Use of apolipoprotein A-I in preparing medicaments for inhibiting G+ bacteria infection induced sepsis and tissue inflammation damnification
An apolipoprotein, sepsis technology, applied in antibacterial drugs, drug combinations, peptide/protein components, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to remove the toxicity of LTA
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0012] Embodiment 1 prepares ApoA-I
[0013] Separate and purify human plasma ApoA-I from human plasma precipitation IV (waste after extracting blood products from blood product enterprises), with a purity of 98% (patent application number 200610029114.4).
[0014] Plasma precipitation IV extracts and purifies ApoA-I through the following steps:
[0015] ①pH 7.365% ethanol-10mM NaHCO 3 liquid extraction;
[0016] ② pH 5.5 isoelectric point precipitation, and dissolved in pH 8.6 Tri-HCl-Urea solution;
[0017] ③Chloroform: ethanol (1:1) degreasing;
[0018] ④Equal volume of ethanol precipitation, take the supernatant;
[0019] ⑤ Concentration, pasteurization after dialysis, sterilization and filtration;
[0020] ⑥ Freeze drying.
Embodiment 2
[0022] ApoA-I inhibits LTA-induced acute lung injury (ALI), sepsis and systemic inflammatory response experiments
[0023] Eighteen BALB / C male mice were randomly divided into three groups:
[0024] (1) LTA group: mice were injected intravenously with LTA (20 mg / kg) to induce sepsis;
[0025] (2) ApoA-I treatment group: intravenous injection of ApoA-I (50 mg / kg) after LTA administration;
[0026] (3) Control group: the mice were injected with normal saline.
