Method and device for measuring central thickness of differential confocal lens
A differential confocal, thickness measurement technology, used in measurement devices, optical devices, optics, etc., to achieve the effects of long working distance, improved measurement accuracy, and fast measurement speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
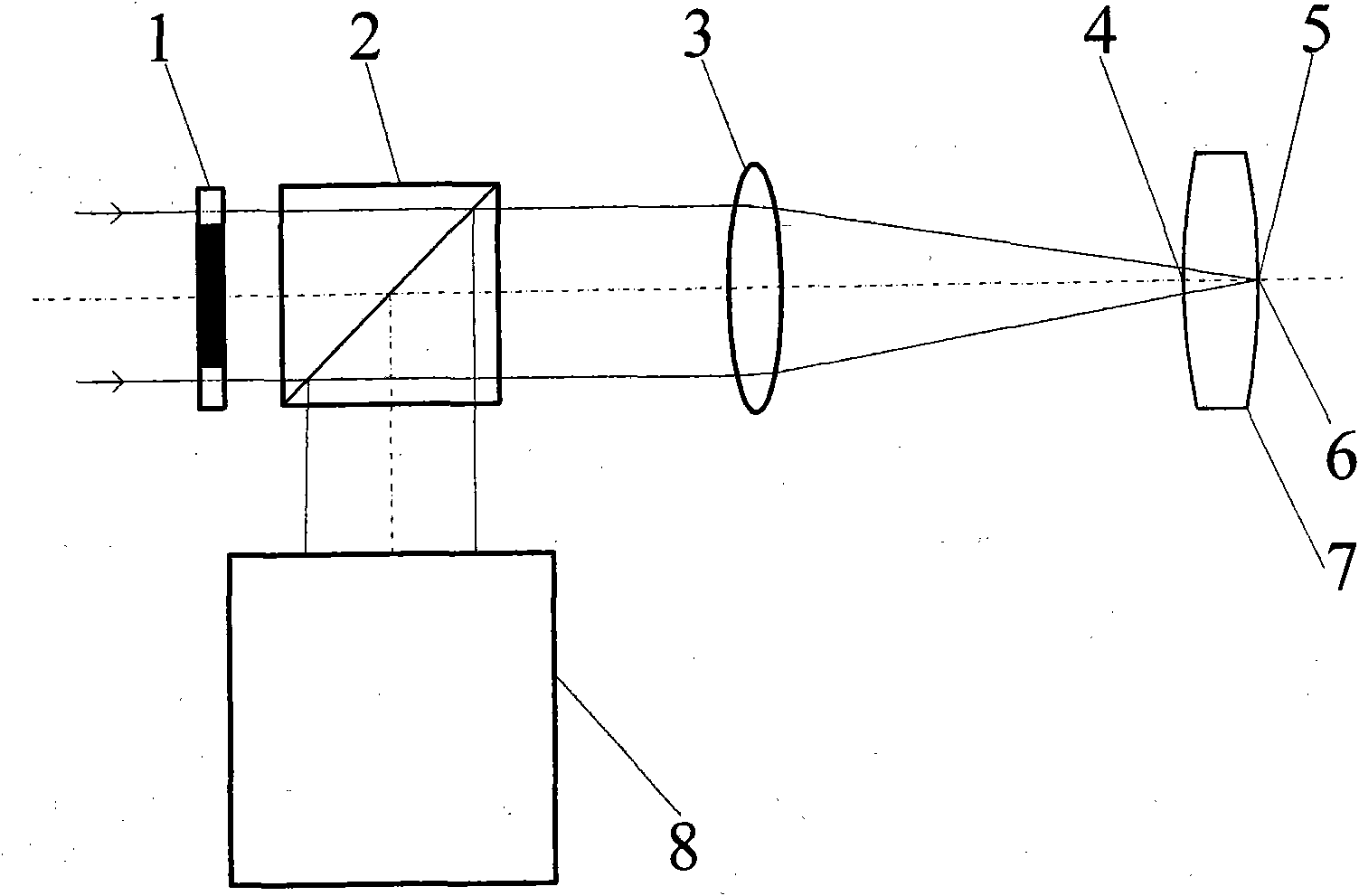
[0050] Such as figure 2 , Figure 5 with Figure 7 As shown, the measurement method of the center thickness of the differential confocal lens, the measurement steps are:
[0051] At first, start the measurement software in the main control computer 35, input relevant parameter, it mainly comprises the radius of curvature r of the front surface of the measured lens 7 1 =90.7908mm, air refractive index n 0 =1 and the refractive index of the measured lens 7 is n=1.5143.
