In-line test device and methods of use
A technology for fluid control devices and valve devices, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, measuring devices, containers for laboratories, etc., and can solve problems such as low efficiency, expensive manufacturing materials, and complicated design and manufacturing.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0132] Example 1: Method of Use of Disease Screening Device: Streptococcus A (Strep-A)
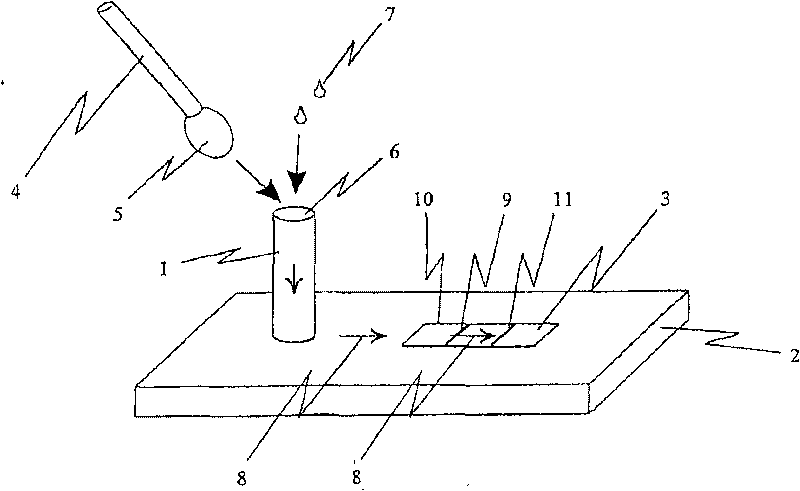
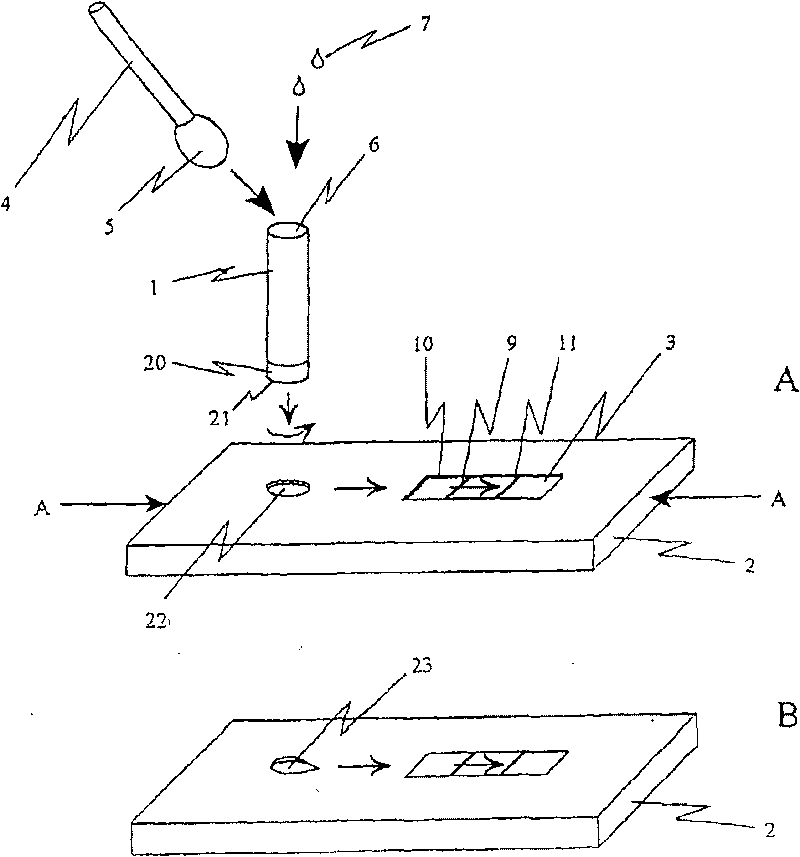
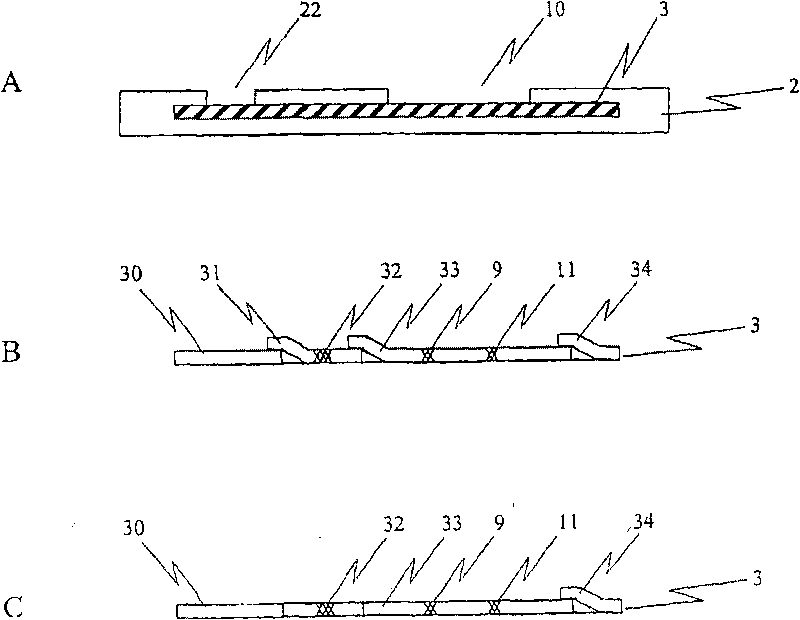
[0133]Use standard man-made fiber swabs or polyester swabs to obtain throat samples from patients showing physical signs and pharyngitis symptoms. Swab the tonsil area of the throat. Place the sample collection chamber of the test device on the test bench with a lateral flow test piece inside, put 4 drops of about 160 microliters of reagent A (2 molar sodium nitrate) and 4 drops of about 160 microliters of reagent B (0.2 molar Acetic acid) is added to the extraction unit. The swab containing the throat sample is inserted into the sample collection chamber and rotated repeatedly for approximately 10 seconds, after which the swab is incubated in the solution for 60 seconds. Thereafter, the valve structure is actuated while the swab remains in the sample collection chamber. The contents of the sample collection chamber, equivalent to approximately 200 microliters, were transferred to t...
Embodiment 2
[0134] Example 2: Method of using the disease detection device: Chlamydia
