Process for preparing n-propanol by hydrogenation of propionaldehyde with cu-zn catalyst
A production process and a technology for n-propanol, applied in the chemical industry, can solve the problems of easy deactivation of cobalt-based catalysts, side reactions of reduction into hydrocarbons, high price, etc., and achieve the effects of low cost, few side reactions, and low price.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
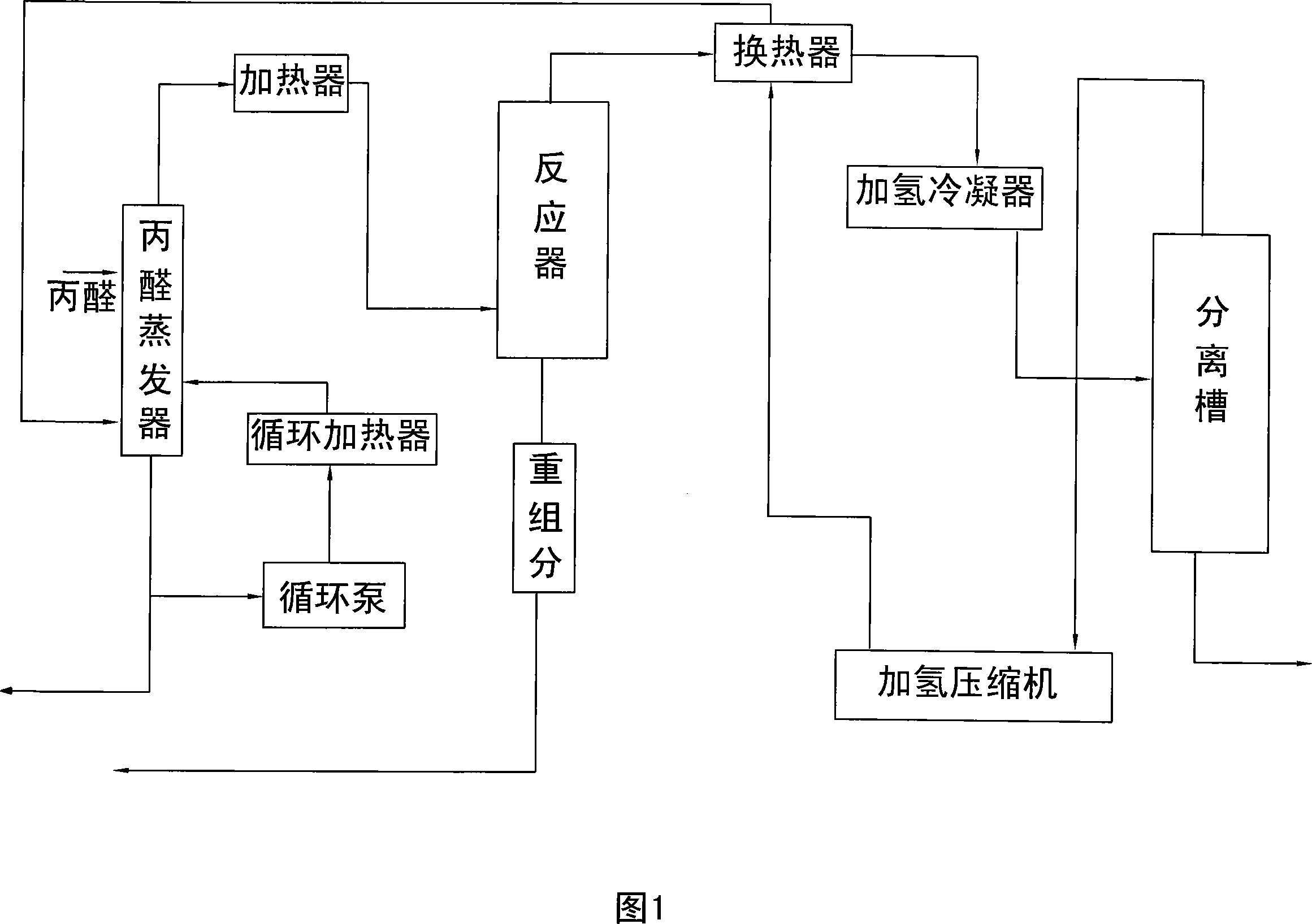
[0020] The molar ratio of propionaldehyde to hydrogen is 1:1, and the composition of the copper-zinc catalyst is: 29.66% of copper oxide, 70% of zinc oxide, 0.07% of aluminum oxide, 0.07% of ferric oxide, and 0.2% of sodium oxide. %.
[0021] Propionaldehyde gas phase hydrogenation reaction temperature is 160°C, reaction space velocity is 0.4h -1 , the hydrogen oil ratio is 3500.
