Method of stabilizing silica-containing anionic microparticles in hard water
A technology of silica and colloidal silica, applied in the fields of silica, chemical instruments and methods, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve problems such as process performance changes and product quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] This example provides a recipe for preparing synthetic dilution water with varying hardness. Unless otherwise specified, this dilution water will be used in the following examples. From any standard chemical supplier, such as Aldrich and Fischer Scientific, reagent grade chemicals such as calcium chloride, magnesium sulfate and sodium bicarbonate can be obtained and can be used without further purification.
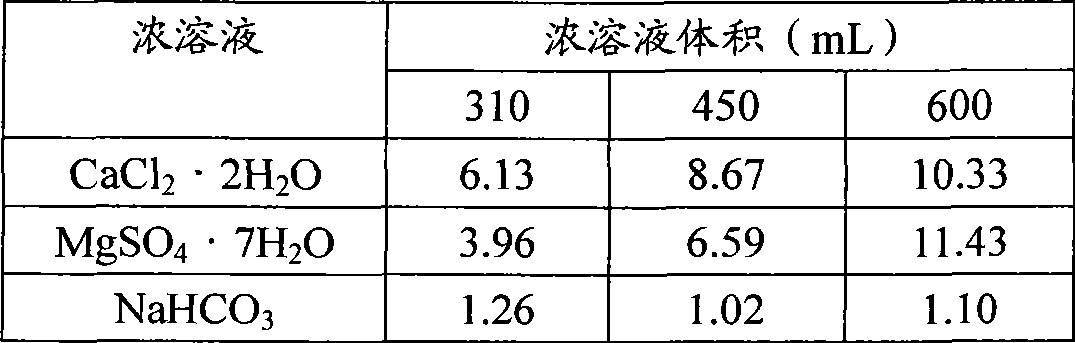
[0108] Use deionized water to prepare CaCl with a concentration of 0.377M 2 ·2H 2 O solution. Similarly, use deionized water to prepare MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O and NaHCO 3 The concentrated solution to produce the following molar concentrations of 0.187M and 0.550M, respectively. These "slurry" solutions are then used to prepare 1 liter of synthetic diluted hard water of the specified hardness.
[0109] Table 2
[0110]
[0111] The representative hardness reducing additives used in the following examples are listed in Table 3.
[0112] table 3
[0113] Representative additive...
Embodiment 2
[0117] The anionic particle product used in this example is a colloidal silica product, hereinafter referred to as CS-A, available from Nalco Company, Naperville, IL. The product is characterized by 11.7% silica, 10.48 product pH, 38.8% S value and 988m by weight 2 / g of surface area. Use synthetic dilution water with a hardness of 310 ppm based on calcium carbonate to dilute the product. The turbidity of dilution water with a hardness of 310 ppm is 0.500 NTU and the pH is 8.64. Place the water in a beaker with a magnetic stir bar. Add CS-A to the water, mix for 5-15 seconds, and then transfer to the sample holder of the Hach 2100AN Turbidimeter. Record the turbidity, NTU, at the indicated time interval. A Mettler Toledo MP220 pH meter with a standard composite electrode was used to measure the pH of the diluted solution. The pH and turbidity are measured at room temperature, that is, at 20°C. The results are summarized in Table 4.
[0118] Table 4
[0119]
[0120] As shown in ...
Embodiment 3
[0122] The anionic particle product used in this study is the product in Example 2, CS-A. Use synthetic dilution water with a hardness of 450 ppm based on calcium carbonate to dilute the product. The turbidity of dilution water with a hardness of 450 ppm is 0.112 NTU and the pH is 8.80. Place the water in a beaker with a magnetic stir bar. Add CS-A to the water, mix for 5-15 seconds, and then transfer to the sample holder of the Hach 2100AN Turbidimeter. Record the turbidity, NTU, at the indicated time interval. A Mettler Toledo MP220 pH meter with a standard composite electrode was used to measure the pH of the diluted solution. The pH and turbidity are measured at room temperature, that is, at 20°C. The results are summarized in Table 5.
[0123] table 5
[0124]
[0125] Table 5 shows that in the case of dilution with water having a hardness of 450 ppm as calcium carbonate, the instability starts at a lower dilution rate than when using 310 ppm hard water. When the dilution w...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight-average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| weight-average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| hardness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com