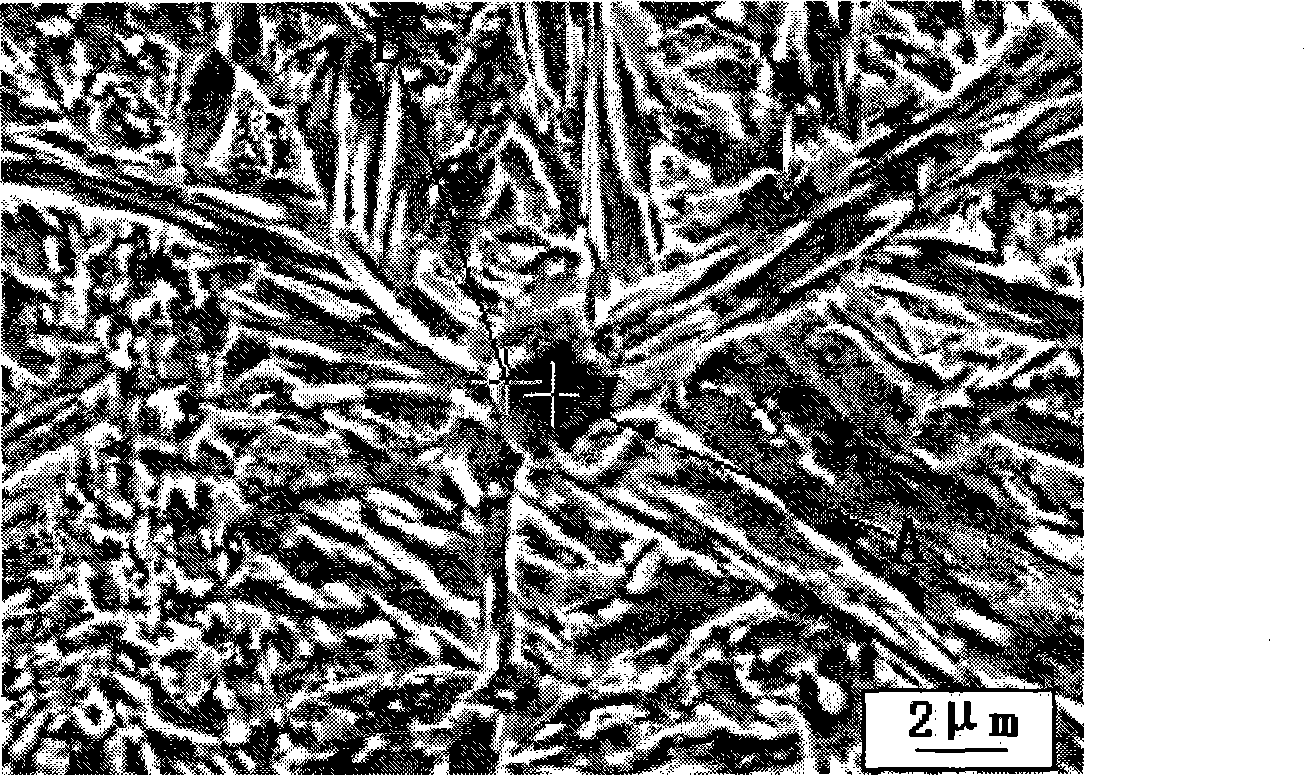
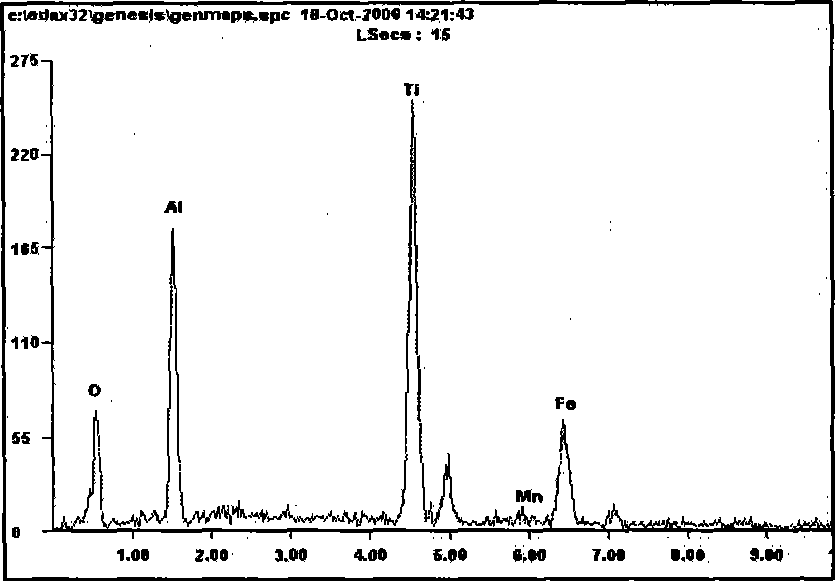
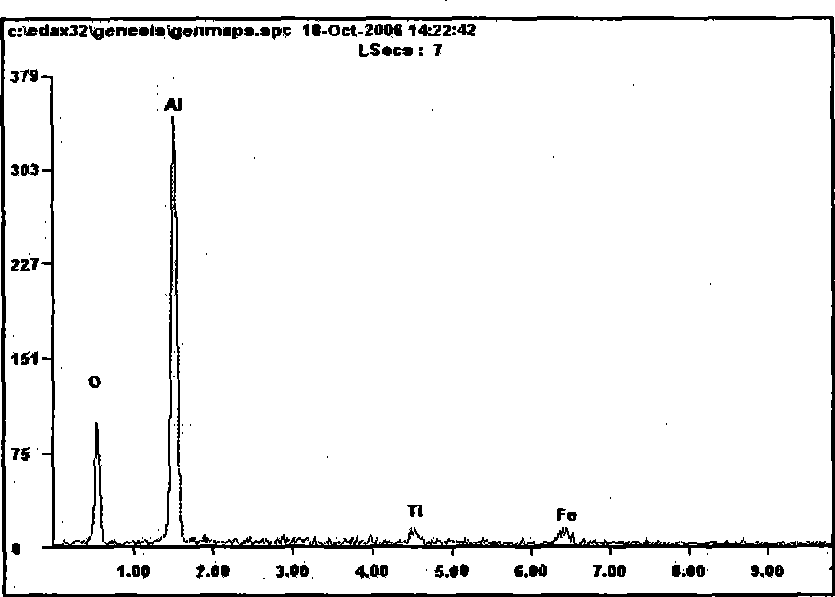
Molten steel deoxygenation method for thinning solidification structure
A technology of solidification structure and molten steel, which is applied in the field of steel smelting, can solve the problems of difficult industrial mass production, and achieve the effects of avoiding large particles of single titanium oxide, eliminating harmful effects, and reducing clogging
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] In MoSi 2 Carry out steel melting and deoxidation experiments in a high-temperature furnace. Before the experiment, put the corundum crucible into the furnace, and at the same time put the steel material to be melted (500g of industrial pure iron) into the corundum crucible, raise the temperature to 600°C, and open the valve of the argon gas cylinder. The bottom of the furnace is fed with high-purity argon for protection to prevent the steel material from being oxidized, and the flow rate is controlled at 1L / min. Raise the temperature to 1600°C and change to automatic constant temperature control, at this time the charge has been completely melted. When deoxidizing, first use SiAlFe alloy (0.44g) containing 28% aluminum for deoxidation, then add carbon powder (0.94g), metal manganese (9.66g), ferrosilicon (2.67g) and ferroniobium (0.34g) alloy for 60 seconds Finally, the sample before titanium treatment was taken with a quartz tube, and the oxygen activity in the steel...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Conduct steel melting and deoxidation experiments in a 200kg high-frequency induction furnace lined with magnesia refractory materials. Before the experiment, put the steel material (industrial pure iron) to be melted into the furnace, raise the temperature to 1600°C, and stop the temperature rise. The steel material has been completely melted. When deoxidizing, first use SiAlFe alloy (0.20kg) containing 28% aluminum for deoxidation, then add carbon powder (0.16kg), metal manganese (3.87kg), ferrosilicon (1.07kg) and ferroniobium (0.20kg) alloy, 200 seconds Finally, the sample before titanium treatment was taken with a quartz tube, and the oxygen activity in the steel was measured with a solid electrolyte oxygen concentration cell rapid oxygen determination probe. The oxygen activity of molten steel before adding titanium was 81×10 -6 , and then add 30% titanium-containing ferro-titanium alloy (0.56kg) for final deoxidation, incubate for 300 seconds, and take a titanium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com