Ammonia nitrogen processing method for hide manufacture wastewater
A technology of tannery wastewater and a treatment method, which is applied in the advanced treatment and reuse of secondary effluent, the treatment of ammonia nitrogen in tannery wastewater by a heterotrophic bacterial biological filter, and the zeolite-autotrophic field, which can solve the problem of low ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency, Can not deal with industrial wastewater, troubles the treatment of industrial wastewater and other problems, to achieve the effect of improving capacity, reducing power consumption, and low operating costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Nitrobacter opacus Sack cultivation:
[0028] Medium preparation: sodium nitrite 1kg; sodium carbonate 1kg; dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.75kg; magnesium sulfate 0.03kg; manganese sulfate 0.01kg; pH 6.5, water to 1000L;
[0029] Nitrobacter opacus Sack was inoculated and cultured with shaking at 24° C. for 5 days to obtain a Nitrobacter opacus Sack culture (a mixture of bacterium and culture medium).
[0030] (2) Nitrosomonas monocella Nelson cultivation:
[0031] Medium preparation: dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 1kg; ammonium sulfate 0.5kg; calcium chloride 7.5kg; sodium chloride 0.3kg; magnesium sulfate 0.03kg; iron sulfate 0.03kg;
[0032] Nitrosomonas monocella Nelson was inoculated and aerated at 24° C. for 5 days to obtain a culture of Nitrosomonas monocella Nelson (a mixture of bacterium and culture medium).
[0033] (3) Culture of Rhodopseudomonas seudanonas palustris:
[0034] Medium preparation: glucose 10kg; potassium nitrate 1kg; calcium chloride 0....
Embodiment 2
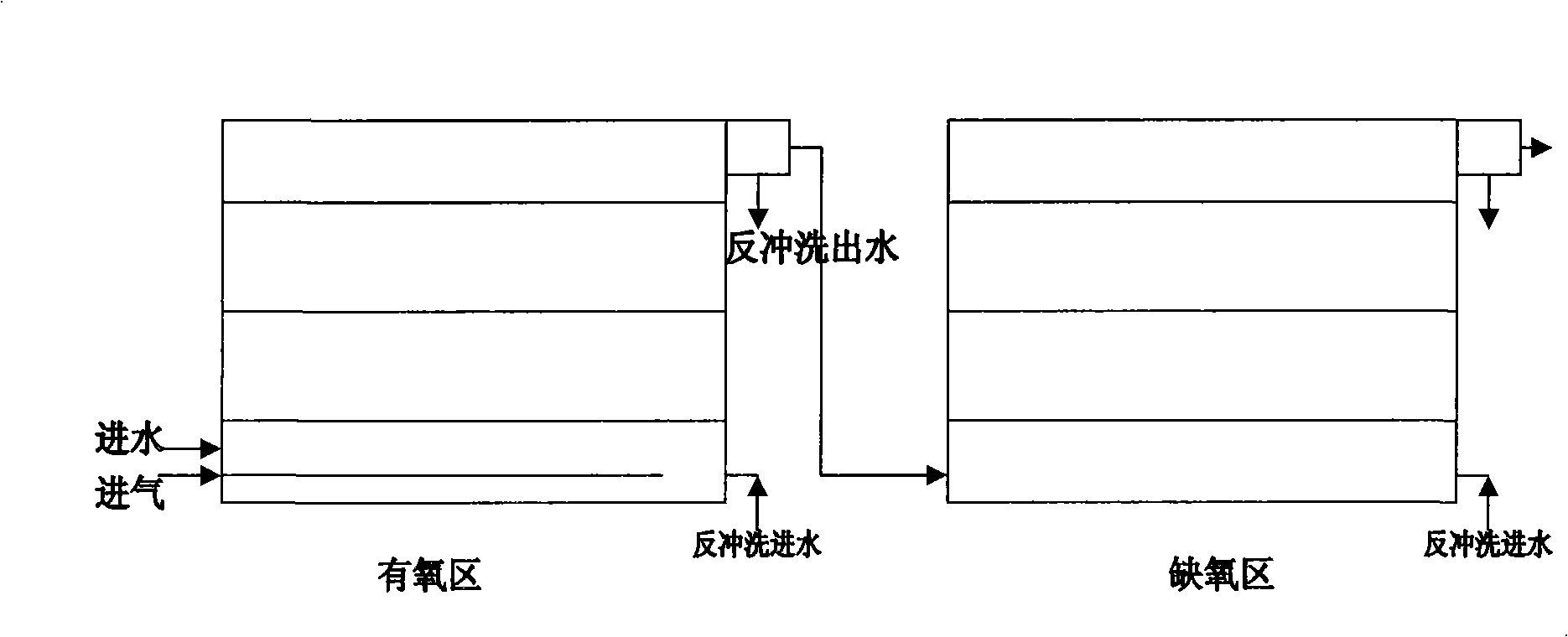
[0037] General treatment of secondary effluent from tanning: biofilter with a height of 2.5m, filled with clinoptilolite fillers with particle sizes of 50mm, 20mm, and 5mm (from bottom to top) at a volume ratio of 1:1:1 (Jinyun, Zhejiang) , the exchange capacity of ammonia nitrogen is 5~10kg / m 3 . Put 20kg of Nitrobacter opacus Sack culture and Nitrosomonas monocella Nelson culture cultivated in Example 1 into the oxygen supply treatment area, ventilate at intervals of 15 minutes per hour, and run continuously for 15 to 20 days to make it hang film on the filler The anoxic treatment area puts in 30kg of the culture of Rhodopseudomonas seudanonas palustris cultivated in Example 1, and runs continuously without ventilation for 20 to 30 days, so that it forms a film on the filler. The secondary effluent of tannery runs for 40 minutes in the oxygen supply treatment area and the anoxic treatment area respectively, the COD of the secondary effluent of tannery is reduced from 100-20...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Advanced treatment of tannery secondary effluent: biofilter with a height of 3.5m, filled with clinoptilolite fillers with particle sizes of 50mm, 20mm, and 5mm (from bottom to top) at a volume ratio of 1:1:1, exchange of ammonia nitrogen The capacity is 5~10kg / m 3 . The oxygen supply treatment area is put into the culture of Nitrobacter opacus Sack cultivated in Example 1 and the culture of Nitrosomonas monocella Nelson, respectively 25kg, ventilated at intervals of 15min per hour, and run continuously for 15 to 20 days to make it hang film on the filler; Put 40kg cultured culture of Rhodopseudomonas seudanonas palustris in the anoxic treatment area, and run continuously without ventilation for 20-30 days to make it hang film on the filler. The secondary effluent of tanning was run for 60 minutes in the oxygen supply treatment area and the anoxic treatment area respectively, the COD of the secondary effluent of tanning was reduced from 100-120mg / L to 20-30mg / L, and th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com