Servo engaging and disengaging gear and its operation mode
A clutch device and operating mode technology, applied in the field of transmission, can solve the problems of high cost, high transmission torque efficiency, small size, etc., and achieve excellent durability and reliability, rapid response, and low heat generation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
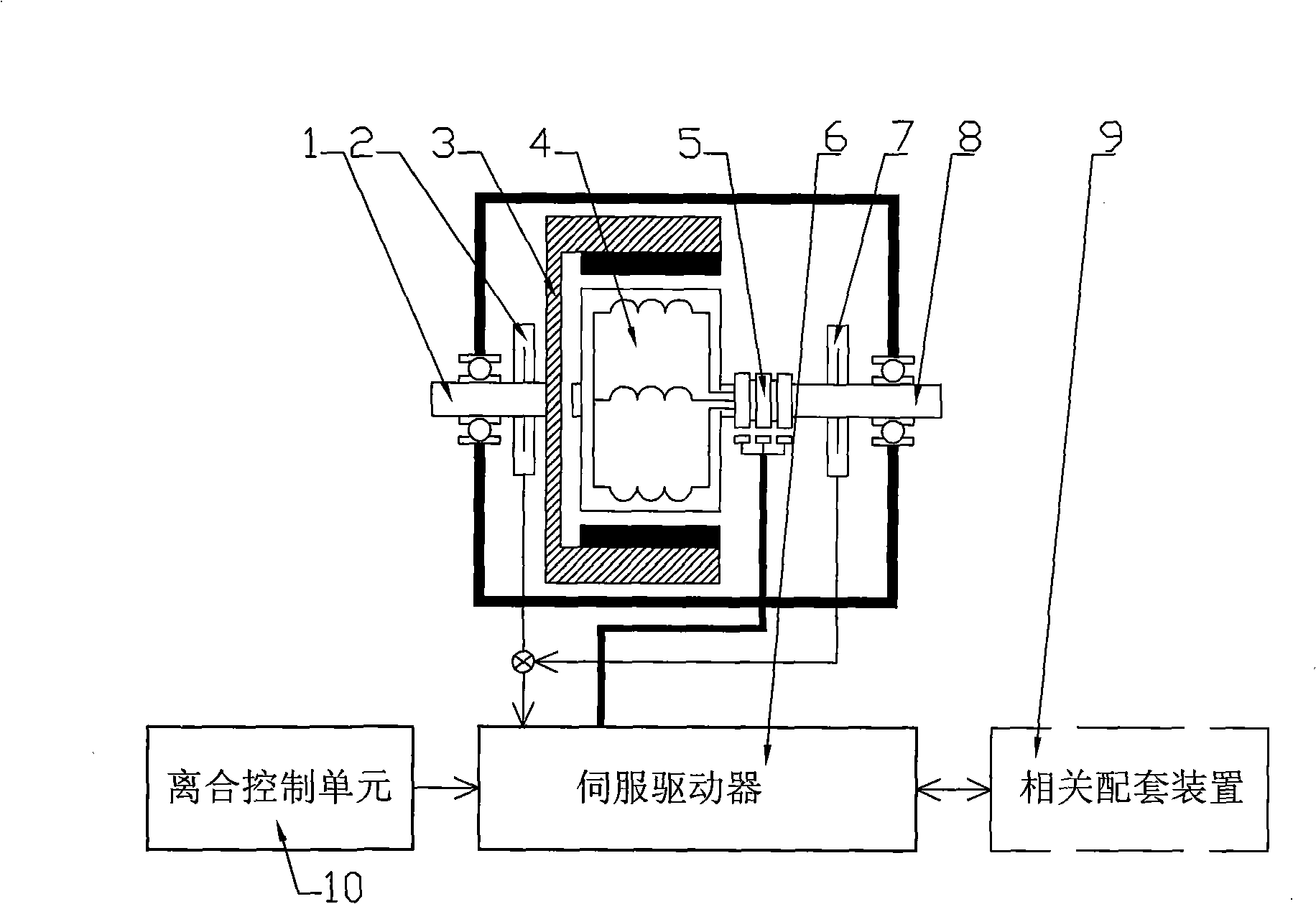
[0039] The structure of the embodiment 1 of the servo clutch device of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the input shaft 1 is connected to the first rotor 3, the first rotor 3 is an outer rotor, embedded with permanent magnet poles, inside it is the second rotor 4, and the second rotor 4 is an inner rotor, which is wound on the iron core winding, the second rotor 4 is connected to the output shaft 8 of the device. The input shaft 1 and the output shaft 8 are on the same straight line. The first rotor 3 provides the second rotor 4 with a radial magnetic field. In this embodiment, the permanent magnet poles embedded in the first rotor 3 and the iron core and windings of the second rotor 4 constitute a permanent magnet synchronous motor, a switched reluctance motor, or a DC motor. A position sensor 2 is installed on the first rotor 3 . A B position sensor 7 is installed on the second rotor 4 shaft, and the A position sensor 2 and the B position sensor 7 a...
