsoidea, and GPDH is coded. G3P (Glycerol-3-phosphate) synthesized through catalysis by GPDH is an important raw material for synthesis of TAG (triacylglycerol), the enzyme participates in mitochondria G3P shuttle, provides electrons for a respiratory chain, is a key enzyme for G3P synthesis, is one of key enzymes for connecting glycometabolism and lipid metabolism and has an important effect on lipid synthesis and energy metabolism in plants; and besides, the gene can remarkably increase the total fatty acid content of cells when utilized to convert yeast cells, plant cells and microalgae cells.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for measuring carbohydrate metabolism ability, and composition for use in said method
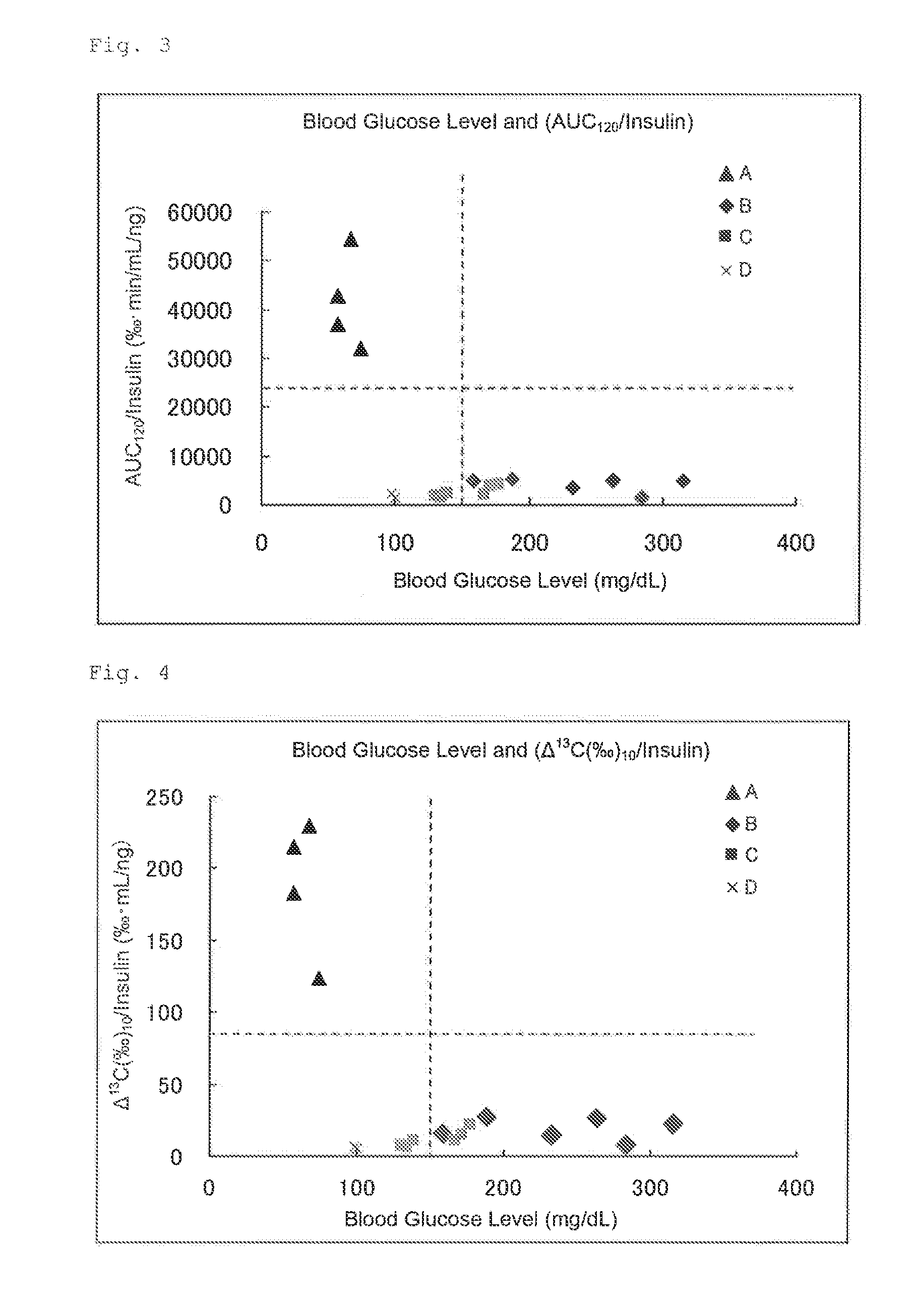
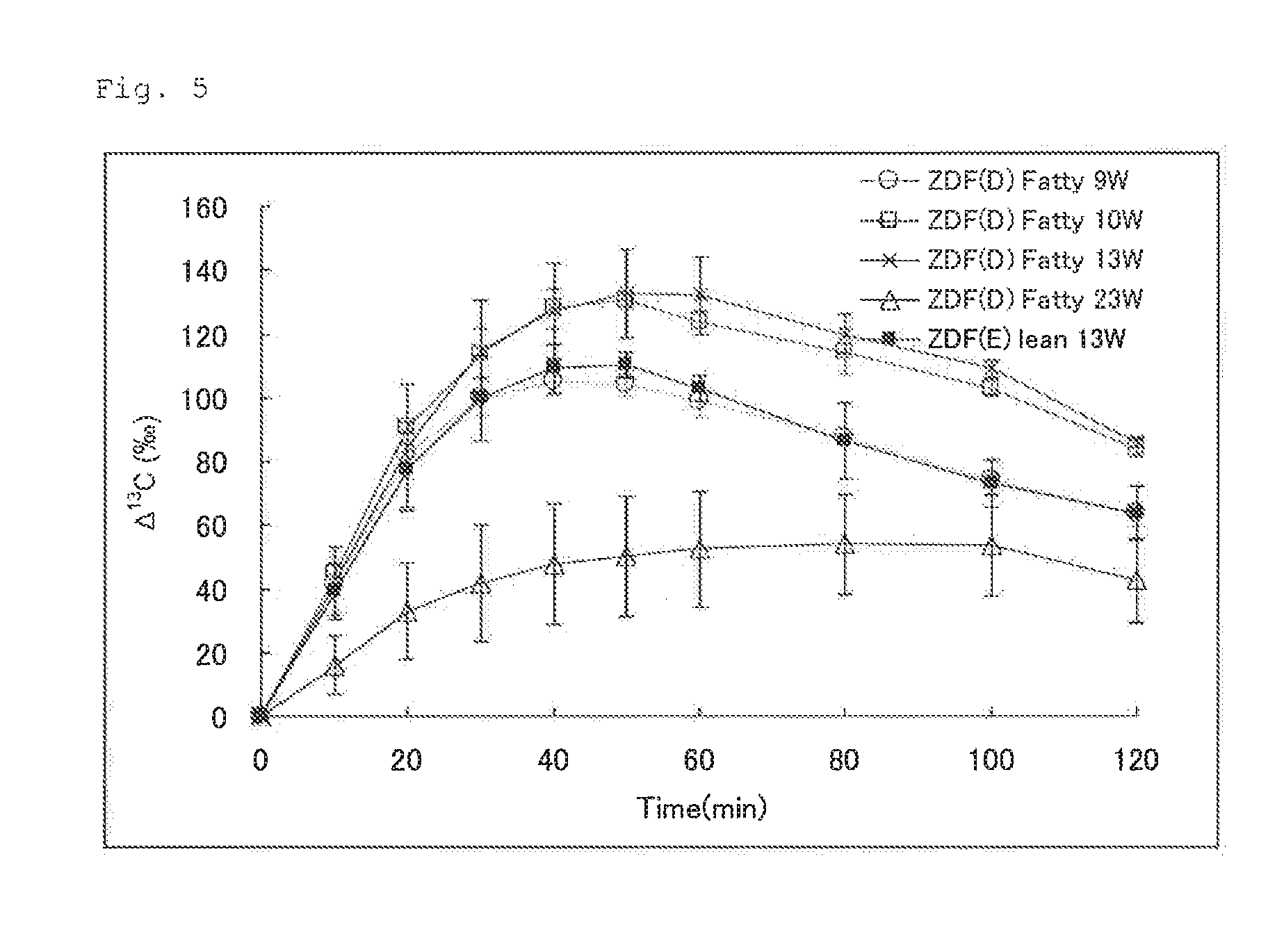
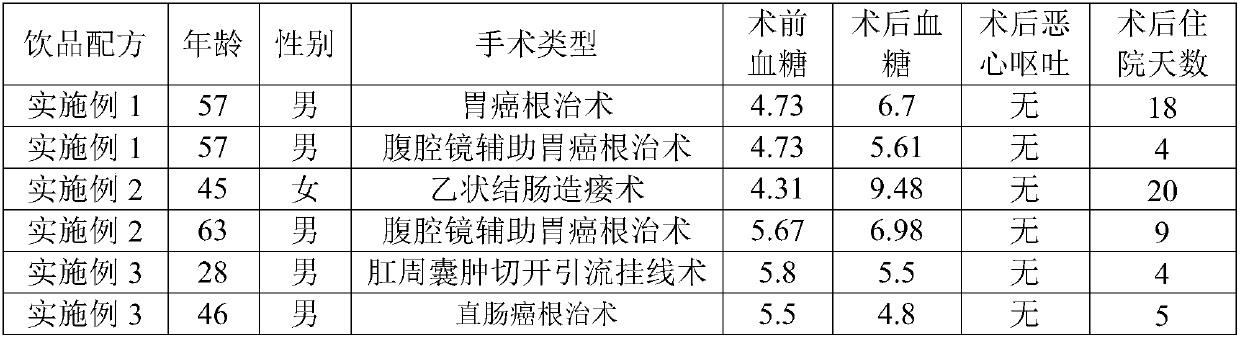
InactiveUS20150204852A1Improve accuracyAchieve rapidityCompounds screening/testingHealth-index calculationMetabolic powerIsotope
This invention provides a method for measuring glucose metabolism ability of a subject and a composition that is suitably used in the method. The method for measuring glucose metabolism ability of the present invention is as follows: a method for measuring glucose metabolism ability of a subject, using a composition for measuring glucose metabolism ability, the composition comprising, as an active ingredient, glucose labeled with at least one isotope of C, wherein the glucose is converted in the body into labeled carbon dioxide that is excreted in expired air, the method comprising steps (a) and (b) below:(a) administering the composition to the subject and collecting expired air; and(b) determining the ratio of labeled CO2 amount to unlabeled CO2 amount or the ratio of labeled CO2 amount to total CO2 amount.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
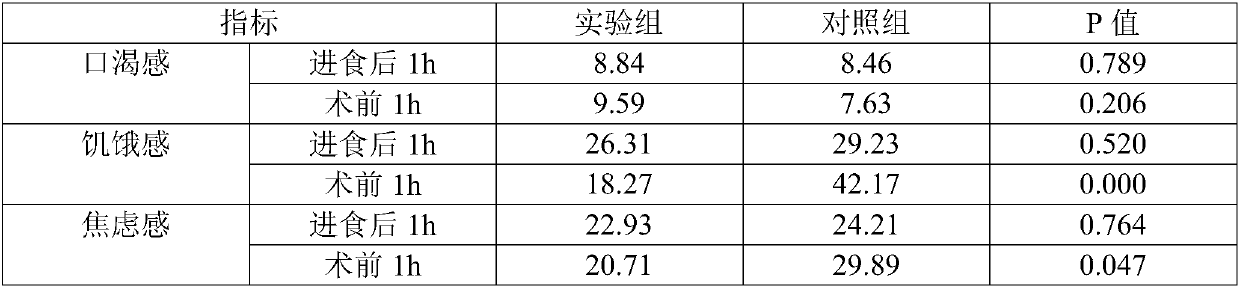
Preoperative and postoperative solid drink and beverage
InactiveCN107927515AFast gastric emptyingNo risk of reflux aspirationInorganic compound food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsMetabolic StressGlycogen
The present invention belongs to the technical field of preoperative and postoperative drink and provides preoperative and postoperative solid drink. The preoperative and postoperative solid drink iscomposed of the following components in parts by weight: a total of 40-60 g of one or more of maltodextrin, isomaltulose, crystalline fructose, glucose and sucrose, 0-15 g of glutamine, 0-5 g of arginine, 0.6-0.8 g of sodium citrate dihydrate, 0.1-0.3 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 0.5-0.9 mg of vitamin B1, 0.5-0.6 mg of vitamin B6, 0.4-0.6 [mu]g of