[0135] A rayon or polyester swab with a plastic stem, or a cytobrush is used to collect an endocervical sample. Keys on the sample collection chamber of the assay device are secured into corresponding keyholes located on the test bench, which is equipped with a lateral flow test strip device. Put 150 microliters of 1 equivalent potassium hydroxide into the sample collection chamber of the device, put the swab or cell brush into the container, rotate for 10-20 seconds and incubate for 5 minutes, after that, add 150 microliters of 1 molar acetic acid ( Containing 0.1% non-ionic active agent 20) into the container. Rotate the swab or cell brush for another 10-20 seconds. The valve mechanism is actuated and the swab or cell brush remains in the extraction device. Depending on whether a swab or a cell brush is used, approximately 150-250 microliters of the extraction vessel contents are filtered throug...
example 3
[0136] Example 3: Method of use of genetically modified crop inspection equipment: BTK protein
[0137] To determine whether cereal seeds or cereal crops have been genetically modified to produce Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. (BtK) protein, randomly select 5-10 grams of grain kernels from seed donors or from various grain ears. Thoroughly grind the sample to ensure homogeneity. Place a portion of the ground sample into the sample collection chamber of the assay device until the sample fills 3 / 4 of the volume of the extraction vessel. Add 500 µl of saline. The ground cereal and saline mixture was incubated for 2 minutes. Carefully transfer the sample collection chamber to the laboratory bench without spilling the contents. The key structure of the sample collection chamber is inserted into the corresponding key hole on the test platform, and the platform contains a lateral flow test piece device for detecting BtK protein. The valve unit is actuated to allow the liquid co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com