Embodiment 2
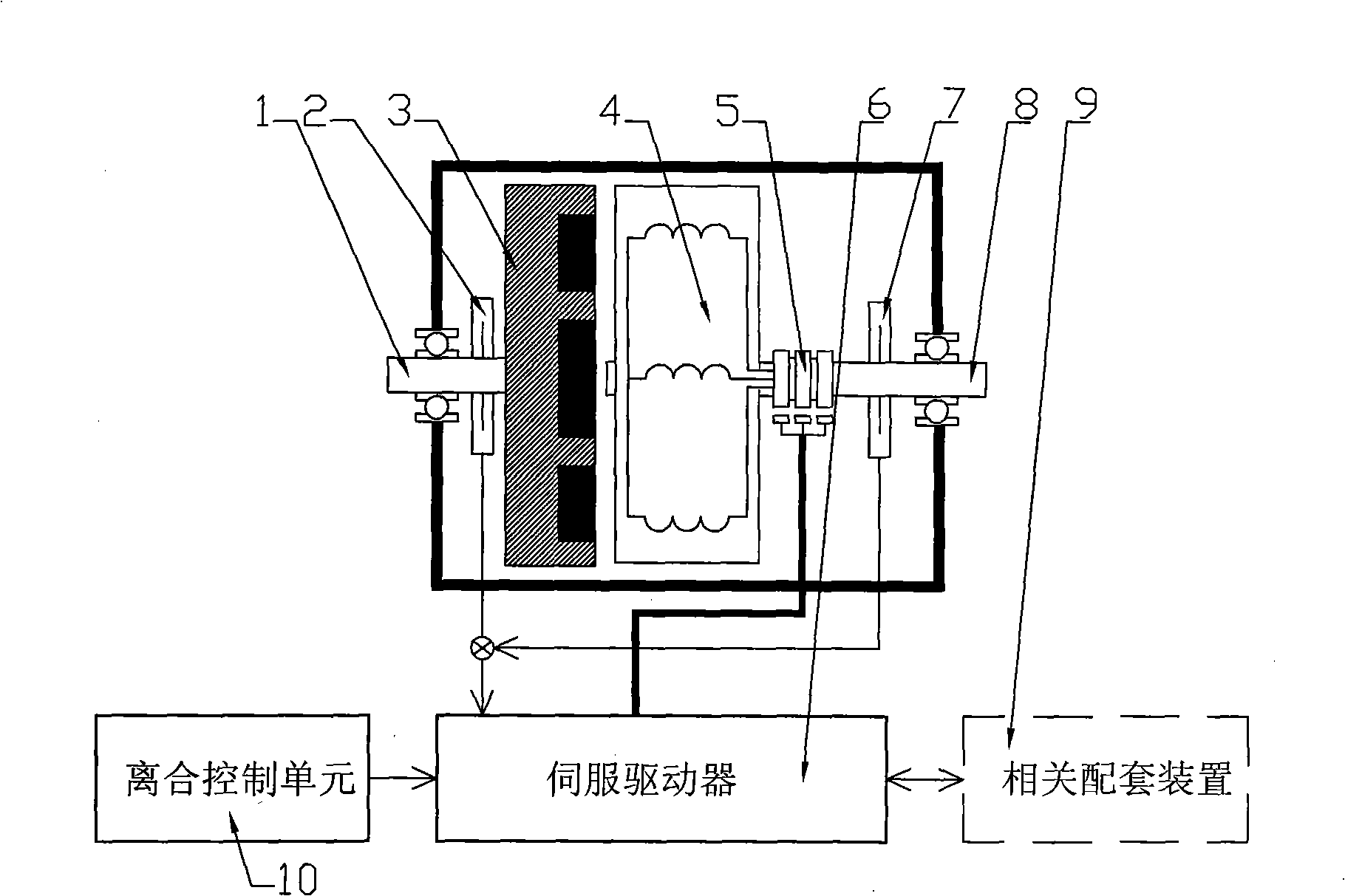
[0050] The structure of embodiment 2 of the servo clutch device of the present invention is as follows: figure 2 As shown, the first rotor 3 and the second rotor 4 are opposite to each other, maintaining an air gap, and the other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1. The two form an axial magnetic circuit structure, and the direction of the air gap magnetic field between the two rotors is axial.
[0051] The operating mode of the embodiment 1 and 2 of the servo clutch device of the present invention is as follows: the servo driver 6 works in the torque servo mode, and the torque value of the master-slave part of the servo clutch linearly follows the torque setting value of the servo driver 6. During the process, the motions of the clutch input shaft 1 and output shaft 8 are determined by their respective synthetic torques, that is, by the electromagnetic torque of the servo clutch and the power torque or load torque on the two shafts 1 and 8 .
