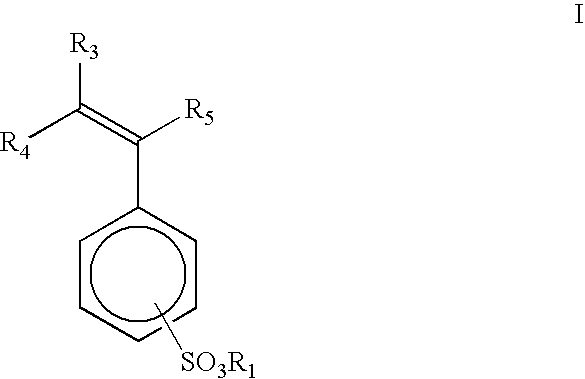
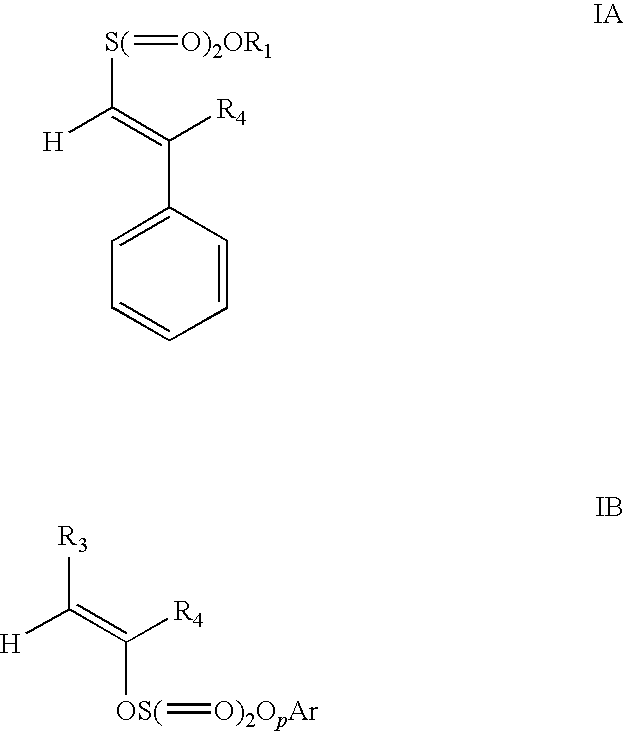
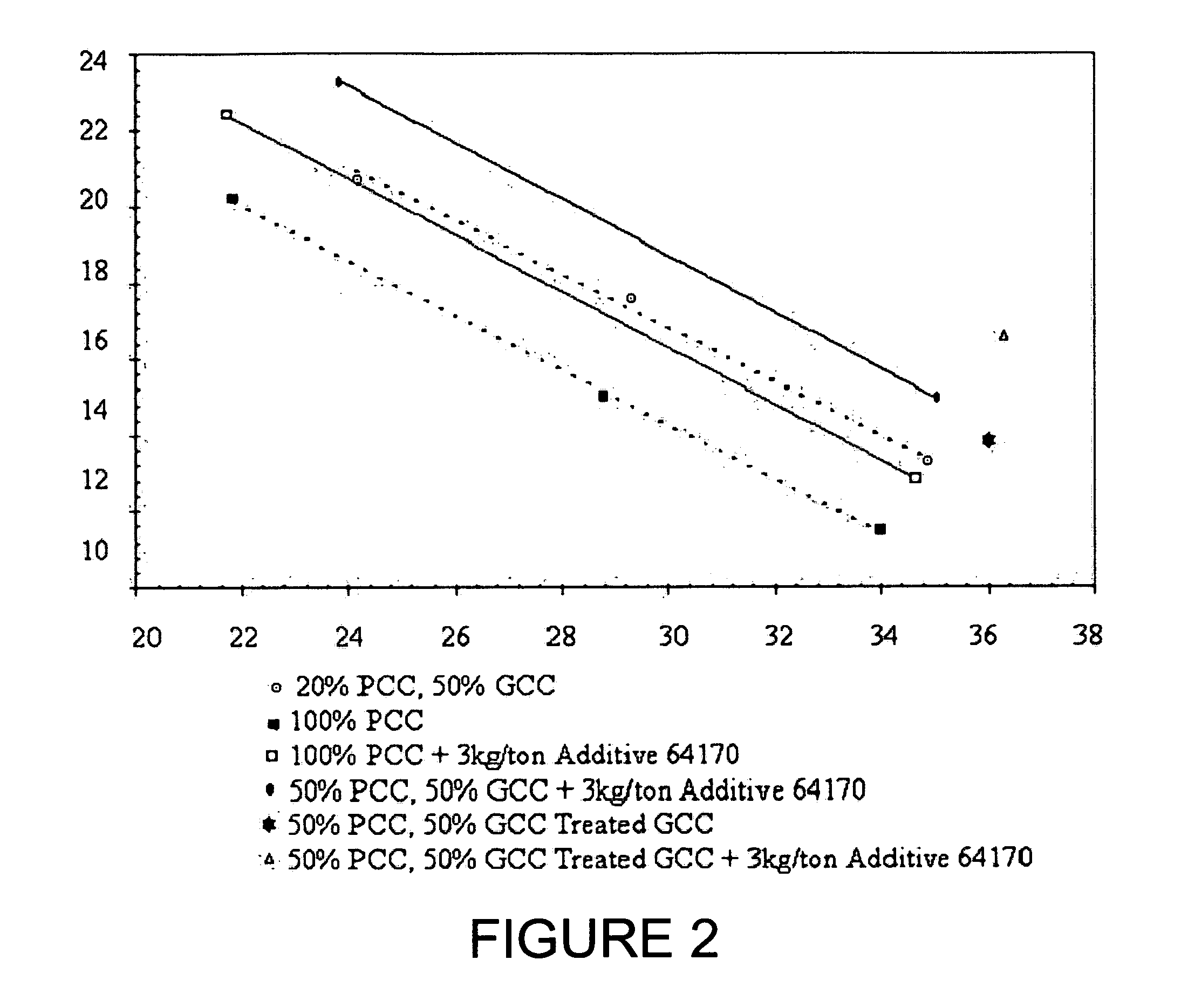
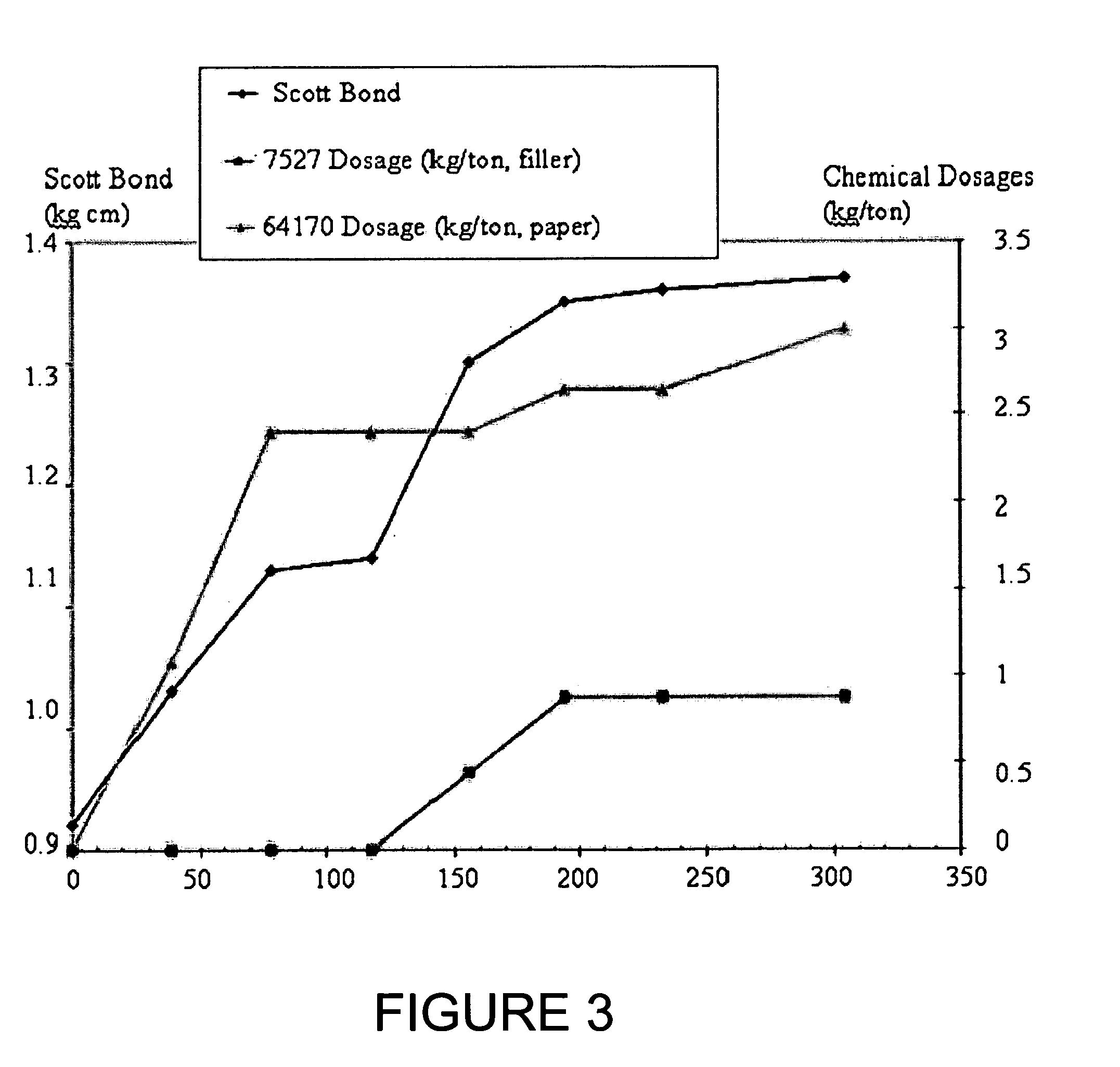
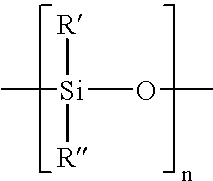
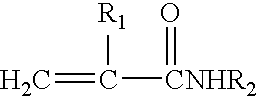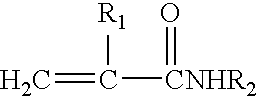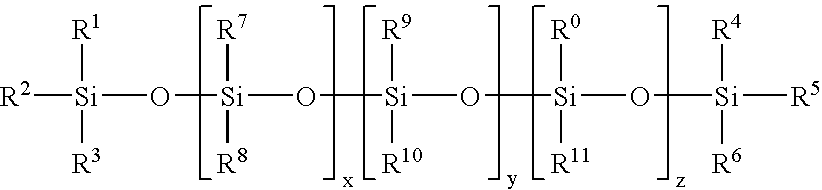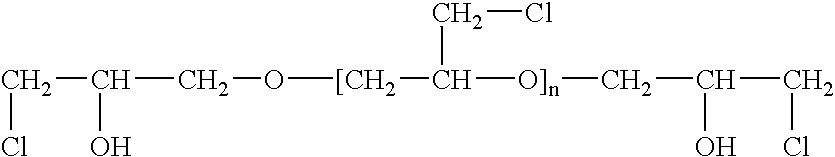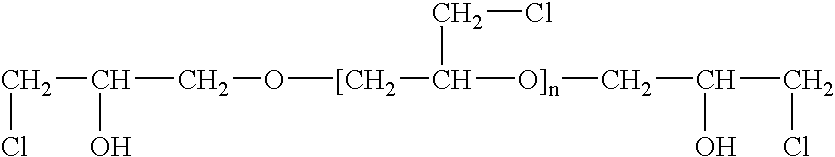Patents
Literature
1101results about "Retention agents addition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bulk enhanced paperboard and shaped products made therefrom
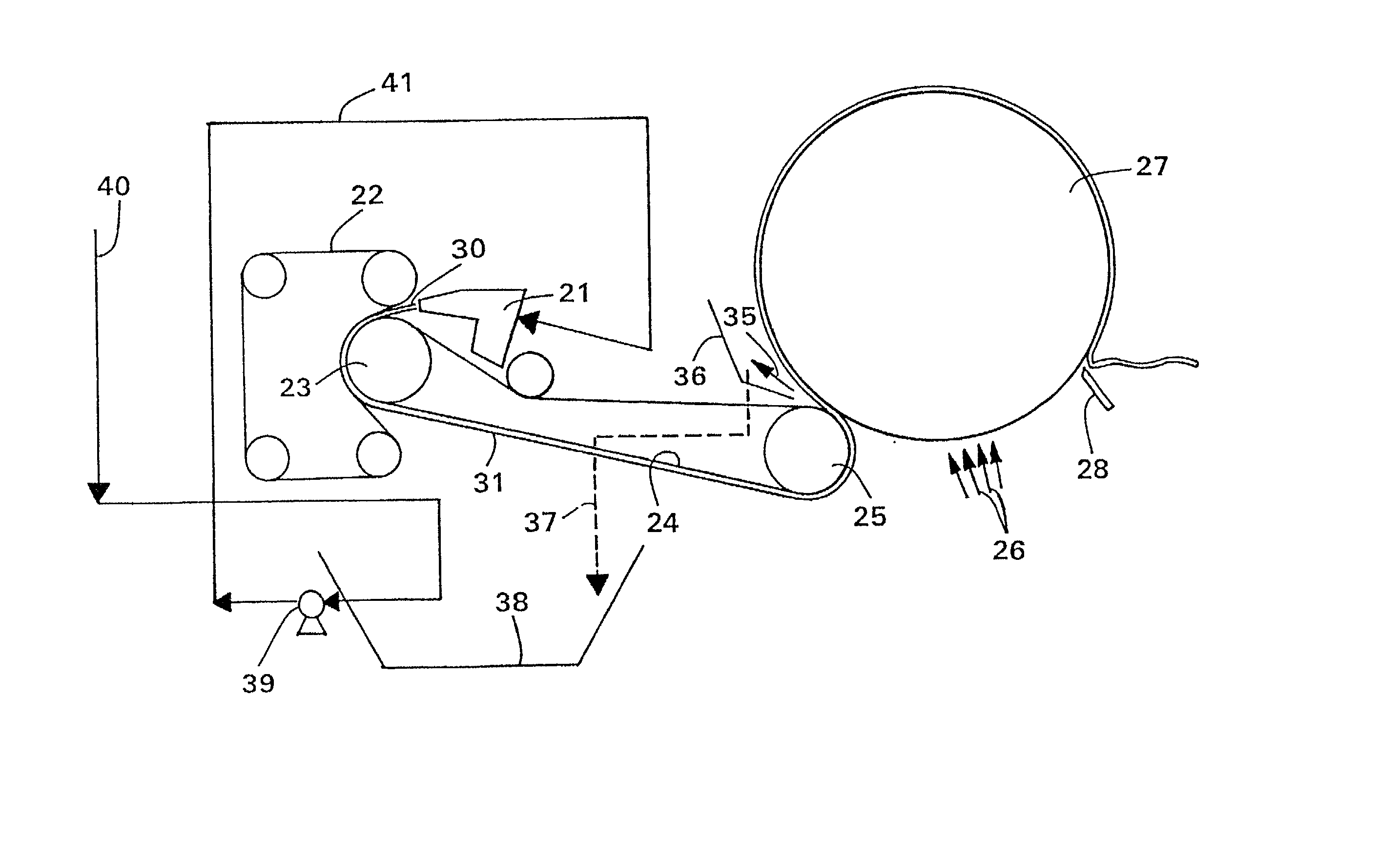
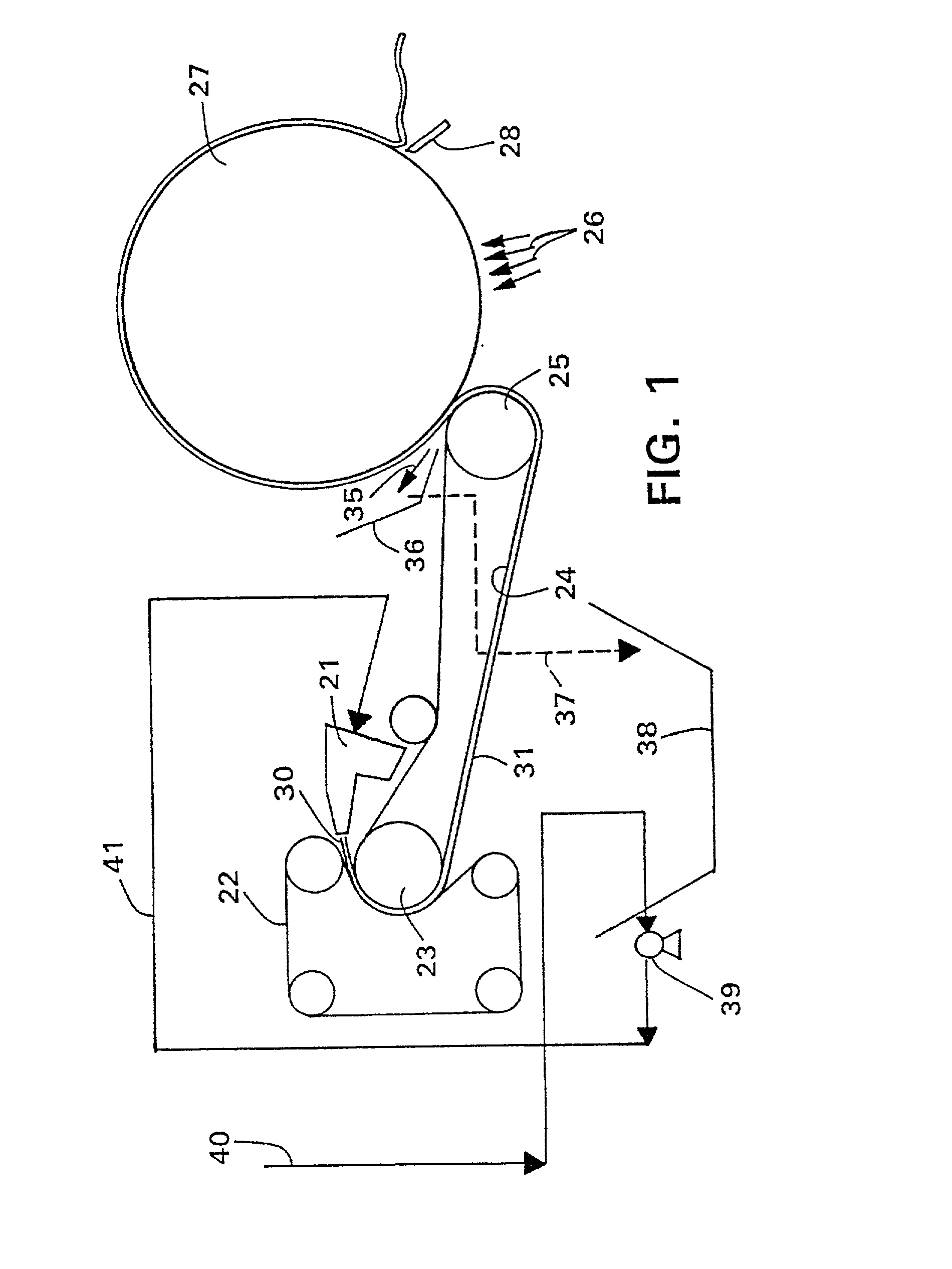
An improved paperboard has been bulk enhanced by retaining a substantial portion of bulk-enhanced additives including expandable microspheres in a suitable distribution within the paperboard. The cellulosic paperboard web has an overall fiber weight (w) of at least 40 lbs. / 3000 square feet and at a fiber density of 3, 4.5, 6.5, 7, 8.3, and 9 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch respectively, has a GM Taber stiffness of at least about 0.00716 w2.63 grams-centimeter / fiber mat density1.63 pounds per 3000 square foot ream at a fiberboard thickness of 0.001 inch, and a GM tensile stiffness of at least about 1890+24.2 w pounds per inch. The high retention of the bulk enhancing additives is believed to result from the incorporation of suitable retention aids. The resulting paperboard has better GM Taber stiffness values and GM tensile stiffness than prior art paperboards. The paperboard also has increased strain to failure and is able to be formed into suitable paperboard containers without loss of integrity. The resulting containers have increased hold times when they contain hot or cold food or drink.