vitamin B12, 2-6 mg of nicotinamide, 1-5 mg of zinc, 170-250 mg of taurine, 10-40 mg of inositol, 0-0.05 g of citric acid, 0.001-0.03 g of potassium sorbate and the balance of water. The invention solves problems of body's glucose metabolismdisturbance, imbalance of internal environment steady state, increases of glycogen catabolism and gluconeogenesis, and accelerations of decompositions of proteins and fats caused by a long-term preoperative and postoperative food and drink fasting, insulin resistance caused by a metabolic stress state of patients, and reduced surgical responsiveness and compliance, and increased intraoperative andpostoperative body stress responses not conducive to intraoperative and postoperative capacity management.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
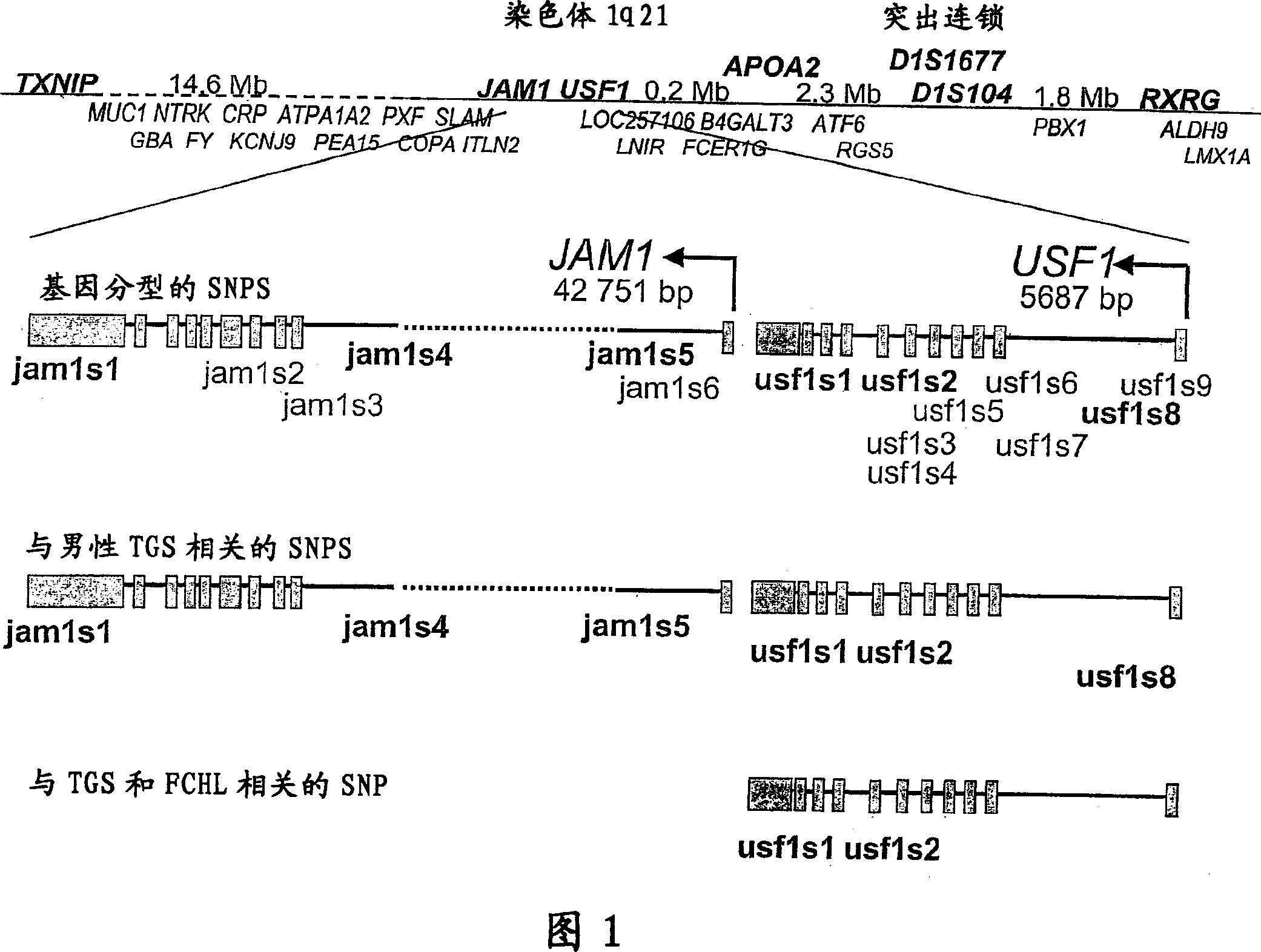
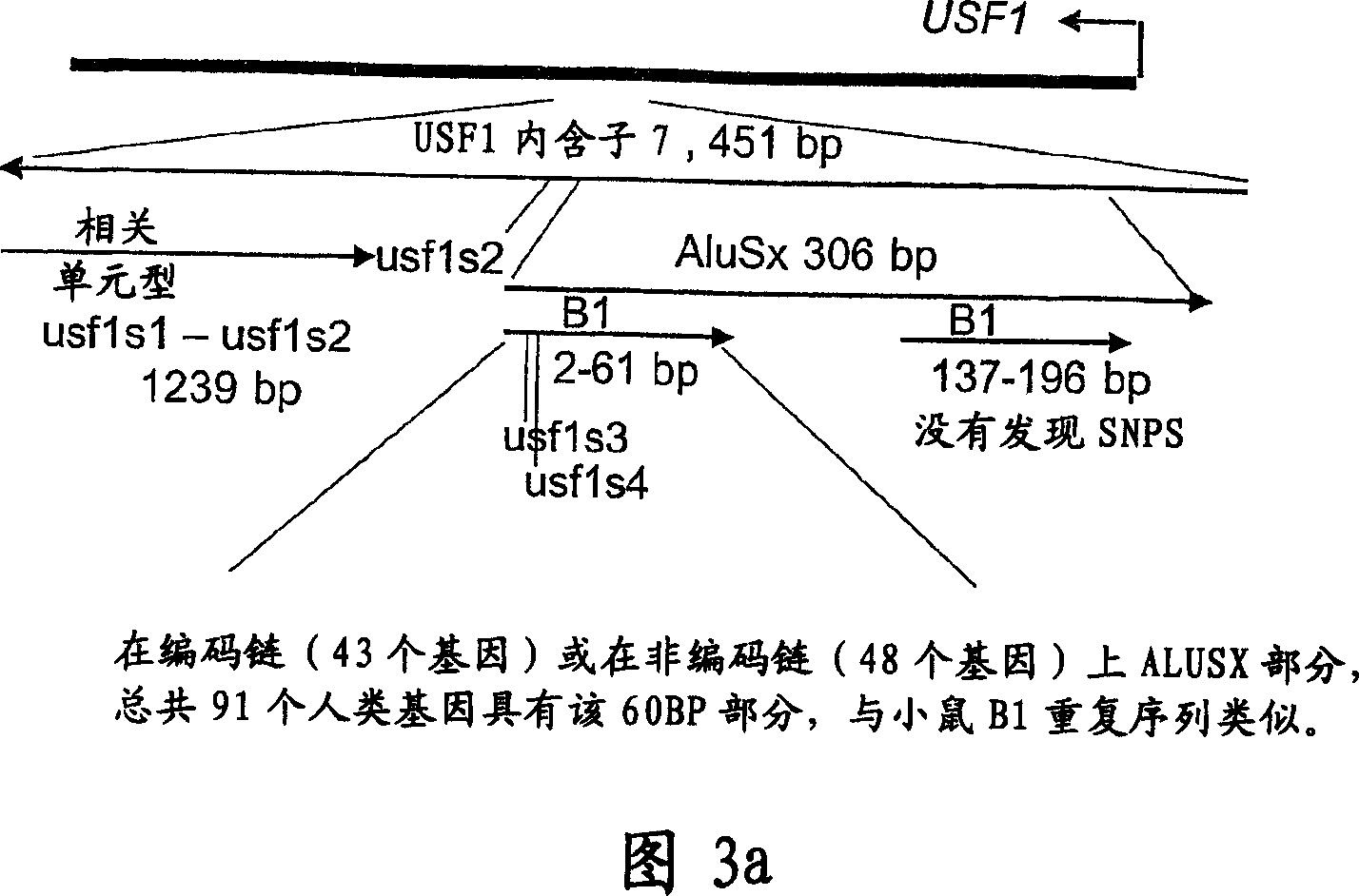
Identification of SNPs associated with hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia and defective carbohydrate metabolism
The present invention relates to a nucleic acid molecule comprising a chromosomal region contributing to or indicative of hyperlipidemias and / or dyslipidemias or defective carbohydrate metabolism, wherein said nucleic acid molecule is selected from the group consisting of: (a) a nucleic acid molecule having or comprising the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein said nucleic acid sequence has one or more mutations having an effect on USFI function; (b) a nucleic acid molecule having or comprising the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein said nucleic acid sequence is characterized by comprising a guanine or an adenine residue in position 3966 in intron 7 of the USF1 sequence; and / or (c) a nucleic acid molecule having or comprising the nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, wherein said nucleic acid sequence is characterized by comprising a cytosine or a thymine residue in position 5205 in, exon 11 of the USF1 sequence; wherein said nucleic molecule extends, at a maximum, 50000 nucleotides over the 5' and / or 3' end of the nucleic acid molecule of SEQ ID NO: 1. The present invention further relates to a diagnostic composition comprising a nucleic acid molecule encoding USF1 or a fragment thereof, the nucleic acid molecule disclosed herein, the vector, the primer or primer pair of the present invention or an antibody specific for USF1. Finally, the present invention relates to the use of the nucleic acid molecule of the invention for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of hyperlipidemia, dyslipidemia, coronary heart disease, type II diabetes, metabolic syndrome, hypertension or atherosclerosis.
