Preparation method for diamine polydactyl acid
A polylactic acid and amine modification technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of diamine-modified polylactic acid, can solve the problems of increasing the possibility of degradation of the main chain of polylactic acid and the large impact on the mechanical properties of modified polylactic acid, so as to reduce the possibility of degradation , avoid direct contact, good mechanical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1, diamine modified D, the preparation of L-polylactic acid
[0040] a, the preparation of maleyl adipamide
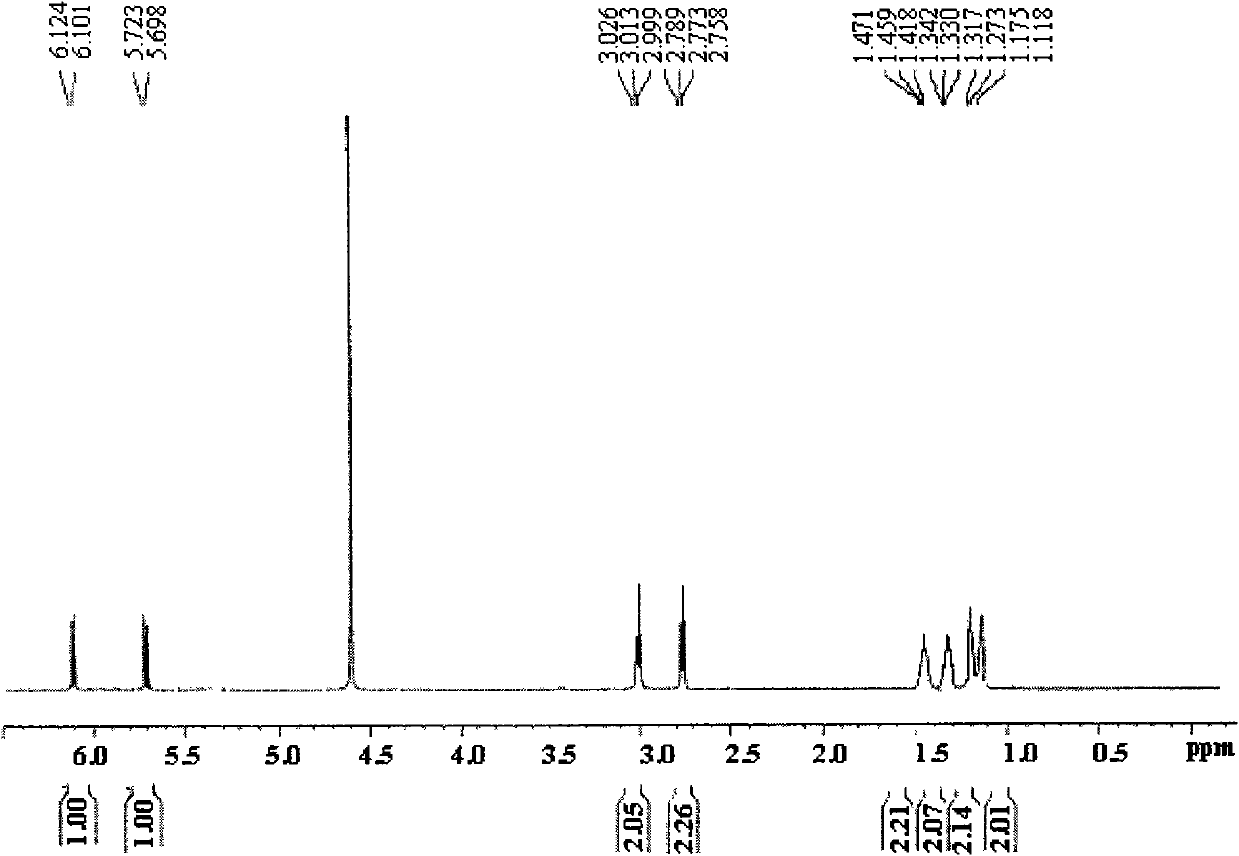
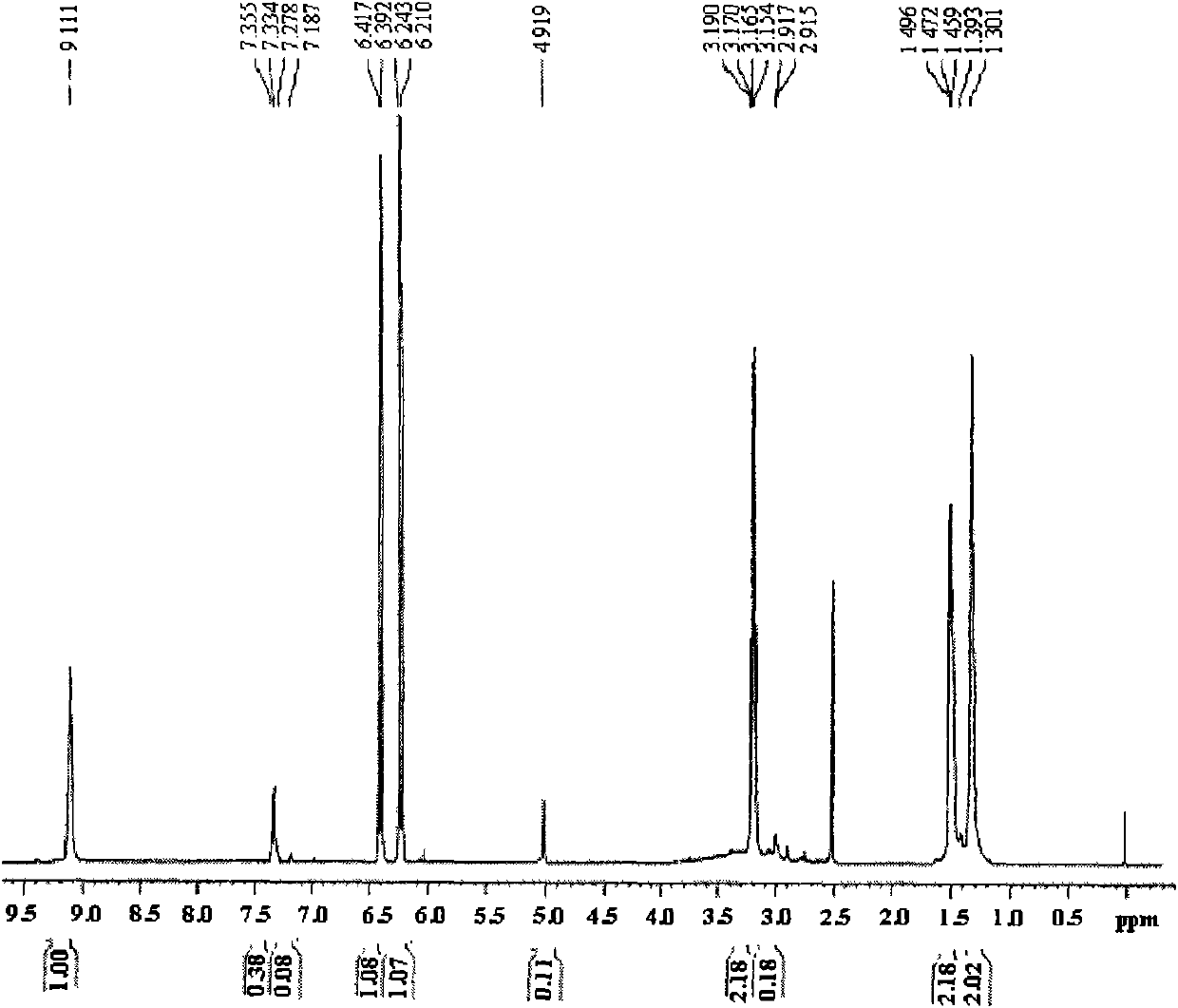
[0041]Dissolve 14.0 g of hexamethylenediamine in 30 mL of DMSO, add 20.2 g of triethylamine, then add 15 mL of 9.8 g of maleic anhydride in DMSO solution dropwise at a temperature of 30°C under stirring conditions, complete the dropwise addition in 0.5 hours, and stir the reaction at room temperature After standing for 2 hours, the layered solution was dropped into excess THF, and the viscous solid precipitate was collected and washed with absolute ethanol to obtain the crude maleamide hexamethylene diamine acid; the crude product was dissolved in a small amount of DMSO and then dripped Add excess THF, collect the precipitated viscous solid precipitate, wash with absolute ethanol, and dry under vacuum at room temperature to obtain pure maleamide hexamethylene diamic acid with a yield of 80%.
