Bridged triphenyl amine compound, and use in electrophosphorescent device
A technology of electrophosphorescence and compounds, which is applied in the field of organic electroluminescent materials, can solve the problems of insufficient luminous efficiency, insufficient rigidity, and insufficient thermal stability of electrophosphorescent devices, and achieve high-efficiency electroluminescent performance and stability Improvement, high thermal stability effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
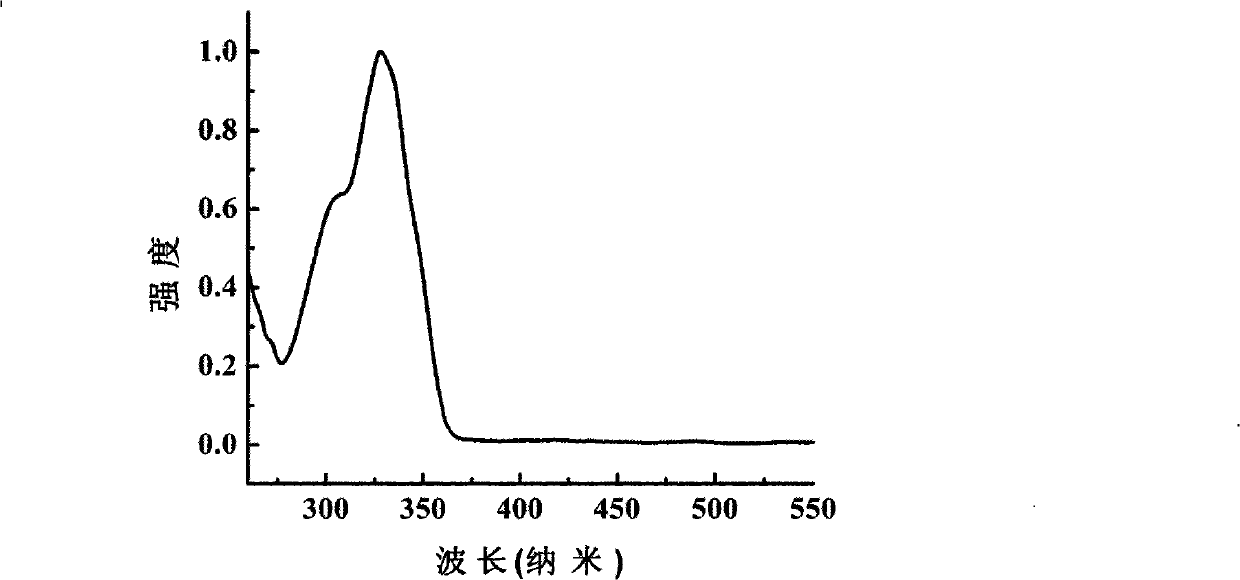
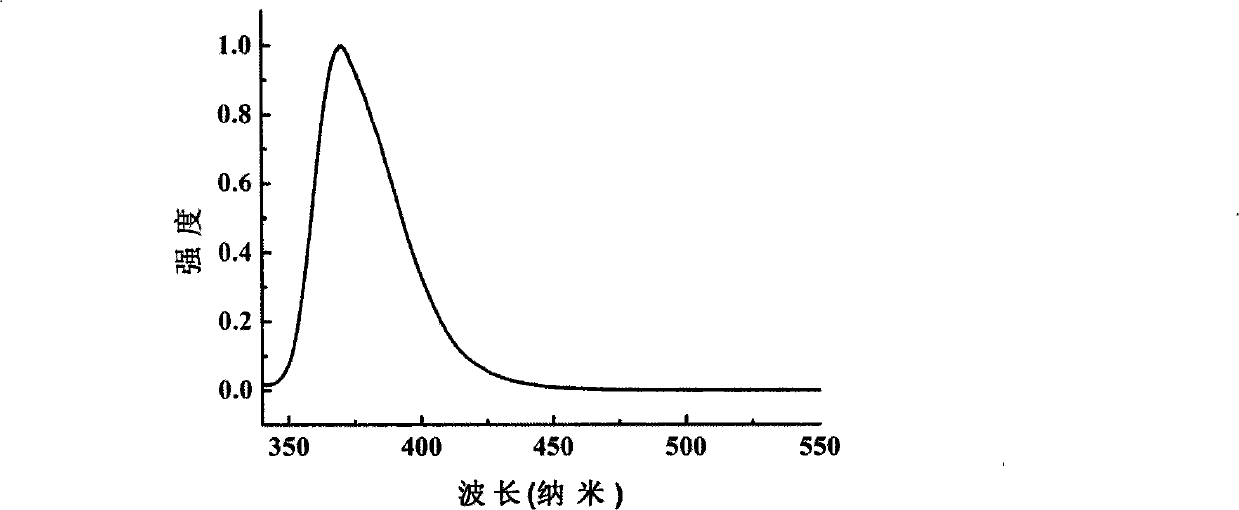
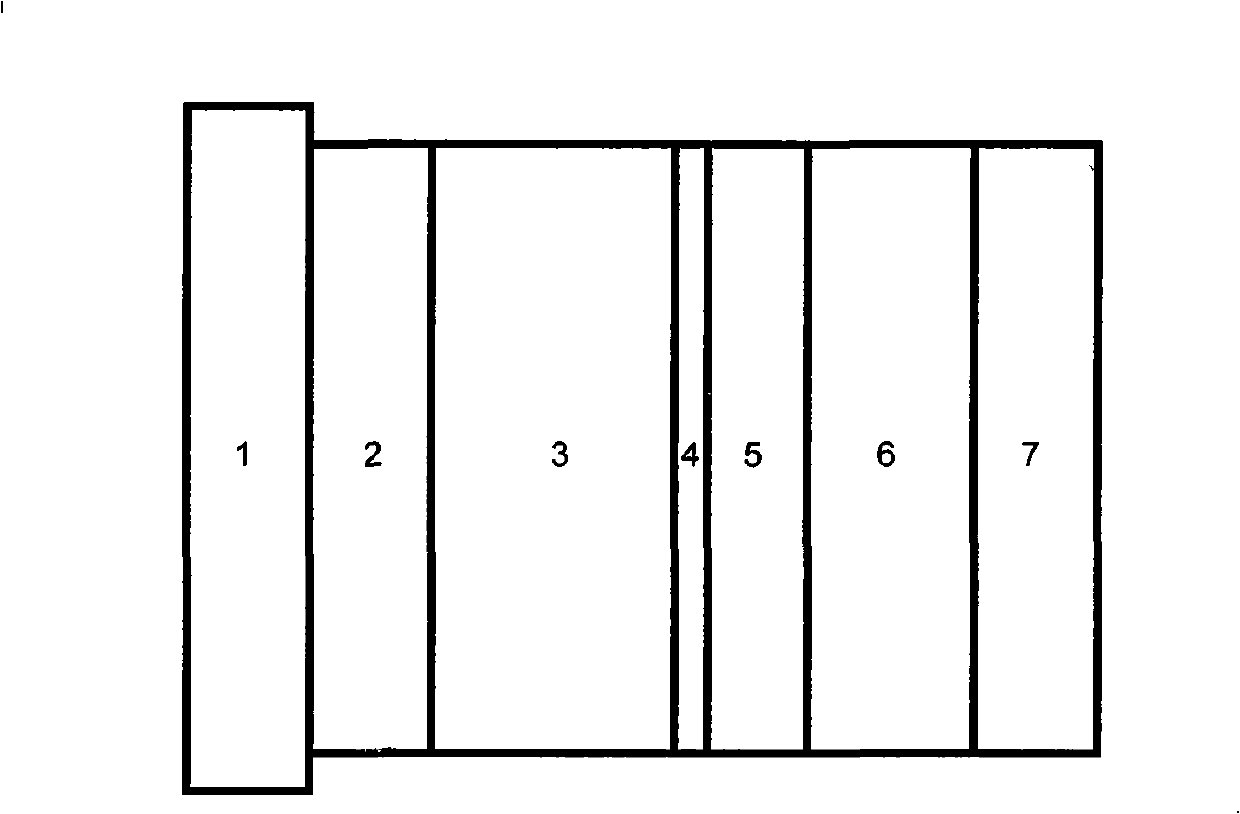
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Preparation of 3,11-bis(triphenylsilyl)-7-tert-butyl-5,5,9,9-tetraphenyl-13b-azinaphthoanthracene (abbreviated as Host1)
[0026]
[0027] 1.4 g of bromobenzene (8.8 mmol) were dissolved in 10 ml of THF in a Schlenk bottle. 3.4ml of n-BuLi (2.6M, 8.8mmol) was dropped into a Schlenk bottle at -78°C, and reacted at -78°C for 1 hour after the drop was completed. 0.83g of dimethyl 2-(diphenylamino)-5-tert-butyl-1,3-isophthalate was dissolved in 10ml of THF and dropped into a Schlenk bottle for 3 hours of reaction. After the reaction was completed, it was quenched with distilled water. extracted