Hafnium compound, hafnium thin film-forming material and method for forming hafnium thin film
A technology of amine compounds and compounds, applied in chemical instruments and methods, compounds of group 4/14 elements of the periodic table, metal material coating technology, etc., can solve problems such as difficult gasification, poor stability, and difficulty in supplying gas , to achieve the effect of stable supply and easy gasification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] [The novel compound CpHf(NMe 2 ) 3 Synthesis]
[0055] Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 29 g of tetrakis(dimethylamino)hafnium and 5.3 g of cyclopentadiene were stirred in 70 mL of benzene for 1 hour. After heating the solution to reflux for 2 hours, benzene was distilled off under reduced pressure. The remaining yellow liquid was subjected to 0.1 torr vacuum distillation at 70-80° C. to obtain 25 g of yellow liquid.
[0056] The yellow liquid boiled at 75°C / 0.2 Torr.
[0057] In addition, the results and spectrum of NMR measurement showed the following resonance lines.
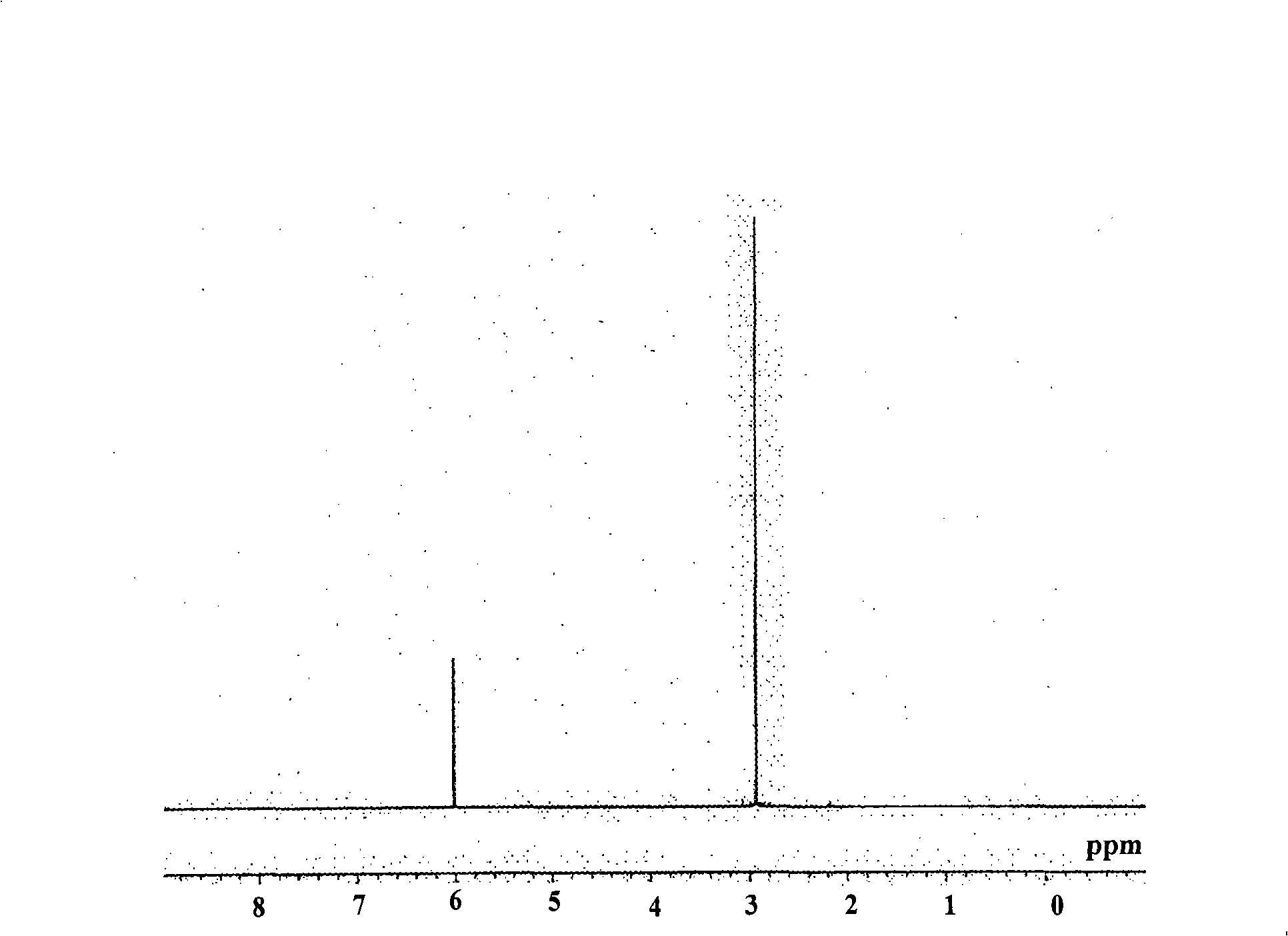
[0058] 1 H-NMR (C 6 D. 6 ): 3.0(s, 18H), 6.0(s, 5H)
[0059] What needs to be explained is that, figure 1 is the NMR spectrum of cyclopentadienyl tris(dimethylamino)hafnium.
