Culture medium for fermenting pleocidin producing bacteria
A spinosad and culture medium technology, applied in fermentation, microorganism-based methods, bacteria, etc., can solve the problems of limited sources, high cost of raw materials, low fermentation units, etc., to achieve increased fermentation units, foam elimination, and rich sources Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0020] Embodiment 1: Determination of the optimal formulation of the medium of the present invention
[0021] 1): Determination experiment of single carbon source type
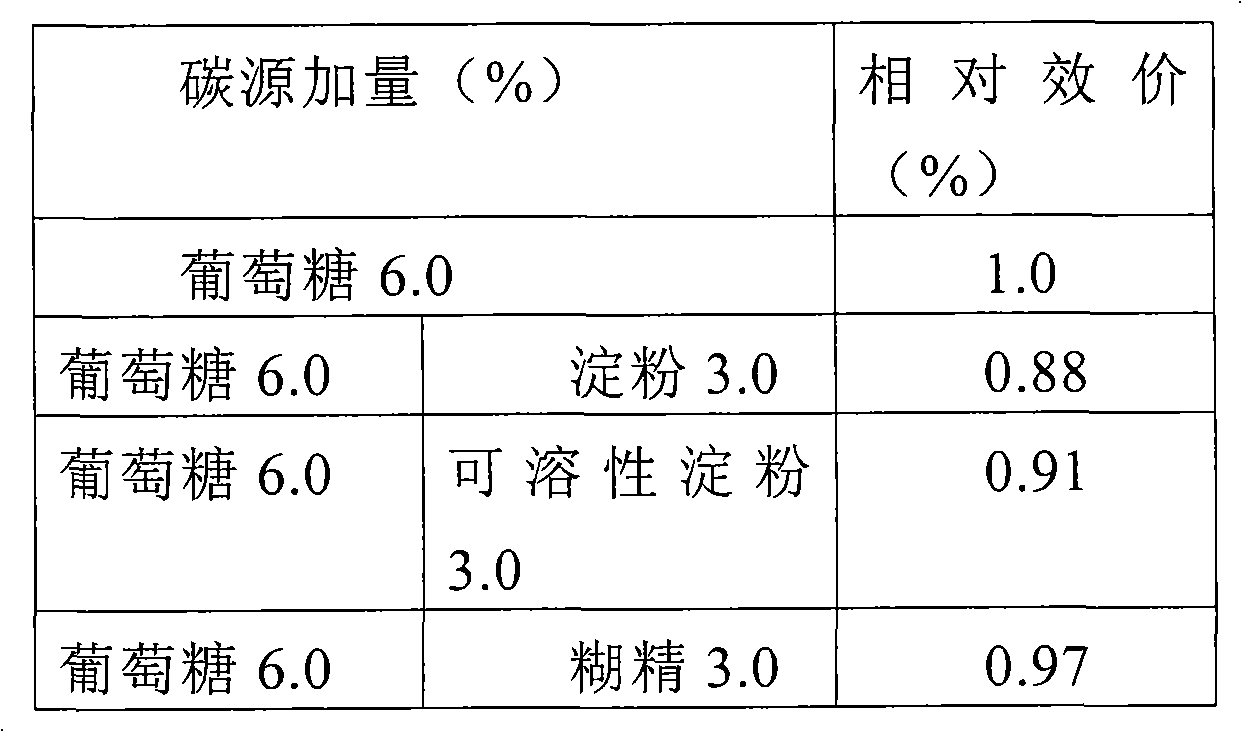
[0022] Method: Taking the formula of the basic fermentation medium as the control, the nitrogen source composition and dosage were unchanged, and glucose, starch, soluble starch, dextrin, fructose, lactose, maltose, sucrose, mannitol and other multi-carbon sources were added to conduct single-factor carbon In the source experiment, the addition amount of each carbon source is equivalent, both are 6%. The shake flask was fermented for 8 days, and the titer was determined by HPLC.
[0023]
[0024] 2): Carbon source combination experiment
[0025] Based on the above results, glucose was selected as the quick-acting carbon source and combined with other late-acting carbon sources. The shake flask was fermented for 8 days, and the titer was determined by HPLC.
[0026]
[0027] 3): Glucose addition exper...
Embodiment 2
[0052]Utilize spinosad to produce bacterium Saccharopolyspora spinosa to ferment, and fermentation medium is configured according to the data listed in the following table (percentage by weight):
[0053] Glucose 5.0, cottonseed meal 2.0, fish meal peptone 1.0, sunflower oil 2.0, lysine 0.2, CaCO 3 0.3 and tap water 89.5.
[0054] Sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes. The inoculum size is 10%, the filling volume is 100ml / 750ml, and it is placed in a constant temperature room at 28°C with a rotary shaker at 250rpm for 8 days. After 8 days of fermentation, take 2ml of fermentation broth, centrifuge to get mycelia, soak in 6ml of acetone overnight, and then centrifuge to get The titer of the supernatant was determined by HPLC, and the fermentation unit was 536mg / L.
Embodiment 3
[0056] Utilize spinosad to produce bacterium Saccharopolyspora spinosa to ferment, and fermentation medium is configured according to the data listed in the following table (percentage by weight):
[0057] Glucose 8.0, cottonseed meal 3.0, fish meal peptone 2.0, sunflower oil 2.0, lysine 0.1, CaCO 3 0.5 and tap water 84.4.
[0058] Sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes. The inoculum size is 10%, the filling volume is 100ml / 750ml, and it is placed in a 28°C constant temperature room with a rotary shaker at 250rpm for 10 days. After 10 days of fermentation, take 2ml of the fermentation broth, centrifuge to get the mycelia, soak in 6ml of acetone overnight, and then centrifuge to get The titer of the supernatant was determined by HPLC, and the fermentation unit was 1150 mg / L.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com