Method for disposing waterworks sludge
A disposal method and technology for water plants, which are applied in dewatering/drying/concentrating sludge treatment, pyrolysis treatment of sludge, etc., can solve the problems of high landfill cost, complex manufacturing process, high energy consumption and production cost, and achieve resource The chemical utilization process is simple, the stability is guaranteed, and the harmless and thorough effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
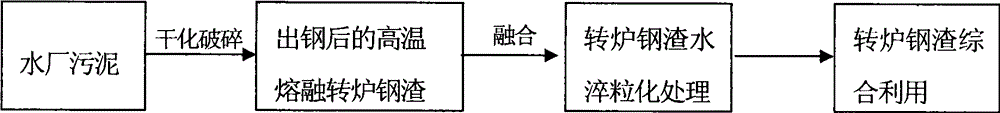
[0028] like figure 1 As shown, an industrial water plant uses river water as raw water. The raw water is used as industrial water after coagulation, precipitation and filtration. The coagulant is polyferric sulfate. Waterworks sludge (mud cake), dry and crush the waterworks sludge (particle size less than 3cm), transport it to a steel factory for converter steelmaking slag, add 10% by weight to high-temperature molten converter steel slag Inside, water plant sludge is added to molten converter steel slag in the slag ladle after tapping. After a period of fusion reaction, the molten converter steel slag fused with water plant sludge is water-quenched and granulated in the drum slag treatment process. After processing, it becomes granular steel slag material. The free calcium oxide (fCaO) of converter steel slag without adding water plant sludge was 8.8, and decreased to 4.2 after adding water plant sludge (Table 1). Organic matter (expressed as total carbon or TC) did not inc...
Embodiment 2
[0032] The used water plant sludge is from an industrial water plant. River water is used as raw water, aluminum sulfate is used as coagulant, and the raw water is obtained after coagulation, sedimentation and filtration. The weight ratio of waterworks sludge to high-temperature molten converter steel slag is 1%. The free calcium oxide (fCaO) value of converter steel slag without adding water plant sludge was 4.5, and decreased to 3.9 after adding water plant sludge (Table 2). During the fusion process, the organic matter in the water plant sludge was removed by high temperature, The organic matter of converter steel slag (represented by total carbon, TC) did not increase. Others are the same as embodiment 1.
[0033] Table 2 Chemical composition of converter steel slag before and after adding 1% water plant sludge (%)
[0034]
Embodiment 3
[0036] All the sludge from the waterworks is obtained from a waterworks, using river water as the raw water, polymerized bis-aluminum iron as the coagulant, and the raw water is obtained after coagulation, precipitation and filtration. It is added to the high-temperature molten converter steel slag at a weight ratio of 5%. The free calcium oxide (fCaO) of the converter steel slag without waterworks sludge was 6.4, which dropped to 2.7 after adding waterworks sludge (Table 3). In the fusion process, the organic matter in the water plant sludge was removed by high temperature, and the organic matter in the converter steel slag (expressed as total carbon, TC) did not increase. Others are the same as embodiment 1.
[0037] Table 3 Chemical composition of converter steel slag before and after adding 5% water treatment sludge (%)
[0038]
[0039] In the present invention, a certain amount of waterworks sludge is added to the high-temperature molten converter steel slag,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com