[0060] And, judging from the above reaction form and NMR spectrum: the obtained yellow liquid is cyclopentadienyl tri(dimethylamino) hafnium [CpHf(NMe 2 ) 3 ].
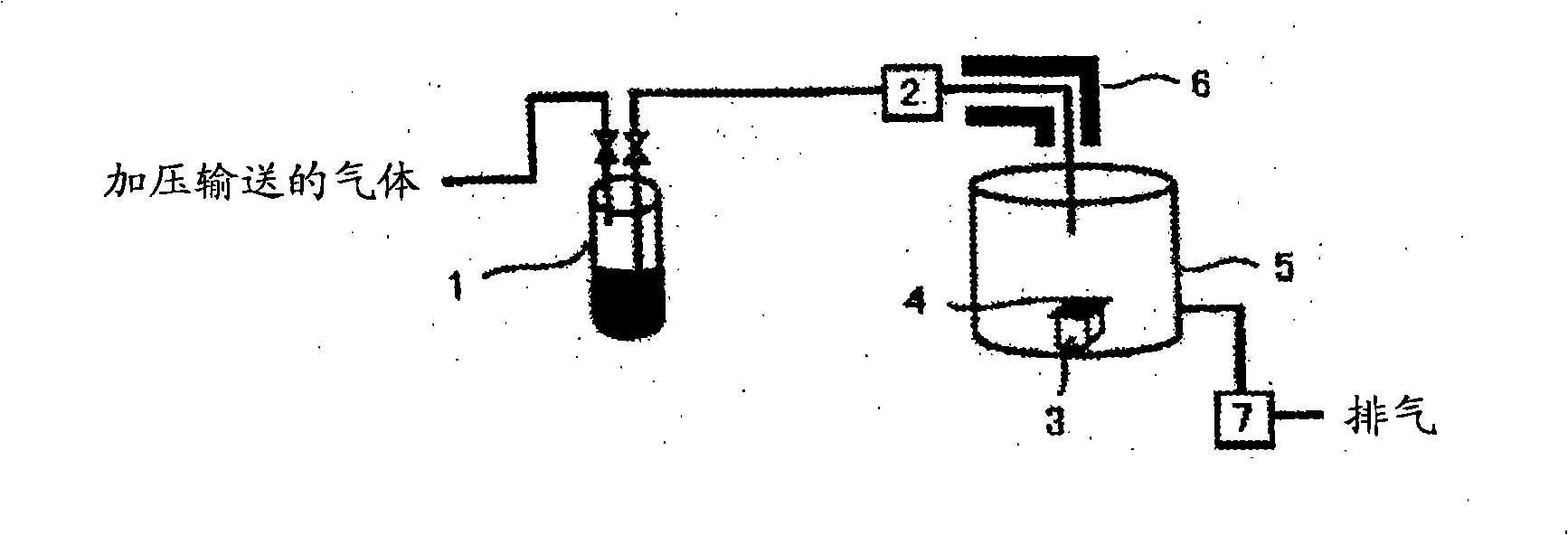
[0061] Next, 150 g of CpHf(NMe 2 ) 3 It was charged int...
Embodiment 2
[0071] [Novel compound (MeCp)Hf(NMe 2 ) 3 Synthesis]
[0072] Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 10 g of tetrakis(dimethylamino)hafnium and 2 g of methylcyclopentadiene were stirred in 35 mL of benzene for 1 hour. After heating the solution to reflux for 2 hours, benzene was distilled off under reduced pressure. The remaining yellow liquid was subjected to 0.1 torr vacuum distillation at 70-80° C. to obtain 11 g of yellow liquid.
[0073] The yellow liquid has a boiling point of 72°C / 0.1 Torr.
[0074] In addition, the results and spectrum of NMR measurement showed the following resonance lines.
