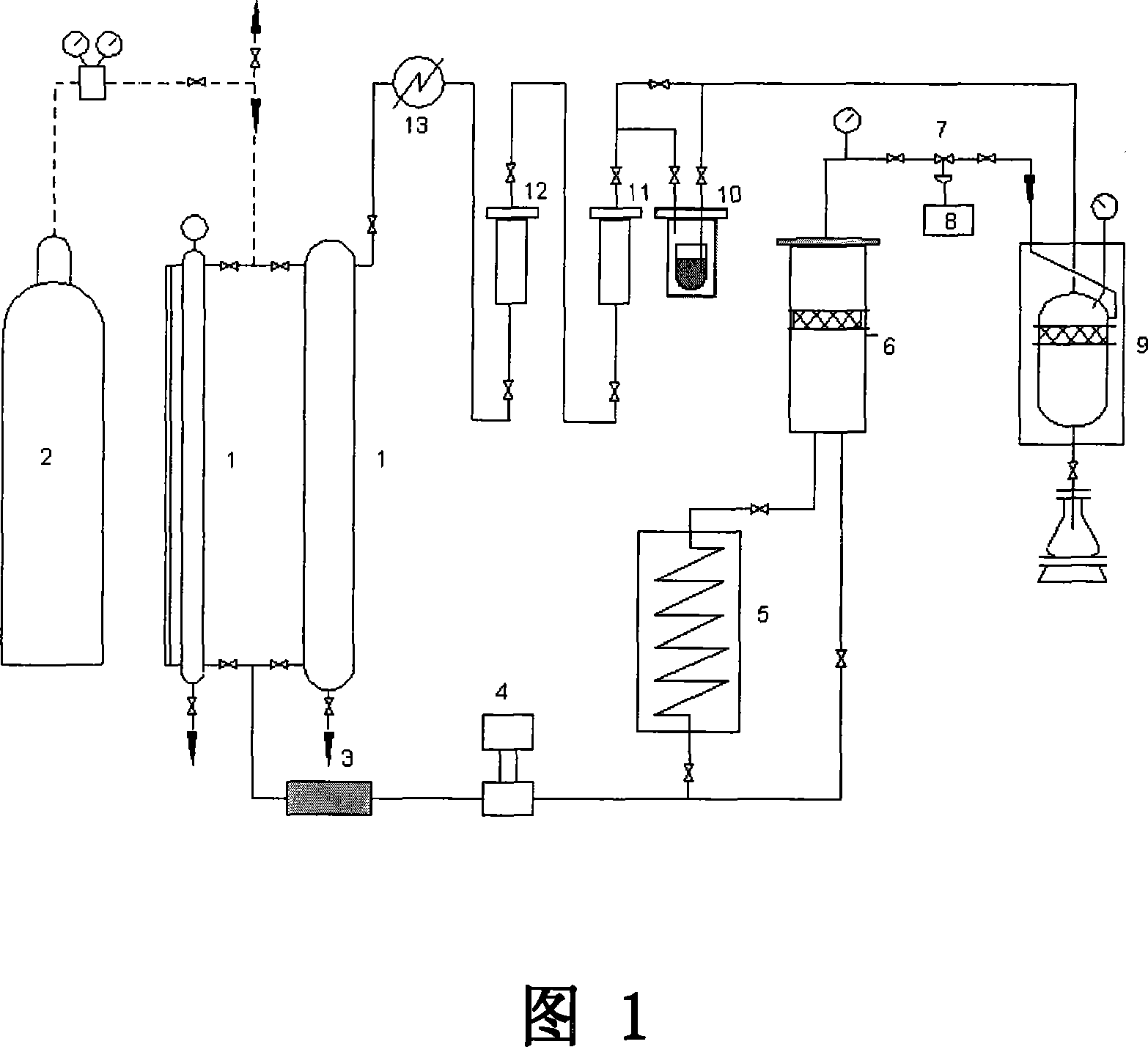
A method for removing residue pesticides from Panax
A technology for residual pesticides and ginseng, which is applied in the field of removal of residual pesticides in ginseng, can solve problems such as difficulty in ensuring no loss of ginsenosides, large solvent flow, and high equipment requirements, and achieves a long history of medicinal use, strong solubility, and easy operation The effect of a wide range of conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Using 300g American ginseng extract as raw material, using propane as solvent, extracting at 65°C and 8.0MPa, the mass mixing ratio of solvent and raw material is 5:1, and the separator temperature is about 75°C. Residual and ginsenoside, the results are shown in Table 1.
[0038] Table 1
[0039] Pesticide name
[0040] It can be seen from Table 1 that the removal rate of γ-BHC and Op-DDT is 100%, and the removal rate of tetrachloronitrobenzene is 61.8%.
[0041] Table 2
[0042] Ginsenoside Rb1 content%
[0043] 3.00
[0044] The loss of ginsenoside Rb1 after extraction was 3.0%, as shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Take American ginseng extract as raw material, use propane as solvent, extract at 80°C, 8.0MPa, extraction time is 120min, the mass mixing ratio of solvent and raw material is 4:1, separator temperature is 65°C, extraction time is 60min, and the extraction is measured. Pesticide residues and saponins in ginseng before and after pesticide residues, the results are shown in Table 3.
[0047] table 3
[0048] Pesticide name
[0049] It can be seen from Table 3 that the removal rate of DDE is 54.7%, the removal rate of pp-DDT is 63.7%, and the removal rate of hexachlorobenzene is 46.3%.
[0050] Table 4
[0051] Ginsenoside Re content%
[0052] As shown in Table 4, the loss of ginsenoside Re was 6.5% after extraction.
Embodiment 3
[0054] American ginseng powder is used as raw material, propane is used as solvent, extraction is carried out at 50°C and 4.5MPa, the mass mixing ratio of solvent and raw material is 1:1, the temperature of separator is about 75°C, and the extraction time is 60min. The results of residues and saponins are shown in Table 5.
[0055] table 5
[0056] Pesticide name
[0057] As can be seen from Table 5, the DDD removal rate is 59.4%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com