Method for efficiently and directionally screening biocontrol bacteria in soil-borne diseases of crops
A soil-borne disease, directional screening technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, bacteria, etc., can solve problems such as poor colonization ability of antagonistic bacteria, and achieve the goal of overcoming poor colonization ability, strong pertinence, The effect of avoiding waste of human and financial resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Screening of Antagonistic Bacteria of Cotton Verticillium Wilt by Plate Confrontation Method
[0038] Specifically include the following steps:
[0039] (1) Strain activation: 115 strains, such as the bacteria NCD-2 strain preserved at low temperature (preservation number: CGMCC1019, see patent number: ZL200310109619.8), were isolated from crop field soil bacteria (Plant Protection of Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences). The Institute collects and isolates from the whole country, mainly in Hebei Province. Partial bacterial strains are shown in Table 1) on NA plate culture medium at 37 DEG C of activation culture, pick single bacterial colony on NA slant culture medium and multiply at 37 DEG C; NA plate medium composition and proportion: beef extract 0.5%, peptone 1.0%, NaCl 0.5%, agar powder 1.5%, the rest is water, pH7.4.
[0040] (2) pathogenic bacteria cultivation: the cotton Verticillium dahliae Kleb strain (Verticillium dahliae Kleb) VD-1...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2 Detection test of the biofilm ability of antagonizing bacteria
[0049] Proceed as follows:
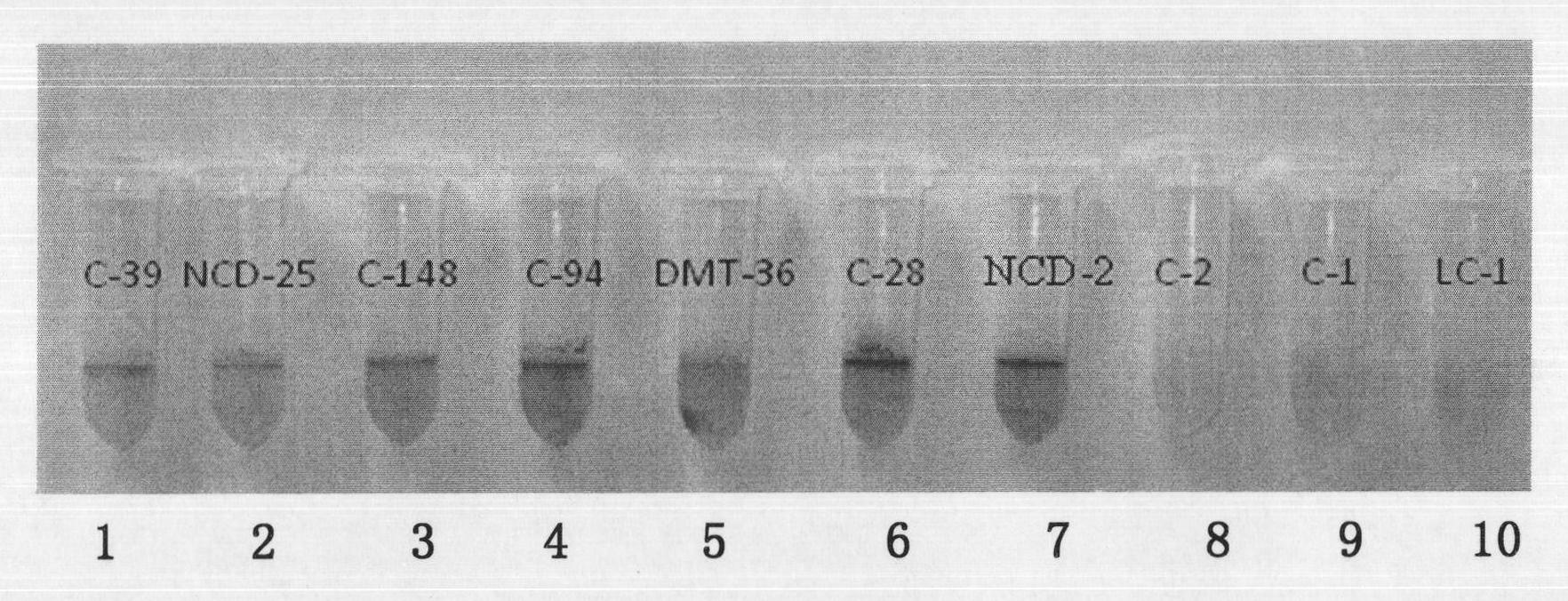
[0050] (1) Strain activation: the 17 strains of antagonistic bacteria screened in Example 1 were respectively activated on the NA plate medium, and a single colony was picked and multiplied on the NA slant medium;
[0051] (2) Bacterial strain liquid culture: 17 strains of antagonistic bacterial strains and 168 bacterial strains after picking up multiplication with sterile bamboo sticks are inoculated in DSM culture medium respectively (its composition and weight percent are: beef extract 1.0%, KCl 0.12 %, MgSO 4 .7H 2 O 0.00144%, Ca(NO 3 ) 2 0.00492%, MnCl 2 0.0000378%, FeSO 4 0.0000456%, the rest is water) and cultured overnight at 37°C. The next day, it was diluted with freshly prepared DSM medium at a ratio of 1:1000. Transfer 0.5ml to a new 2.0ml centrifuge tube, and culture at 37°C for 48h.
