Novel lipases and uses thereof
A polynucleotide and carrier technology, applied in the field of lipase and its application, can solve the problem of reducing the hardening rate of softened debris
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0209] Fermentation of Aspergillus niger
[0210] The lipolytic enzymes encoded by the nucleotide sequences SEQ ID NO: 2, SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4 provided herein were constructed as follows: construction of expression plasmids containing DNA sequences, transformation of A. niger strains with such plasmids , and Aspergillus niger strains were cultured in the following manner.
[0211] Fresh spores of A. niger (10 6 -10 7 ) was inoculated in 20 ml CSL-medium (100 ml flask with a lid) and cultured at 34° C. and 170 rpm for 20-24 hours. After inoculating 5-10 ml CSL preculture in 100 ml CSM medium (500 ml capped flask), the strain was fermented at 34°C and 170 rpm for 3-5 days.
[0212] Cell-free supernatants were obtained by centrifugation (30 min, 5000 rpm) in 50 ml Greiner tubes. Pre-filter the supernatant on a GF / A Whatman Glass microfiber filter (150 mm AE) to remove larger particles, adjust to pH 5 with 4N KOH (if necessary), and filter over a 0.2 μm (bottle top)...
Embodiment 2
[0216] Purification of the lipolytic enzyme of the present invention
[0217] Step 1 - Preparation of ultrafiltrate
[0218] The culture supernatant obtained according to Example 1 was subjected to ultrafiltration to remove low-molecular contamination that may affect the enzyme activity assay and baking test. Ultrafiltration of 30 ml of the supernatant was carried out in a Millipore Labscale TFF system equipped with a filter membrane (with a cut-off of 10 kDa).
[0219] Depending on the color of the samples, wash them with 40 volumes of cold 100 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6.0 (containing 0.5 mM CaCl 2 ) wash 3-5 times. The final volume of the enzyme solution was 30ml, also called "ultrafiltrate".
[0220] The total protein content of the samples was determined using the Bradford method (The Protein Protocols Handbook, 2nd edition, Edited by J.M. Walker, Humana Press Inc, Totowa 2002, p15-21).
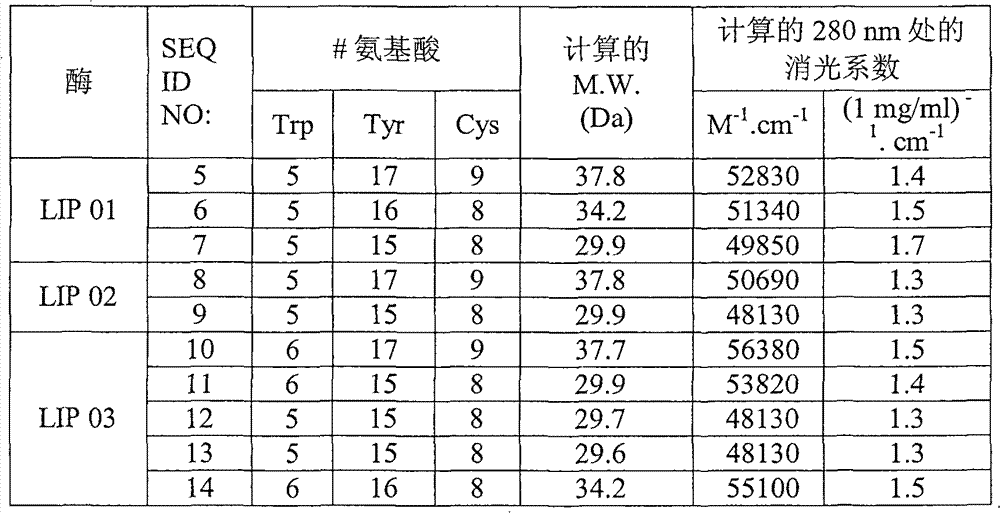
[0221] Step 2 - Determination of lipolytic enzyme concentration by A280 and HPSE...
Embodiment 3
[0229] activity measurement
[0230] The ultrafiltrate obtained in Example 2 can be used to perform the following enzyme activity measurements to establish the following lipolytic enzymes:
[0231] ·Lipase
[0232] · Phospholipase A1 or A2
[0233] · Lysophospholipase
[0234] ·Galactose esterase activity
[0235] specificity.
[0236]Lipase activity was measured spectrophotometrically by using the chromogenic substrate p-nitrophenyl palmitate (pNPP). In this assay, the chromogenic substrate p-nitrophenyl ester (pNPP) is dissolved in 2-propanol and suspended in phosphate in the presence of 0.1% gum arabic and 0.25% sodium deoxycholate Buffer pH 7.4. The lipase was incubated with this substrate solution at 37°C and the p-nitrophenyl (pNP) formation was measured at 405 nm for 2.6 minutes. This assay can also be performed at different pH values to determine the pH dependence of lipase. It should be understood that different buffers may be required at different pH valu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com