Organic light-emitting device and manufacture method of light extraction structure thereof
A technology of an organic light-emitting device and a manufacturing method, which is applied in the field of optoelectronics, can solve the problems of low light extraction efficiency and lack of total reflection light of OLEDs, and achieve the effects of improving light extraction efficiency, eliminating total reflection, and improving lifespan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1 (organic light-emitting device)
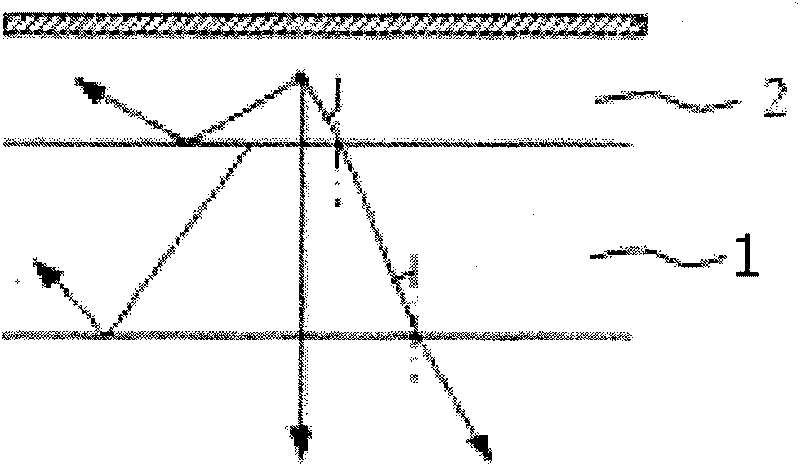
[0032] figure 2 , image 3 and Figure 6 A specific embodiment of the organic light-emitting device of the present invention is shown.
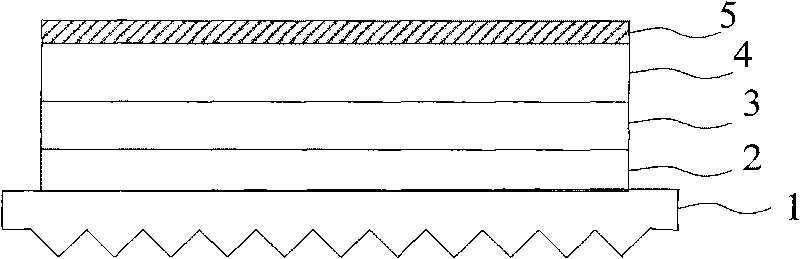
[0033] Such as figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the organic light emitting device includes a substrate 1 , a transparent anode 2 , an organic hole transport layer 3 , a light emitting layer and an electron transport layer 4 and a cathode 5 . The transparent anode 2 is located on the substrate 1 , the organic hole transport layer 3 is located on the transparent anode 2 , the light emitting layer and the electron transport layer 4 are located on the organic hole transport layer 3 , and the cathode 5 is located on the light emitting layer and the electron transport layer 4 .
[0034]The substrate 1 is made of single crystal yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG), its refractive index is 1.83-1.87, and its thermal conductivity is 0.11W / cm·K (300k). The substrate 1 is made of a material with high...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2 (organic light-emitting device)
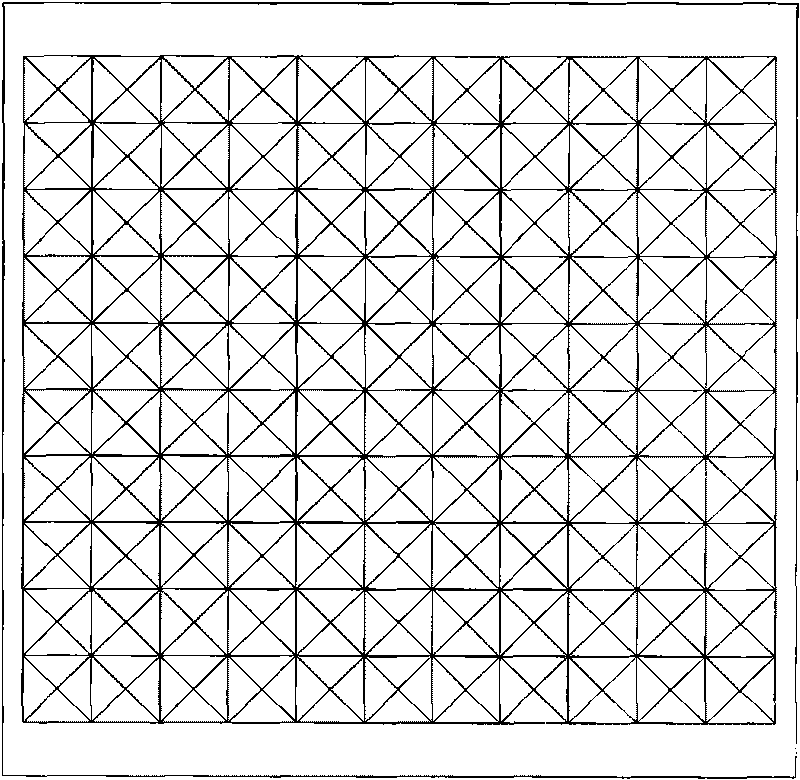
[0037] Figure 4 and Figure 5 Another specific embodiment of the organic light-emitting device of the present invention is shown.
[0038] The difference between this organic light-emitting device and Embodiment 1 is that the shape of the light extraction structure on the surface of the substrate 1 facing away from the transparent anode is different, and in this embodiment, each facet of the light extraction structure forms a regular truncated inverted cone; The substrate 1 is made of aluminum nitride with a refractive index of 1.87-2.20 and a thermal conductivity of 1.4-2W / cm·K (300k).
[0039] The principle of improving the light extraction efficiency of the organic light-emitting device is the same as that of the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3 (Manufacturing method of a light extraction structure of an organic light-emitting device)
[0041] The light extraction structure on the substrate 1 in Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 is fabricated by the following steps:
[0042] 1. On the surface of the substrate 1, use magnetron sputtering or plasma chemical vapor deposition to make a silicon dioxide or silicon nitride masking layer, and on the surface of the substrate 1 (the surface facing away from the optically transparent layer 2 on the organic light-emitting device) , facing the air) on the masking layer to form a pattern by photolithography, the surface of the substrate located under the reserved part of the masking layer is shielded, and the rest is exposed;
[0043] 2. Heat 85% phosphoric acid to 150-170°C for dehydration for 10 minutes, then mix it with 98% sulfuric acid at a ratio of 3:1, and slowly raise the temperature to 190-300°C to obtain an etching solution;
[0044] 3. Preheat the substr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com