Method for microbe fuel battery and power generation by using straw stalk
A fuel cell and microorganism technology, applied in biochemical fuel cells and other directions, can solve the problems of non-direct utilization of straw solids and ineffective utilization of crop straws, and achieve the effects of alleviating the energy crisis, saving energy consumption and saving costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
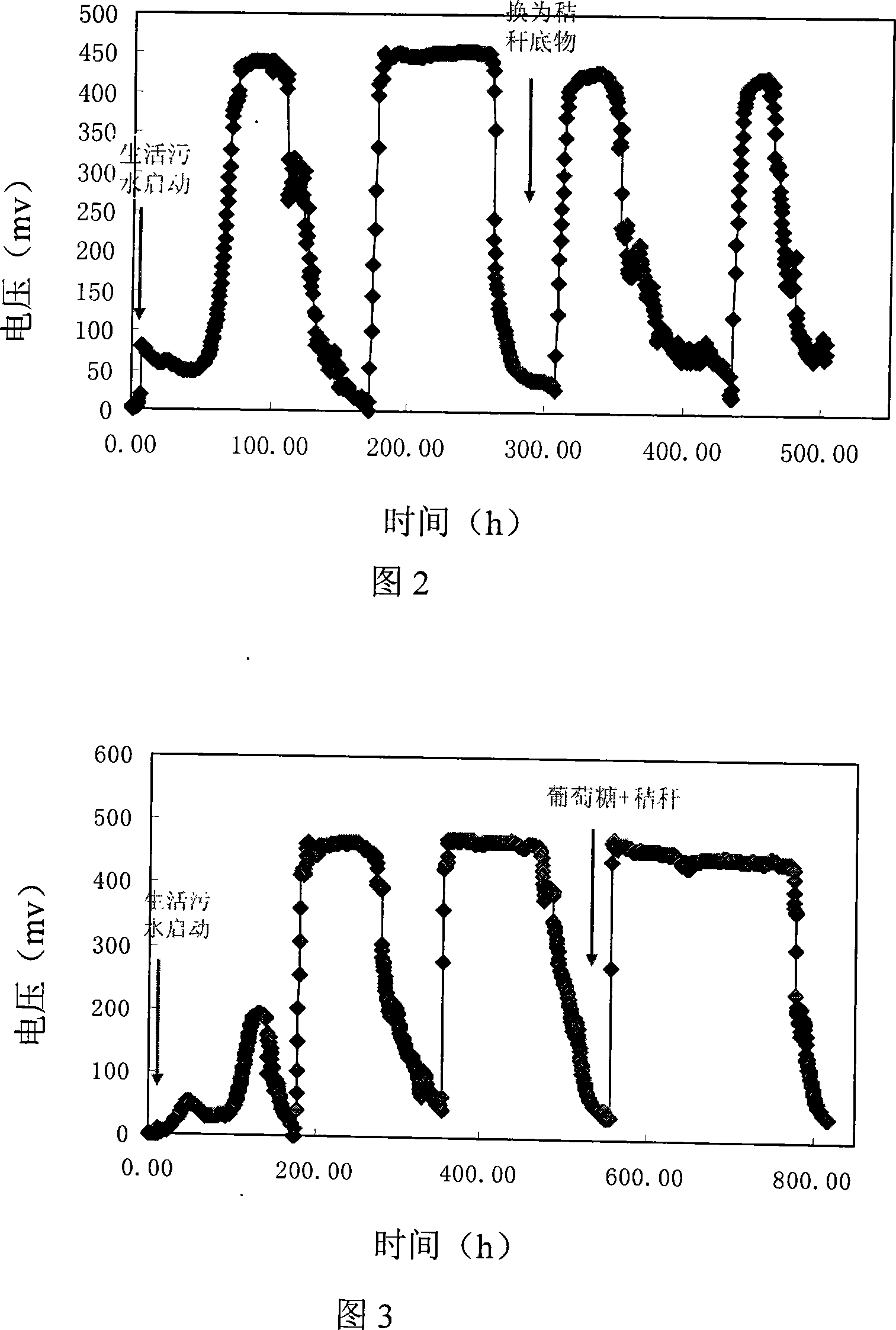
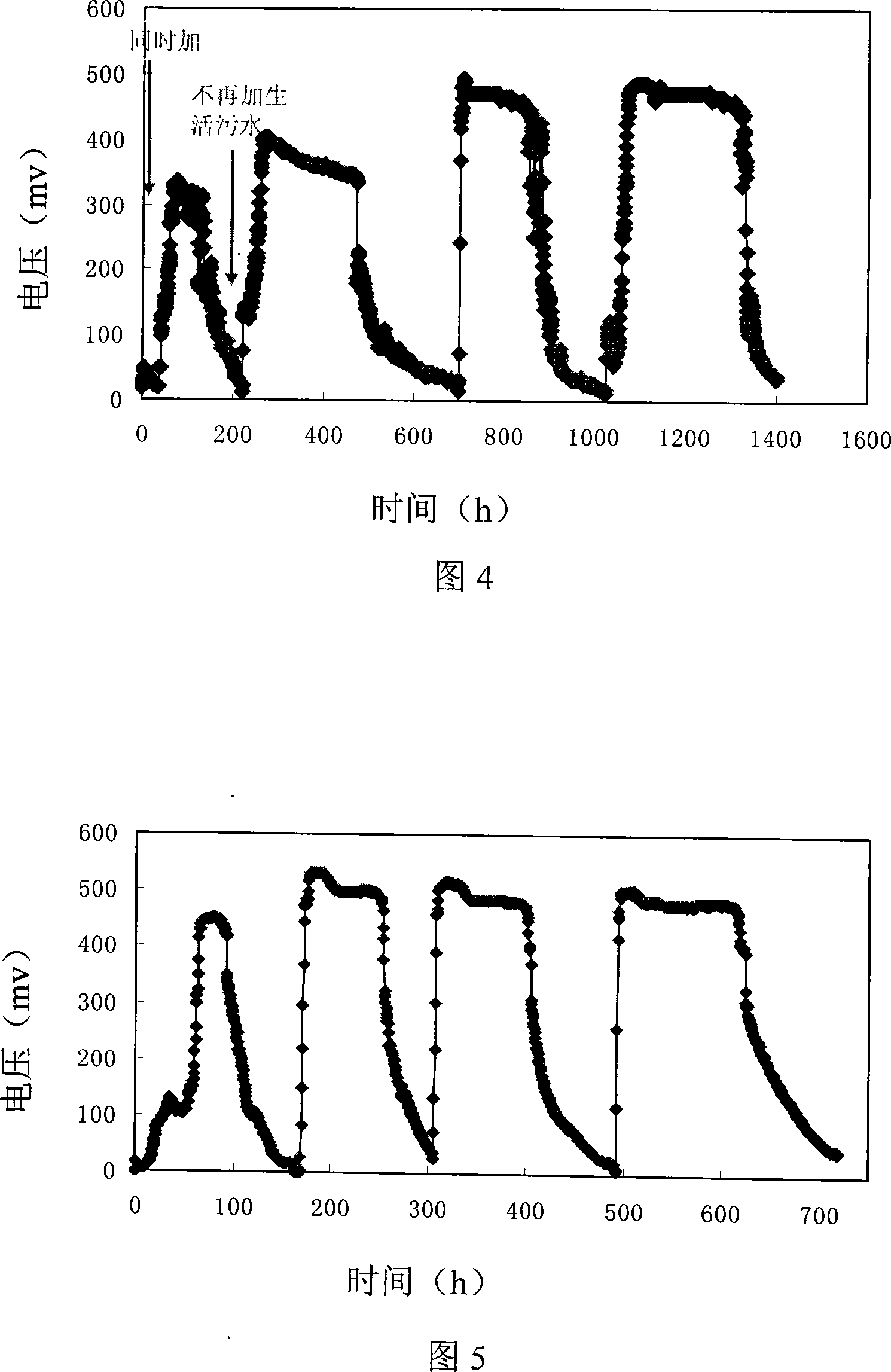
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
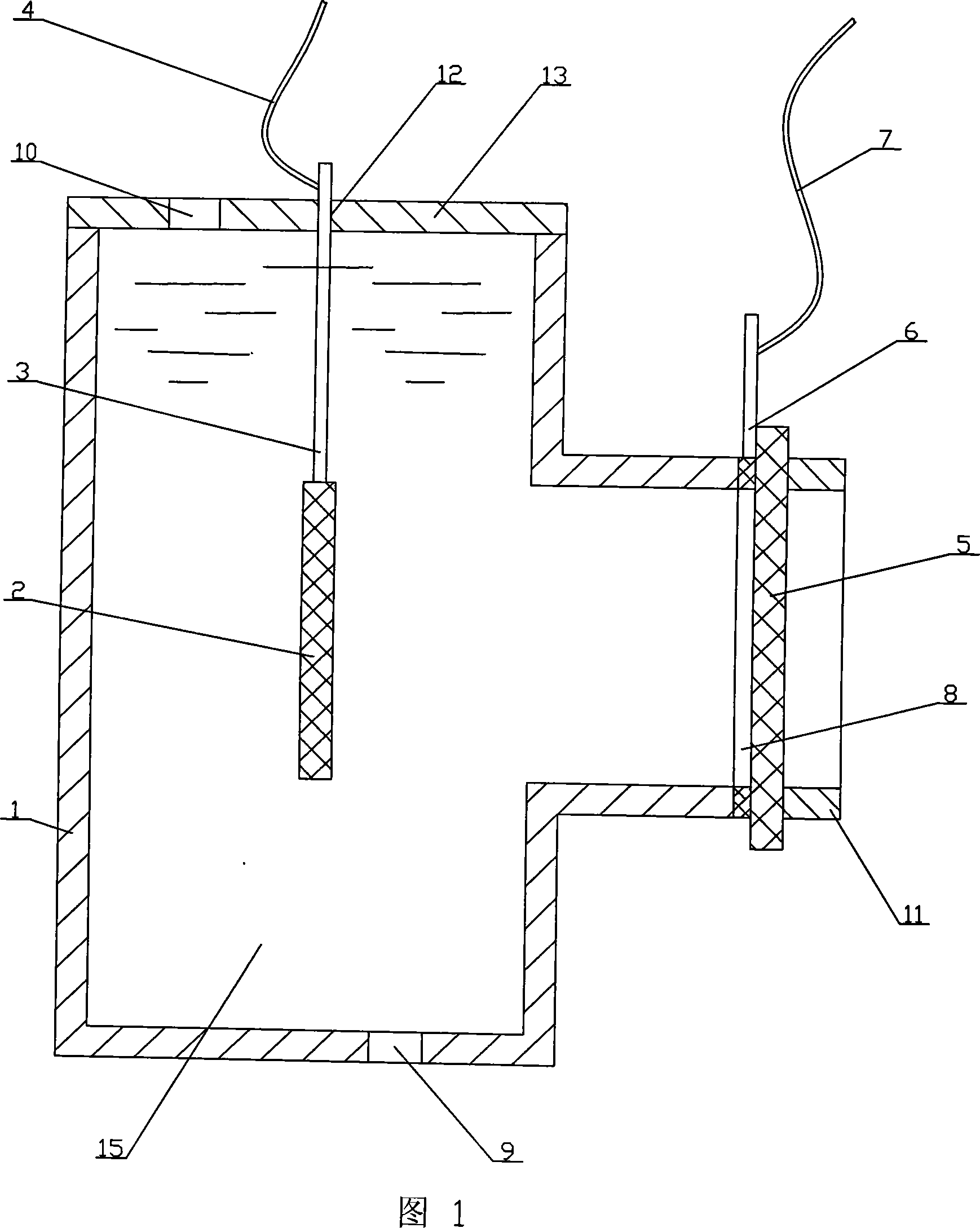
[0011] Specific embodiment one: (referring to Fig. 1) the microbial fuel cell of the present embodiment is made up of container 1, catalytic anode 2, titanium wire 3, anode wire 4, air cathode 5, titanium sheet 6, cathode wire 7, washer 8, cathode The cover 11 and the sealing cover 13 are composed; the section shape of the container 1 is a sideways "convex" shape, the small end of the container 1 is open, and the large end is closed; the top of the large end of the container 1 is closed with a sealing cover 13, and the sealing cover 13 is provided with an inlet The feed opening 10 and the small hole 12, the upper part of the titanium wire 3 is fixedly connected with the small hole 12, the lower end of the titanium wire 3 is fixedly connected with the upper end of the catalytic anode 2, the bottom of the large end of the container 1 is provided with a discharge port 9, and the open end of the container 1 Gasket 8, air cathode 5 and cathode cover 11 are arranged in sequence and t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0013] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the catalytic anode 2 is made of any one of carbon paper, carbon cloth, carbon fiber, carbon nanotube, glassy carbon, graphite felt, particle graphite, nickel foam and stainless steel plate made. Other structures and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0014] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the air cathode 5 is made of any one of carbon paper, carbon cloth, and graphite; and the air cathode 5 is loaded with 0.10-0.35 mg / cm 2 Pt catalyst. Other structures and connections are the same as in the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com