Mg-Li-Ho alloy, and fused salt electrolysis preparation and apparatus thereof
A molten salt electrolysis and alloy technology, applied in the field of alloys, can solve the problems of reduced electrolysis temperature, large metal loss, environmental pollution, etc., and achieve the effects of shortening the production process, prolonging the service life, and reducing the production cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
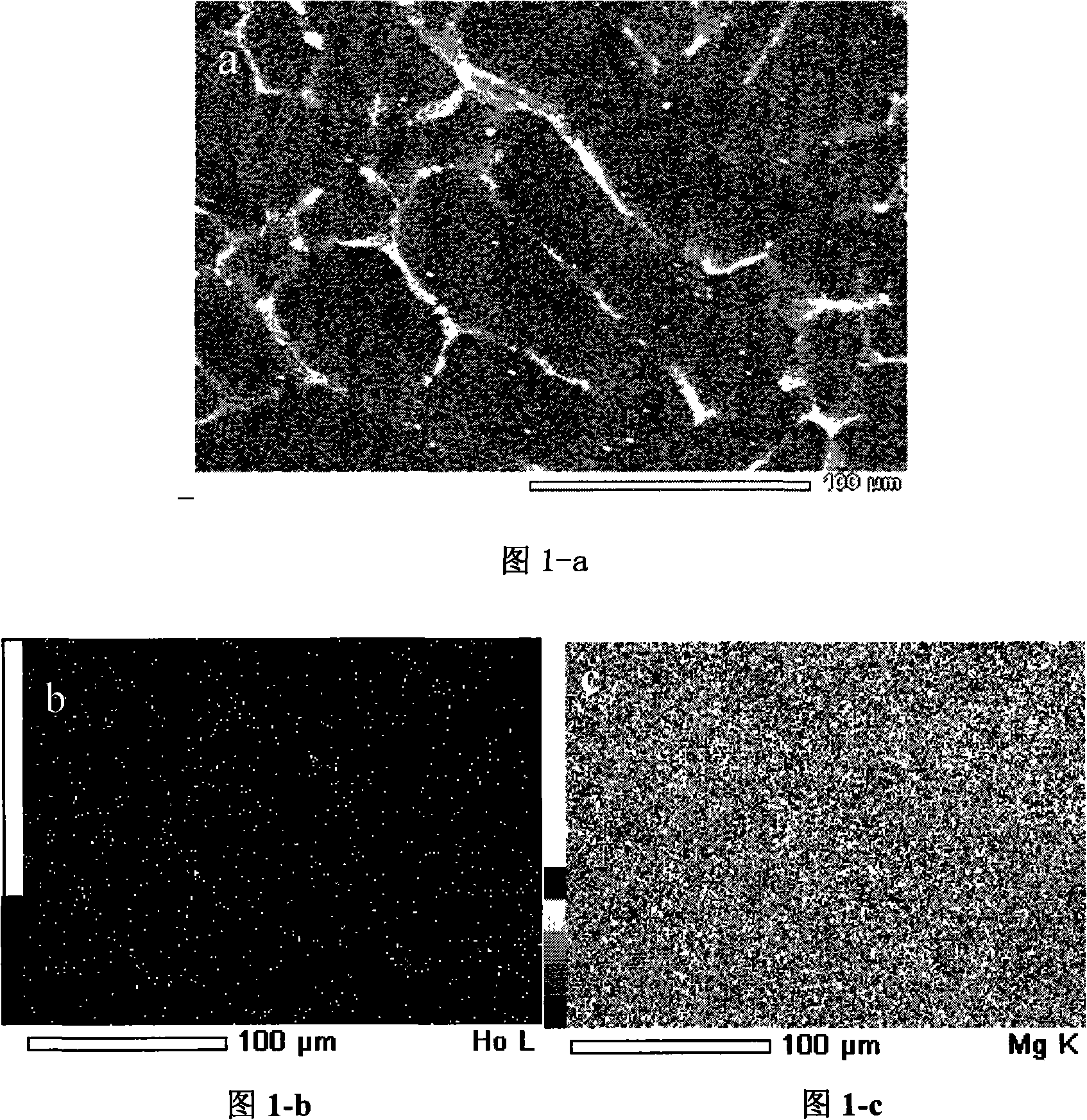
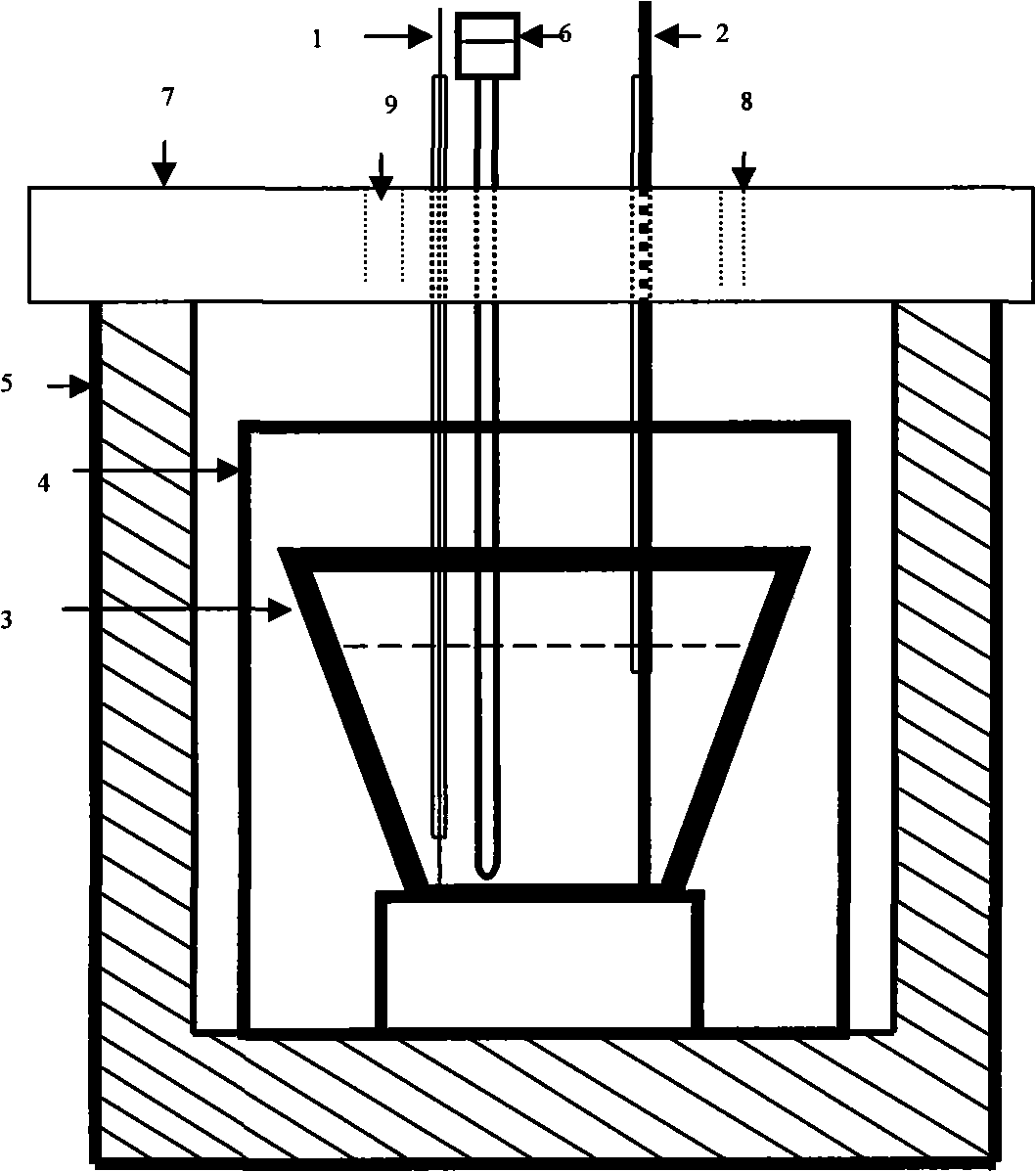
[0016] Embodiment 1: with MgCl 2 +LiCl+KCl+KF is the electrolyte system, the mass percentage of each component is 5.1%, 46.2%, 46.2%, 2.5%, and then according to MgCl 2 10% of the weight is added with holmium oxide, the inert metal molybdenum (Mo) is used as the cathode, graphite is used as the anode, and the electrolysis temperature is 665°C, the sinking cathode method is adopted, the pole distance is 4cm, and the cathode current density is 12A / cm 2 , anode current density 0.5A / cm 2 , the cell voltage is 5.3-5.8V, after 1 hour of electrolysis, a Mg-Li-Ho alloy is deposited near the cathode in the molten salt electrolytic cell, and the contents of magnesium, lithium, and holmium are respectively: 74.6%, 11.7%, and 13.7%. The molten salt electrolysis device of the magnesium-lithium-holmium alloy of the present invention is composed of a molybdenum cathode 1 of an outer corundum tube, a graphite anode 2 of an outer quartz tube, a corundum crucible 3, a stainless steel inner sle...
Embodiment 2
