Monoclonal antibody resistant to vole babesia and application thereof
A technology of Babesia vole and monoclonal antibody is applied in the field of blood protozoa control of parasitic diseases, which can solve the problems of low detection rate, high technical and experimental skills requirements of testing personnel, and difficulty in batch testing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Preparation of Babesia microti rBmLDH monoclonal antibody
[0023] 1.1 Cloning and expression of Babesia microti LDH gene
[0024] Use PCR primers to clone the corresponding gene, use Babesia microti PRA-99 strain DNA as a template, use cloning primers (BmLDH-F1 / BmLDH-R1), after sequencing and identifying the correct sequence, use expression primers containing restriction sites (BmLDH-F2 / BmLDH-R2) was amplified, and the amplified fragment was double digested and inserted into the expression vector pET-28a for prokaryotic expression.
[0025] The specific primer sequences are as follows (the primers are synthesized by Shanghai Sangong Biotechnology Co., Ltd.):
[0026] BmLDH-F1 / BmLDH-R1
[0027] Upstream primer (or forward primer, the same below): BmLDH-F1: ATGCATTCGTTAAAAGAAGAATTTCTG
[0028] Downstream primer (or reverse primer, the same below): BmLDH-R1: TTATAGTTGGATATCTTTCTGTGTGTTC
[0029] BmLDH-F2 / BmLDH-R2
[0030] Upstream primer: BmLDH-F2: ATGCA...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Embodiment 2: Enzyme activity detection of recombinant rBmLDH protein
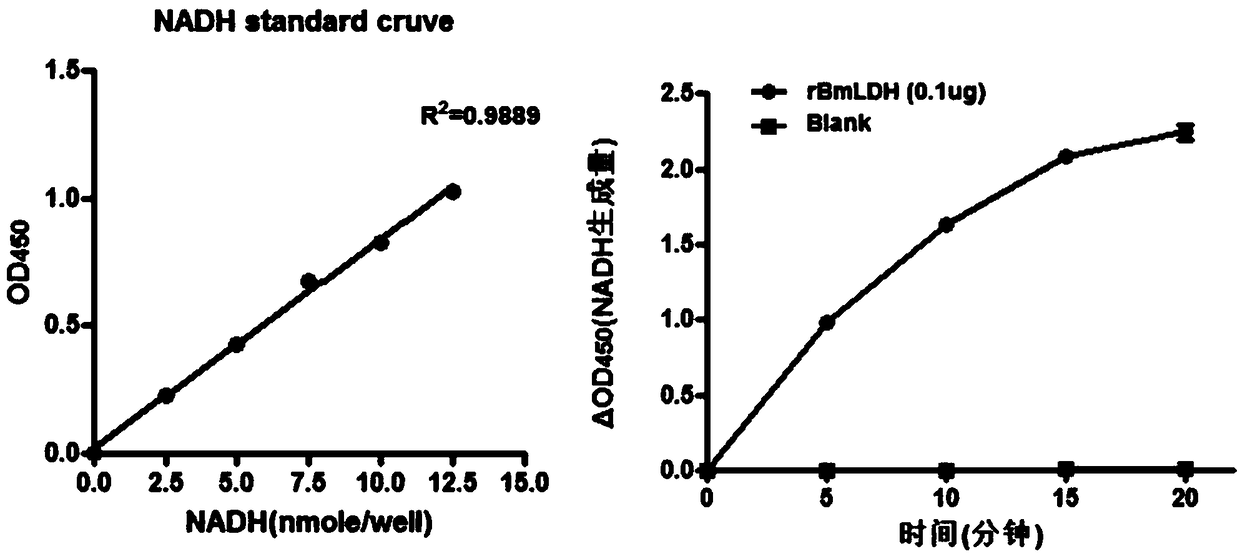
[0049] (1) Sample preparation: The rBmLDH protein concentration was determined by the BCA method and the protein concentration was adjusted to 1 mg / mL, and the recombinant protease activity was measured using a protein concentration of 0.1 μg.
[0050] (2) Preparation of LDH standard curve: add 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10uL of 1.25mM NADH standard (in duplicate) into 96-well plate to generate 0 (blank), 2.5, 5, 7.5, 10 and 12.5 nmole / well standard. Add LDH assay buffer to a final volume of 50 µL.
[0051] (3) Experimental procedure for enzyme activity determination: take 48 μL of assay buffer and 2 μL of substrate mixture, and mix well.
[0052] (4) Add 50 μL of enzyme activity reaction mixture to each well, and use horizontal vibration or a pipette to mix well. Avoid light during the experiment.
[0053] (5) After 2-3 minutes, take the initial measurement. Absorbance at 450 nm was initially measured ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: Identification of reactogenicity of recombinant protein rBmLDH
[0056] The purified recombinant protein rBmLDH was first subjected to SDS-PAGE electrophoresis, and then transferred to the NC membrane at a voltage of 50V. After 3h, the NC membrane was blocked with TBST-5% skimmed milk powder for 1h, and washed 3 times with TBST, 5min each time; Put the NC membrane into 1:100 dilution of Babesia microti positive serum and negative serum, incubate at room temperature for 1 hour, wash 3 times with TBST, each time for 5 minutes; add secondary antibody (1:5000 dilution of rabbit anti-mouse IgG), room temperature Incubate for 1 hour, wash 3 times with TBST, and add BCL to develop color after 5 minutes each time. The results of Western blot showed that the purified rBmLDH had a specific reaction at 30kDa with positive sera, but had no reaction with negative sera (see figure 2 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com