Trace element selenium slow-release type artificial tooth root based on nanometer tube array surface
A nanotube array and artificial tooth root technology, which is applied in dentistry, dental preparations, dental prostheses, etc., can solve problems that do not involve the surface preparation of metal substrates, achieve good osteogenesis effects, promote deposition growth, and facilitate loading Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
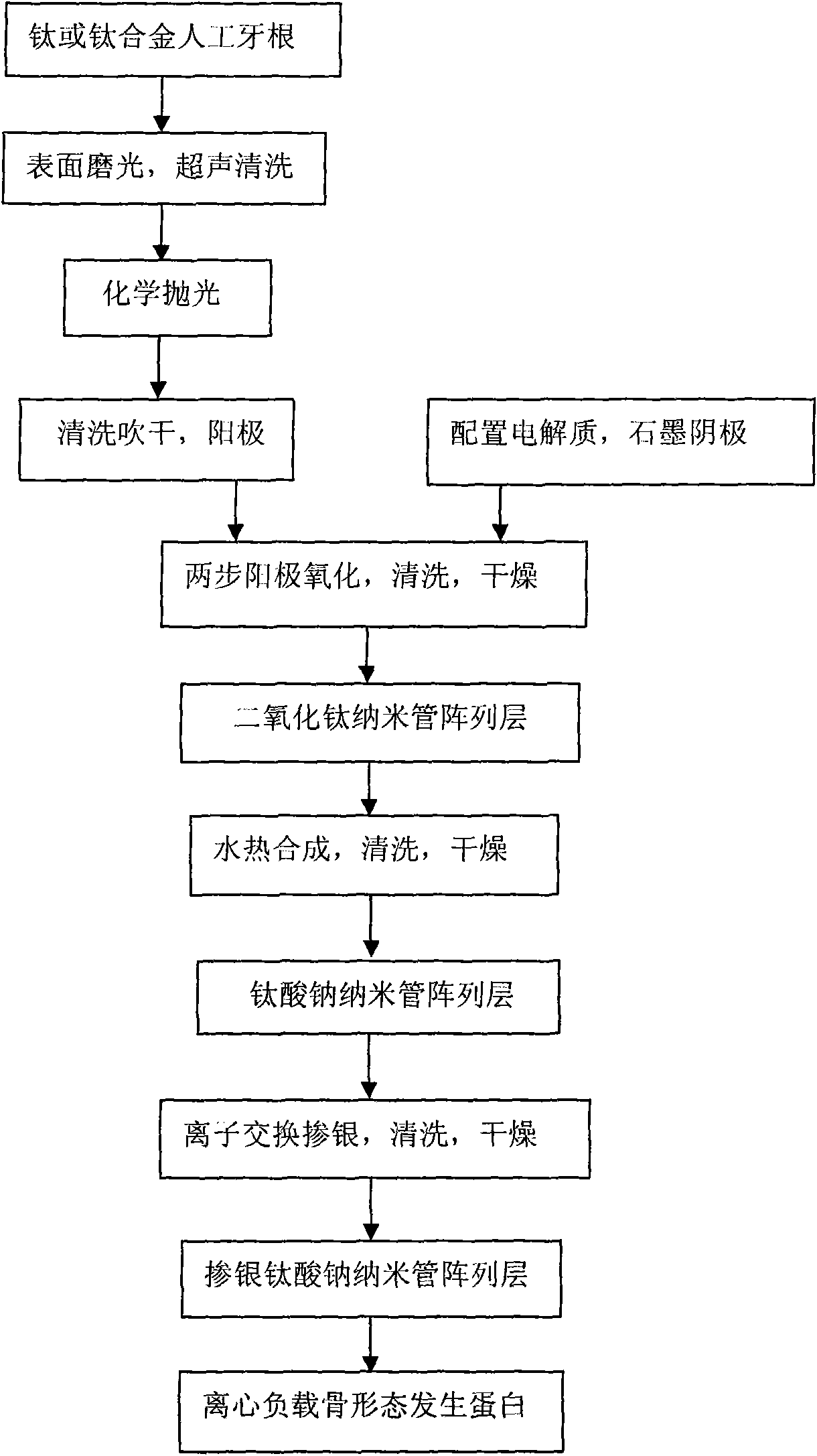
[0027] (1) First choose pure titanium to process the artificial tooth root;
[0028] (2) Surface pretreatment of the artificial tooth root: After the surface is polished, it is washed with acetone, deionized water and absolute ethanol in sequence for 10-30 minutes, followed by HF and HNO 3 and water (volume ratio: 1:4:5) chemically polish for 20-40 seconds, rinse thoroughly with deionized water, and dry for use;
[0029] (3) Preparation of aqueous organic electrolyte solution: using ethylene glycol as a solvent, other active ingredients are: water 2vol% (volume percent), phosphoric acid 4vol% (volume percent), ammonium fluoride 0.3wt% (mass percent);
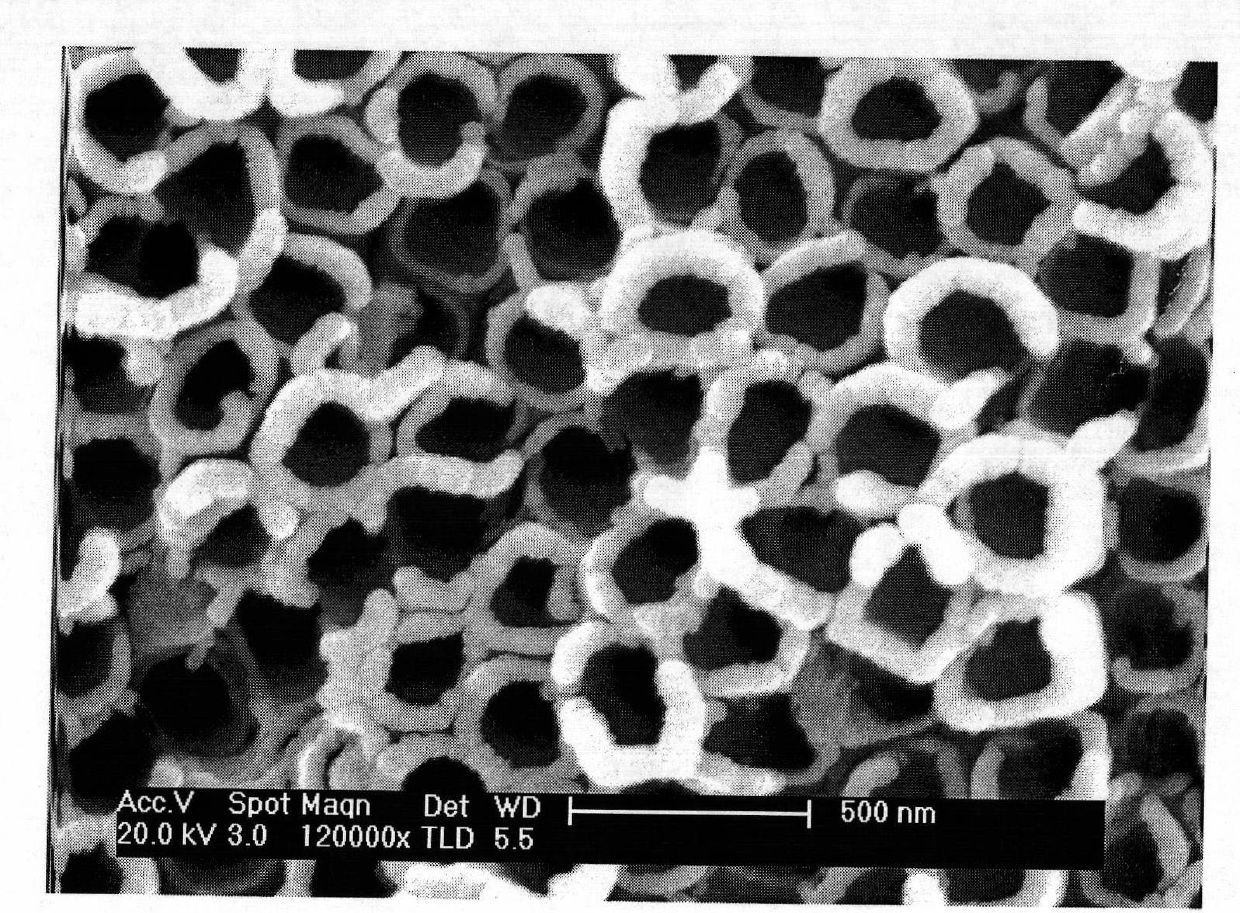
[0030](4) Titanium dioxide nanotubes were prepared by two-step anodization; the surface pretreated artificial tooth root was used as the anode, graphite or platinum sheet was used as the cathode, and the first anodization was performed in an aqueous organic electrolyte solution. The specific anodization parameters were: voltage ...
Embodiment 2
[0035] (1) First choose titanium to process the artificial tooth root;