Owner:NAT PUBLIC HEALTH INST
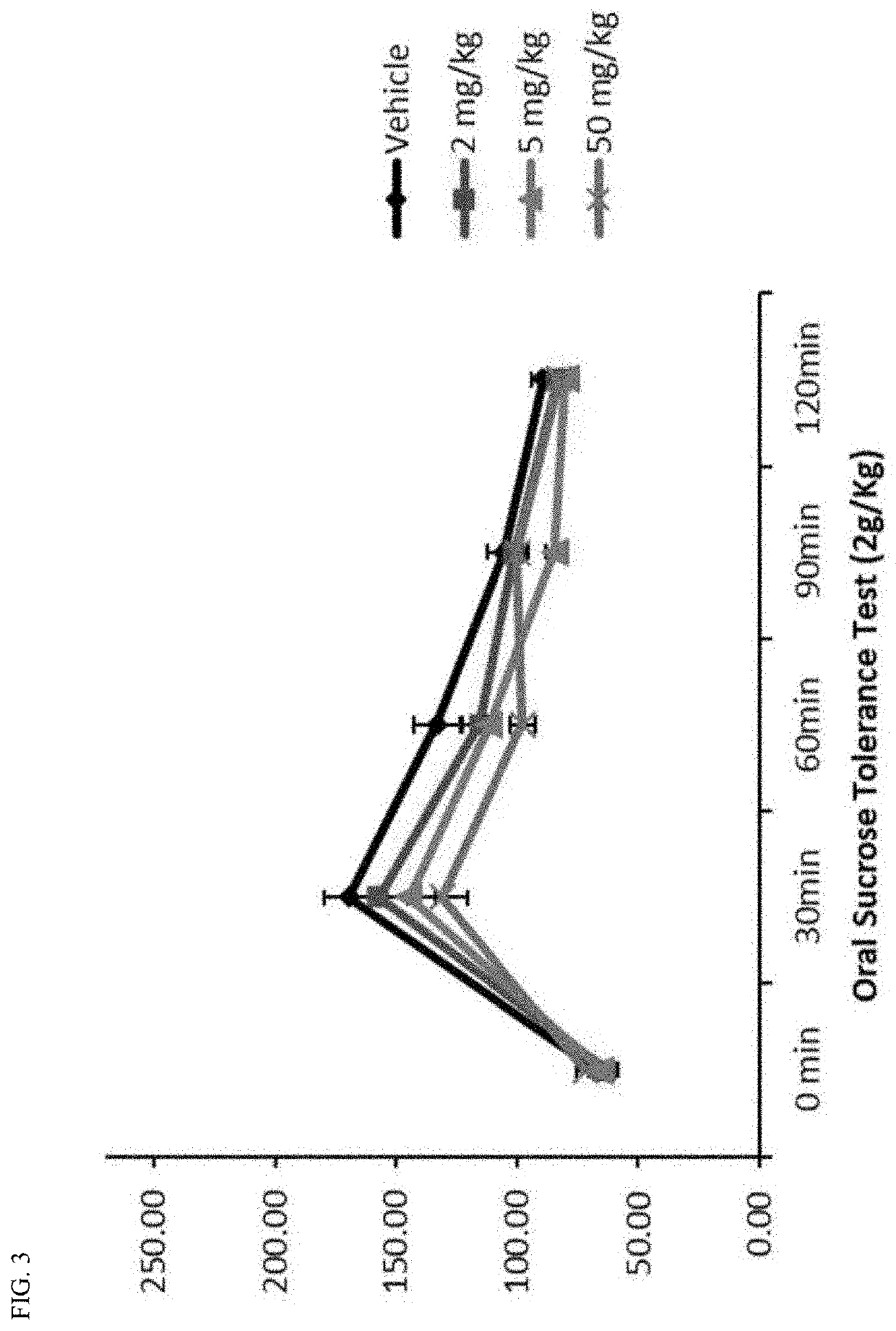
Non-invasive near-infrared light-controlled nano material for treating diabetes mellitus
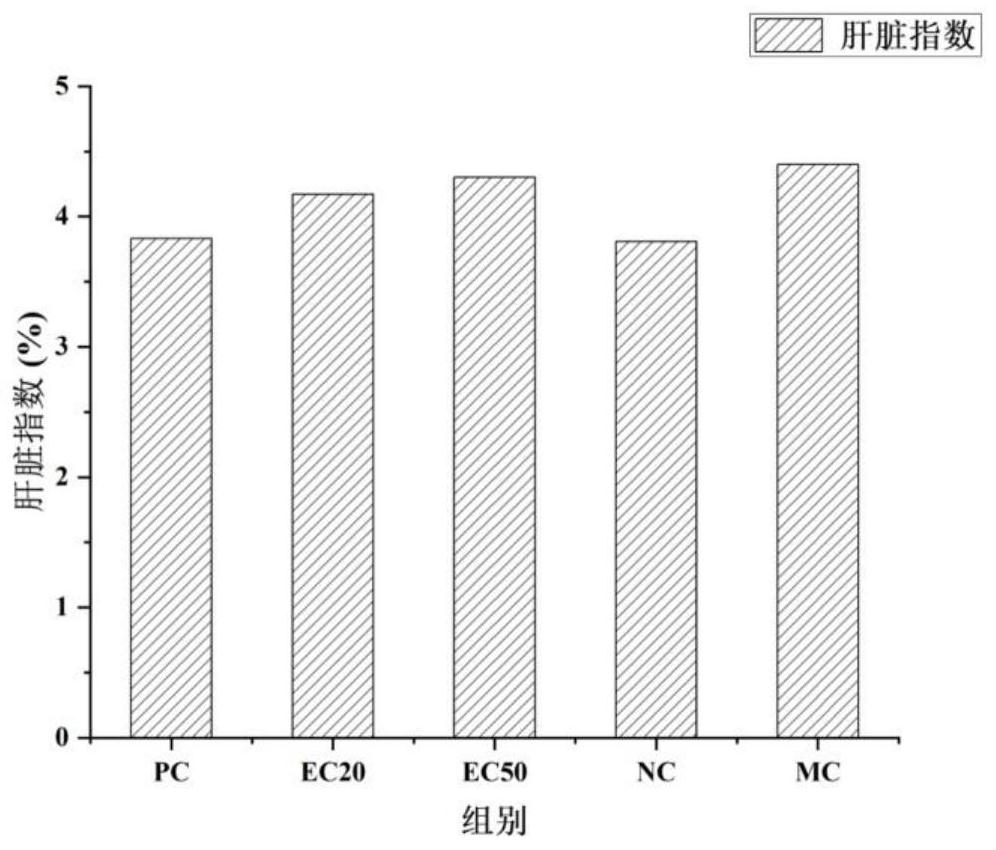
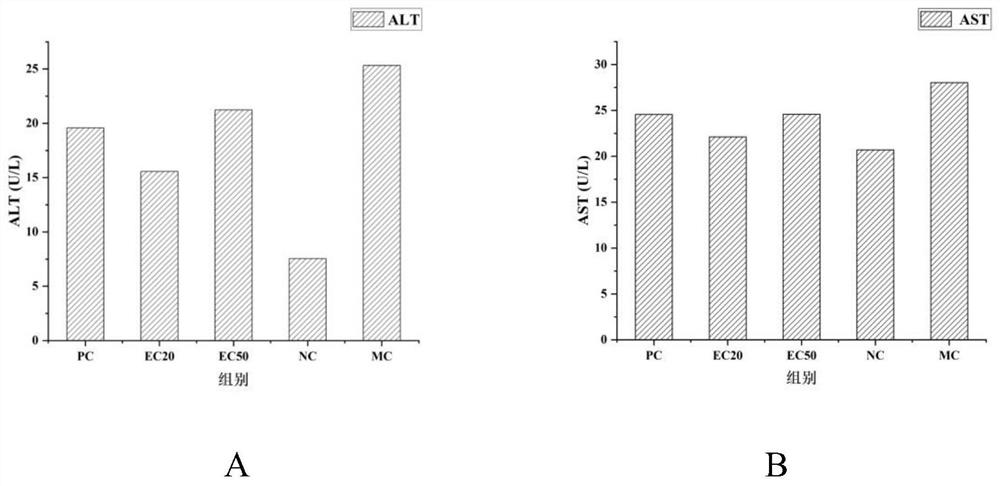
ActiveCN111840551AAvoid takingGet rid of the bondagePowder deliveryMaterial nanotechnologyFluorescenceGlycan metabolism
The invention relates to a non-invasive near-infrared light-controlled nano material for treating diabetes mellitus, and claims to protect the application of an up-conversion fluorescence nano material in preparation of a tool for treating diabetes mellitus. The up-conversion fluorescence nano material comprises a rare earth element doped inorganic nano material, a hepatocyte targeting molecule and a water-soluble polymer. The invention discloses a new application of the non-invasive up-conversion fluorescent nano material. An invasive optical fiber does not need to be implanted into an animalthrough an operation during diabetes treatment, near-infrared light with high tissue penetrability is used for exciting an up-conversion nano material in a living body, and light in the near-infraredband is converted into visible light through the up-conversion material so that photosensitive protein is activated, and glucose metabolism related signal pathways in cells are remotely regulated andcontrolled without relying on insulin under the condition of high time-space resolution, glycogen synthesis is promoted, glycogenesis is inhibited, and the blood glucose level is reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for quantitative determination of regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate
ActiveCN106092944AComparableStable and reliable share of glycolytic pathwayColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveQuantitative determination
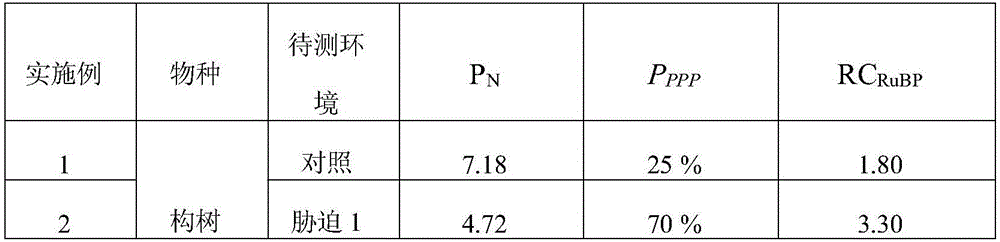
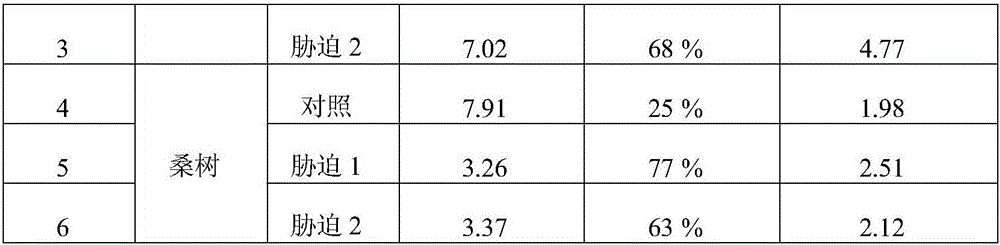
The invention discloses a method for quantitative determination of regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate. The method comprises the following steps: selecting the second, the third and the fourth completely spread leaves, performing non-destructive determination on apparent photosynthesis rate, taking a mean value of three leaves to represent the apparent photosynthesis rate PN of the plant; then taking the leave which has measured apparent photosynthesis rate, shearing the leave and fully mixing the leave, taking 0.1 g of the material for enzyme liquid extraction; respectively determining the phosphofructokinase vitality and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme vitality expressed by the change value at unit volume and unit time in the extracted enzyme