[0042] figure 1 Maleyl hexamethylene diamine acid prepar...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Embodiment 2, the preparation of diamine modified D, L-polylactic acid
[0053] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0054] c. Modification of polylactic acid with amino-protected maleic hexamic acid (solution graft polymerization method)
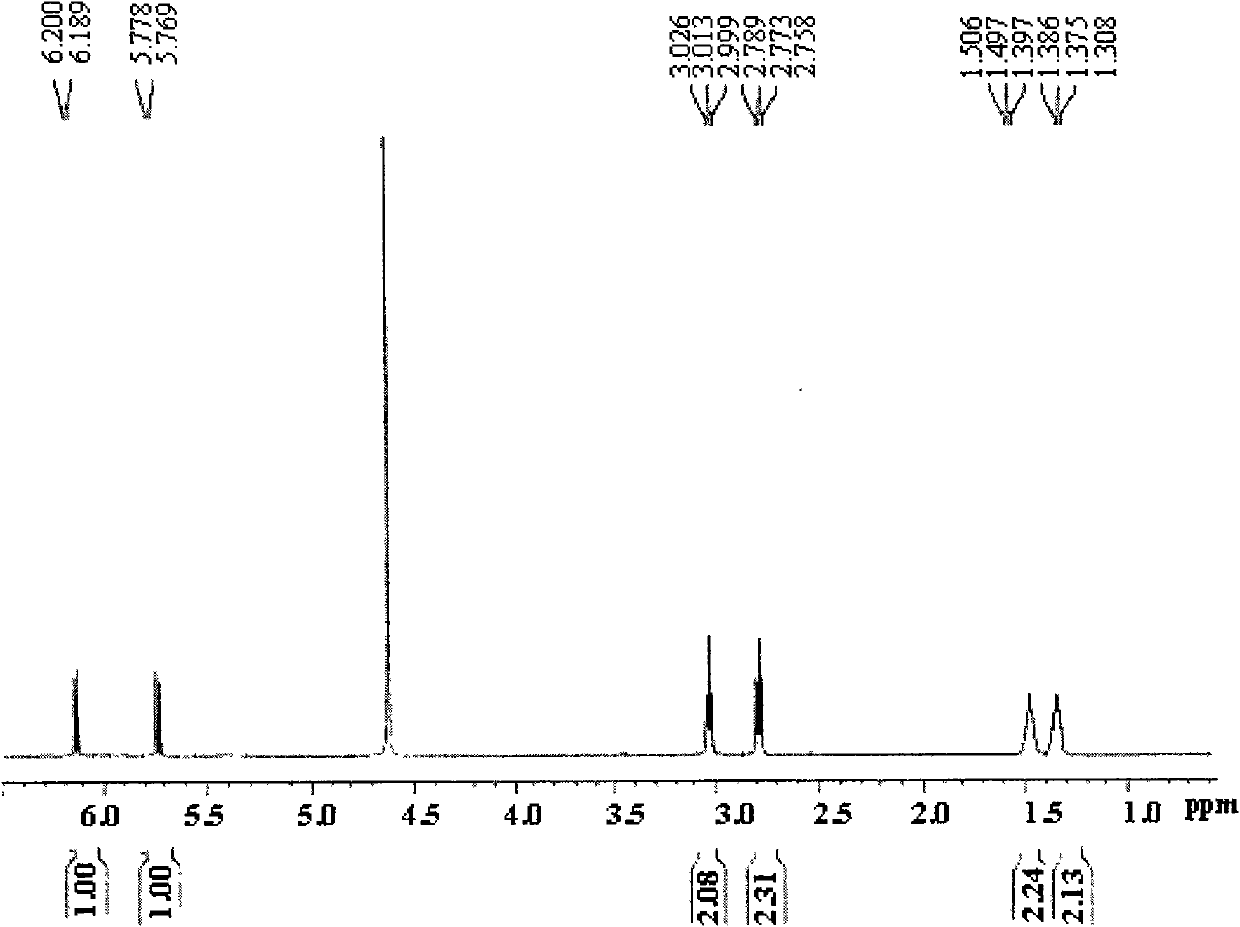
[0055] Dissolve 5.0 g of D, L-polylactic acid (molecular weight: 50,000) and 0.5 g of maleamide adipamide acid whose amino groups are protected by CBZ in 30 mL of DMSO, blow nitrogen gas for 8 minutes, and add 0.225 g of BPO (D, L-poly The mass ratio of lactic acid, CBZ-protected maleic hexamethylene diamine acid and BPO is 100:10:4.5), reacted for 12 hours at a temperature of 80°C under nitrogen protection conditions, cooled rapidly to room temperature to terminate the reaction, and dropped the reaction solution into In excess absolute ethanol, collect the precipitated film-like solid precipitate, and dry it in vacuum at room temperature to obtain the crude product of CBZ-protected maleamide hexamethylene a...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Embodiment 3, diamine modified D, the preparation of L-polylactic acid
[0057] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0058] c. Modification of polylactic acid with amino-protected maleic hexamic acid (solution graft polymerization method)
[0059] Dissolve 5.0 g of D, L-polylactic acid (molecular weight: 50,000) and 1.0 g of CBZ-protected maleic hexamethylene diamine acid in 30 mL of DMSO, blow nitrogen gas for 8 minutes, and add 0.4 g of BPO (D, L-polylactic acid, The mass ratio of CBZ-protected maleyl hexamethylene diamine acid to BPO is 100:20:8), reacted for 10 hours at a temperature of 120-130°C under nitrogen protection conditions, cooled rapidly to room temperature to terminate the reaction, and dropped the reaction solution into In excess absolute ethanol, collect the precipitated film-like solid precipitate, and dry it in vacuum at room temperature to obtain the crude product of CBZ-protected maleamide hexamethylene acid-modified polyl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com