[0036] (2) Surface pretreatment of the artificial tooth root: After the surface is polished, it is washed with acetone, deionized water and absolute ethanol in sequence for 30-60 minutes, followed by HF and HNO 3 and water (volume ratio: 1:4:5) chemically polish for 40-60 seconds, then rinse thoroughly with deionized water, and blow dry with a hair dryer for use;
[0037] (3) Preparation of aqueous organic electrolyte solution: using ethylene glycol as a solvent, other active ingredients are: water 2vol% (volume percent), phosphoric acid 4vol% (volume percent), ammonium fluoride 0.5wt% (mass percent);
[0038] (4) Preparation of titanium dioxide nanotubes by two-step anodic oxidation: the surface pretreated artificial tooth root is used as the anode, graphite is used as the cathode, and the first anodic oxidation is carried out in an aqueous organic electrolyte solution. The specific anodic oxidation para...
Embodiment 3
[0043] (1) First choose pure titanium to process the artificial tooth root;
[0044] (2) Surface pretreatment of the artificial tooth root: After the surface is polished, it is washed with acetone, deionized water and absolute ethanol in sequence for 60-90 minutes, followed by HF and HNO 3 and water (volume ratio: 1:4:5) chemically polish for 60-80 seconds, then rinse thoroughly with deionized water, and blow dry with a hair dryer for use;
[0045] (3) Preparation of aqueous organic electrolyte solution: using ethylene glycol as a solvent, other active ingredients are: water 4vol% (volume percent), phosphoric acid 6vol% (volume percent), ammonium fluoride 0.5wt% (mass percent);
[0046] (4) Preparation of titanium dioxide nanotubes by two-step anodic oxidation: use the artificial tooth root with the surface pretreated as the anode, and the platinum sheet as the cathode, and perform the first anodic oxidation in an aqueous organic electrolyte solution. The specific anodic oxida...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com