liquid, calculating phosphopentose pathway proportion in the glycometabolism according to a formula, and then multiplying by the apparent photosynthesis rate of the plant leave to obtain the regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate. The method can realize rapid quantitative determination of the regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate, and has the advantages of less step, simple calculation, and comparability and reliability of the determination result.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Production method of glucosamine
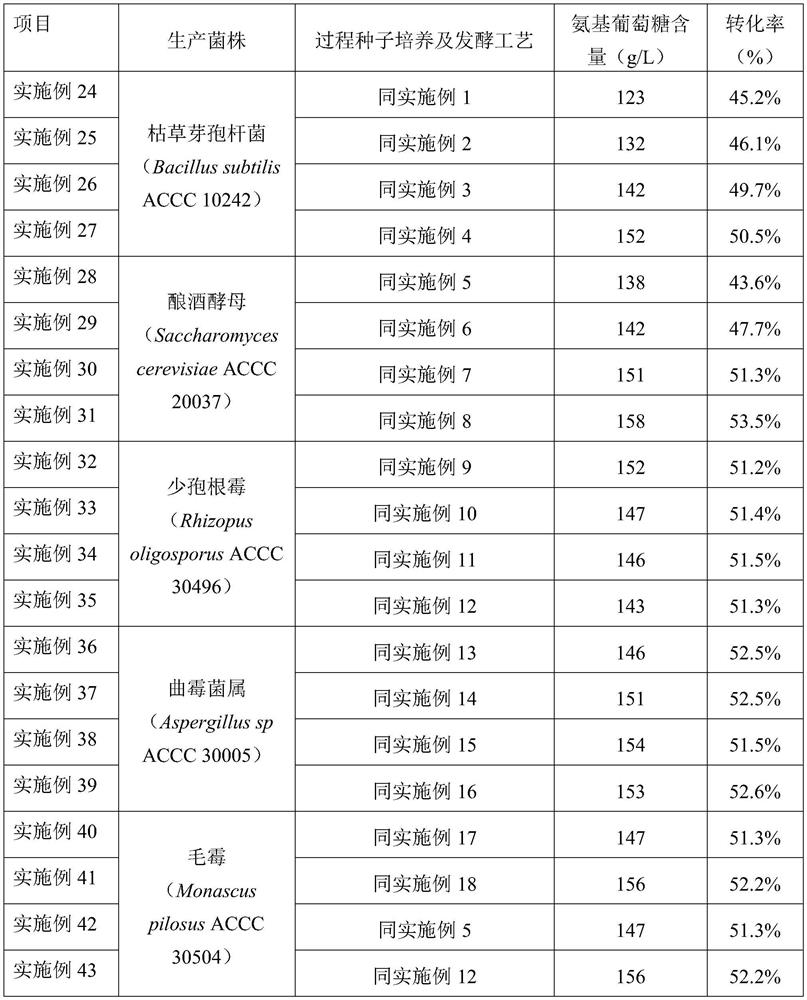
PendingCN112592944AMeet growth needsPromote metabolic synthesisFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyFermentation broth
The invention belongs to the field of glucosamine production, and relates to a production method of glucosamine. The production method comprises the steps of: in the glucosamine fermentation process,monitoring at least one of an oxygen consumption rate, an oxidation-reduction potential, acetic acid concentration and a specific carbon dioxide release rate in fermentation liquor on line, and controlling the numerical value within a specific range by stages. According to the method provided by the invention, at least one of the oxygen consumption rate, the oxidation-reduction potential, the acetic acid concentration and the specific carbon dioxide release rate in the fermentation liquor is monitored and controlled on line to feed back process parameters of the regulation and control process,so that the thallus growth requirement can be met, glucosamine metabolic synthesis is effectively promoted, and the conversion rate is increased; and the content and conversion rate of the glucosamine in the obtained fermentation product are both high.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA KINGDOMWAY PHARMA LTD +1
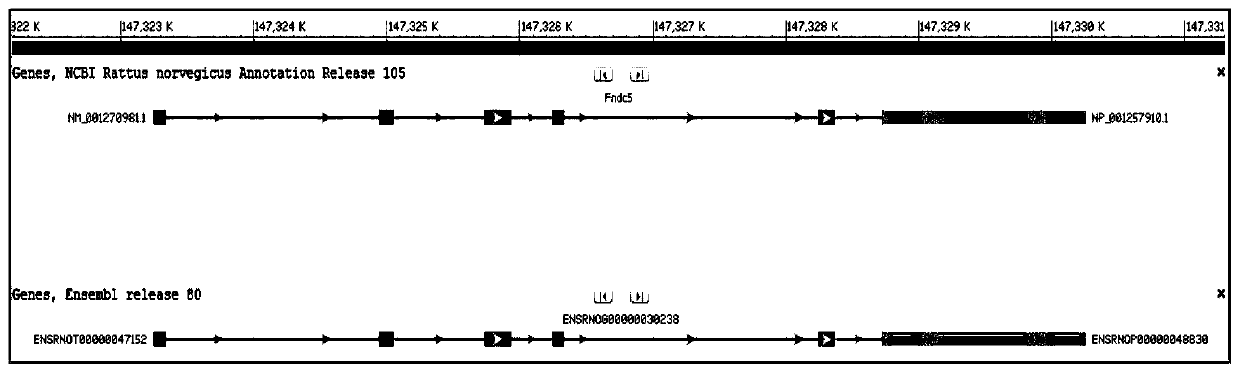
Construction method of FNDC5 gene knock-out rat model, and application
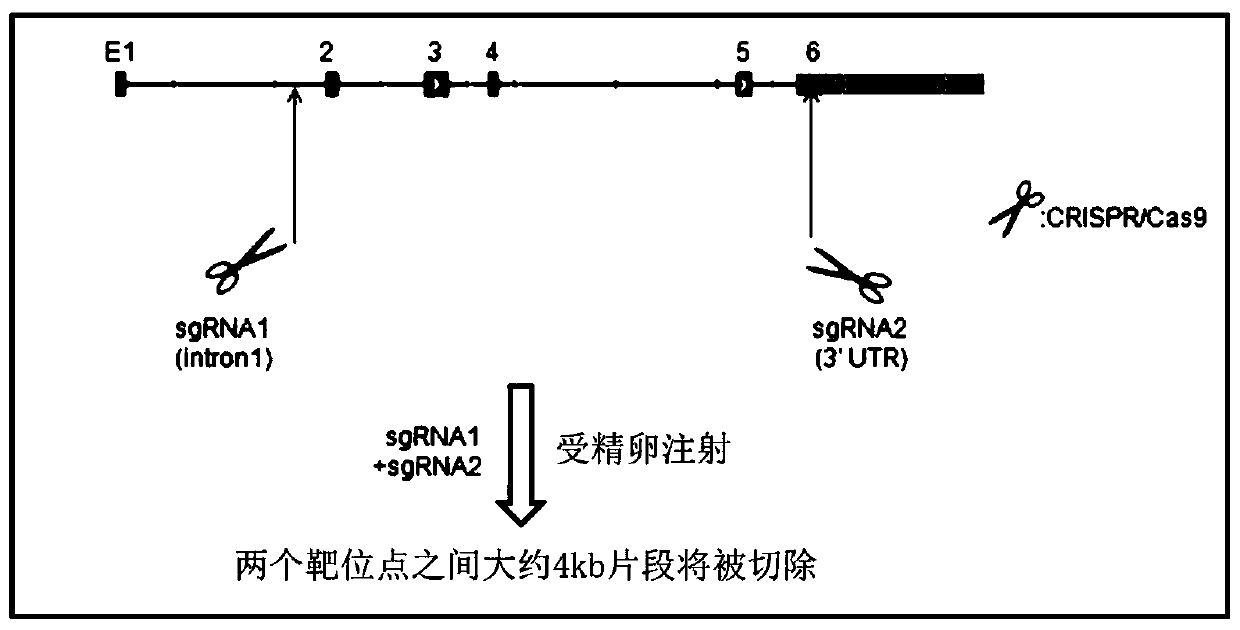
InactiveCN111394353AEasy to prepareReliable production methodConnective tissue peptidesStable introduction of DNAPhysiologyPancreatic hormone
The invention discloses a construction method of an FNDC5 gene knock-out rat model, and an application. The invention discloses two sgRNAs in accordance with a FNDC5 gene of a rat, and a correspondingtarget gene sequence, and the two sgRNAs are respectively designed on FNDC5 genes Intron1 and 3'UTR. The sgRNAs can be applied to construction of a rat animal model having insulin resistance and glycometabolism disorders. The invention provides a simple reliable economic animal model making method having insulin resistance and glycometabolism disorders.