Owner:DIXIE CONSUMER PROD
Method for making hydrophobically associative polymers, methods of use and compositions
InactiveUS6417268B1Cosmetic preparationsSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningHydrophilic monomerSludge
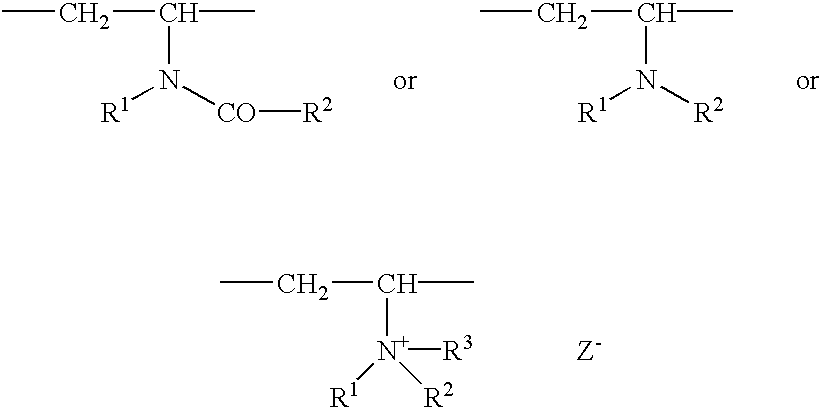
Method for producing an hydrophobically associative polymer is provided which is characterized by forming a monomer solution comprising a surfactant, at least one hydrophobic ethylenically unsaturated monomer, at least one hydrophilic monomer selected from nonionic ethylenically monomers, cationic ethylenically unsaturated monomers, anionic ethylenically unsaturated monomers or mixtures thereof, and water; forming a salt solution comprising a multivalent salt and water; mixing the monomer solution and salt solution to form a mixed solution; and charging the mixed solution with an initiator, thereby polymerizing the monomers to form the hydrophobically associative polymer in a dispersion. Aqueous dispersion containing the hydrophobically associative polymer formed by the method. The aqueous dispersion containing the hydrophobically associative polymer may be used in a paint formulation, in a mobility control fluid useful in enhanced oil recovery, in a secondary or tertiary oil recovery system, in an enhanced oil recovery method, in a cementious composition, in an oil well drilling mud formulation, in a fracturing fluid formulation, in a wastewater treatment system, or in a dewatering sludge system.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