[0052] Then, the collimated light source 28 is turned on, and the parallel light emitted by it passes through the annular pupil 1 with a light transmission diameter of 6.8mm-9.6mm, passes through the beam splitting system 2, and converges at the focal point through the 35mm objective lens 3 with a top focal length, forming a hollow The light cone, after the light is reflected by the surface of the measured lens 7, is reflected by the objective lens 3 and the beam splitting system 2 again and enters the beam...
Embodiment 2
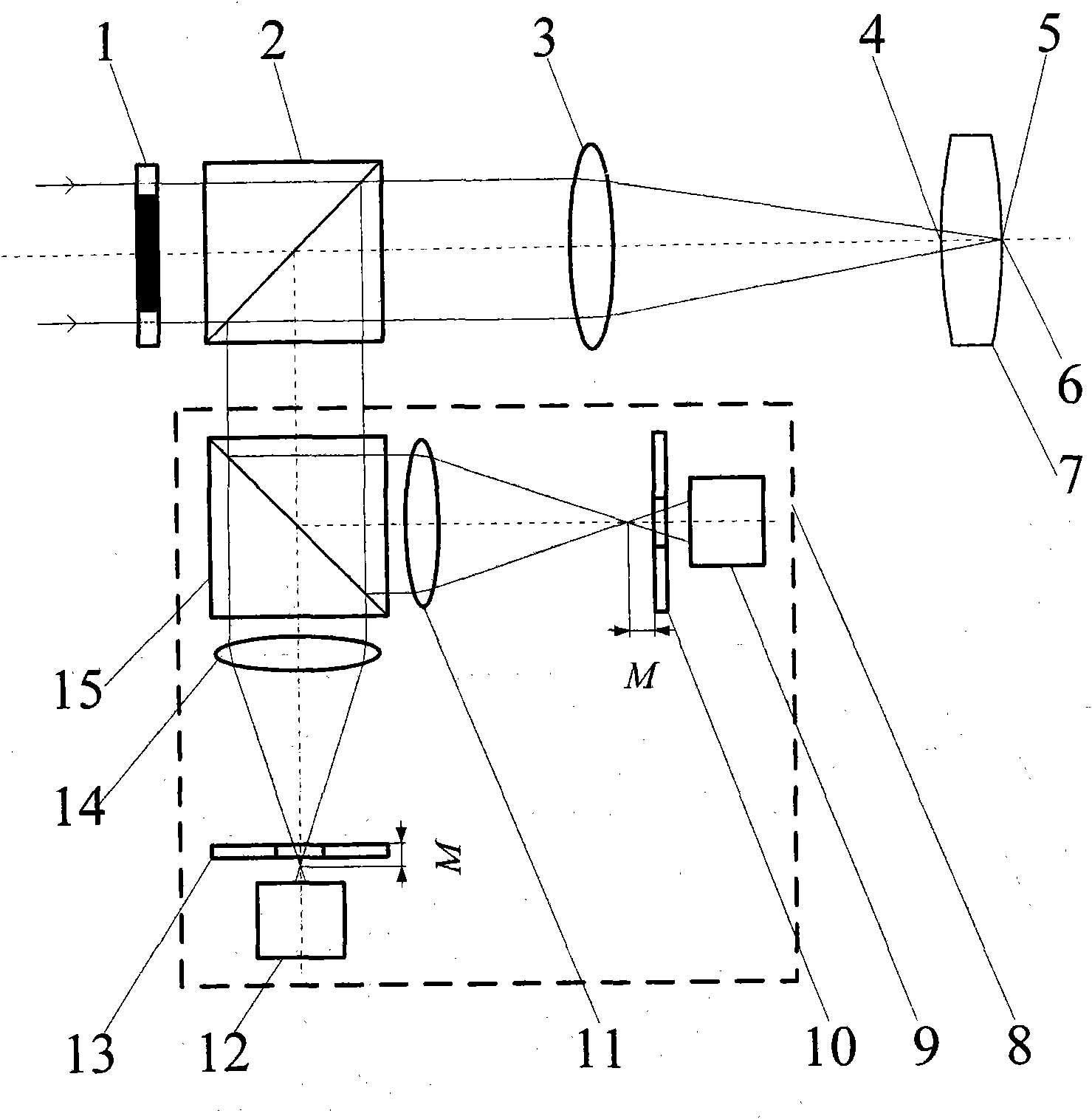
[0062] Such as image 3 , Figure 5 with Figure 7 As shown, the embodiment one figure 2 The differential confocal system in is replaced by image 3 The differential confocal system in the above can constitute the second embodiment. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that after the light enters the differential confocal system 8, the beam splitter 20 divides the light into two paths, the transmitted light illuminates the pre-focus CCD detector 18 after passing through the first lens 19, and the reflected light passes through the second lens 17 Back-illumination CCD detector 16 after focus. The remaining measurement methods and devices are the same as those in Example 1.