Owner:CHINA INST OF SPORT SCI
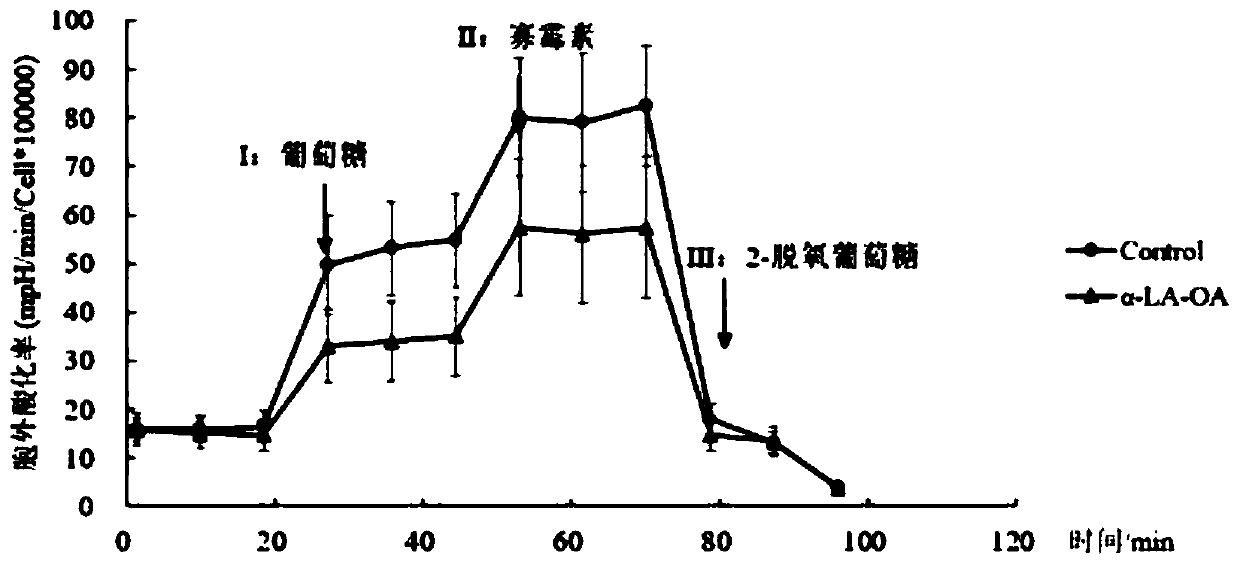
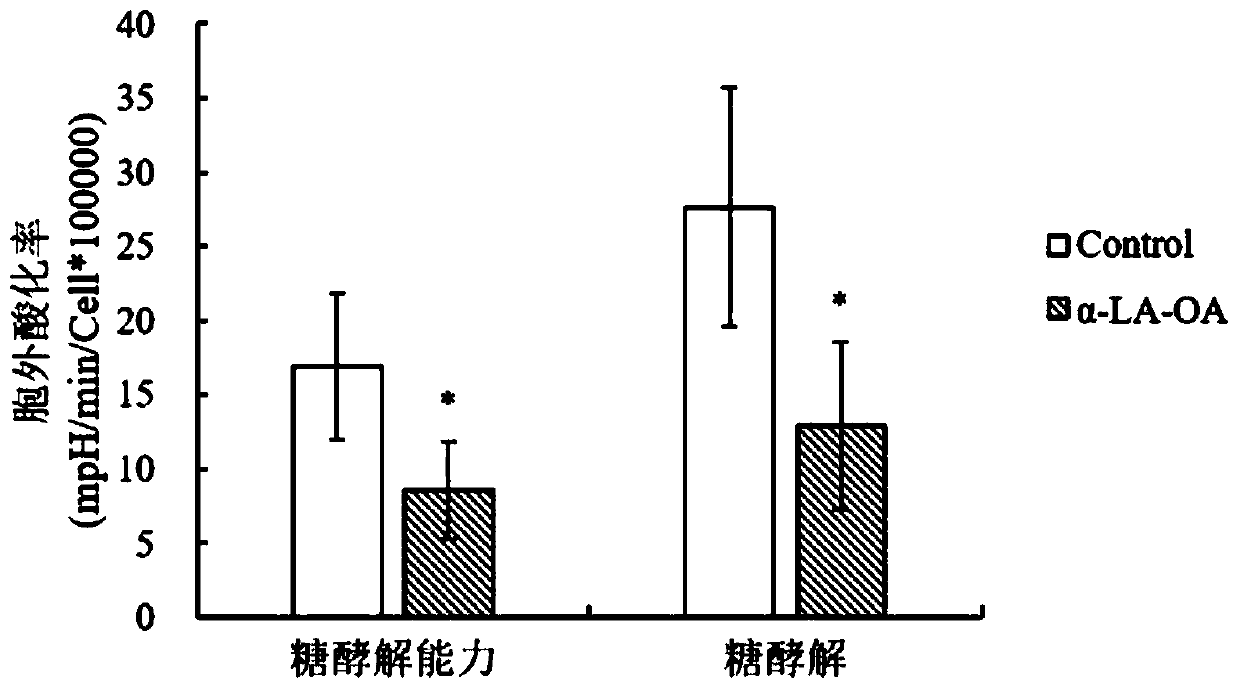
Application of lactalbumin-oleic acid composite to preparation of medicines for restraining energy metabolism of tumor cells
InactiveCN110478475AInhibition of energy metabolismReduce productionPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGlycolytic ProcessProtein target
The invention discloses an application of a lactalbumin-oleic acid composite to preparation of medicines for restraining energy metabolism of tumor cells, and finds that alpha-LA-OA can resist the glycolysis process of tumor cells and reduce the consumption of oxygen by an aerobic respiration process of a mitochondrion and the generation amount of ATP. In addition, the invention further finds thatthe alpha-LA-OA can reduce generation of ATP in an HepG2 cell glucose metabolism way, so that the effect of restraining energy metabolism of tumor cells can be achieved; an HepG2 tumor cell model isused for confirming that the alpha-LA-OA can notably promote expression of mTORC2 target protein Rictor, mSin1 and Ser473-Akt, and the expression amount of various enzymes in the glycolysis way can benotably reduced. The alpha-LA-OA can activate an mTORC2 signal route, and can restrain activity of key enzymes in the glucose metabolism way, so as to reduce the energy metabolism for restraining tumor cells, by ATP.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Composition, glucose metabolism-improving agent, and method for improving glucose metabolism
InactiveUS20140050805A1Excellent glucose metabolism-improving effectImprove securityBiocideMetabolism disorderPANAX NOTOGINSENG ROOTPerylene derivatives
A composition, including: (A) Panax notoginseng; and at least one of (B) a Piper longum extract and (C) vitamin B1, a salt thereof or a derivative thereof.
