Method for separating vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate monoester from vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinate diester
A technology of polyethylene glycol succinate and polyethylene glycol succinic acid, which is applied in the field of separation of vitamin E polyethylene glycol succinic acid mono- and di-esters, can solve unseen and complicated problems, and achieve low consumption , high degree of automation and high efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
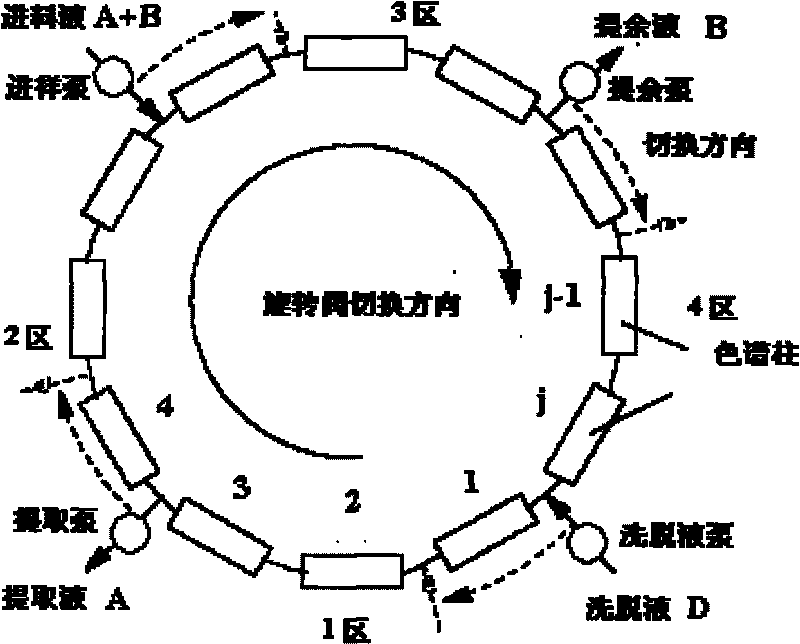
[0026] Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography System C9812 (Norr, Germany), equipped with 8 chromatographic columns (ID 1×15cm), 2 in each zone, the stationary phase filled in the chromatographic column is octadecylsilane bonded silica gel, particle size 50 μm. The mobile phase was acetonitrile / isopropanol solution (50 / 50, v / v), and the temperature was 35°C. The sample used for feeding is TPGS 1000 mixed solution, concentration: 200mg / ml, wherein the monoester content is 68.3%, and the diester content is 31.4%.
[0027] A. Operating conditions:
[0028] Injection liquid flow rate: UF=1ml / min
[0029] Eluent flow rate: UD=5.7ml / min
[0030] Raffinate flow rate: U R =3.0ml / min
[0031] Extraction flow rate: U E =3.7ml / min
[0032] Switching time: t s =144s
[0033] B. Finished product analysis:
[0034] The raffinate and extract composition were analyzed by HPLC. The purity of TPGS monoester in the raffinate is 98.2%, and the yield is 99.2%; the purity of TPGS diester i...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography System C9812 (Norr, Germany), equipped with 24 chromatographic columns (ID 1×15cm), 6 in each zone, the stationary phase packed in the chromatographic column is octadecylsilane bonded silica gel, particle size 5 μm. The mobile phase was acetonitrile / isopropanol solution (70 / 30, v / v), and the temperature was 0°C. The sample used for feeding is TPGS 400 mixed solution, concentration: 20mg / ml, wherein the monoester content is 20.1%, and the diester content is 79.8%.
[0037] A. Operating conditions:
[0038] Injection liquid flow rate: U F =1ml / min
[0039] Eluent flow rate: U D =8.18ml / min
[0040] Raffinate flow rate: U R =3.2ml / min
[0041] Extraction flow rate: U E =5.9ml / min
[0042] Switching time: t s =180s
[0043] B. Finished product analysis:
[0044] The raffinate and extract composition were analyzed by HPLC. The purity of TPGS monoester in the raffinate is 99.9%, and the yield is 99.9%; the purity of TPGS diester...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Simulated Moving Bed Chromatography System C9812 (Norr, Germany), equipped with 32 chromatographic columns (ID 1×15cm), 8 in each zone, the stationary phase packed in the chromatographic column is octadecylsilane bonded silica gel, particle size 20 μm. The mobile phase was acetonitrile / isopropanol solution (50 / 50, v / v) at a temperature of 50°C. The sample used for feeding is TPGS 400 mixed solution, concentration: 300 mg / ml, wherein the monoester content is 55.1%, and the diester content is 44.6%.
[0047] A. Operating conditions:
[0048] Injection liquid flow rate: U F =2ml / min
[0049] Eluent flow rate: U D =21.2ml / min
[0050] Raffinate flow rate: U R =9.19ml / min
[0051] Extraction flow rate: U E =14.0ml / min
[0052] Switching time: t s =60s
[0053] B. Finished product analysis:
[0054] The raffinate and extract composition were analyzed by HPLC. The purity of TPGS monoester in the raffinate is 98.9%, and the yield is 99.9%; the purity of TPGS diest...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com