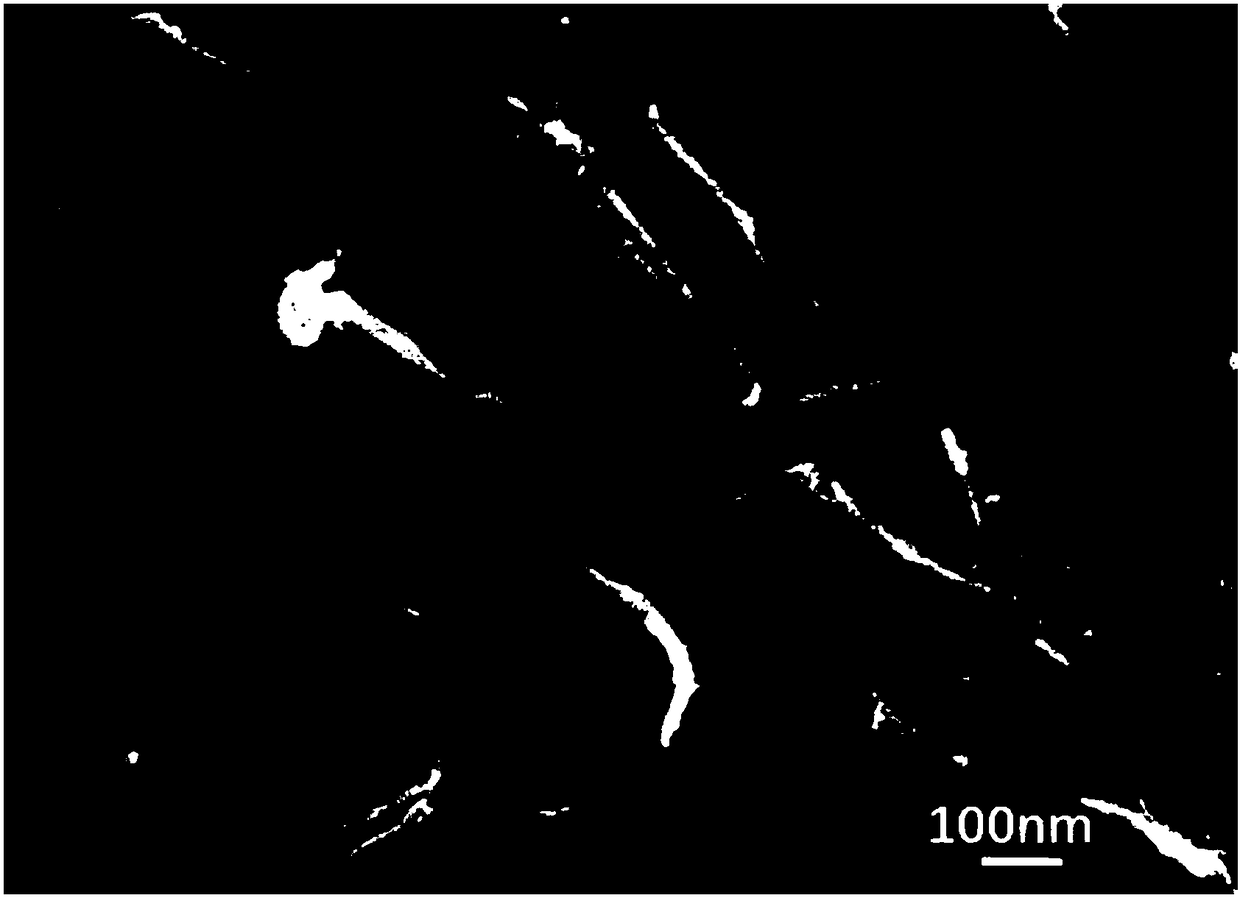
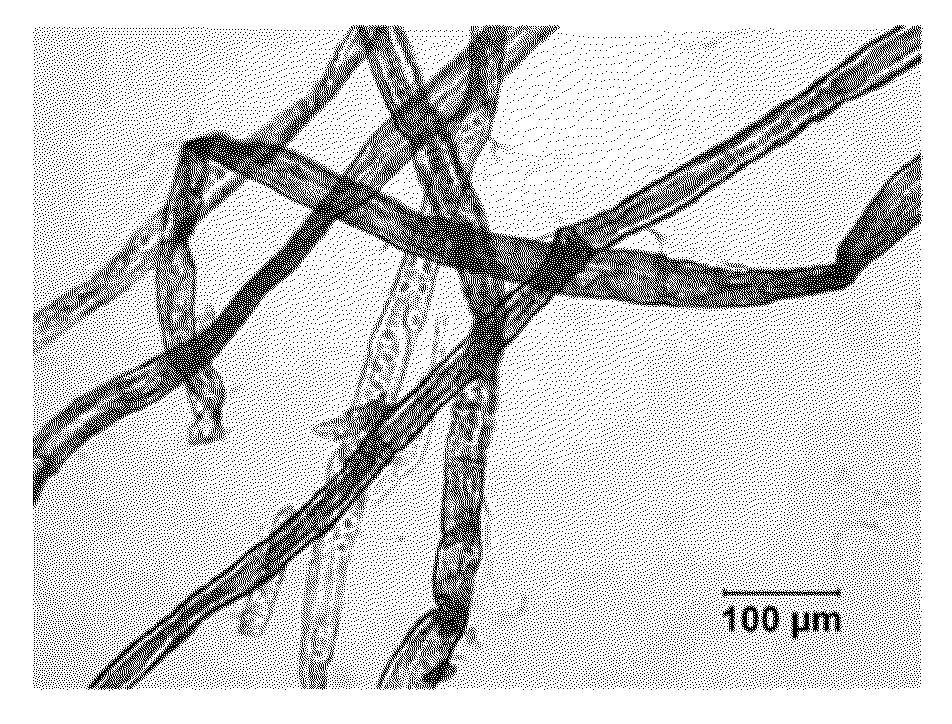
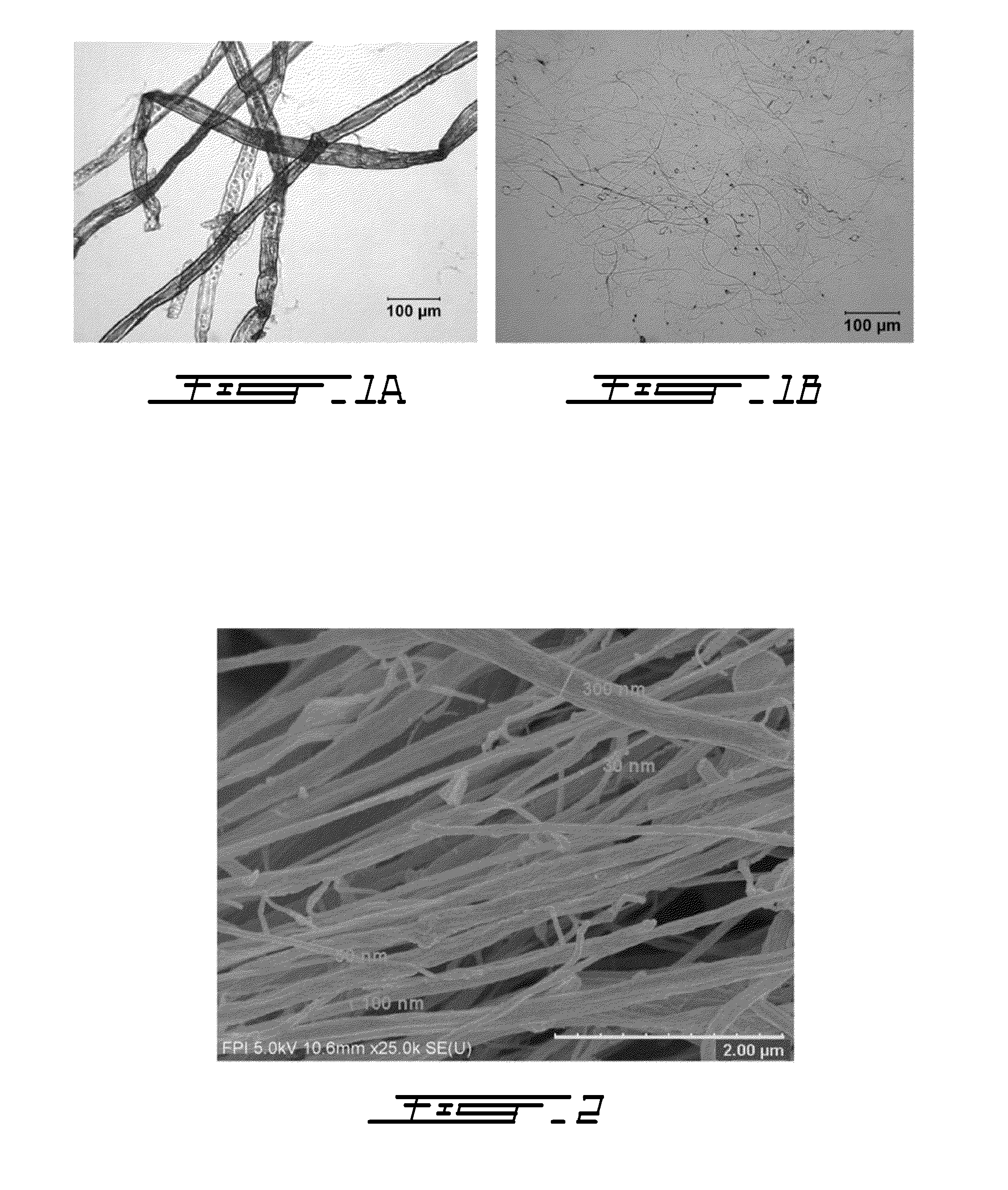
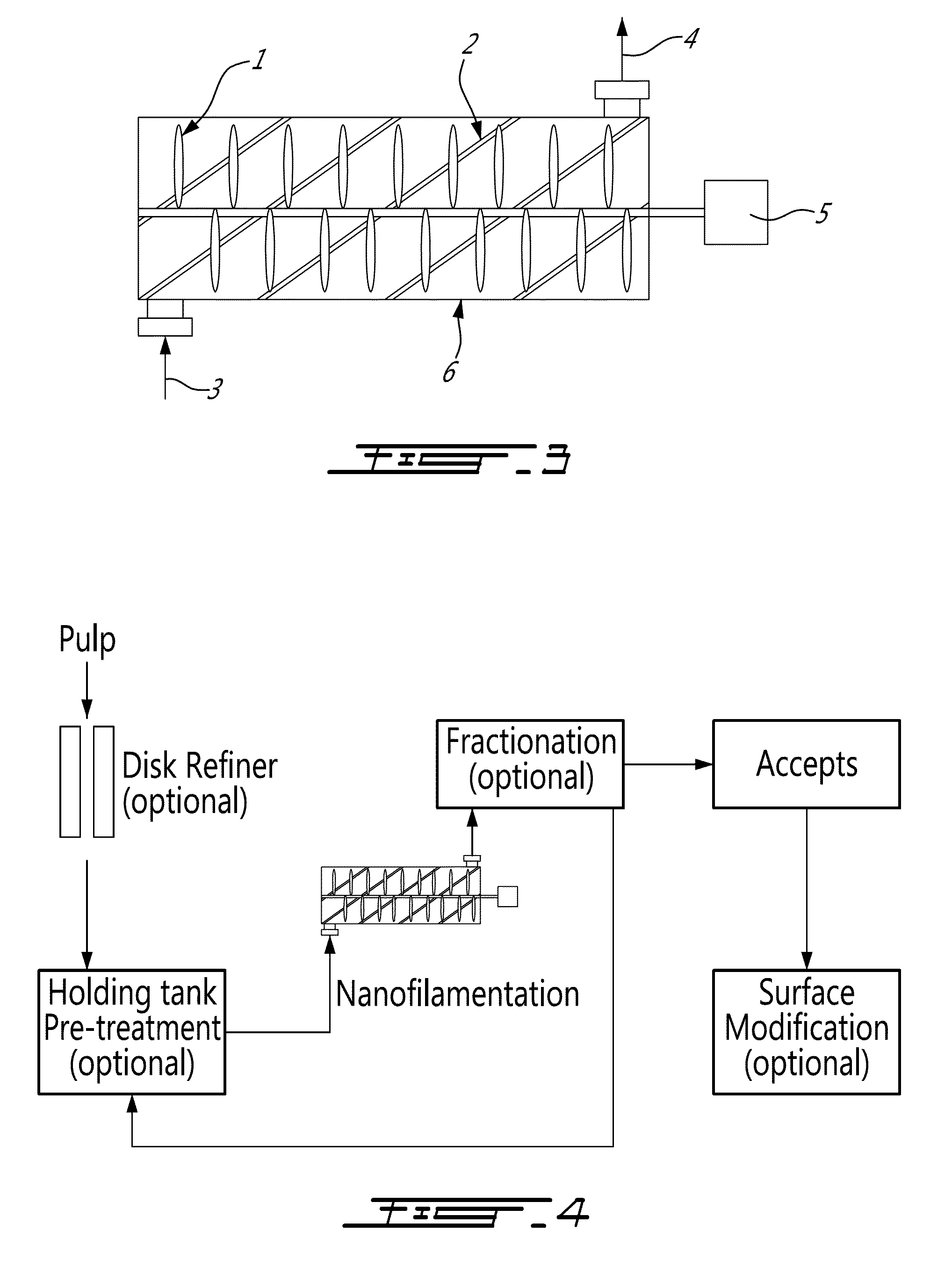
Cellulose nanofilaments and method to produce same
ActiveUS20110277947A1Improve strength propertiesMaterial nanotechnologyNatural cellulose pulp/paperPolymer sciencePaperboard
Cellulose nanofilaments from cellulose fibers, a method and a device to produce them are disclosed. The nanofilaments are fine filaments with widths in the sub-micron range and lengths up to a couple of millimeters. These nanofilaments are made from natural fibers from wood and other plants. The surface of the nanofilaments can be modified to carry anionic, cationic, polar, hydrophobic or other functional groups. Addition of these nanofilaments to papermaking furnishes substantially improves the wet-web strength and dry sheet strength much better than existing natural and synthetic polymers. The cellulose nanofilaments produced by the present invention are excellent additives for reinforcement of paper and paperboard products and composite materials, and can be used to produce superabsorbent materials.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Method for reducing the polymer and bentonite requirement in papermaking
The present invention relates to a method for reducing the polymer and bentonite requirement in papermaking wherein medium and high molecular weight polymers are reacted with bentonite. Further, mechanical shearing of the furnish after polymer addition is not required.