Owner:LION CORP
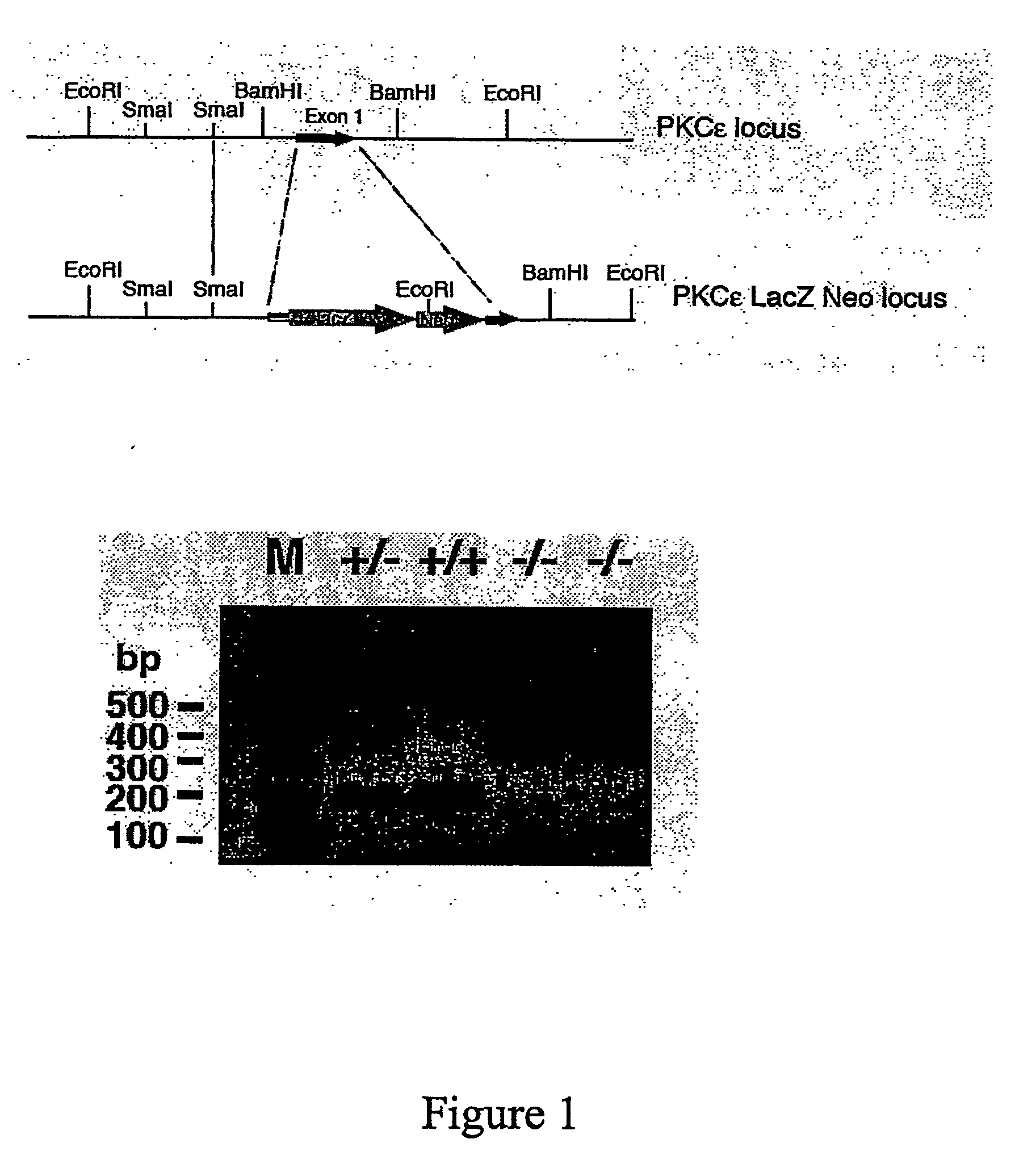
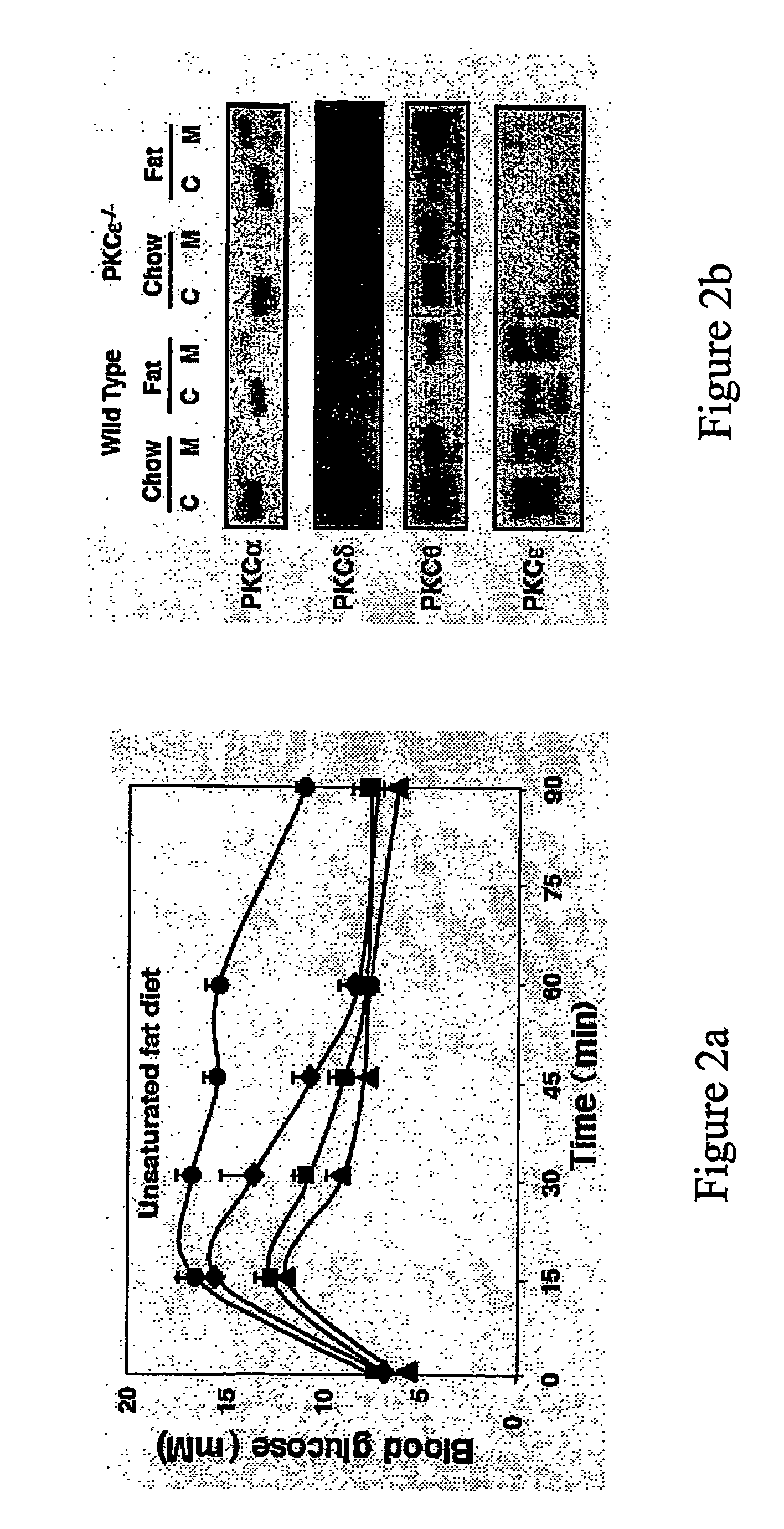
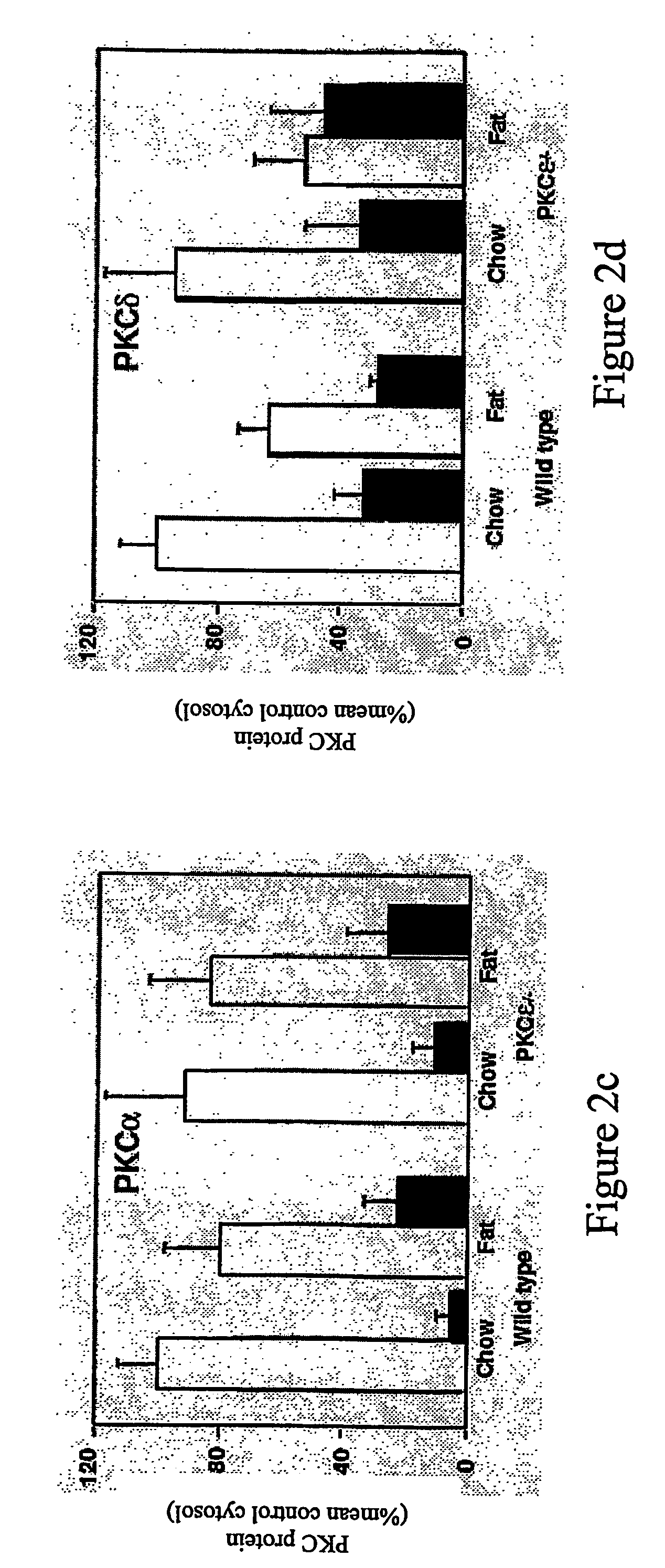
Methods for Identifying Modulators of Protein Kinase C-Epsilon (Pkce) and Method of Treatment of Aberrant Glucose Metabolism Associated Therewith
ActiveUS20080263689A1Preventing compensation of lipid-induced glucose intoleranceReduced liver-mediated clearanceBiocideOrganic active ingredientsAssayProtein Kinase C-epsilon
The present invention provides novel cell-based and animal-based assays for determining antagonists of PKCε and uses of the isolated antagonist compounds for modulating insulin clearance and secretion. The invention also provides novel animals and cells such as animals and cells suitable for use in the assays.
