Primer pair for detecting citrus canker pathogenic bacteria and detection method thereof
A citrus canker bacterium, detection column technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the lack of obvious symptoms of disease-resistant or non-susceptible varieties, complicated biochemical identification of citrus canker sores, and other diseases Confusion and other problems, to achieve high accuracy, high sensitivity, and good primer specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Primer design and synthesis
[0027] According to the reported region sequence of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv.citri OPM-12 SCARfragment (gb|AF312370.1) of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv.citri, the primer sequences were designed as follows:
[0028] SEQ ID NO.1 (forward): 5'-ACGCTCGATCTGCACCTATT-3';
[0029] SEQ ID NO. 2 (reverse): 5'-CCAACGAGTCTCAAAGCATCA-3'.
[0030] According to the reported primers, the primer sequences are:
[0031] SEQ ID NO.3 (forward): 5'-CGCCATCCCCACCACCACCACGAC-3';
[0032] SEQ ID NO. 4 (reverse): 5'-AACCGCTCAATGCCATCCACTTCA-3'.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Collection of bacteria
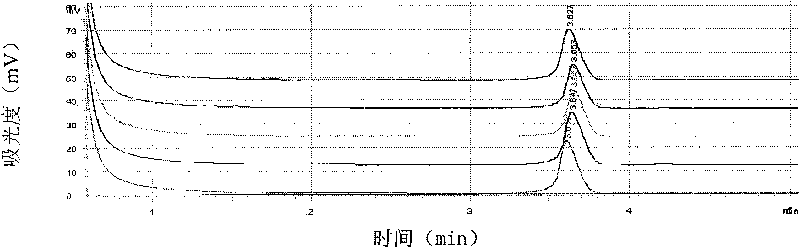
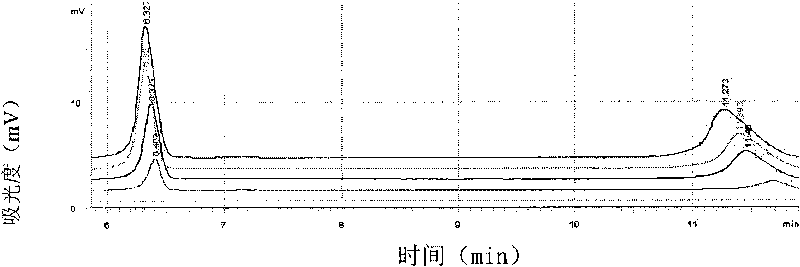
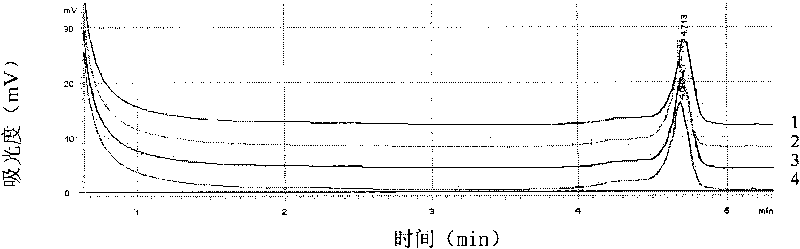
[0035] Colonies grown on the plate: Pick at least 5 colonies directly into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube with the inoculation loop, add 1mL sterilized water to shake fully, centrifuge at 8000g for 3min, discard the supernatant, then add 1mL sterilized water to the tube, repeat three times , Take the precipitate to extract DNA, and perform double PCR-DHPLC detection.
[0036] Citrus leaves or materials: Use a 6mm hole puncher to punch 50 small holes on citrus leaves. If there are lesion materials, take the lesion parts, or take about 1g of diseased tissue materials and add 1mL sterilized distilled water to fully shake and wash. The liquid was centrifuged at 8000 g for 5 min, the supernatant was discarded, and the precipitate was taken to extract DNA, which was detected by double PCR-DHPLC.
Embodiment 3
[0038] Bacterial DNA Extraction
[0039] 1) Add 600 μL of TE buffer, 30 μL of 10% SDS solution, and 15 μL of 20 mg / mL proteinase K to the precipitate, mix well, and incubate in a water bath at 37° C. for 1 h.
[0040] 2) Add an equal volume of chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (24:1), and mix well. Centrifuge at 10,000 g for 5 min, and transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube.
[0041] 3) Add an equal volume of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), mix well, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 5 min, and transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube.
[0042] 4) Add 0.6 times the volume of isopropanol, mix gently, precipitate at -20°C for 1 hour, centrifuge at 10,000 g for 5 minutes, and discard the supernatant.
[0043] 5) Add 1 mL of 70% ethanol to wash the precipitate, centrifuge at 8000 g, discard the supernatant, and dry in the air.
[0044] 6) Add 50 μLTE buffer to dissolve the DNA precipitate, and store it for a long time at -20°C for future use.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com