Novel medical uses of aporphine alkaloid and derivative thereof
A technology of alkaloids and derivatives, which is applied in the pharmaceutical composition of pharmaceutical active ingredients, aporphylloid alkaloids and their derivatives, and application fields in the development of antifungal drugs, so as to reduce adverse reactions, increase efficacy, and reduce The effect of dosage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
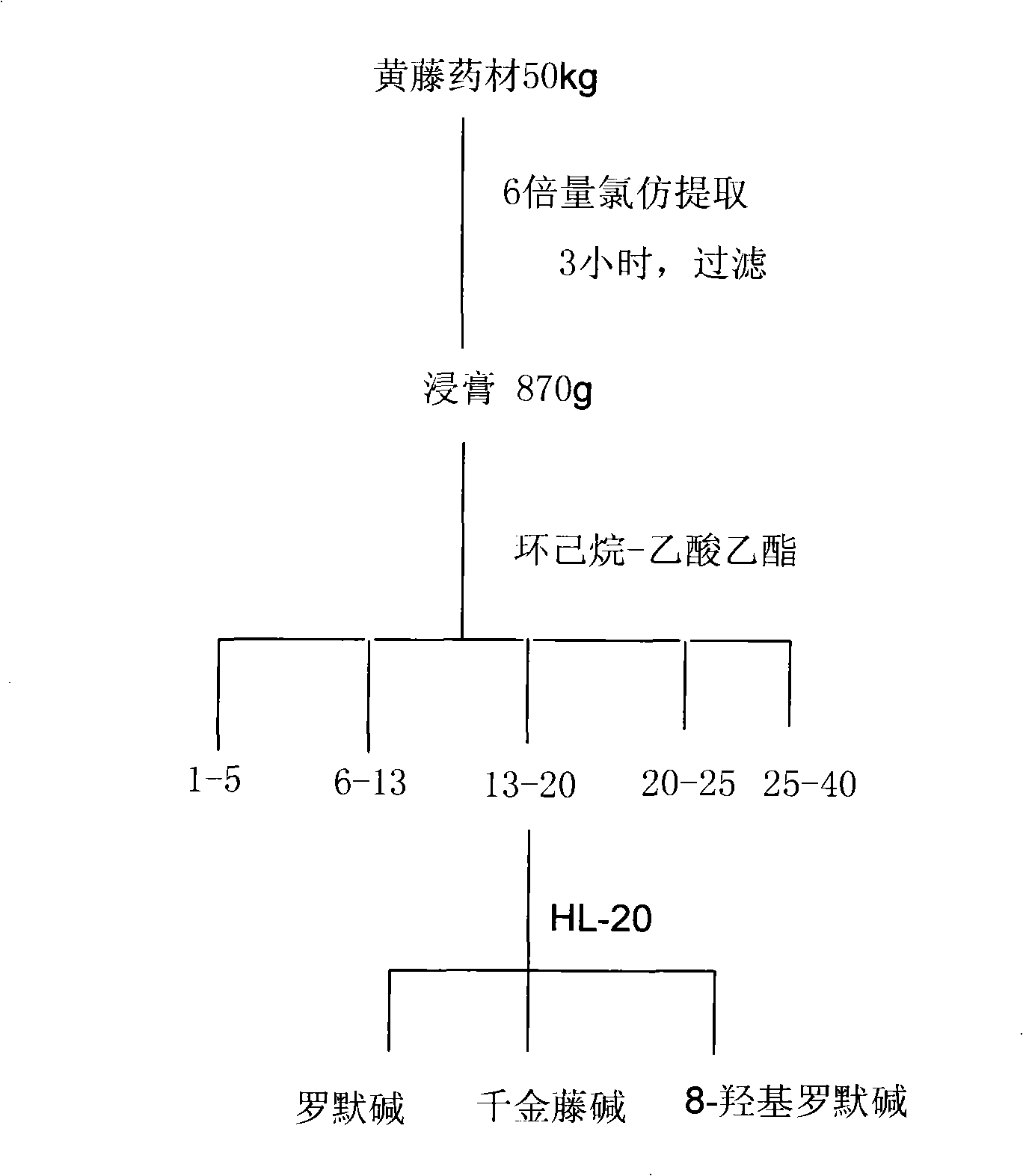
[0021] Example 1: Extraction and separation of monomeric alkaloids 1-III from Huangteng.
[0022] Take 50 kg of fresh yellow vine (Fibraurea recisa Pierre.), crush it, add 10 times the amount of chloroform, stir and extract at room temperature for 6 hours, filter, and recover the solvent from the filtrate under reduced pressure to obtain 470 g of yellow extract.