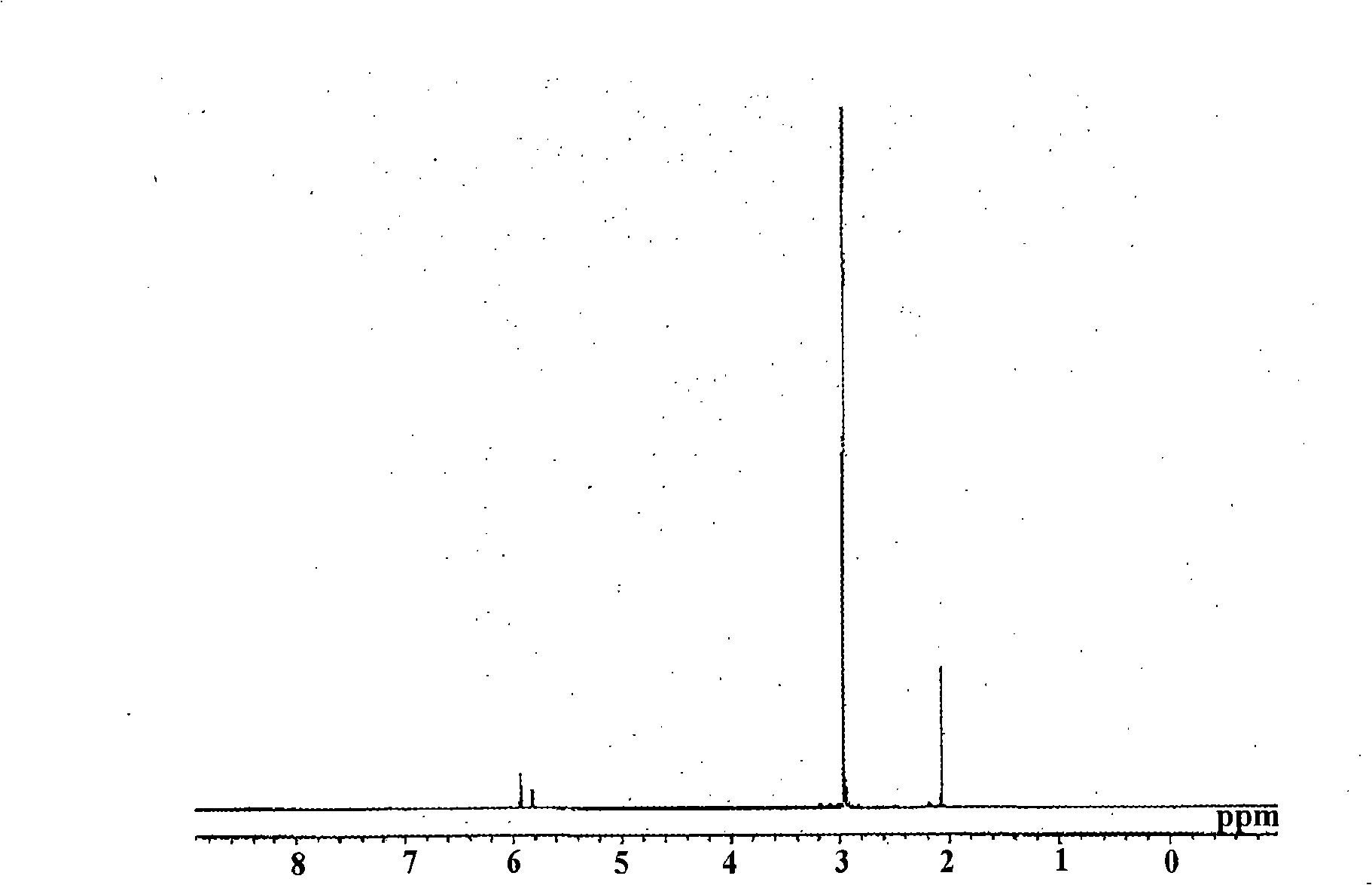
[0075] 1 H-NMR (C 6 D. 6 ): 2.1(s, 3H), 3.0(s, 18H), 5.8(m, 2H), 5.9(m, 2H)
[0076] What needs to be explained is that, image 3 is the NMR spectrum of methylcyclopentadienyl tris(dimethylamino)hafnium.
[0077] Moreover, judging from the above reaction form and NMR spectra: the obtained yellow liquid is methylcyclopentadienyl tris(dimethylamino)hafnium [(MeCp)Hf(NMe 2 ) 3 ]. ...
Embodiment 3
[0085] [Novel compound (EtCp)Hf(NMe 2 ) 3 Synthesis]
[0086] Under a nitrogen atmosphere, 25 g of tetrakis(dimethylamino)hafnium and 7 g of ethylcyclopentadiene were stirred in 60 mL of benzene for 1 hour. After heating the solution to reflux for 2 hours, benzene was distilled off under reduced pressure. The remaining yellow liquid was subjected to 0.1 torr vacuum distillation at 70-80° C. to obtain 19 g of yellow liquid.
[0087] The yellow liquid boiled at 78°C / 0.2 Torr.
[0088] In addition, the results and spectrum of NMR measurement showed the following resonance lines.
[0089] 1 H-NMR (C 6 D. 6 ): 1.1(t, 3H), 2.5(q, 2H), 3.0(s, 18H), 5.9(m, 2H), 6.0(m, 2H)
[0090] What needs to be explained is that, Figure 4 is the NMR spectrum of ethylcyclopentadienyl tris(dimethylamino)hafnium.
[0091] Moreover, judging from the above reaction form and NMR spectrum: the obtained yellow liquid is ethylcyclopentadienyl tri(dimethylamino) hafnium [(EtCp)Hf(NMe 2 ) 3 ].
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com