Coding and decoding method for determined nucleic acid sequence
A nucleic acid sequence and coding method technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of large number of samples and low sample throughput, and achieves simple method, simplified operation process, and wide application. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
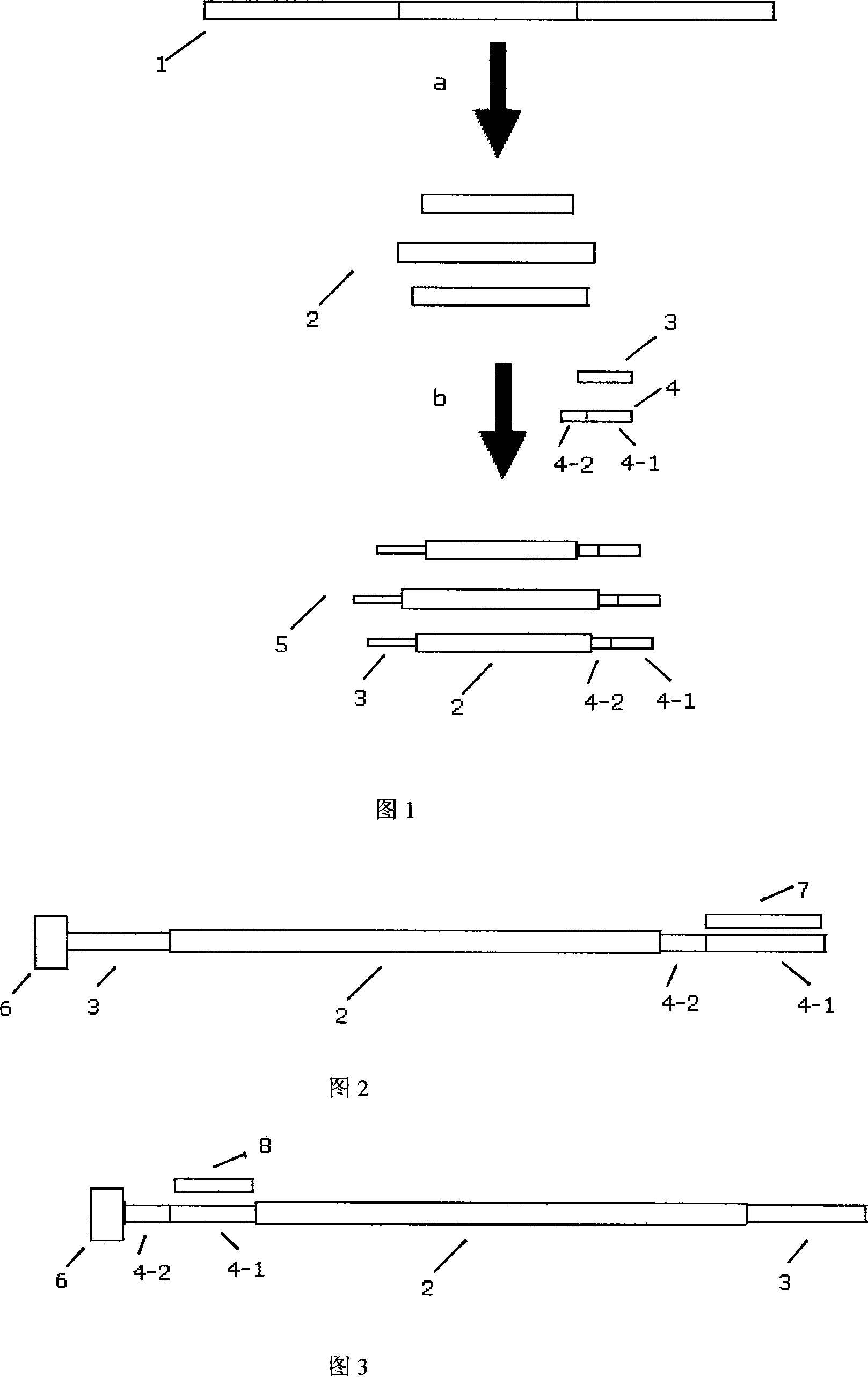
[0026] Example 1: High-throughput analysis of DNA sequences encoding different samples.
[0027] Cut different sample DNA sequences with enzymes (or sonicate) into fragments with a size of 50-100 bases, and connect these fragmented nucleic acid sequences with a pair of linkers under the action of ligase (one of which is a universal linker) One sub-oligonucleotide sequence is completely complementary to the sequence of the amplification primer, and the other is a unique known sequence code corresponding to different samples and a fragment of the same oligonucleotide sequence as the sequencing primer.
[0028] The fragmented nucleic acid sequence connected by these tethers and the complementary sequence of the fixed linker are transferred to microbeads for emulsion parallel PCR reaction to amplify the fragmented whole human genome. These microbeads are immobilized on the plate substrate, and sequencing templates of DNA sequences of different samples are obtained by enzyme digest...
example 2
[0030] Example 2: Expression analysis of mRNA sequences encoding different sources.
[0031] Step 1: Extract cellular mRNA from various sources, and use magnetic beads to immobilize 30 T nucleotide chains to purify mRNA by hybridizing mRNA.
[0032] Step 2: respectively reverse transcribe into cDNA, and use RNaseH, DNA polymerase, etc. to synthesize the second strand.
[0033] Step 3: Digest the above double-stranded nucleic acid sequence with an endonuclease (Sau 3AI) that recognizes four bases, and wash the magnetic beads with a buffer.
[0034] Step 4: under the action of ligase, add the above-mentioned digested double-stranded nucleic acid sequence to the linker primer 3 (the primer has a recognition site of endonuclease Acu I).
[0035] Step 5: Digest the product of step 4 with Acu I. A cDNA library of adapter primer 3 followed by 16 unknown sequences to be tested was obtained.
[0036] Step 6: The product of step 5 is connected with a linker primer 4 to complete the e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com