[0017] Embodiment 2: with MgCl 2 +LiCl+KCl+KF is the electrolyte system, the mass percentage of each component is 10%, 42.6%, 42.6%, 4.8%, and then according to MgCl 2 5% by weight of holmium oxide is added, the inert metal molybdenum (Mo) is used as the cathode, graphite is used as the anode, the electrolysis temperature is 740°C, the sinking cathode method is adopted, the pole distance is 4cm, and the cathode current density is 12A / cm 2 , anode current density 0.5A / cm 2 , the cell voltage is 6.4-6.6V, after 2 hours of electrolysis, a Mg-Li-Ho alloy is deposited near the cathode in the molten salt electrolytic cell, and the contents of magnesium, lithium, and holmium are respectively: 67.7%, 28.1%, and 4.2%.
Embodiment 3
[0018] Embodiment 3: with MgCl 2 +LiCl+KCl+KF is the electrolyte system, the mass percentage of each component is 13.6%, 40.9%, 40.9%, 4.6%, and then according to MgCl 2 3.3% by weight of holmium oxide is added, the inert metal molybdenum (Mo) is used as the cathode, and graphite is used as the anode. Under the electrolysis temperature of 700°C, the sinking cathode method is adopted, the pole distance is 4cm, and the cathode current density is 12A / cm 2 , anode current density 0.5A / cm 2 , the cell voltage is 6.9-7.1V, after 2 hours of electrolysis, a Mg-Li-Ho alloy is deposited near the cathode in the molten salt electrolytic cell, and the contents of magnesium, lithium, and holmium are respectively: 68.4%, 30.7%, and 0.9%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com