[0023] Dissolve this extract in an appropriate amount of acetone and adsorb it on about 600g of diatomaceous earth, separate it by 5000g silica gel column chromatography, and use cyclohexane-ethyl acetate (100:0-100:30) gradient elution, each fraction accepts 1000mL. The solvents of each fraction were recovered under reduced pressure, and after checking by thin-layer chromatography (TLC), similar fractions were appropriately combined. The combined fractions with antifungal activity were purified by repeated silica gel column chromatography and Sephadex HL-20 chromatographic column separation (methanol or acetone elu...
example 2
[0024] Example 2: Physicochemical and Spectroscopic Data of Monomeric Compounds.
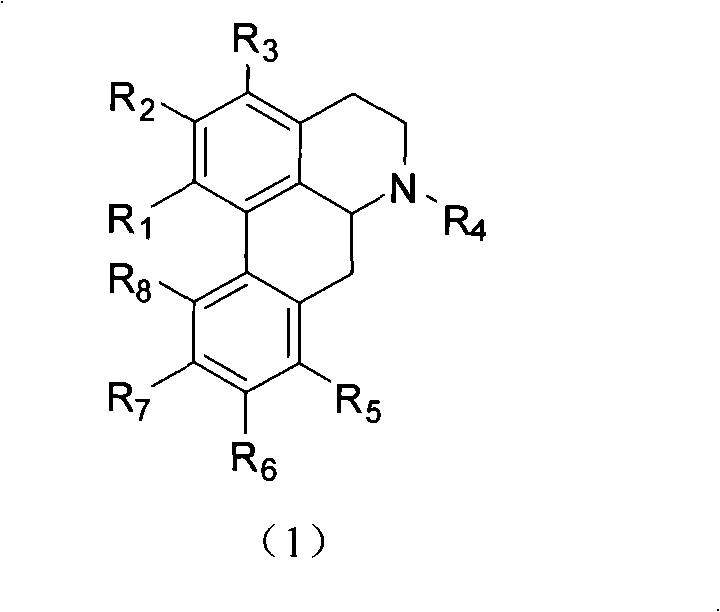
[0025] Romer's base: pale yellow blocky crystal (cyclohexane), potassium iodide reagent reaction is positive, melting point mp81 ~ 82 ℃. MS m / z 279 (M + ), 243, 219. 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 , δ): 6.56 (1H, s, 3-H), 2.72~3.20 (a total of 7H, m, 4, 5, 7-H 2 , 6a-H), 2.61 (3H, s, N-CH 3 ), 5.93, 6.08 (each 1H, s, -OCH 2 O-), 7.21-7.34 (3H, m, 8, 9, 10-H), 8.07 (1H, d, J=8.4Hz, 11-H). 13 C-NMR (CDCl3 , δ): 142.6 (s, C-1), 146.7 (s, C-2), 107.4 (d, C-3), 126.6 (s, C-3a), 29.1 (t, C-4), 53.5 (t, C-5), 62.0 (d, C-6a), 34.6 (t, C-7), 135.4 (s, C-7a), 127.3 (d, C-8), 127.5 (d, C- 9), 128.2(d, C-10), 128.6(d, C-11), 131.1(s, C-11a), 116.4(s, C-1a), 126.9(s, C-1b), 100.7( t,-OCH 2 O-), 43.8 (q, N-CH 3 ).
[0026] 8-Hydroxyromer's base: Light yellow blocky crystals (methanol), positive for potassium iodide reagent, melting point 219.0-221.0°C. MS m / z295 (M + ), 265, 169, 114. 1 H-NMR (CDCl 3 , δ): 6....
example 3
[0028] Example 3 Antifungal activity of aporphyrin alkaloids in vitro
[0029] 1. Experimental materials
[0030] 1.1 Test drug
[0031] 8-Hydroxyromer's base, Stephanine, romer's base: monomeric compounds extracted and isolated from Huangteng.
[0032] Fluconazole: Shaanxi Zhonglin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., batch number 20070309.
[0033] Dimethyl sulfoxide: Shanghai Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd., batch number W20040422.
[0034] 8-Hydroxyromer's base, stepherine, and romer's base were prepared with dimethyl sulfoxide to a concentration of 2560 μg / ml, and fluconazole was prepared with sterile water for injection to a concentration of 64 μg / ml. Store at 20°C. Before the experiment, the drug was taken out in a 40°C water bath to melt, mixed well, and the pharmacodynamic test was carried out respectively.
[0035] 1.2 Experimental strains
[0036] Candida albicans strains: standard strain (ATCCY0109) provided by the Second Military Medical University, clinical strains (28, 94...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com