Method for preparing light absorption layer of CuInSe2 (CIS) based thin film solar cell
A technology for solar cells and light-absorbing layers, applied to coatings, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve problems such as loss, complex equipment structure, and many defects in the absorption layer, and achieve high production efficiency and simple equipment structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
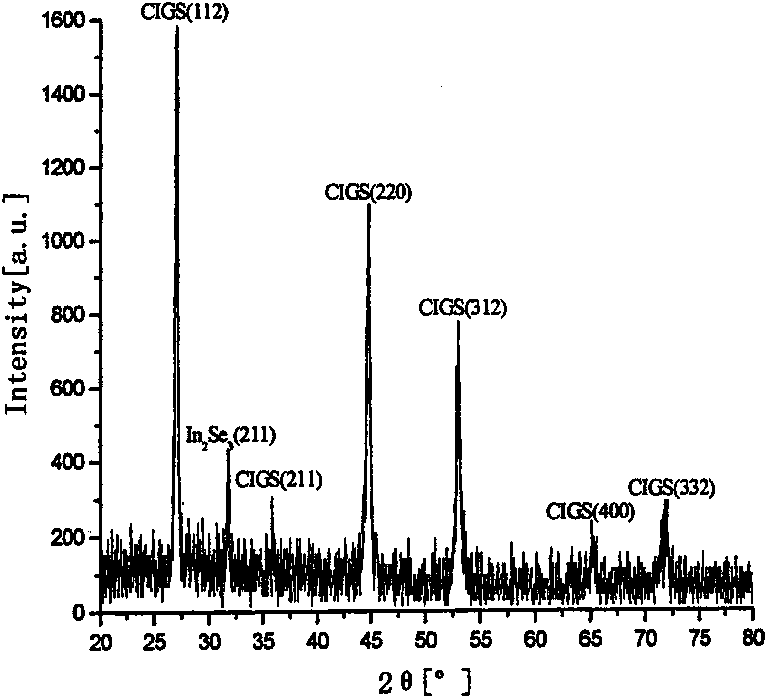
[0025] The sputtering target used is CuIn with a purity of 99.99%. 0.7 Ga 0.3 Se 2.2 Ceramic target, the size is φ70×3mm, (CuIn 0.7 Ga 0.3 Se 2.2 The ceramic target is commercially available and produced by Beijing Changhao Youyan New Material Technology Development Co., Ltd. CuIn used in the following examples 0.7 Ga 0.3 Se 2.2 The ceramic target is the same as this) The X-ray diffraction pattern of the ceramic target used is as follows image 3 shown. The preparation steps of this embodiment are as follows:
[0026] (1) Cut the soda glass into a substrate of 10×10mm, put it into deionized water and ultrasonically clean it for 5 minutes to remove the debris generated during the cutting process, then put it into acetone and ultrasonically clean it for 15 minutes to remove the oil stain on the surface of the substrate, Put the substrate into alcohol and ultrasonically clean it for 2 minutes, and finally dry the substrate for use;
[0027] (2) Put the cleaned soda glas...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The sputtering target used is CuIn with a purity of 99.99%. 0.7 Ga 0.3 Se 2.2 Ceramic target, the size is φ70×3mm, the preparation steps are as follows:
[0034] (1) Cut the soda glass into a substrate of 10×10mm, put it into deionized water and ultrasonically clean it for 5 minutes to remove the debris generated during the cutting process, then put it into acetone and ultrasonically clean it for 15 minutes to remove the oil stain on the surface of the substrate, Put the substrate into alcohol and ultrasonically clean it for 2 minutes, and finally dry the substrate for use;
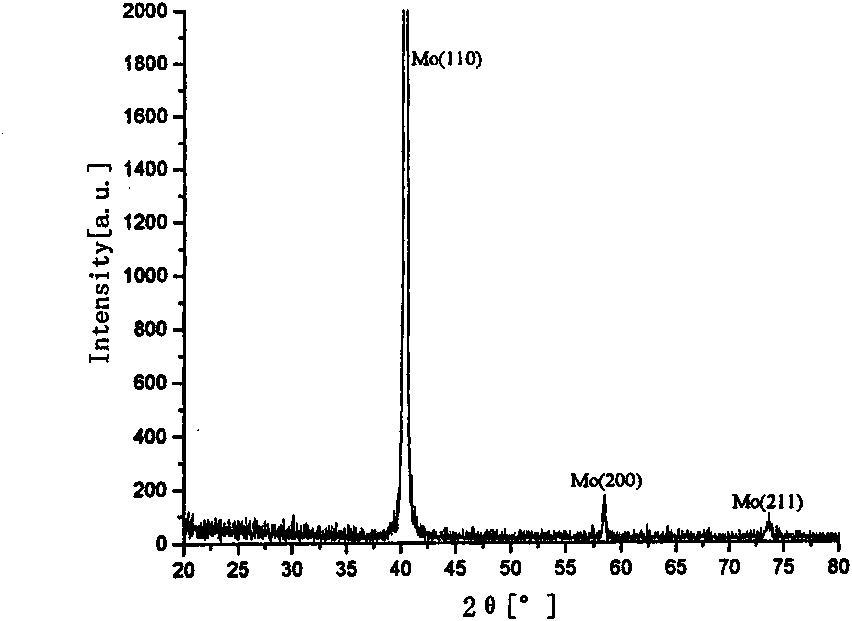
[0035] (2) Put the cleaned soda glass substrate into the cavity of the magnetron sputtering equipment, install the Mo target material (the Mo target material purity is 99.99%) in the cavity, the target base distance is 50mm, and then align the cavity The body is evacuated to a vacuum degree of less than 3.0×10 -3 Pa, then argon gas was introduced, the pressure was adjusted to 1Pa, sputtering wa...
Embodiment 3
[0040] The sputtering target used is CuIn with a purity of 99.99%. 0.7 Ga 0.3 Se 2.2 Ceramic target, the size is φ70×3mm. The preparation steps are as follows:
[0041] (1) Cut the soda glass into a substrate of 10×10mm, put it into deionized water and ultrasonically clean it for 5 minutes to remove the debris generated during the cutting process, then put it into acetone and ultrasonically clean it for 15 minutes to remove the oil stain on the surface of the substrate, Put the substrate into alcohol and ultrasonically clean it for 2 minutes, and finally dry the substrate for use;
[0042] (2) Put the cleaned soda glass substrate into the cavity of the magnetron sputtering equipment, install the Mo target material (the purity of the Mo target material is 99.99%) in the cavity, the target base distance is 60mm, and then evacuate to a vacuum degree less than 3.0×10 -3 Pa, then argon gas was introduced, the pressure was adjusted to 1Pa, sputtering was started, and the sputte...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resistivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com