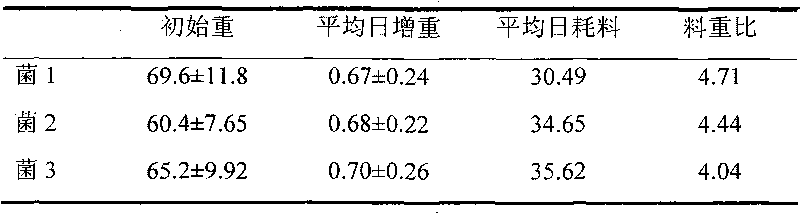
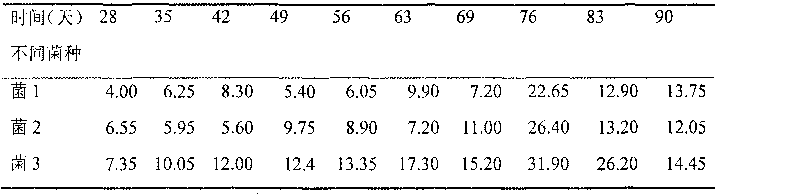
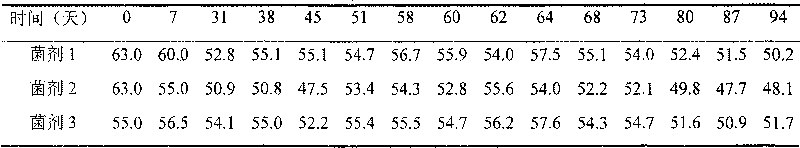
Compound microbial culture starter and application thereof
A technology of compound microorganisms and starters, applied in the direction of microorganisms, microorganisms, methods based on microorganisms, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the application effect and promotion and application process of fermentation bed cultivation, restricting the promotion and application of fermentation bed cultivation technology, and increasing the application of high input prices Cost and other issues, to achieve stable application effects, improve animal resistance, and highly targeted effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] (1) Cultivation of strains
[0041] 1. Yeast culture method
[0042] Preparation of culture solution: yeast extract 0.5%, peptone 0.5%, glucose 0.5%, in a production tank, heated to 90°C, and kept at 90°C for 2 hours. Then cool to about 33°C. Access to 0.01% Saccharomyces cerevisiae original bacteria (Saccharomyces cerevisiae CICC 31011 Sichuan Food Fermentation Industry Research and Design Institute).
[0043] Cultivation conditions: 33°C to 34°C with stirring for 12 hours.
[0044] The produced yeast liquid is put into 4℃ refrigeration for later use.
[0045] 2. Bacillus subtilis cultivation method
[0046] 2.1 Cultivation of strains
[0047] 2.1.1 Preparation of culture medium
[0048] Plate solid medium: beef extract 0.5%, yeast extract 0.5%, glucose 0.5%, peptone 1%, NaCl 0.5%, agar 2%, diluted with distilled water or non-ionized water, pH 7.2.
[0049] Liquid culture medium: Soy Peptone 2%, Sucrose 2%, Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate 0.2%, Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate 0.1%, Mangan...
Embodiment 2
[0074] Example 2 Assemble a composite microbial starter
[0075] Step 1. Mix the bacterial liquid prepared in Example 1 in the following volume ratio:
[0076] Bacillus subtilis: Bacillus natto: yeast: lactic acid bacteria=3:3:3:1 ratio is mixed, stabilizer is added according to a volume-to-mass ratio of 1 / 10,000, sealed, and stored under dark conditions.
[0077] The stabilizer is prepared by mixing sodium dihydrogen phosphate: disodium hydrogen phosphate at a mass ratio of 2:1.
[0078] Step 2. Product testing
[0079] The number of live yeast ≥10 8
[0080] The number of viable Bacillus subtilis ≥10 7
[0081] The number of viable bacteria of Bacillus natto≥10 7
[0082] Number of live lactic acid bacteria≥10 7
Embodiment 3
[0083] Example 3. Application of composite microbial starter
[0084] Step 1 Multiplication
[0085] 1. Take a container of more than 10 kg, such as a water tank, a plastic bucket, or a stainless steel bucket, and it must be cleaned without any greasy or chemical residues.
[0086] 2. Pour 1 kg of brown sugar into 10 kg of water, stir until it is fully dissolved and boil, then naturally cool to about 35°C, add 1 kg of the composite microbial starter prepared in Example 2, and then culture it naturally.
[0087] 3. During the cultivation process, keep the ambient temperature at 30-35°C, stir once every 4-8 hours, and it will become probiotics after 48 hours.
[0088] 4. After the cultured bacteria liquid is stirred, a small mineral water bottle can be used to scoop out a bottle of the bacteria liquid for observation. If the bacteria liquid has a better propagation effect, a thin layer of white sediment will appear on the bottom of the bottle after a few hours.
[0089] (2) Matters needing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com