Owner:BASF CORP
Method of using aldehyde-functionalized polymers to enhance paper machine dewatering
InactiveUS20050161181A1Accelerates the dehydration processNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFiberPaper sheet
A method of enhancing the dewatering of a paper sheet on a paper machine comprising adding to the paper sheet about 0.05 lb / ton to about 15 lb / ton, based on dry fiber, of one or more aldehyde functionalized polymers comprising amino or amido groups wherein at least about 15 mole percent of the amino or amido groups are functionalized by reacting with one or more aldehydes and wherein the aldehyde functionalized polymers have a molecular weight of at least about 100,000.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Process for production of paper or board
ActiveUS9605382B2Improve propertiesReinforcing agents additionPaper/cardboardCardboardPulp and paper industry
Owner:KEMIRA OY
Aqueous dispersion polymers
InactiveUS6020422AOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsInorganic compound additionEmulsionWater soluble
Water soluable, aqueous salt solution dispersible polymers and aqueous salt solutions containing dispersed polymers are produced by polymerization of ethylenically unsaturated soluble monomers in an aqueous salt solution in the presence of at least one carbohydrate. The polymers and aqueous salt solutions containing the dispersed polymers are useful for paper making, water clarification and emulsion breaking.
Owner:BETZEARBORN INC
Method of using aldehyde-functionalized polymers to enhance paper machine dewatering
A method of enhancing the dewatering of a paper sheet on a paper machine comprising adding to the paper sheet about 0.05 lb / ton to about 15 lb / ton, based on dry fiber, of one or more aldehyde functionalized polymers comprising amino or amido groups wherein at least about 15 mole percent of the amino or amido groups are functionalized by reacting with one or more aldehydes and wherein the aldehyde functionalized polymers have a molecular weight of at least about 100,000.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Retention and drainage aids
The present invention describes polymeric retention and drainage aids for cellulosic fiber compositions and methods of use of the same.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Swollen starch-latex compositions for use in papermaking
InactiveUS7074845B2High retention rateEasy to drainPigmenting treatmentNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaperboardPapermaking
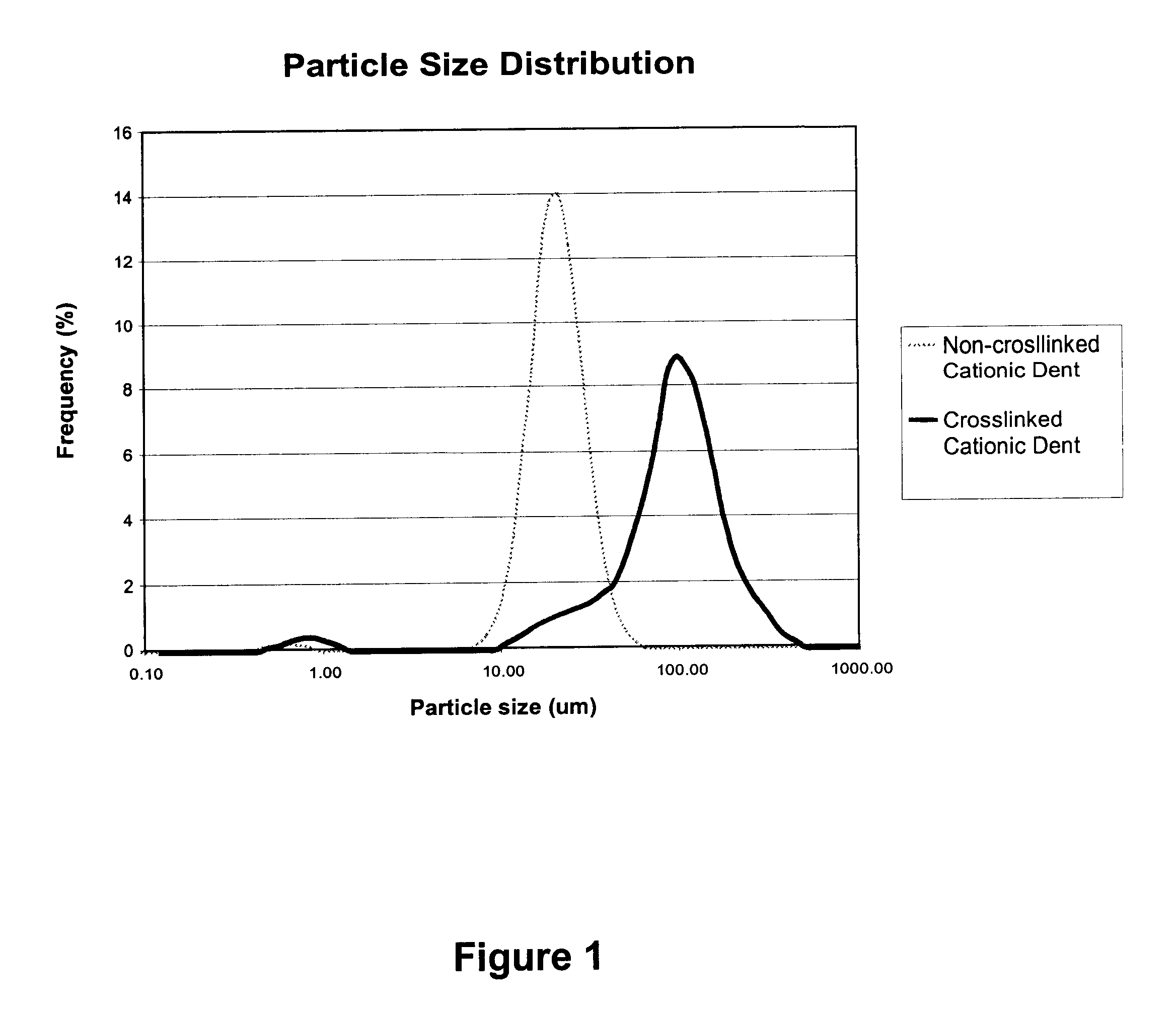
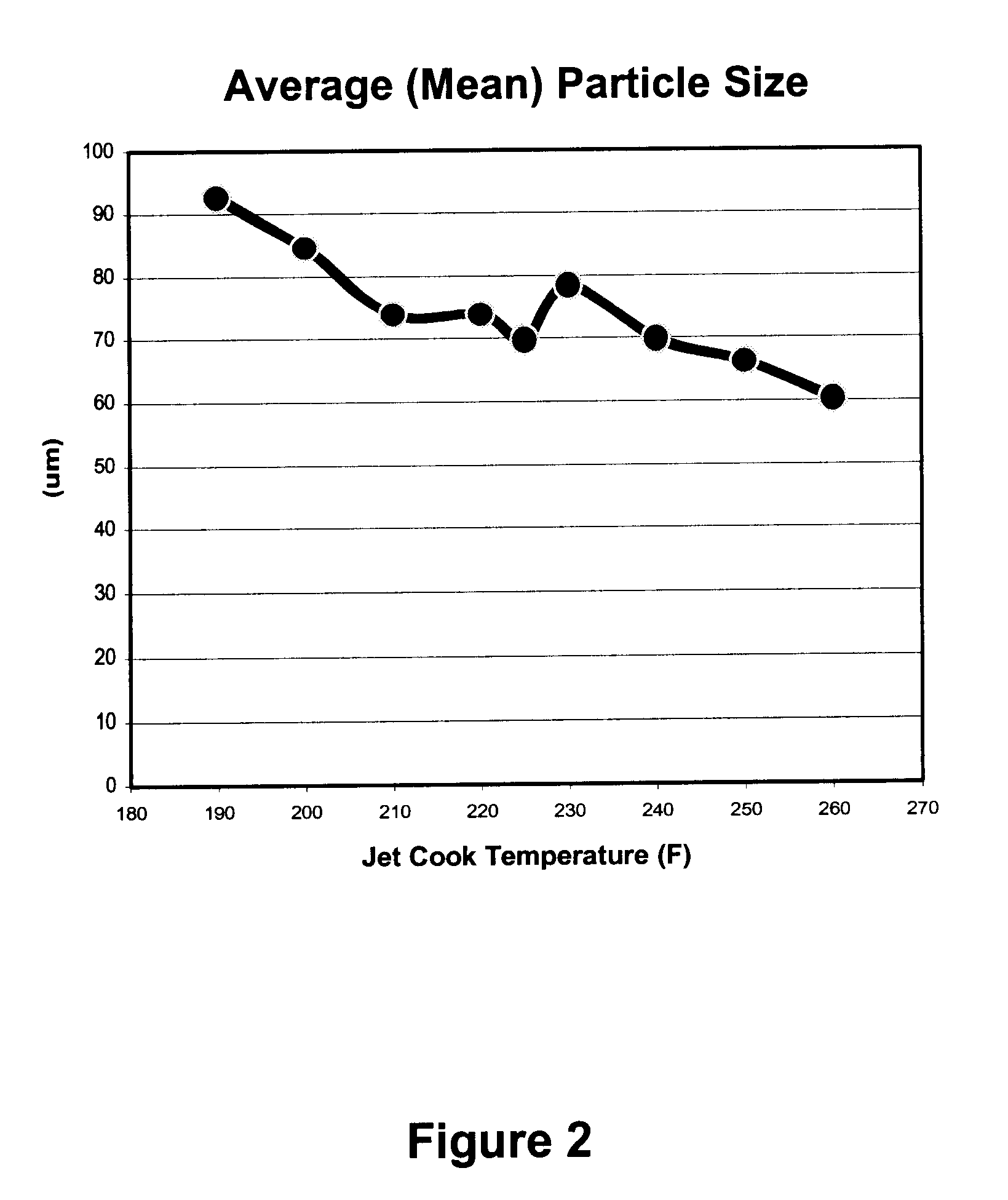
A novel filler treatment comprising the preparation of swollen starch-latex compositions, prepared in the presence or absence of co-additives, and the addition of the said composition to a filler suspension, has been developed. Use of the treated filler during papermaking improves filler retention and produces filled papers where addition of the filler has only a minimal negative effect on strength properties. The swollen starch-latex compositions can be prepared in a batch or jet cooker, or by mixing with hot water under controlled conditions (i.e., temperature, pH, mixing, mixing time) in order to make the starch granules swell sufficiently to improve their properties as a filler additive but avoiding excess swelling leading to their rupture. The swollen starch-latex composition is then rapidly mixed with the filler slurry, preferably in a static mixer, and added to the papermaking furnish at a point prior to the headbox of the paper machine. The starch-latex composition can be used with wood-free or wood-containing furnishes. The treated filler is easily retained in the web during papermaking, improves drainage, and gives sheets having good formation. Sheets made with the treated fillers have higher bonding and tensile strengths than sheets produced using filler treated with either swollen starch alone or latex alone. Retention and drainage are further improved when conventional retention aid chemicals are added to the furnish containing the treated filler. The use of swollen starch-latex compositions could allow the papermaker to increase the filler content of the paper without sacrificing dry strength properties or increasing the amount, and hence the cost, of the retention aid added. The combination of swollen starch and latex could be used as furnish additives in the manufacture of both filled grades and grades that contain no filler such as sack papers and paperboard products.