with ether, the organic phase was separated, washed three times with water, anhydrous Na 2 SO 4 dry. The organic solvent was spin-dried to obtain a light green solid. The crude product was dissolved in 30ml of glacial acetic acid, heated to reflux at 110°C, and 3ml of concentrated HCl was carefully added dropwise to react for 3h. After the reaction, the solution was poured i...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Preparation of 3,11-bis(triphenylsilyl)-7-tert-butyl-5,5,9,9-tetrakis(p-tolyl)-13b-azanaphthoanthracene (abbreviated as Host2)
[0032]
[0033] Using a method similar to Example 1, the difference is that p-methylbromobenzene is used as a starting material instead of bromobenzene to obtain 3,11-bis(triphenylsilyl)-7-tert-butyl-5, 5,9,9-Tetrakis(p-tolyl)-13b-azinaphthoanthracene, the yield is 47%. 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 , δ): 7.42-7.34(m, 18H), 7.30-7.25(m, 16H), 7.01-6.90(m, 12H), 6.80-6.73(m, 8H), 2.31(s, 6H), 2.25(s , 6H), 1.08(s, 9H); 13 CNMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ,δ):144.04,143.56,143.30,140.15,139.12,136.43,135.65,135.54,134.79,134.39,131.39,129.44,129.13,128.61,128.15,127.89,126.38,125.06,116.96,99.83,56.83,34.55,31.60, 21.29, 21.12. Anal. Calcd. for C 88 h 75 NSi 2 (%): C, 87.88; H, 6.29; N, 1.16. Found: C, 88.36; H, 5.96; N, 0.85. MS (MALDI-TOF) m / z 1201.9 [M + ].
Embodiment 3
[0035] Preparation of 3,11-bis(9-phenylfluorenyl)-7-tert-butyl-5,5,9,9-tetraphenyl-13b-azinaphthoanthracene (abbreviated as Host3)
[0036]
[0037] 0.31 g of 7-tert-butyl-5,5,9,9-tetraphenyl bridged triphenylamine (0.5 mmol), and 0.258 g of 9-phenyl-9-fluorenol (1 mmol) were put into 50 ml round bottom flasks respectively. 10 ml of dichloromethane were added. Carefully add 0.15ml BF 3 ·Et 2 O (1.1 mmol, 7.73M). Reaction at room temperature for 2h. After the reaction was completed, methanol was first added, followed by water to quench, and the organic phase was separated. Column separation with petroleum ether:dichloromethane=2:1 (volume ratio) yielded 0.47 g of white solid with a yield of 86%. Characterization analysis confirmed that the white solid was Host3. 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 , δ): 7.67(d, J=7.2Hz, 4H), 7.27-7.25(m, 6H), 7.19-7.02(m, 24H), 6.99-6.81(m, 16H), 6.74-6.62(m, 4H ), 1.04(s, 9H); 13 C NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ,δ):151.66,151.46,146.86,146.22,146.06,14...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| luminance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com