Owner:GARVAN INST OF MEDICAL RES
Construction method for producing succinic acid Escherichia coli gene engineering bacteria by means of xylose-metabolism
InactiveCN102618477AIncrease biomassTo achieve the purpose of isolating bacteriaBacteriaOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Use of glucose deficient Streptococcus thermophiles strains in a process for producing fermented milk products
ActiveUS11160288B2Promote growthImprove the level ofMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention relates to the use of a Streptococcus thermophilus strain with a deficiency in glucose metabolism for improving growth of a Lactobacillus strain in a process for producing a fermented milk product.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Enzyme composition for sugar metabolic regulation
InactiveUS20210177026A1Regulate the absorption of glucoseOxidoreductasesGlycosyltransferasesAmylaseSucrose
Disclosed is an enzyme composition for regulating sugar metabolism which can regulate the absorption of glucose into the body by converting the carbohydrates in food to a form of sugar that is not absorbed in the stomach and the like before being decomposed in the small intestine into glucose by the activity of various enzymes such as maltase, sucrase, or lactase and the like and absorbed, wherein the enzyme composition includes: one or more enzymes selected from the group consisting of glucoamylase, sucrase and lactase; glucose oxidase; and transglucosidase.
Owner:HWANG JI HWAN +1
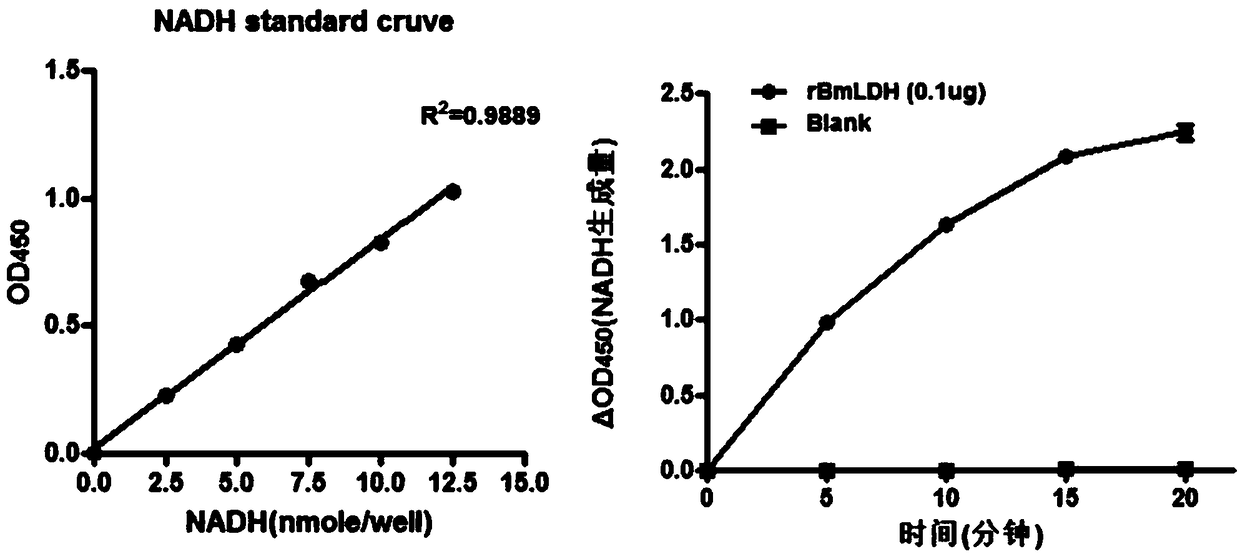
Monoclonal antibody resistant to vole babesia and application thereof
ActiveCN108314735AImmunogenicBiological material analysisTissue cultureImmunofluorescenceWestern blot
The invention discloses a monoclonal antibody resistant to vole babesia. The monoclonal antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain HA5-E4 having a collection number of CCTCC NO: 201835. Aiming atlactic dehydrogenase LDH in a glucide metabolic pathway of the vole babesia, the protein has immunogenicity, and a monoclonal antibody aiming at rBmLDH is prepared; Western blot detection proves thatthe monoclonal antibody is capable of specifically recognizing the vole babesia but cannot recognize the LDH of the host. Therefore, the monoclonal antibody can be applied to detection of vole babesia in infection cells through an immumofluorescence method.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Nucleic acid construct for gene therapy of glycometabolism-related diseases
The invention relates to the technical field of gene therapy or biological medicine, in particular to a nucleic acid construct for gene therapy of glycometabolism-related diseases; the nucleic acid construct comprises polynucleotide for coding GLP-1 or an analogue thereof; the total number of the GLP-1 or the analogue thereof is more than two; the GLP-1 and the GLP-1 are connected through polynucleotide for coding a connecting peptide; the GLP-1 and the analogue thereof are connected through the polynucleotide for coding the connecting peptide; or the analogue of the GLP-1, the GLP-1 and the analogue are connected through the polynucleotide for coding the connecting peptide. The nucleic acid construct disclosed by the invention can be used for efficiently expressing the GLP-1 with the activity and the analogue thereof in vivo and in vitro, so that a technical route is provided for developing medicines for treating glycometabolism-related diseases such as type 2 diabetes, body metabolic disorder, diabetes-related complications and obesity which have great potential.
Owner:KANGLIN BIOTECHNOLOGY (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Sugar control composition containing quinoa and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112826014APrevent diseaseImprove metabolic disordersFood ingredient functionsInsulin responseReceptor
The invention discloses a sugar control composition containing quinoa and preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: respectively weighing the following components in percentage by mass: 25-40% of quinoa, 10-20% of purple rice, 10-20% of white kidney beans, 10-20% of oats and 10-20% of walnuts, the sum of the mass percentages of the components being 100%; in the formula, vitamin B1 in the quinoa and coarse cereals in the formula can maintain normal glycometabolism and nerve conduction functions of diabetic patients, and can help diabetic patients to maintain capillary health and avoid microangiopathy; so that the composition is capable of improving the kidney cell metabolism disorder caused by hypertension, wherein magnesium can better help the blood sugar of the diabetic patient to be converted into energy, and meanwhile insulin response is improved. In addition, the n-3 series of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the walnuts can help and enhance cell activity, then increase insulin receptors, make insulin very sensitive, increase blood sugar consumption and convert blood sugar into glycogen.