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Method for producing corrugated paper with ultralow gram weight and high strength
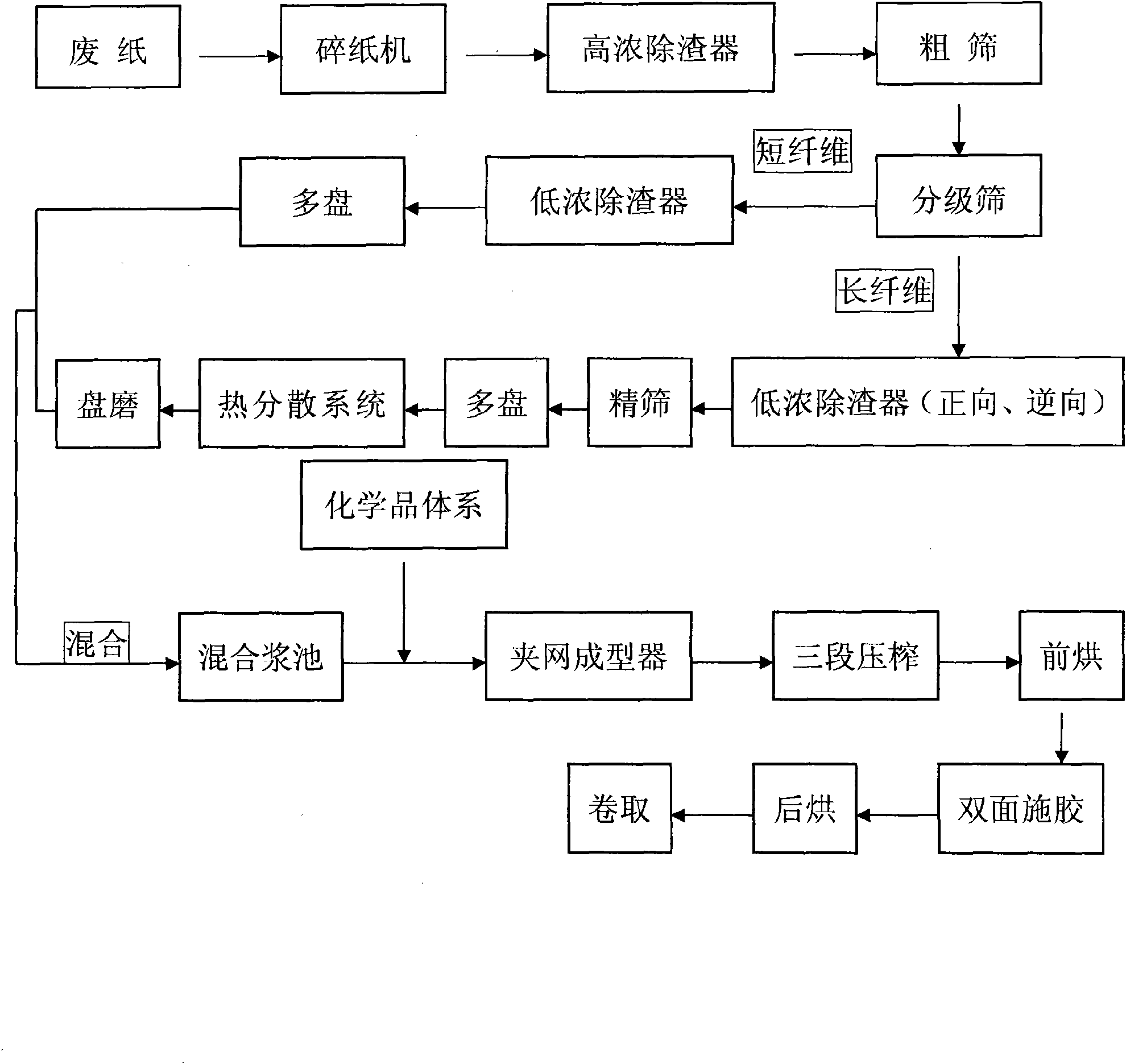
The invention discloses a method for producing corrugated paper with ultralow gram weight and high strength. The method comprises the following technological steps: 1) mixing; 2) addition of water for size degradation to prepare pulp; 3) pulp combination and purification treatment; 4) medium-concentration pulping; 5) addition of a chemical medicine system into the pulp; 6) twin-wire forming, water filtration and paper-making with the pulp; 7) three-stage squeezing dehydration; 8) prebaking and drying; 9) double-faced sizing; 10) postbaking and drying; and 11) coiling. The method utilizes pulping and paper-making process combination and completely utilizes secondary fiber to make the corrugated paper with ultralow gram weight and high strength so as to reduce the gram weight of the corrugated paper, save the fiber amount, reduce the production cost, and simultaneously reduce the energy consumption and the discharge capacity and improve the economic benefit.
Owner:DONGGUAN NINE DRAGONS PAPER IND
Process for the production of paper
InactiveUS6113741AGood effectImprove retentionNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperWater flowCellulose fiber
The invention relates to a process for the production of paper on a paper machine containing a dilution headbox in which a main aqueous flow containing cellulosic fibres and filler is mixed in said headbox with a diluting aqueous flow to form a resulting aqueous flow which is ejected onto a wire and dewatered to form a web of paper, wherein one or more components providing improved retention are introduced into the main aqueous flow and an additive resulting in slower dewatering and / or being selected from non-ionic and anionic organic polymers is introduced into the diluting aqueous flow.
Owner:EKA CHEM AC LTD
Method of increasing retention in papermaking using colloidal borosilicates
InactiveUS6361653B2Additional componentPromote flocculationNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperSilicateChemistry
The invention comprises a borosilicate retention aid composition and a method for improving the production of paper by addition of the borosilicate. The borosilicate may be utilized in conjunction with a high molecular weight synthetic flocculent and / or starch, with or without the addition of a cationic coagulant. The borosilicate material is preferably a colloidal borosilicate. Methods for the preparation of the borosilicate material are disclosed.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Cosmetic compositions containing water-soluble polymer complexes
A composition for treating a keratin based substrate that includes a cosmetically acceptable medium containing a water-soluble interjacent complex. The water-soluble interjacent complex includes a first water-soluble polymer and a second water-soluble polymer formed by polymerizing one or more water-soluble monomers in the presence of the first water-soluble polymer. The water-soluble interjacent complex is characterized in that it forms a solution in water that is free of insoluble polymer particles. The water-soluble interjacent complex is used in a method of treating a keratin based substrate, whereby a cosmetically acceptable medium is applied to the substrate and contains from 0.1-20% by weight of the water-soluble interjacent complex.