[0052] When the i...
Embodiment 3
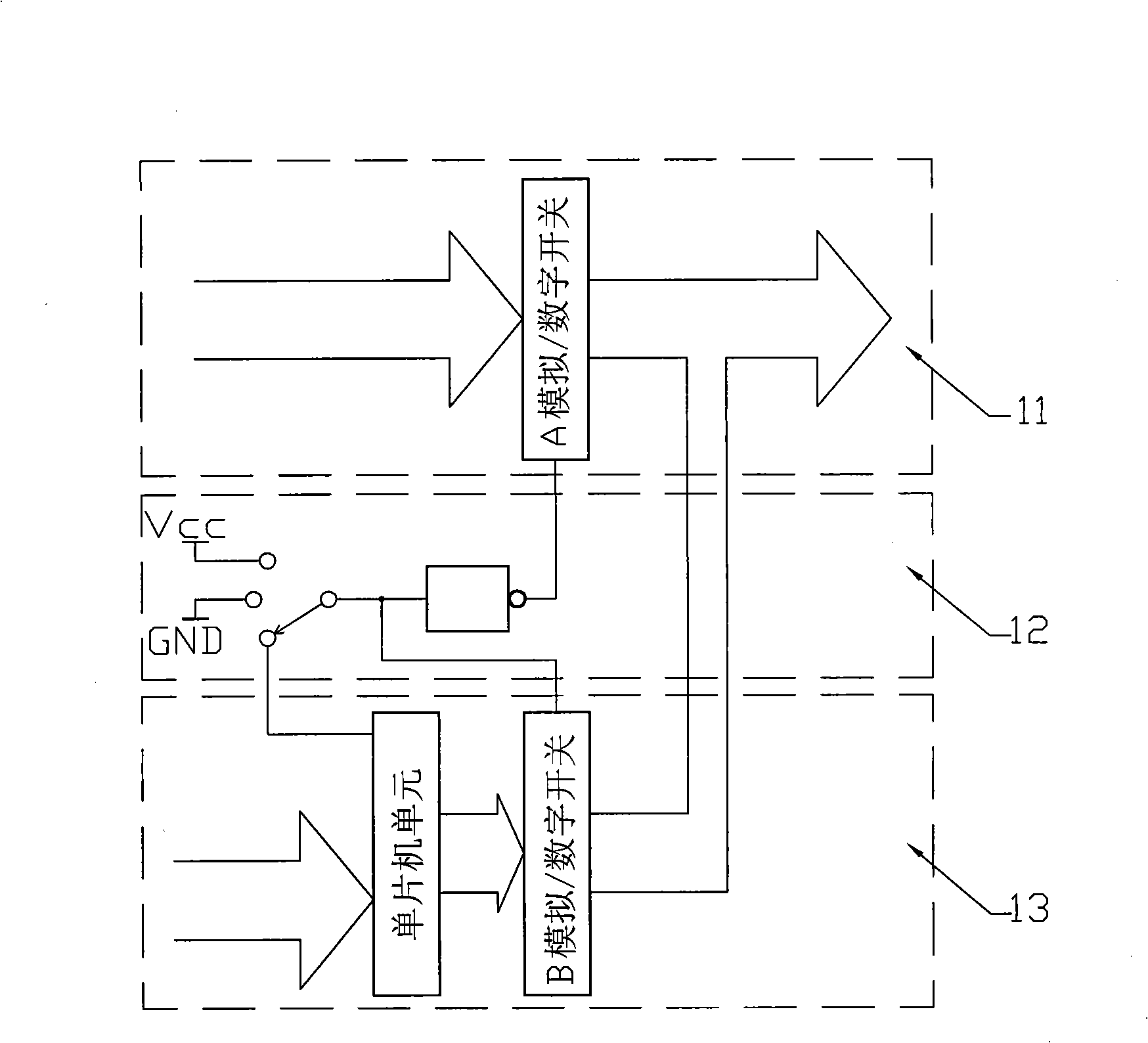
[0066] The structure of embodiment 3 of the servo clutch device is mostly the same as that of embodiment 1 or 2, the difference is: the first rotor 3 is replaced with A position / speed sensor 2, and the second rotor 4 is replaced with B The position / speed sensor 7, the A position / speed sensor 2 and the B position / speed sensor 7 are connected to the servo driver 6 after the difference calculator, or the two position and speed sensors are connected to the servo driver 6 containing the difference calculator. The position and speed signals obtained by the two sensors 2 and 7 are sent to the servo driver 6 as the relative position and speed signals of the first and second rotors 3 and 4 after difference calculation; The servo driver of the / position servo unit, the servo driver 6 has a control port connected with the clutch control unit 10 for the speed / position setting signal and the torque limit signal, and works in a speed / position servo mode with a torque limit value.
[0067] I...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com