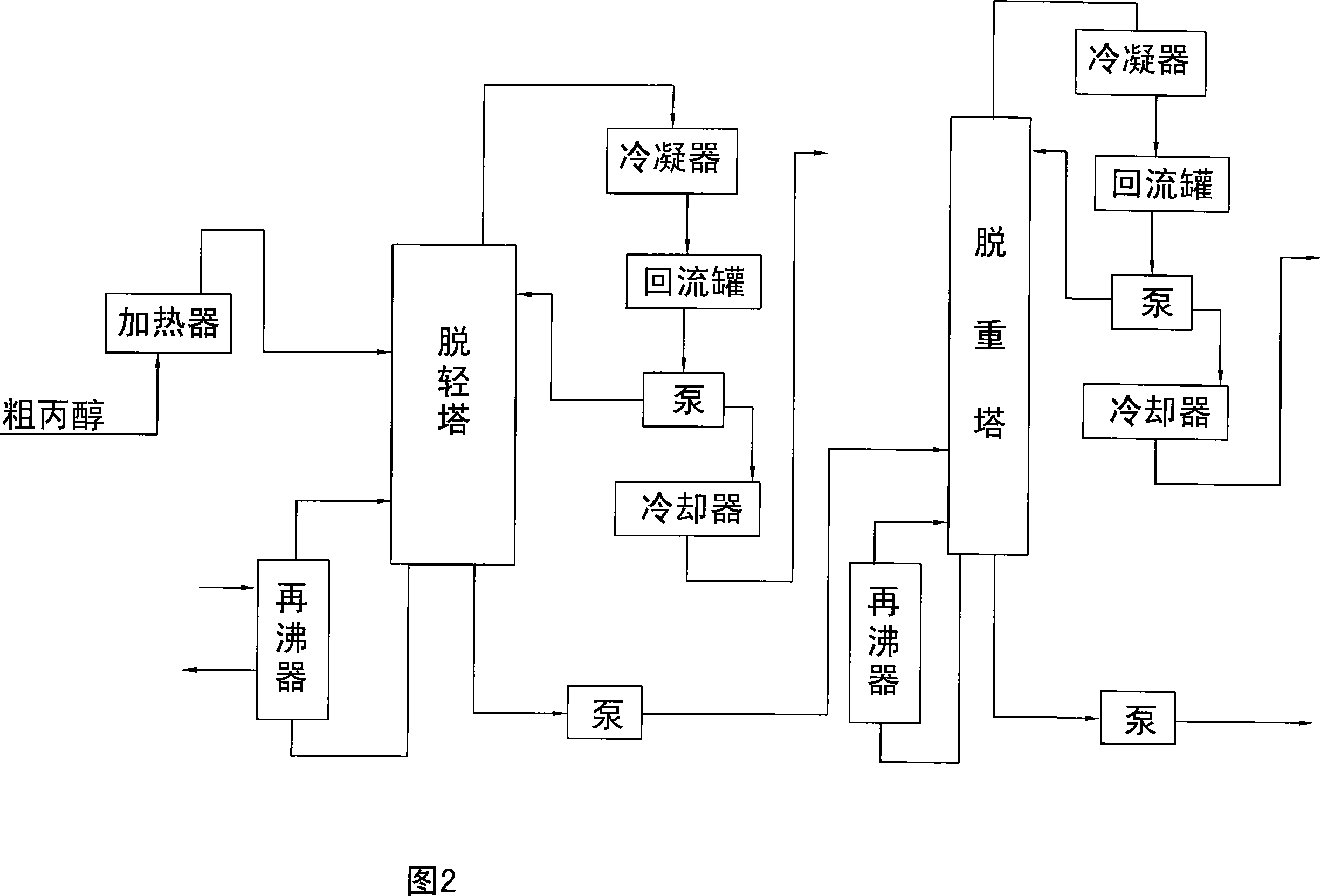
[0022] Crude propanol enters the delightening tower to remove light components, the temperature at the bottom of the delightening tower is 90°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 76°C. The heavy components are removed in the weight-removing tower, the temperature at the bottom of the weight-removing tower is 92°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 94°C.
[0023] The purity of the product n-propanol is 99.76%.
Embodiment 2
[0025] The molar ratio of propionaldehyde to hydrogen is 1:2, and the composition of the copper-zinc catalyst is: 31.3% copper oxide, 68.3% zinc oxide, 0.11% aluminum oxide, 0.09% iron sesquioxide, and 0.2% sodium oxide. %.
[0026] Propionaldehyde gas phase hydrogenation reaction temperature is 170°C, reaction space velocity is 0.5h -1 , the hydrogen oil ratio is 4500.
[0027] Crude propanol enters the delightening tower to remove light components, the temperature at the bottom of the delightening tower is 92°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 80°C. The heavy components are removed in the weight-removing tower, the temperature at the bottom of the weight-removing tower is 98°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 96°C.
[0028] The purity of the product n-propanol is 99.85%.
Embodiment 3
[0030] The molar ratio of propionaldehyde to hydrogen is 1:3, and the composition of the copper-zinc catalyst is: 45% copper oxide, 54.5% zinc oxide, 0.06% aluminum oxide, 0.14% iron oxide, and 0.3% sodium oxide. %.
[0031] Propionaldehyde gas phase hydrogenation reaction temperature is 180°C, reaction space velocity is 0.55h -1 , the hydrogen oil ratio is 4800.
[0032] Crude propanol enters the delightening tower to remove light components, the temperature at the bottom of the delightening tower is 98°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 90°C. The heavy components are removed in the weight-removing tower, the temperature at the bottom of the weight-removing tower is 100°C, and the temperature at the top of the tower is 105°C.
[0033] The purity of the product n-propanol is 99.88%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com