Liquid-applied sound dampening
A sound-absorbing, liquid-state technology that solves inefficiencies and high costs in the field of compositions for automotive applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1: Preparation of an aqueous dispersion of phosphorus-containing polymer particles
[0049] A monomer emulsion was prepared by mixing 576 g of deionized (DI) water, 21.1 g of dodecylbenzenesulfonate surfactant (23% by weight active), 38.6 g of ethoxylated monoalkylsulfosuccinic acid Ester surfactant (30% active by weight), 38.6g acrylic acid, 1255.3g butyl acrylate, 154.8g acrylonitrile, 425g styrene and 57.9g phosphoethyl methacrylate (50% active). At 87°C, add 664 g of deionized water, 12.6 g of dodecylbenzenesulfonate (23%), 1.44 g of sodium sulfate and 0.4 g of 4-hydroxy TEMPO (5% active), equipped with a stirrer and A 5-liter four-neck round bottom flask of the condenser was charged with 102.7 g of the monomer emulsion, followed by 5.9 g of sodium persulfate dissolved in 32.4 g of deionized water and washed into the flask with an additional 22.6 g of deionized water. After 10 minutes, the remaining monomer emulsion and a solution of 5.9 g sodium persulfate...
Embodiment 2A-B
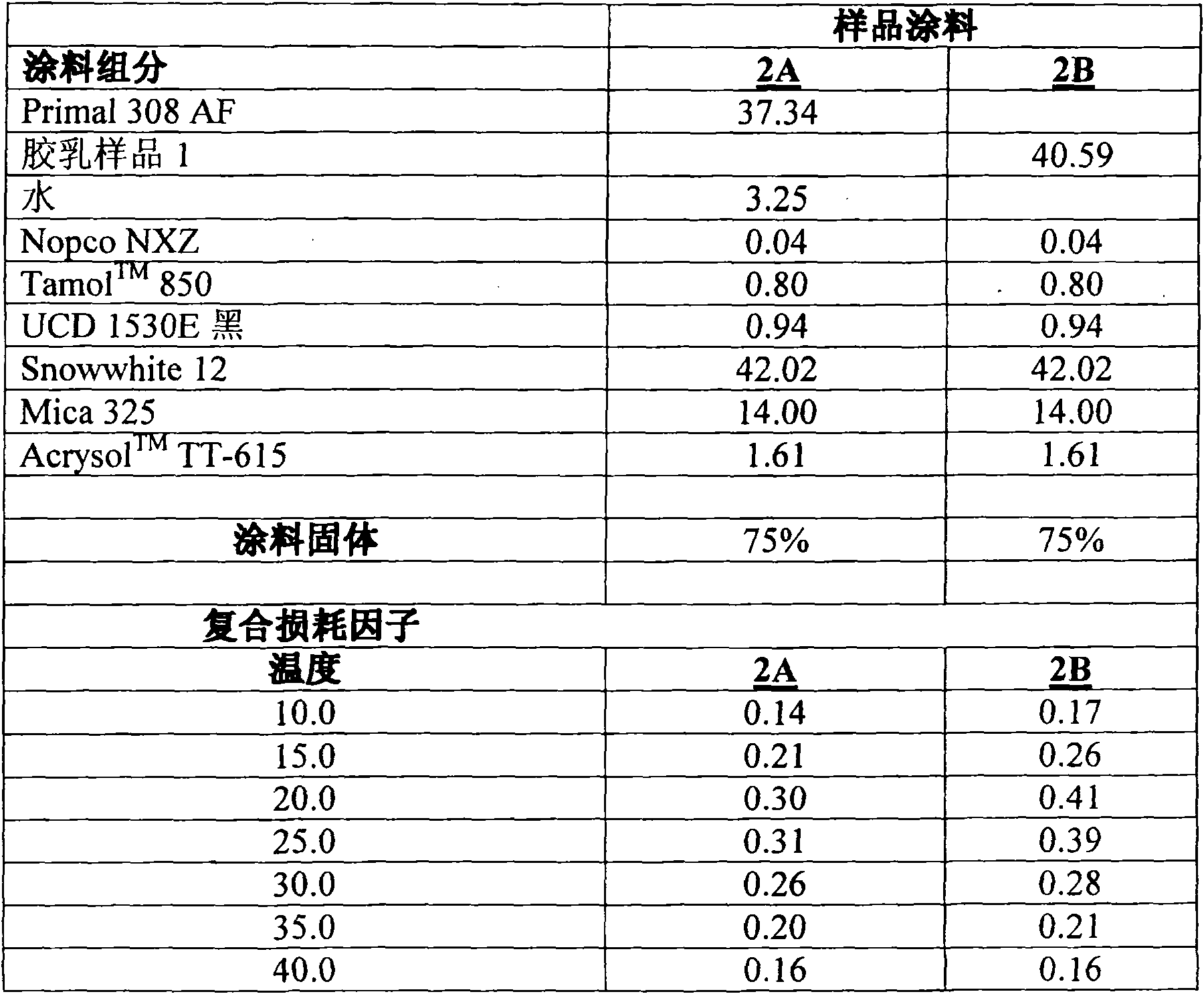
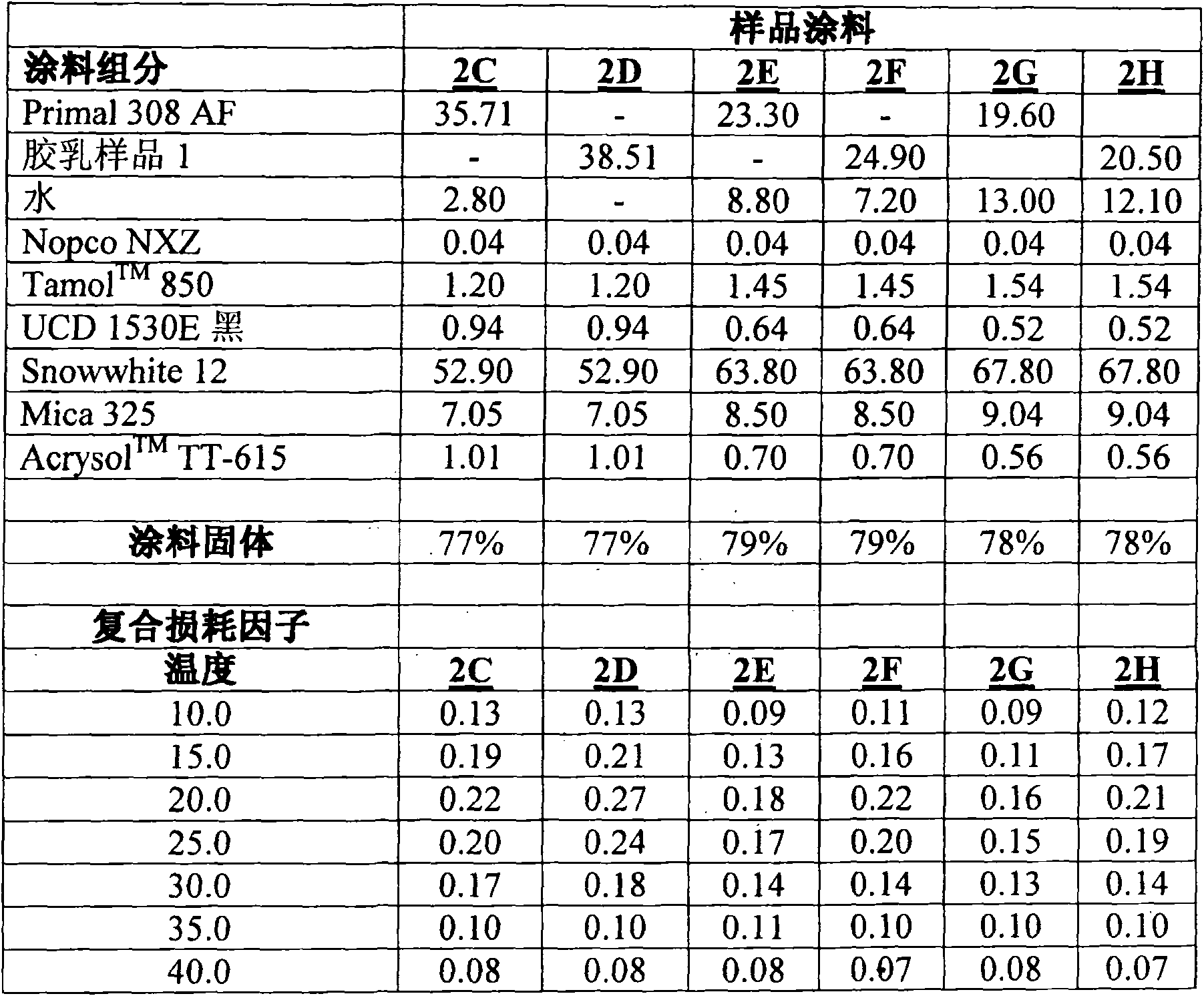
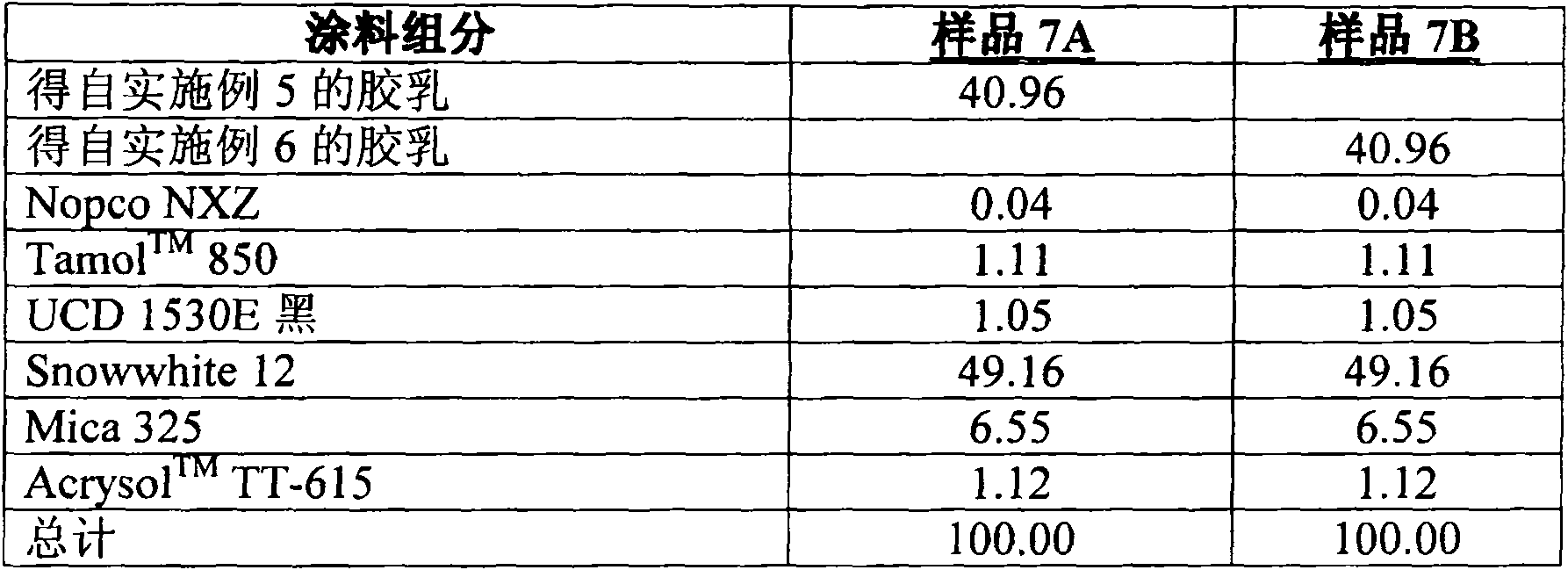
[0050] Examples 2A-B: Coating Formulations and Composite Loss Factors
[0051] The components used in the table below are: Primal 308 AF (styrene-acrylate adhesive), commercially available from Rohm and Haas Company, Philadelphia, PA; Foamaster Nopco NXZ, available from Cognis; Tamol TM 850 Dispersant and UCD 1530E Black Colorant, available from Rohm and Haas Company; Snowwhite 12 (calcium carbonate), available from Omya, Inc.; Mica 325, available from Asheville Mica Company; and Acrysol TM TT-615, a thickener (hydrophobically modified alkaline swellable emulsion (HASE)), also available from Rohm and Haas Company. These materials were used to make the following coating formulations.
[0052]Composite loss factor ("CLF") calculations at various temperatures were performed according to ASTM E-756 test method, with further test specifications derived from SAE J-1637 test method for Oberst Bar testing. Will weigh 3.0kg / m 2 The dry paint was applied to samples 2A and 2B. Will ...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Preparation of Aqueous Dispersions of Phosphorus-Containing Polymer Particles
[0057] A monomer emulsion was prepared by mixing 969 g butyl acrylate, 34 g phosphoethyl methacrylate, 680 g methyl methacrylate, 17 g urea methacrylate, 477 g deionized (DI) water, and 18.7 g 60 wt. Ammonium alkylphenoxy polyethoxy sulfate (ammonium alkylphenoxy polyethoxy sulfate) surfactant aqueous solution, and emulsified with stirring. Next, 2.5 g of a 60% by weight aqueous solution of alkylphenoxypolyethoxyammonium sulfate surfactant and 1000 g of deionized water were added to a 5-liter multi-necked flask equipped with mechanical stirring. The contents of the flask were then heated to 85°C under a nitrogen atmosphere. To the contents of the stirred flask was added 92 g of the monomer emulsion, followed by 2.6 g of APS in 100 g of deionized water, followed by 1.7 g of sodium carbonate in 100 g of deionized water. The total addition time for the co-feed of the monomer emulsion and 2.6 ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com