Novel method for extracting and purifying beer malt root phospholipase D
A technology of phospholipase and a new method, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, hydrolytic enzymes, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve unseen problems and achieve the effect of high enzyme activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] : The crushing treatment of beer malt root
[0046] An appropriate amount of malt root is crushed through an 80-mesh sieve, then a small amount of quartz sand is added to the mortar for mechanical grinding for 15 minutes, and then compound enzymes (1.0% cellulase and 0.6% pectinase) are added at pH 5.5, 40 Under the condition of ℃, enzymatic hydrolysis for 4 hours to break the cell wall to obtain the sample to be separated and purified.
Embodiment 2
[0047] : Extraction and separation of phospholipase D
[0048] The sample after the wall breaking treatment was added with a material-to-water ratio of 1:11, extracted in water for 24 hours at 20°C and pH 5.5, centrifuged, the supernatant was taken, and 1:4 alcohol was added for precipitation. Leave it for 3 hours, centrifuge to remove the supernatant, and harvest the extract-like precipitate.
Embodiment 3
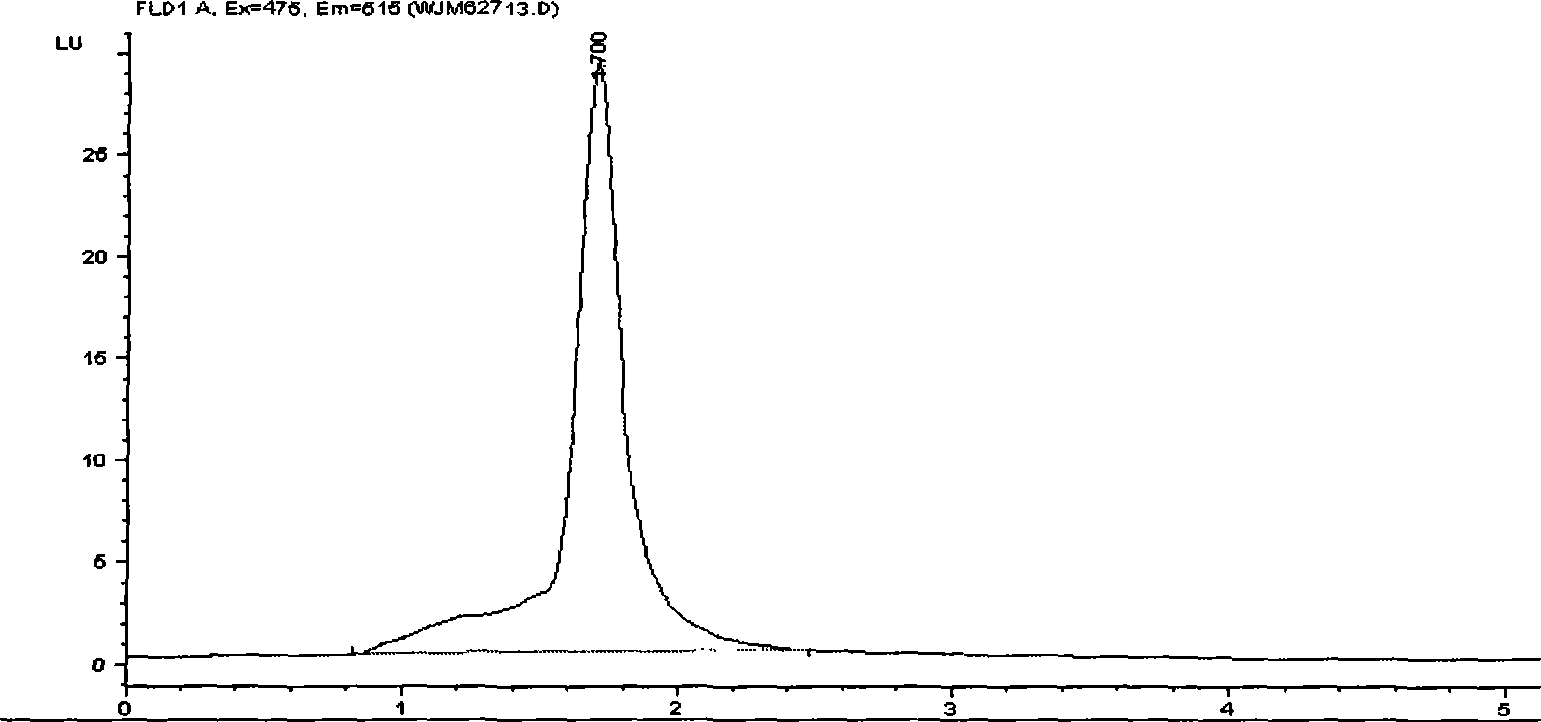
[0049] : Purification of Phospholipase D
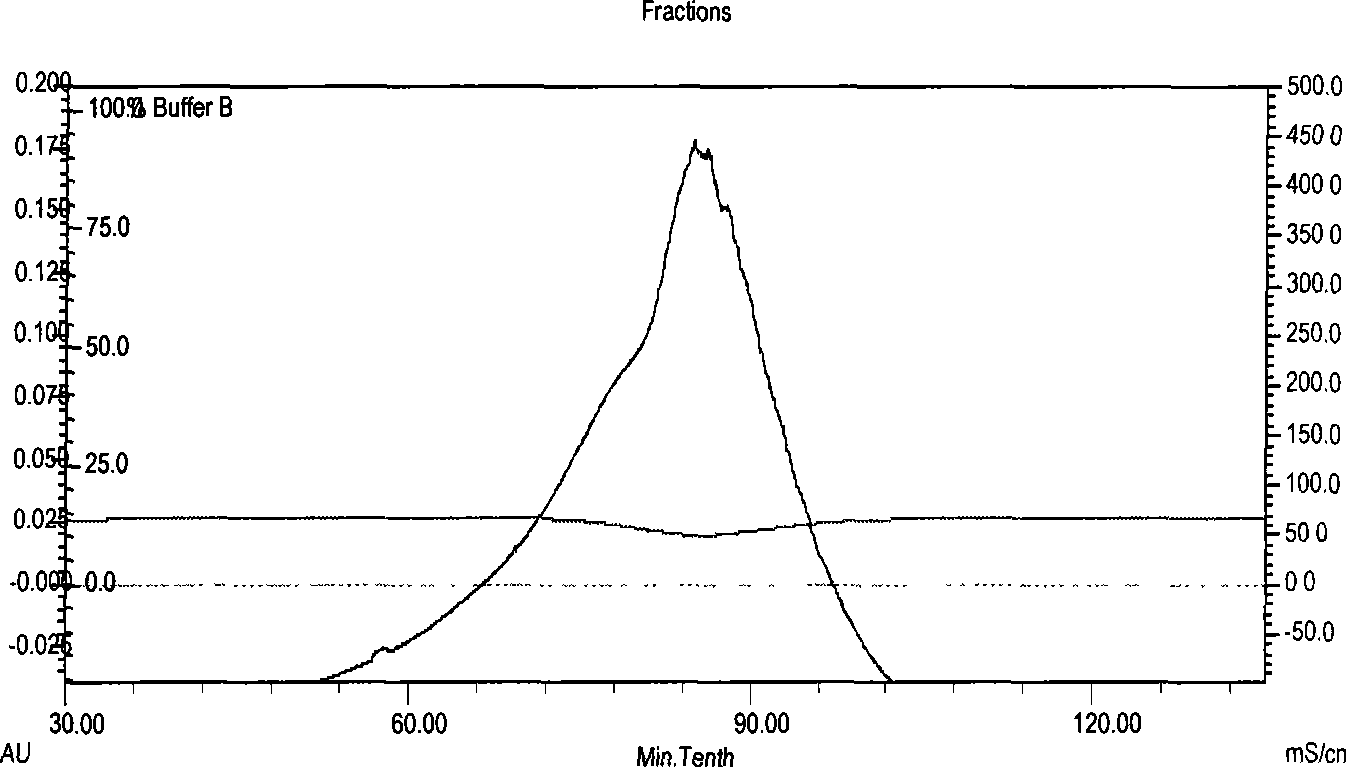
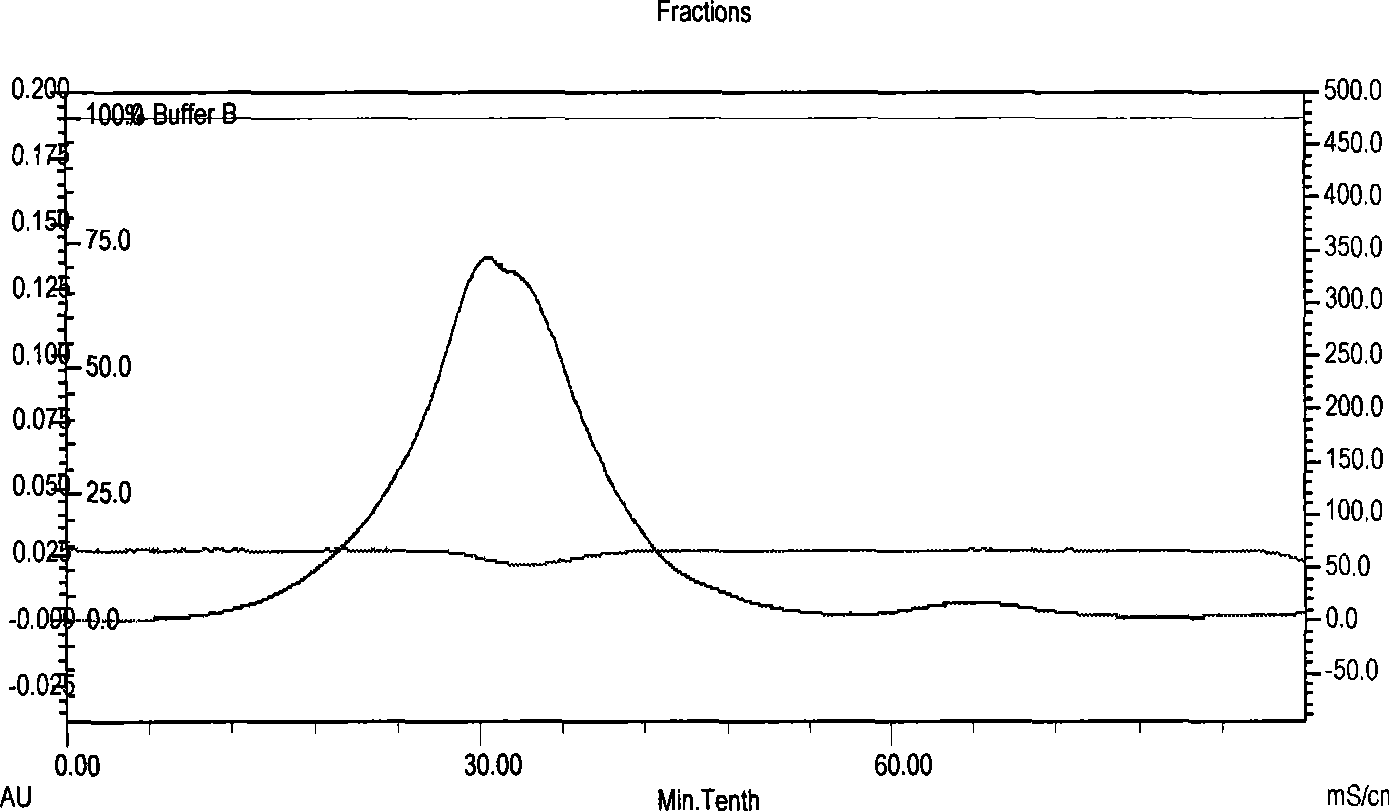
[0050] The invention adopts epichlorohydrin to activate the carrier and the coupling ligand. Take Sepharose 4B with a precipitation volume of 10mL in a G2 funnel, filter it to semi-dry, first rinse with about 100mL 0.5mol / L NaCl solution, and then wash with 100mL distilled water to remove the protective agent and preservative therein. Drain about 6g semi-dry product, put it in a 50mL Erlenmeyer flask, add 6.5mL 2mol / L NaOH, 2mL epichlorohydrin and 15mL 56% dimethyl sulfoxide, mix well, shake gently at 40°C for 2 hours, then transfer the gel to the G2 funnel, rinse with distilled water to remove excess reagent, and finally use about 100mL 0.2mol / L Na 2 CO 3 Wash with pH 9.5 buffer. Conjugation experiments were then performed as soon as possible. Transfer the activated Sepharose 4B to the Erlenmeyer flask. With 10mL 0.2mol / L Na 2 CO 3 , 2 g of phosphatidylcholine was dissolved in a pH9.5 buffer, and then transferred to a Erlenmey...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com