Owner:SOLVAY USA
Starch compositions and methods for use in papermaking
InactiveUS6451170B1Drainage and retention property is alteredImprove performanceNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingChemistry
Owner:CARGILL INC
Method of increasing filler content in papermaking
ActiveUS20100126684A1Avoid problemsNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperPapermakingCellulose fiber
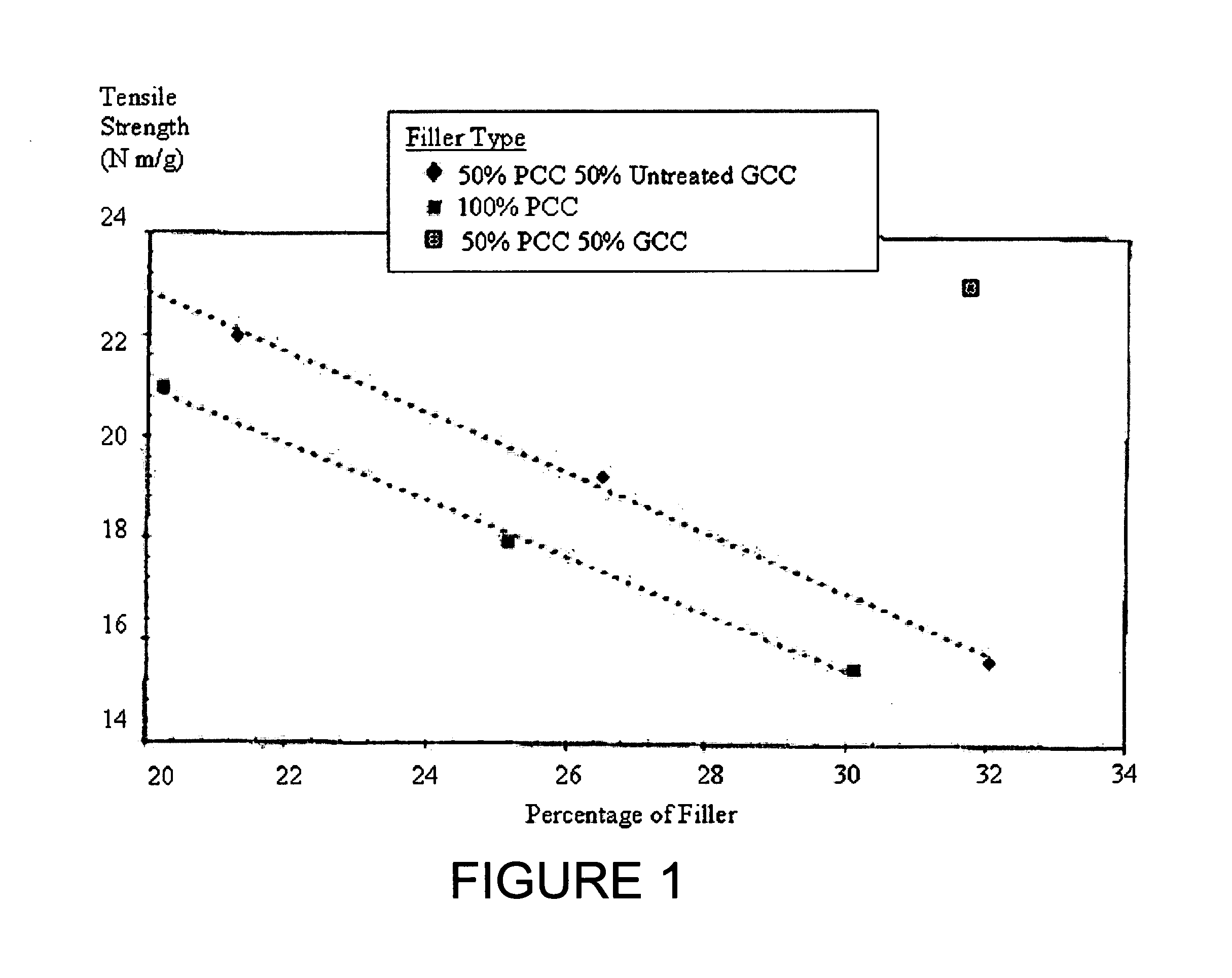
The invention provides a method of producing paper with a higher proportion of mineral filler particles than is otherwise be possible without the expected loss in paper strength. The method allows for the use of the greater amount of filler particles by coating at least some of the filler particles with a material that prevents the filler materials form adhering to a strength additive. The strength additive holds the cellulose fibers together tightly and is not wasted on the filler particles. The method is particularly effective when the filler particles are a PCC-GCC blend and when the GCC particles are coated with the adherence preventing coating.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Soft and durable tissue products containing a softening agent
InactiveUS20060137842A1Reduce hydrophobicityHigh retention rateNatural cellulose pulp/paperMechanical working/deformationCellulose fiberAcid anhydride
Fibrous products containing a durable softening agent are disclosed. The softening agent generally comprises a polysiloxane containing a plurality of first functional groups. In order to improve the wet retention of the softening agent on cellulosic fibers, the softening agent is reacted with a retention agent. The retention agent generally comprises a cationic polymer having a second functional group. In one embodiment, for instance, the softening agent contains epoxy groups or anhydride groups, while the retention agent contains amine groups. Products that may be made according to the present invention include tissue products, wipes and other absorbent articles.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
White craft paper and production method thereof
ActiveCN103437242AImprove retentionHigh whitenessDefoamers additionSpecial paperManufacturing technologyProcess engineering
The invention relates to a white craft paper and a production method thereof, and belongs to the pulping papermaking production field. The white craft paper comprises a surface layer, a core layer, a substrate and surface gluing layers (comprising a right-side gluing layer and a wrong-side gluing layer). The quantitative range of the white craft paper is 125-200g / m<2>, wherein the weight ranges of the surface applying layers, the surface layer, the core layer and the substrate are 2-5g / m<2>, 20-24g / m<2>, 30-35g / m<2> and 75-150g / m<2>. The invention also relates to the making method of the white craft paper which is a gluing squeezing making technology. The white craft paper produced through the making technology has the advantages of high whiteness, high strength, good printing performance, low cost and environmental protection, and can satisfy clients' requirements.
Owner:JIAN GRP
Mold-resistant gypsum panel paper
InactiveUS20120088114A1Improves biocide retentionReduce the amount requiredFibreboardNatural cellulose pulp/paperSlurryGypsum
A mold resistant gypsum panel having improved mold- and fungal-resistance to the gypsum panel facing paper is provided. Mold-resistant gypsum panels include a gypsum core formed from a gypsum slurry that has voids as a result of foaming of the gypsum slurry. A first paper is located on one side of the gypsum core and a second paper opposes the first paper. A first paper comprises at least one liner ply and at least one filler ply. A second paper also comprises at least one liner play and at least one filler ply. The first and second papers may be substantially the same. At least one of the first paper and the second paper also includes a biocide having 75% retention of the biocide. Also included in at least one of the first and second paper are a retention aid and a sizing agent.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Cationization modification method for nano-crystalline cellulose and preparation method of high-strength cigarette paper
ActiveCN102180979ALess investmentHigh strengthReinforcing agents additionPaper/cardboardFiberReaction temperature
The invention belongs to the field of production of special paper, and in particular relates to a cationization modification method of nano-crystalline cellulose and a method for preparing high-strength cigarette paper from the modified nano-crystalline cellulose. Specific to the characteristic of high specific surface area of nano-crystalline cellulose, KOH and a method for adding an etherification reaction accelerant are adopted, the reaction temperature is lowered below 50 DEG C, cationization modification is performed on the nano-crystalline cellulose, and the modified nano-crystalline cellulose has the characteristics of retention and enhancement, so that the modified nano-crystalline cellulose has a wider application prospect; in the method for preparing cigarette paper, softwood pulp is not used, and higher natural air permeability and higher bonding strength of a product are ensured under the condition of reducing broadleaf wood fiber devillicate and fibrillation, so that energy consumption in the production process of paper, in particular in the pulping process, is remarkably lowered, equipment investment of a paper mill is reduced, high-strength cigarette paper is manufactured, the page quality is improved, higher strength and air permeability of the product are achieved, and the requirements on energy conservation and emission reduction are met.
Owner:MUDANJIANG HENGFENG PAPER CO LTD
Fibrous substrate containing fibers and nanofibrillar polysaccharide
A single-layer fibrous substrate comprising, by dry weight compared with the weight of the substrate:between 39.9 and 87.9% natural fibers refined to above 50° SR;between 12 and 60% nanofibrillar polysaccharide; andbetween 0.1 and 4% of at least one retention agent.