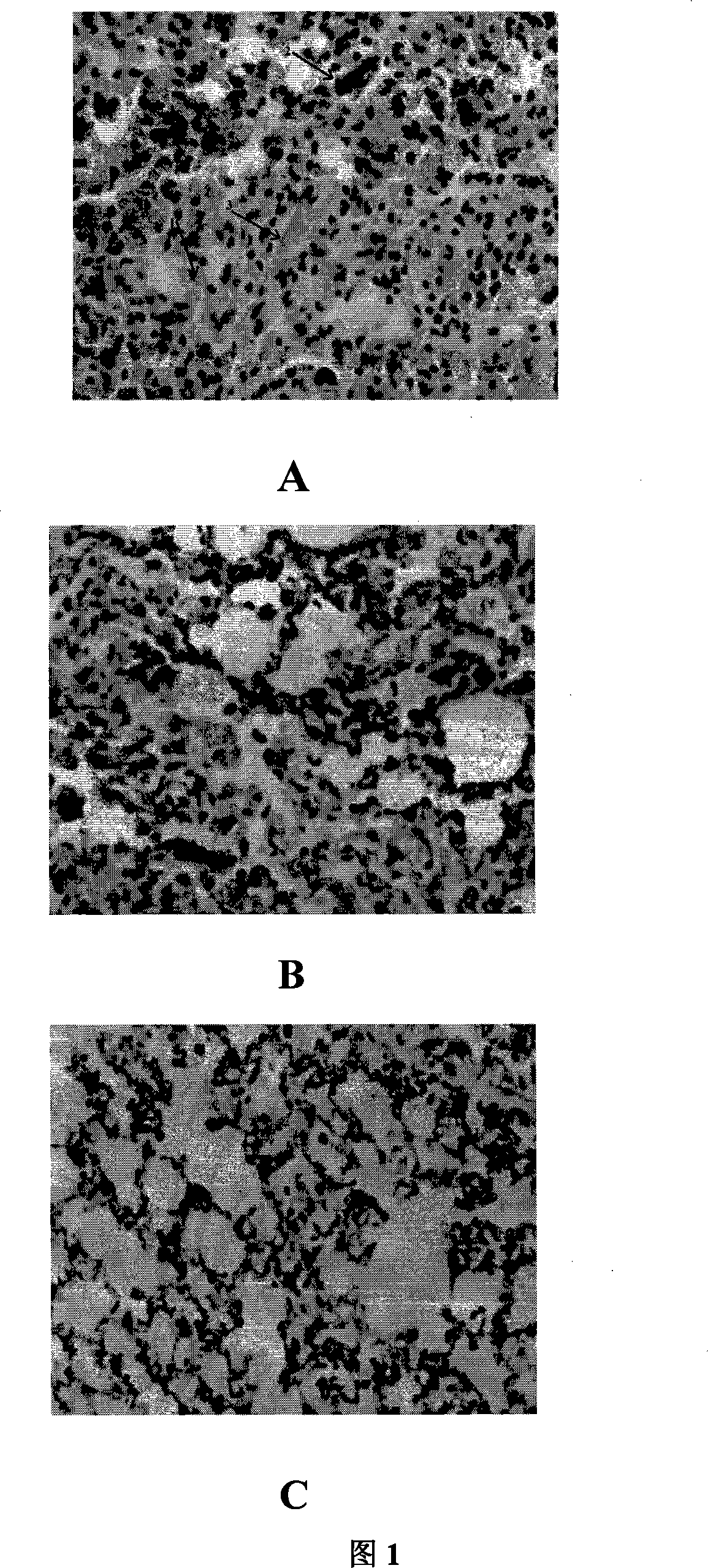
[0027] Blood samples were taken 24 hours after administration of ApoA-I to determine the concentrations of plasma IL-1β and TNF-α. The right lung was removed, and histological microscopic examination was performed after HE staining; the left lung was removed, and the concentrations of IL-1β and TNF-α in alveolar bronchial lavage fluid were determined. The results showed that: compared with the lung tissue morphology of the normal control group (Figure 1C), the lung tissue of the LTA group showed acute lung injury, show...
Embodiment 3
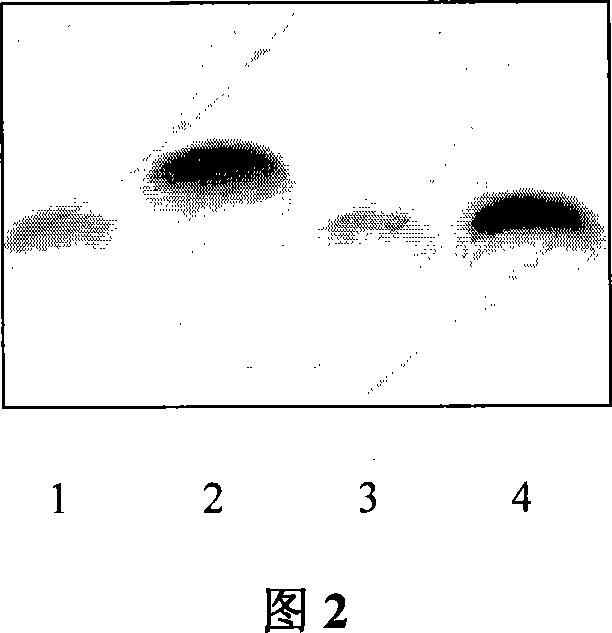
[0037] ApoA-I inhibits LTA to activate macrophages to release inflammatory factors to kill L-929 cells Experiments Isolate mouse peritoneal macrophages by conventional methods.
[0038] Divided into four groups: (1) LTA treatment group; (2) LTA+0.25μgApoA-I group; (3) LTA+12.5μgApoA-I group; (4) LTA+25μgApoA-I group. After co-cultivation in each group, macrophages were isolated, and then added to L-929 cells. After co-cultivation, the death rate of L-929 cells in each group was measured by MTT method.
[0039] The results showed that ApoA-I inhibited the release of inflammatory factors from macrophages activated by LTA, and presented a dose-effect curve.
[0040] Table 3 shows the killing effect of ApoA-I on L-929 cells by inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors from macrophages activated by LTA.
[0041] table 3
[0042] Group (n=4)
[0043] ** P<0.01, compared with group (1).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com