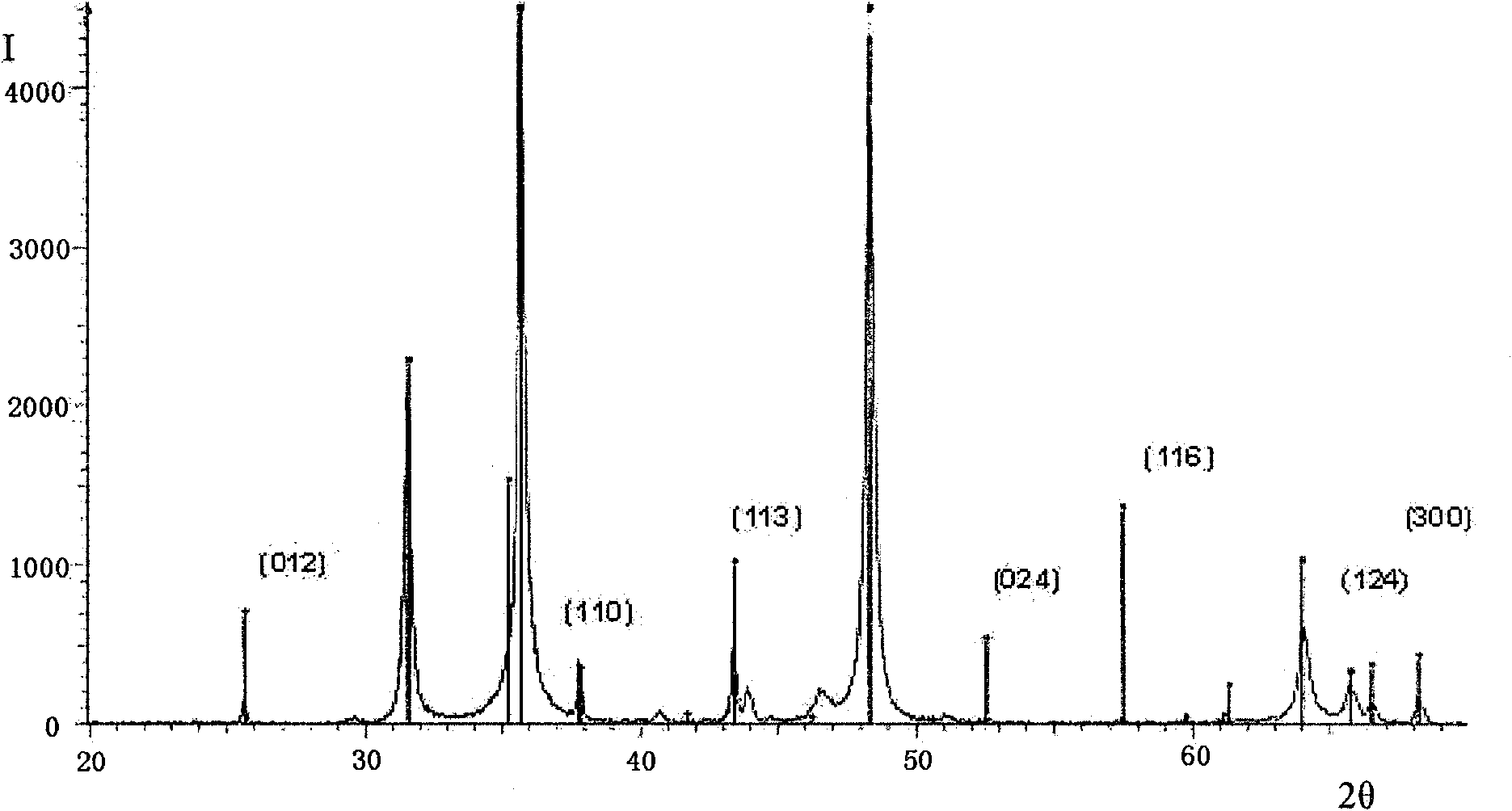
Method for producing PVD coatings
A coating and oxide technology, applied in the field of high-power pulse magnetron sputtering, can solve the problems of porous microstructure and unsuitable coating application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
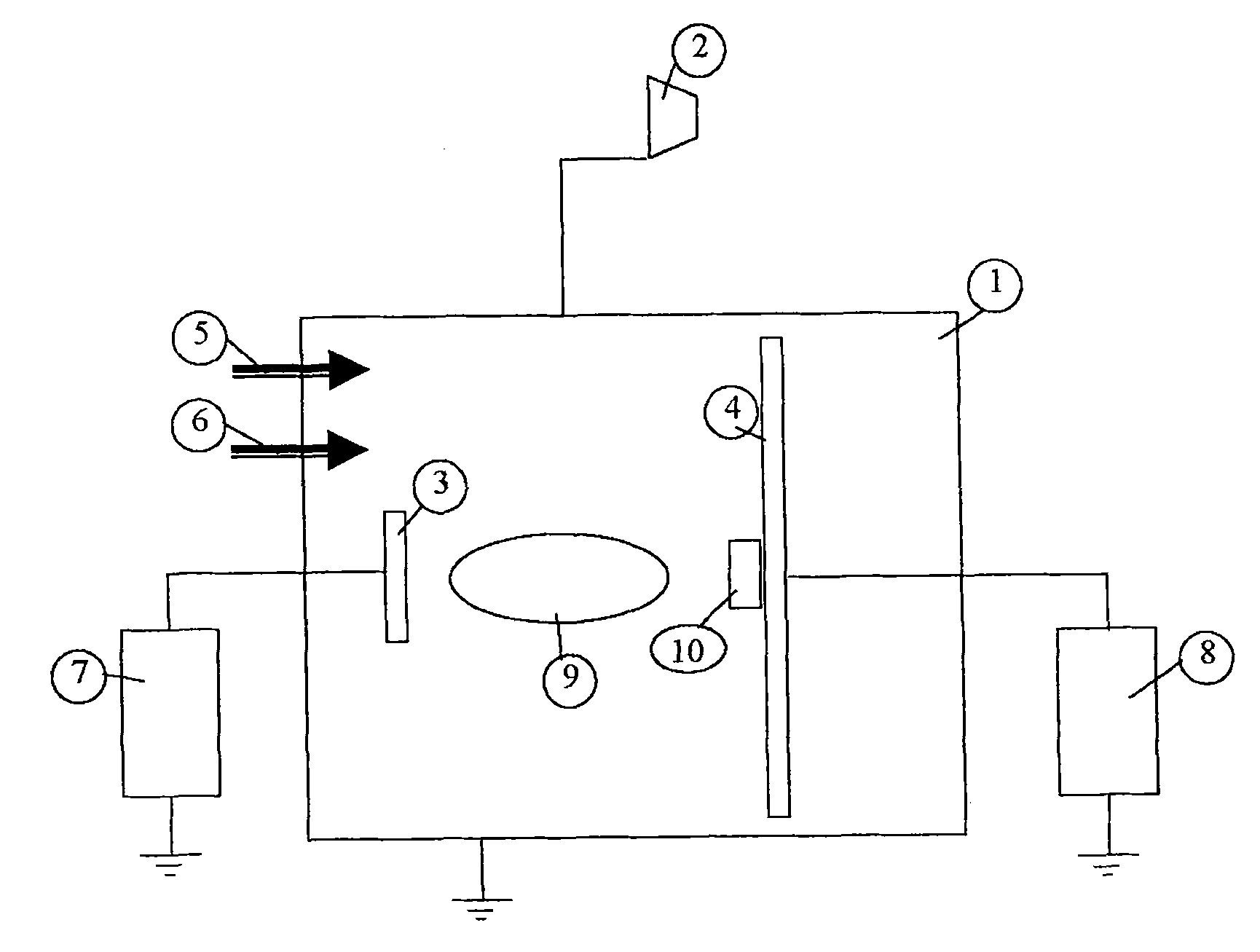
[0035] see figure 1 , cutting tool inserts of commercial grade H10F of composition WC10% Co and insert type SNUN1204 (dimensions 12x12x4 mm) were coated in an ultrahigh vacuum deposition system according to the following. Clean the blade (10) using standard procedures and place it on the base (4) operable to rotate during deposition with a 200cm 2 The area is at the position of about 10 cm above the magnetron sputtering target (3). The base (4) is electrically floating. The target (3) is an Al disk with a diameter of 50 mm and a thickness of 3 mm. Deposition was carried out in a vacuum chamber (1) which was first evacuated to 5×10 -7Torr. The blade (10) is heated to a surface temperature of approximately 600°C before deposition begins. Argon was used as sputtering gas, which was introduced into the chamber (1 ) via a first mass flow controller (5). A constant flow of 100 seem argon was used, which resulted in a total pressure of 6 mTorr in chamber (1).
[0036] Depositi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com