[0052] (3) Crystal violet staining: Add 550 μl of 0.1-0.3% ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Calcium Phytate Hydrolysis Ability Determination Test
[0055] The specific method is as follows:
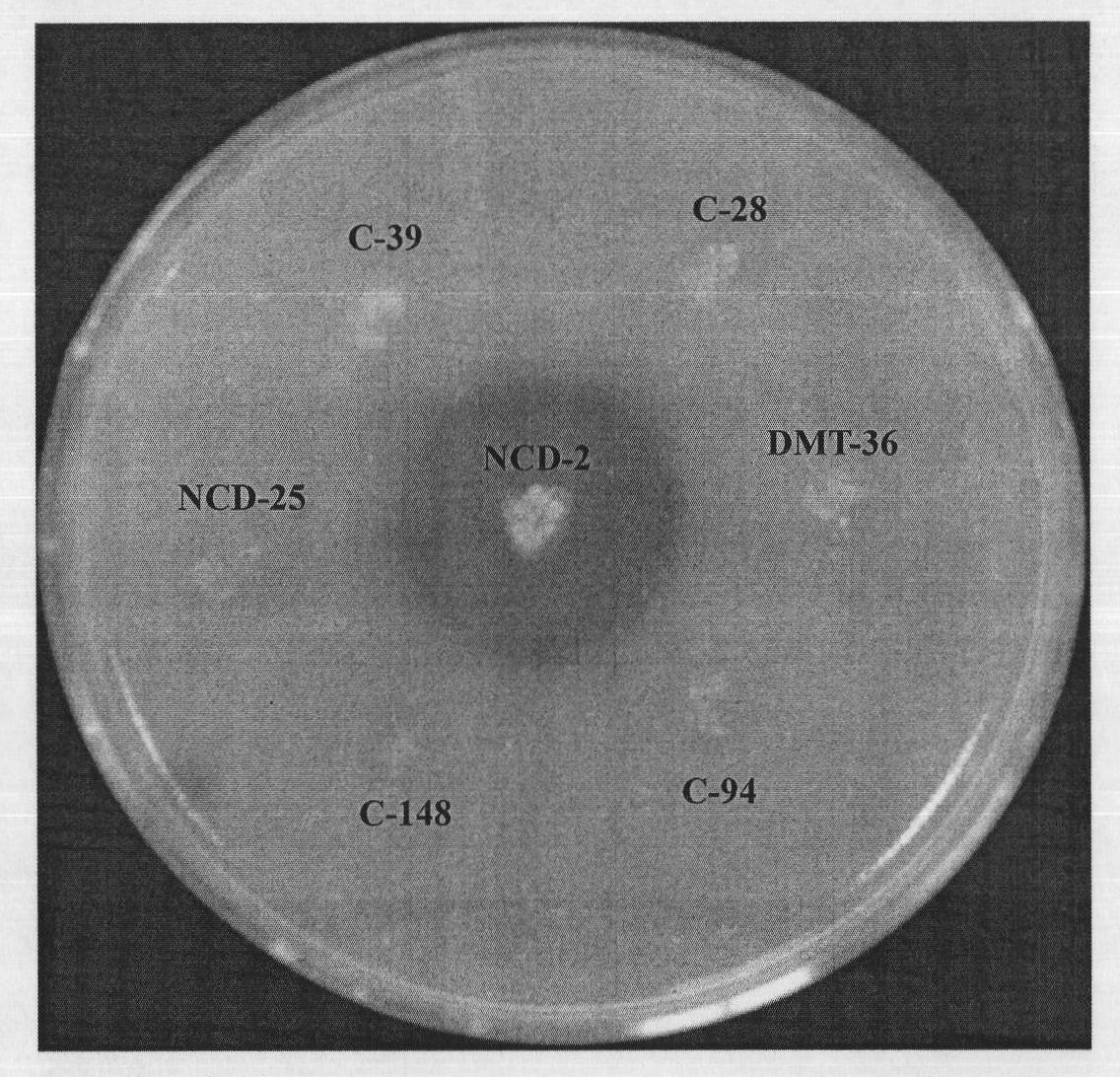
[0056] (1) Strain activation: the numbered NCD-2 and C-39, NCD-25, C-148, C-94, DMT-36, and C-28 bacterial strains screened out in the embodiment 2 of cryopreservation were respectively placed in Activate on NA plate medium, pick a single colony and multiply on NA slant medium;
[0057] (2) the above-mentioned 7 strains of bacterial strains for testing are connected to the phytase detection medium with sterilized toothpicks respectively (its composition and weight percentage are: sucrose 0.2%, KCl 0.2% g, MnSO 4 0.6%, NH 4 NO 3 0.4%, calcium phytate 8.0%, MgSO 4 0.7%, Fe2(SO 4 ) 3 0.7%, agar powder 4.0%, all the other are water; pH7.0), after 37 ℃ of cultivations for 5 days, it is found that only the NCD-2 bacterial strain has a large and transparent digestion circle on the phytase detection medium ( figure 2 ). It shows that the NCD-2 strain can sec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com