Owner:AHLSTROM MUNKSJO OYJ
Opacity enhancement of tissue products with thermally expandable microspheres
InactiveUS20020104632A1Lose weightInorganic fibres/flakesNatural cellulose pulp/paperFiberMicrosphere
The present invention is generally directed to an opaque tissue product and a process for making the same. The tissue products of the present invention comprise thermally expandable microspheres which impart increased opacity to the tissues. The thermally expandable microspheres are added to a fiber furnish during the wet end of a manufacturing process for bath tissue, facial tissue, towels, or the like.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Process for the production of paper
InactiveUS6100322AImprove performanceHigh retention ratePaper/cardboardInorganic compound additionInorganic saltsPolymer science
The invention relates to a process for the production of paper from a suspension of cellulose containing fibers, and optional fillers, comprising adding to the suspension a low molecular weight cationic organic polymer, a high molecular weight cationic or amphoteric polymer and anionic inorganic particles, forming and draining the suspension on a wire, wherein the low molecular weight polymer has a molecular weight below 700,000 and the high molecular weight polymer has a molecular weight above 1,000,000, said polymers being simultaneously added to the suspension. The invention further relates to a polymer mixture in the form of an aqueous dispersion comprising at least one high molecular weight cationic or amphoteric acrylamide-based polymer having a molecular weight above 1,000,000, at least one low molecular weight cationic organic polymer having a molecular weight below 700,000 and at least one water-soluble inorganic salt, the weight ratio of said high molecular weight polymer to said low molecular weight polymer being within the range of from 9:1 to 1:2.
Owner:EKA CHEM AC LTD
Composition Containing Amphoteric Water-Soluble Polymer
InactiveUS20080230193A1Improve filtration rateExcellent peelabilityNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperFlocculationPolymer science
An object of the present invention is to provide a composition excellent in various flocculation performances for various sludge and papermaking systems, especially excellent as a polymer flocculant, and provide a sludge-dewatering agent excellent in dewatering performances for various sludge, especially excellent in flocculationability, as well as a retention aid which can realize a high retention and ensure excellent formation of paper and which is easy to use.A composition is provided, which comprises two or more amphoteric water-soluble polymers in combination shown below, the polymers being obtained by polymerizing a cationic radical-polymerizable monomer and an anionic radical-polymerizable monomer in a presence of a polysaccharide.1. A combination of a polymer satisfying the molar ratio of the cationic radical-polymerizable monomer to the anionic radical-polymerizable monomer (hereinafter referred to as Ca / An) of Ca / An≧1, and a polymer satisfying Ca / An<1, or2. a combination of two kinds of polymers satisfying Ca / An≧1.
Owner:TOAGOSEI CO LTD
Enzymatic pre-treatment of market pulp to improve fiber drainage and physical properties
ActiveUS20170328006A1Increasing pulp drainage and strength propertyQuality improvementMicroorganism/enzyme additionPaper recyclingFiberPulp and paper industry
Owner:ENZYMATIC DEINKING TECH LLC
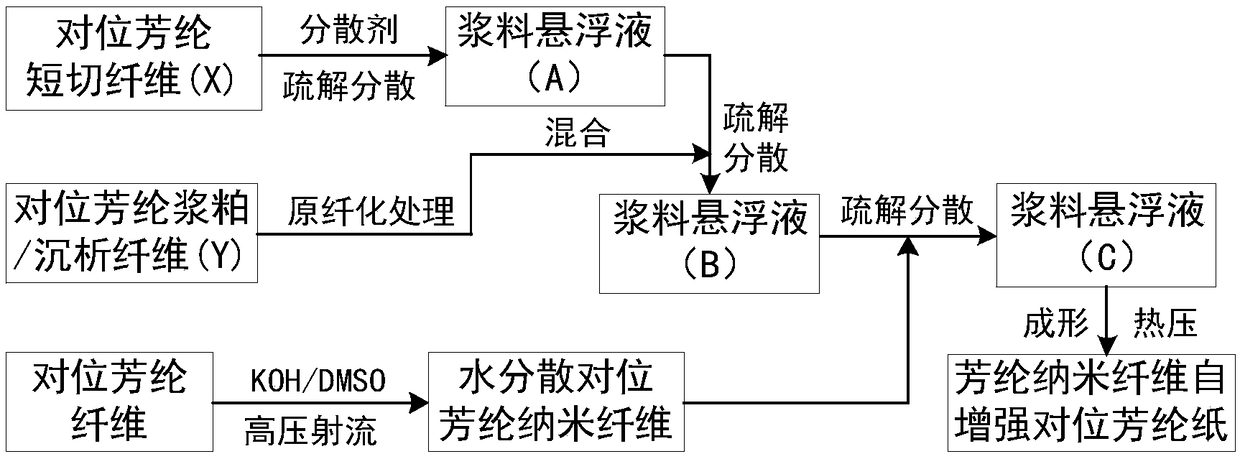
PPTA paper using aramid nanofiber for self-reinforcement and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108265566AUnique nanoscale structureLarge aspect ratioSpecial paperPaper/cardboardNano structuringHigh surface
The invention discloses a PPTA paper using aramid nanofiber for self-reinforcement and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes: utilizing para-aramid paper nanofiber with the advantages of special nano-structure, small fiber diameter, large length-diameter ratio, high surface activity, excellent heat resistance and the like as the self-reinforcement material of para-aramid paper, conducting mixing, defibering and dispersion on aramid chopped fiber, pulp or fibrid and aramid nanofiber to make a uniform suspension, carrying out papermaking shaping, squeezing and drying, andfurther performing hot-pressing on a hot press to obtain aramid paper. The introduced aramid nanofiber enables nanoscale aramid fiber and an aramid nanofilm formed thereby to reach the good interfacefilling, coating and enhancement effects, provides more binding sites for the combination of components, at the same time reduces the pores and holes between components, significantly improves the bonding strength between the aramid paper components, and greatly enhances the mechanical and insulation properties.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hydroxyalkyl cationic guar gum and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN1757827ASolve forming problemsImprove adsorption capacityPaper/cardboardRetention agents additionAlcoholGraft reaction
A process for preparing the cationic hydroxyalkyl guar gum includes such steps as dispersing the raw powder of guar gum in the aqueous solution of low-carbon alcohol, adding high-alkaline catalyst, immersing, adding cationic etherifying agent, cationic graft reaction, adding phase-transfer catalyst and alkoxy etherifying agent, hydro-xyalkylating reaction, neutralizing and filtering. It can be used as the retention aid or filter aid of paper pulp.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Process for improving dry strength and drainage of paper and paperboard
InactiveUS20060162886A1Good drainageImprove dry strengthNatural cellulose pulp/paperSpecial paperCellulosePaperboard
A process is provided of providing glyoxylated polymer additives to a paper making process which brings about improvements in drainage properties of a cellulosic pulp material along with the ability to increase the dry strength of a resulting paper product. The process uses concentrated glyoxal to generate a working solution of a glyoxylated polymer additive which can be generated on site in a paper mill and used within a 24 to 48 hour interval. The ability to glyoxylate polymers in a working solution concentration provides for a more active additive and which can be supplied in a more economical fashion than conventional glyoxylated polymers.
Owner:PARADIGM CHEM & CONSULTING
Manufacture of cellulosic pulp sheets
InactiveUS20150027651A1Natural cellulose pulp/paperPulp properties modificationEthylene HomopolymersWater soluble
A pulp making process in which fibrous cellulosic material is pulped to form an aqueous suspension of cellulosic material, the suspension is drained through a screen to form a pulp sheet and that the pulp sheet is dried to form a dry market pulp, in which a water soluble cationic polymer is added to the suspension as the sole drainage aid wherein the water-soluble cationic polymer is either,i) a copolymer comprising (a) between 1 and 70 mole % (meth) acrylamide and (b) between 30 and 99 mole % (meth) acryloyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride with an intrinsic viscosity between 5 and 9 dl / g; orii) a hydrolysed homopolymer of vinylformamide comprising between 1 and 100 mole % vinyl amine units and having a K value of between 45 and 240.The process of the invention provides improved drainage time and solids content of the dewatered pulp.
Owner:SOLENIS TECH CAYMAN
Epichlorohydrin-based polymers containing primary amino groups used as additives in papermaking
Disclosed is a method for manufacture and application of a polymeric papermaking additive, which can be used in paper manufacture as an agent for improving retention, drainage, product strength and paper machine operation. The additive according to this disclosure is a polymer of epichlorohydrin and contains primary amino groups. Under neutral or acidic conditions these primary amino groups become cationic, which assures good adsorption of the polymer onto anionic fibres and fines of pulps used for production of paper or paperboard. By adsorbing on several fibres or fines, the polymer can increase the retention of fines and fillers. Primary amino groups of this polymer can also form chemical bonds with carbonyl groups of cellulose, lignin and hemicellulose, which are especially abundant in the fibres and fines of mechanical pulps. The cross-linking of fibres and fines by chemical bonds can increase the initial strength of wet web and the strength of rewetted paper. Mechanical pulps contain high negative charge and tend to deactivate many conventional cationic polymers. Because of its high cationic charge and the ability to form chemical bonds with mechanical pulp, novel papermaking additive according to this invention is particularly suitable for improving the retention and the strength of paper made from fibrous pulp suspensions that contain at least a portion of mechanical pulp. If the polymer has a high molecular weight it can be use as a single component retention and strength additive. If the polymer has a relatively low molecular weight, it can be conveniently used as coagulant and can be combined with a high-molecular-weight, low-charge-density polymer that serves as a flocculent.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com