Embodiment 3
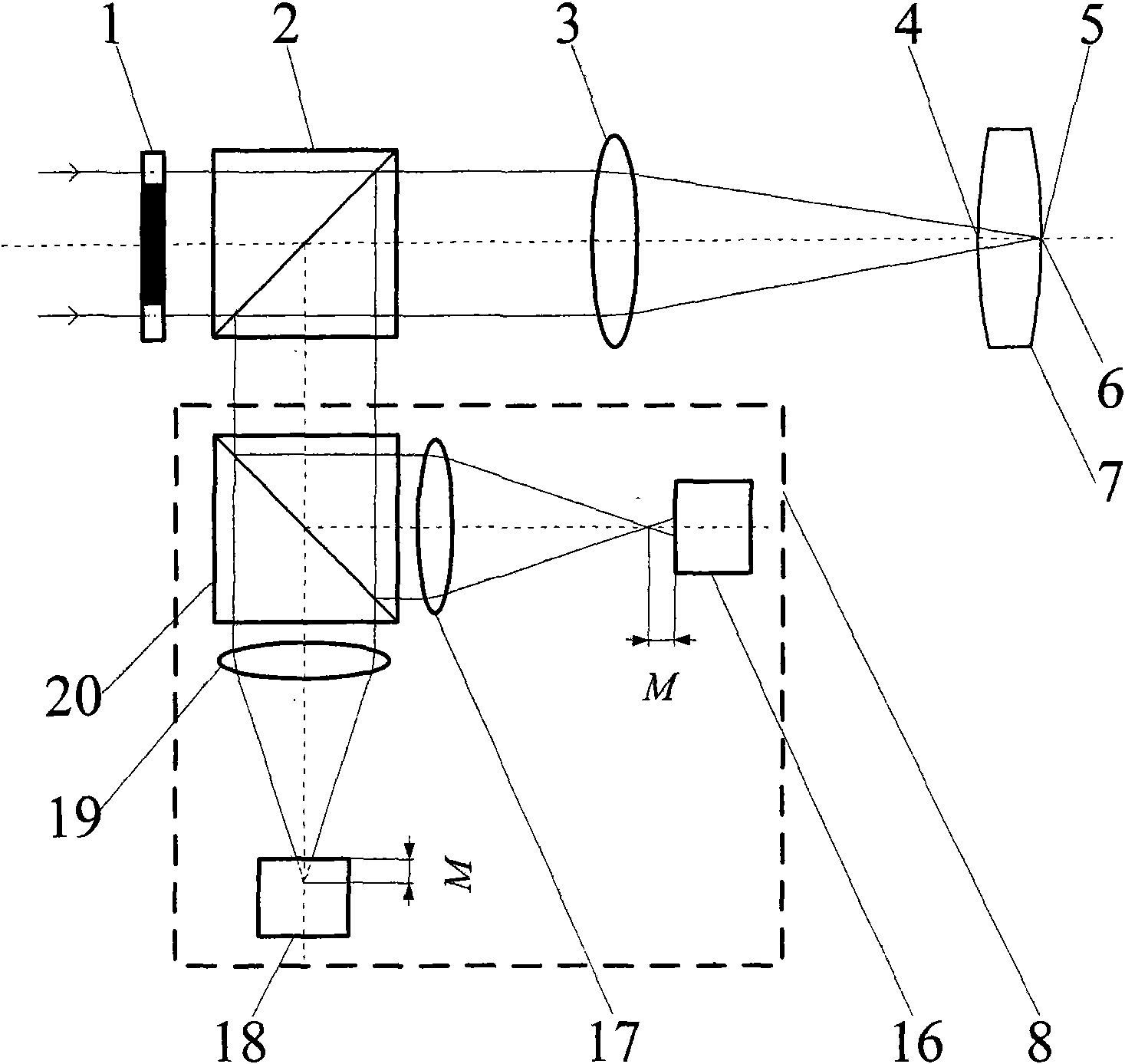
[0064] Such as Figure 4 , Figure 5 with Figure 7 As shown, the embodiment one figure 2 The differential confocal system in is replaced by Figure 4 The differential confocal system in the above can constitute the second embodiment. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that after the light enters the differential confocal system 8, the beam splitter 27 divides the light into two paths, and the transmitted light passes through the first lens 26 and the pre-focus microscopic objective lens 25 and passes through the first CCD detector 24. The surface is imaged, and the reflected light is imaged on the surface of the second CCD detector 21 after passing through the second lens 23 and the after-focus microscopic objective lens 22 . The remaining measurement methods and devices are the same as those in Example 1.
[0065] This embodiment realizes the non-contact high-precision measurement of the lens center thickness through a series of measures, realizes the method and devic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com