Owner:XIAN MEDICAL UNIV
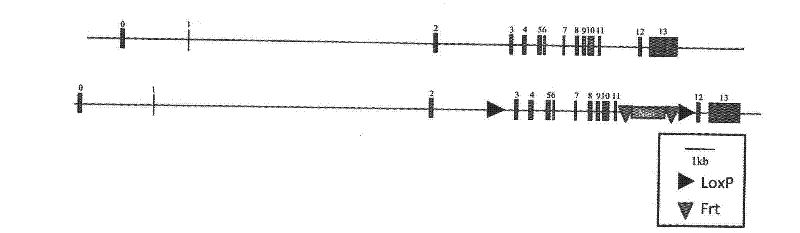
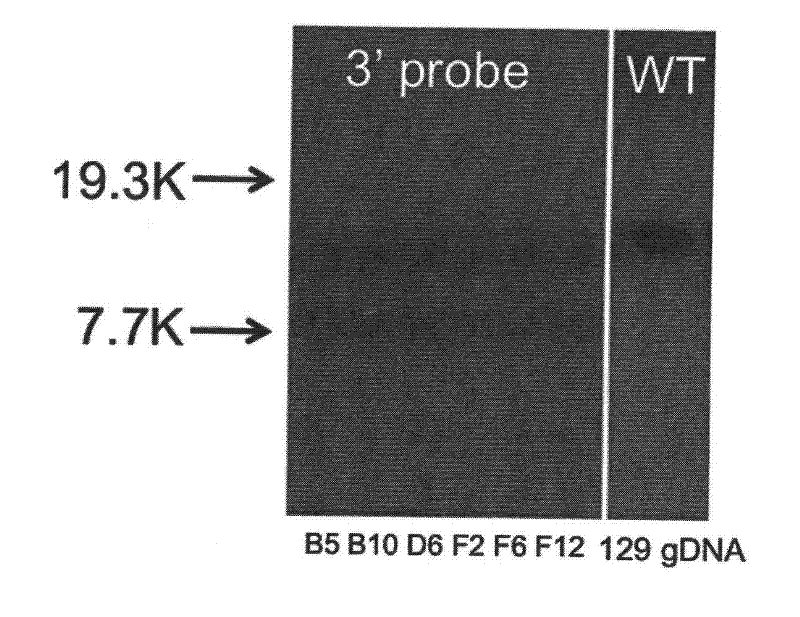
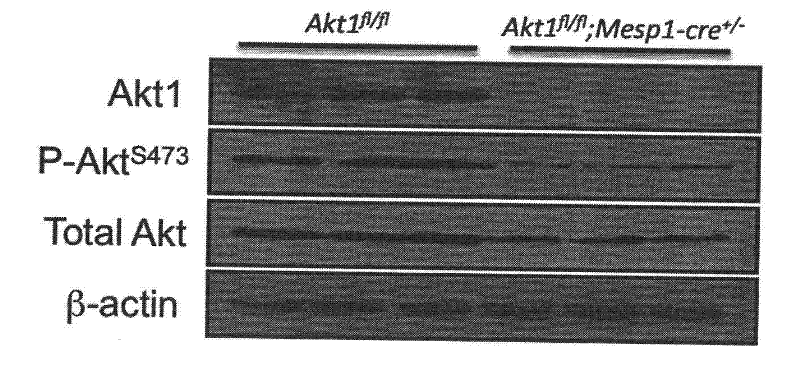
Establishment of Kinase protein Akt1 conditional gene knockout mice model and application
InactiveCN102477421AReveal biological functionPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical drugEnzyme protein
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Kinase protein Akt1 conditional gene knockout non-human mammal model and application of the method. The invention further discloses a method for screening compounds for preventing or treating cardiomegaly and glucose metabolic disorders by the Kinase protein Akt1 conditional gene knockout non-human mammal model, and application of the model that Akt1 and upstream and downstream biological signal transduction pathways of the Akt1 serve as medicine intervention targets to treat cardiomegaly and glucose metabolic disorders.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Application of epimedin C in prevention and treatment of acute alcoholism
ActiveCN113456660AGood control effectRelief of clinical manifestationsOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryNervous systemTG - Triglyceride
The invention discloses an application of epimedin C in prevention and treatment of acute alcoholism, and belongs to the technical field of biological medicine. The invention discloses that the epimedin C can shorten the sobering time and sleepiness time of an acute alcoholism model animal, prolong the drunkenness latency period, reduce the levels of total bilirubin, total cholesterol and triglyceride in serum, reduce the activity levels of glutamic-pyruvic transaminase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase in serum, increase the content of reduced glutathione, reduce the content of malondialdehyde, can maintain normal forms and structures of liver tissues and cells, regulate proteome expression of acute alcoholism animals, repair damage of nervous systems, improve oxidative stress states of organisms and improve glycometabolism and lipid metabolism, so that the epimedin C can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and treating acute alcoholism. The epimedin C is used for preparing a medicine for preventing and treating acute alcoholism in the form of a medicinal preparation such as aerosol and the like. The invention is helpful for promoting the research and development process of acute alcoholism prevention and treatment medicines, and also provides a thought for development and utilization of epimedium resources.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV +1
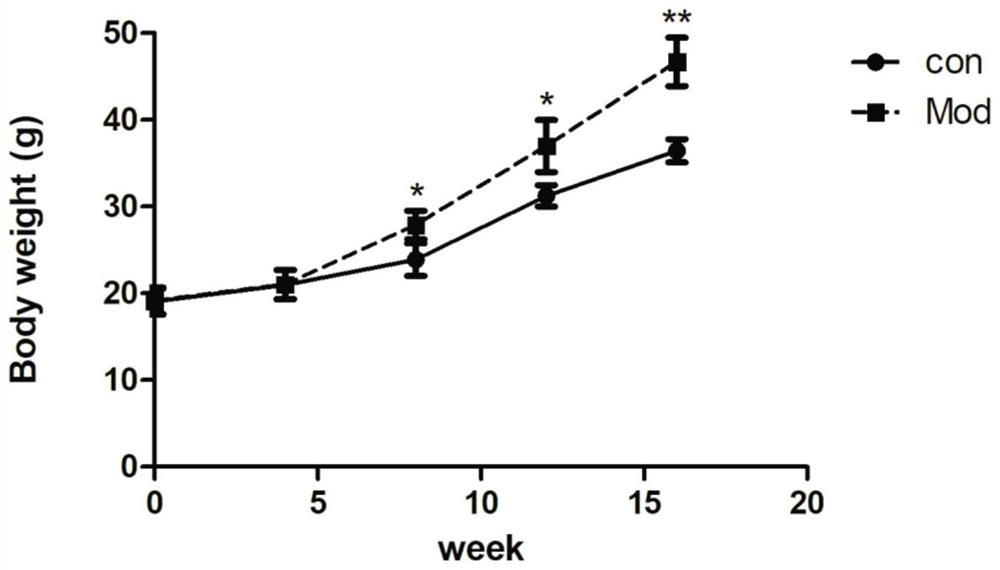
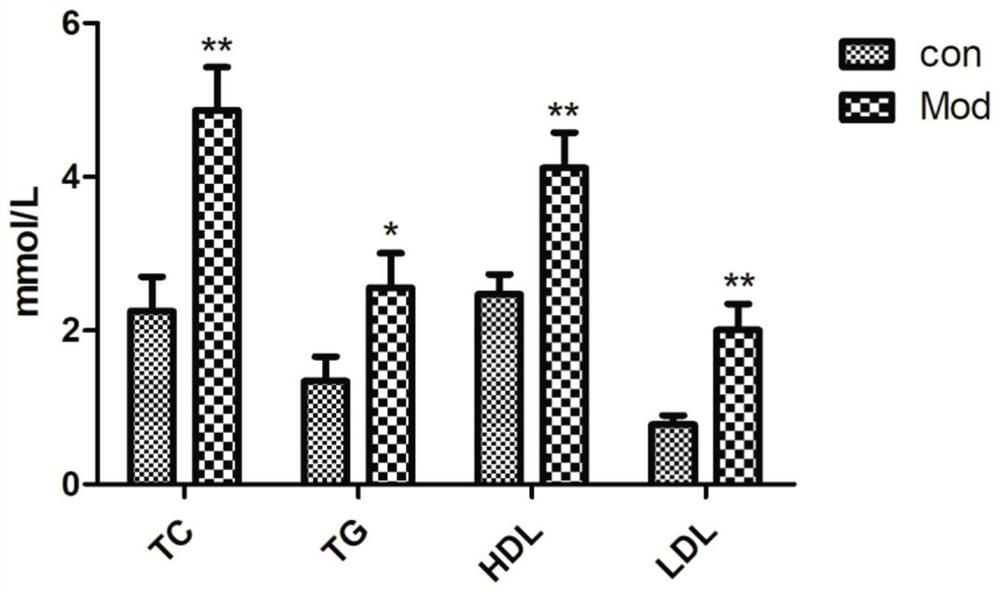
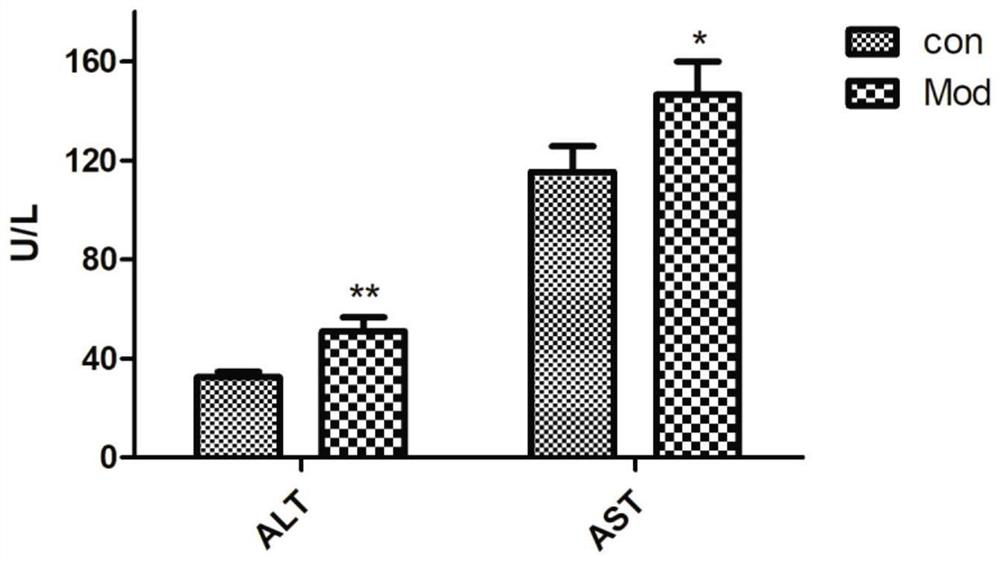
Non-alcoholic fatty liver animal model and establishment method
The invention relates to the technical field of animal model establishment, in particular to a non-alcoholic fatty liver animal model and an establishment method. The animal model is established by adopting an NR4A1- / -gene knockout mouse. The NR4A1- / -gene knockout mouse is adopted to establish the non-alcoholic fatty liver animal model, the relationship between the NR4A1- / -gene and glycometabolism and fat metabolism of the liver is fully utilized, the glycolipid metabolism of the NR4A1- / -gene knockout mouse is disturbed, and fat can be deposited on the liver after high-fat feeding, so that the non-alcoholic fatty liver is formed; the method is simple to operate and obvious in effect. The animal model has the characteristics of obesity, dyslipidemia and the like, and has high similarity with NAFLD clinical pathology.
Owner:北京基谱生物科技有限公司
Genetic engineering bacterium for producing succinic acid, and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN102864116BEasy to buildThe fermentation method is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliButanedioic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium strain for producing succinic acid. The genetic engineering bacterium strain is named as Escherichia coli BA016, the preserving number registration number CCTCC NO is M 2012350. The invention further provides a construction method of the strain and a method for producing succinic acid by fermentation, recombinant escherichia coli can grow by glucose metabolism through joint excessive expression of exogenous pyruvic carboxylase and nicotinic acid ribose phosphate transferase, generation of by-product pyruvic acid is reduced, and accordingly the yield and production intensity of succinic acid are greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com