Preparing methods of polyisoprene emulsion and rubber thereof
A technology of polyisoprene and isoprene, which is applied in the field of preparation of polyisoprene emulsion and its rubber, can solve problems such as potential safety hazards, removal of organic solvents, cumbersome recycling process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
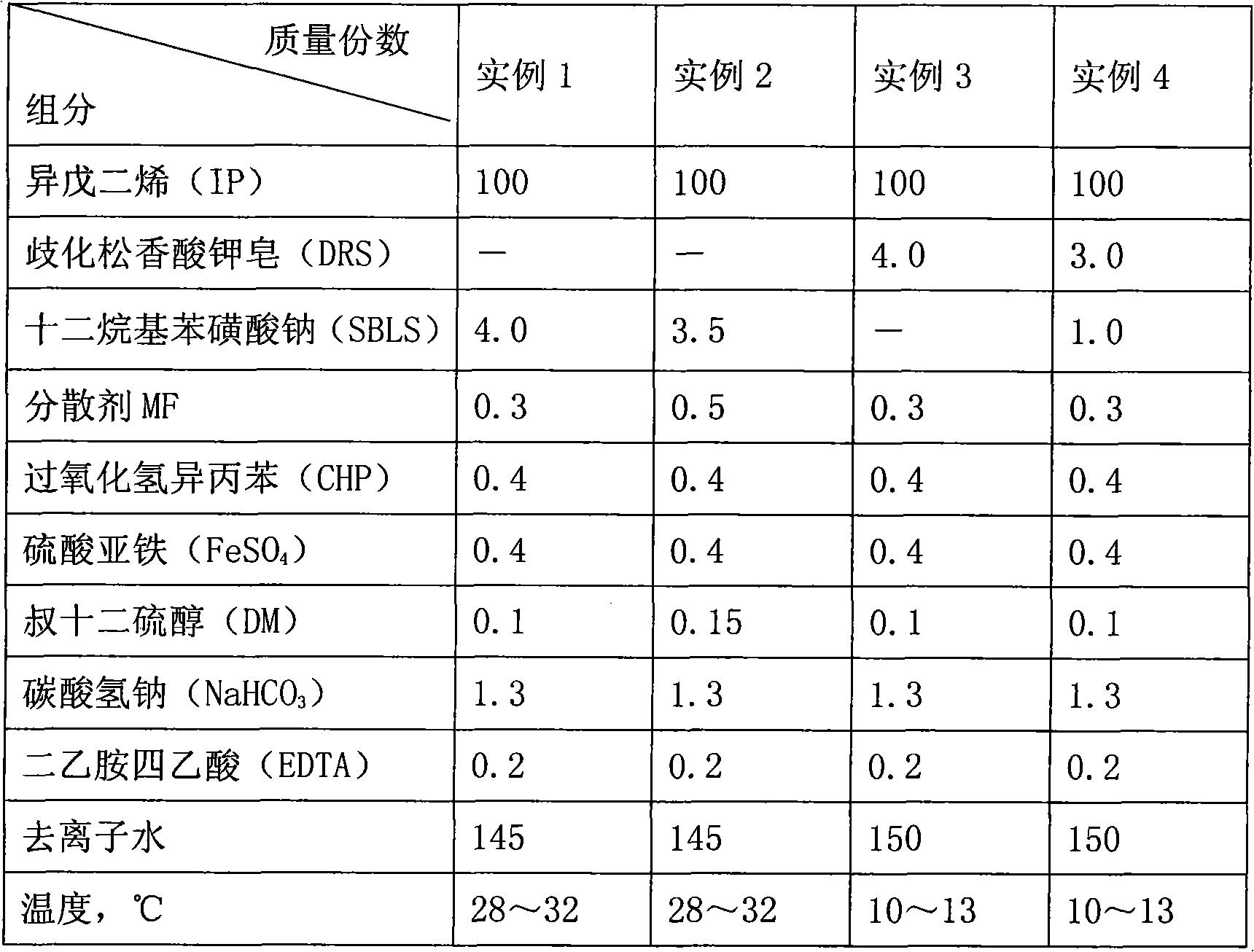
[0041] After passing nitrogen gas to the bottom of the polymerization tank for 30 minutes, add 100 parts of deionized water, all SBLS, EDTA, MF and NaHCO 3 , stirring and dissolving into an aqueous phase. Add all IP and CHP into the monomer tank, stir and dissolve to form an oil phase. 45 parts of deionized water, all FeSO 4 Add the reducing agent to the kettle, stir and dissolve to form an aqueous solution. Control the kettle temperature at 28°C to 32°C, start adding IP dropwise, and finish dropping in 8 to 10 hours. Add 80% FeSO synchronously 4 Aqueous solution, drop in 8 to 10 hours. When the conversion reaches 60%, add the remaining 20% FeSO 4 aqueous solution. Continue to react for 10-15 hours, when the conversion rate reaches above 85%, add 0.2 part of diethanolamine and 1 part of antioxidant 264. After the reaction is terminated, the polyisoprene latex is sent to a degassing tank, and unreacted monomers are removed by flashing and steaming to obtain a stable wh...
example 2
[0045] The dodecanethiol in Example 1 is adjusted to 0.15 parts, SBLS is 3.5 parts, and MF is 0.5 parts. The material consumption is as shown in Table 1, and other process conditions are unchanged. The obtained emulsion had a solid content of 36.2%, a pH of 7.1, and a particle diameter of 183 nm. The physical and mechanical properties of the obtained rubber blocks are shown in Table 2.
example 3
[0047] After passing nitrogen gas to the bottom of the polymerization tank for 30 minutes, add 100 parts of deionized water, all DRS, EDTA, MF and NaHCO to the reactor according to Table 1 3 , stirring and dissolving into an aqueous phase. Add all IP and CHP into the monomer tank, stir and dissolve to form an oil phase. 50 parts of deionized water, all FeSO 4 Add the reducing agent to the kettle, stir and dissolve to form an aqueous solution. Control the temperature of the kettle at 10°C to 13°C, start adding IP dropwise, and finish the dropwise in 10-15 hours. Add 80% FeSO synchronously 4 Aqueous solution, drop in 10~15 hours. When the conversion reaches 60%, add the remaining 20% FeSO 4 aqueous solution. Continue to react for 15-25 hours, when the conversion rate reaches above 85%, add 0.2 part of diethanolamine and 1 part of antioxidant 264. After the reaction is terminated, the polyisoprene latex is sent to a degassing tank, and unreacted monomers are removed by f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com