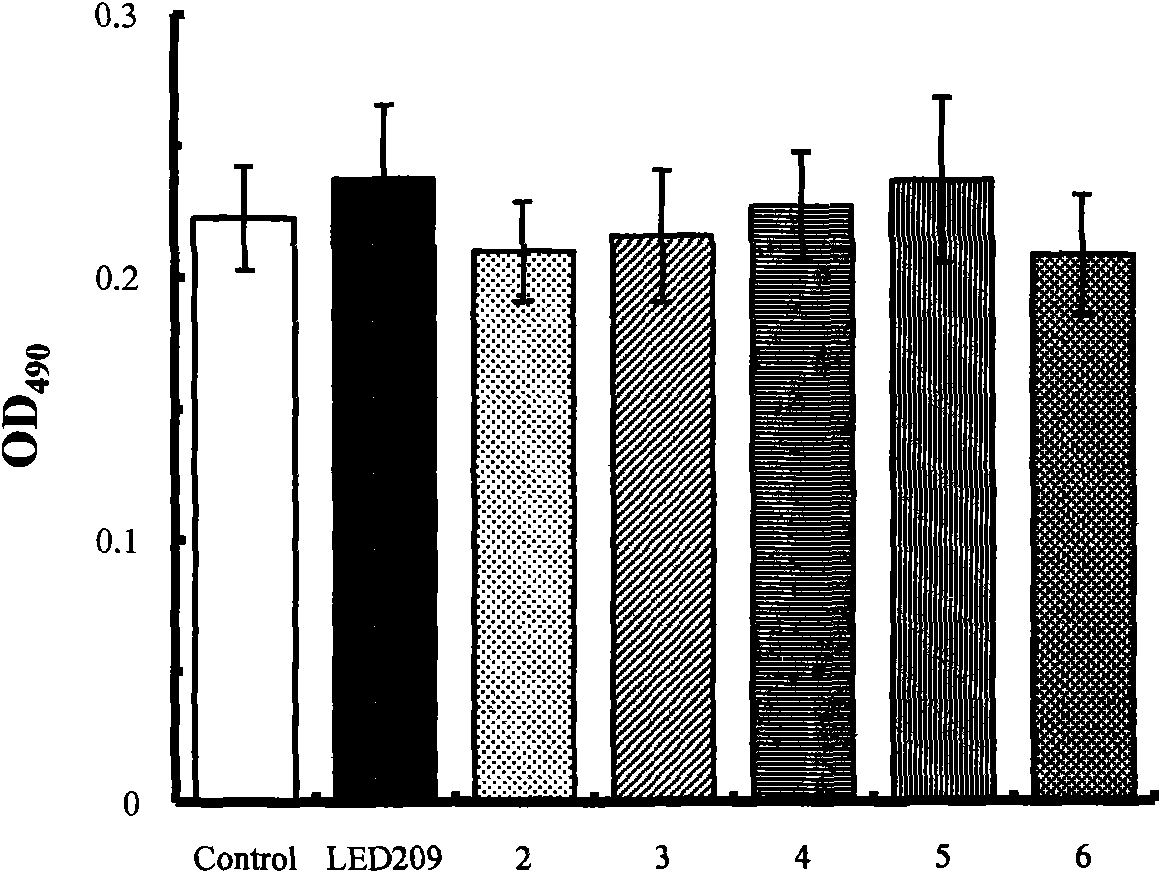
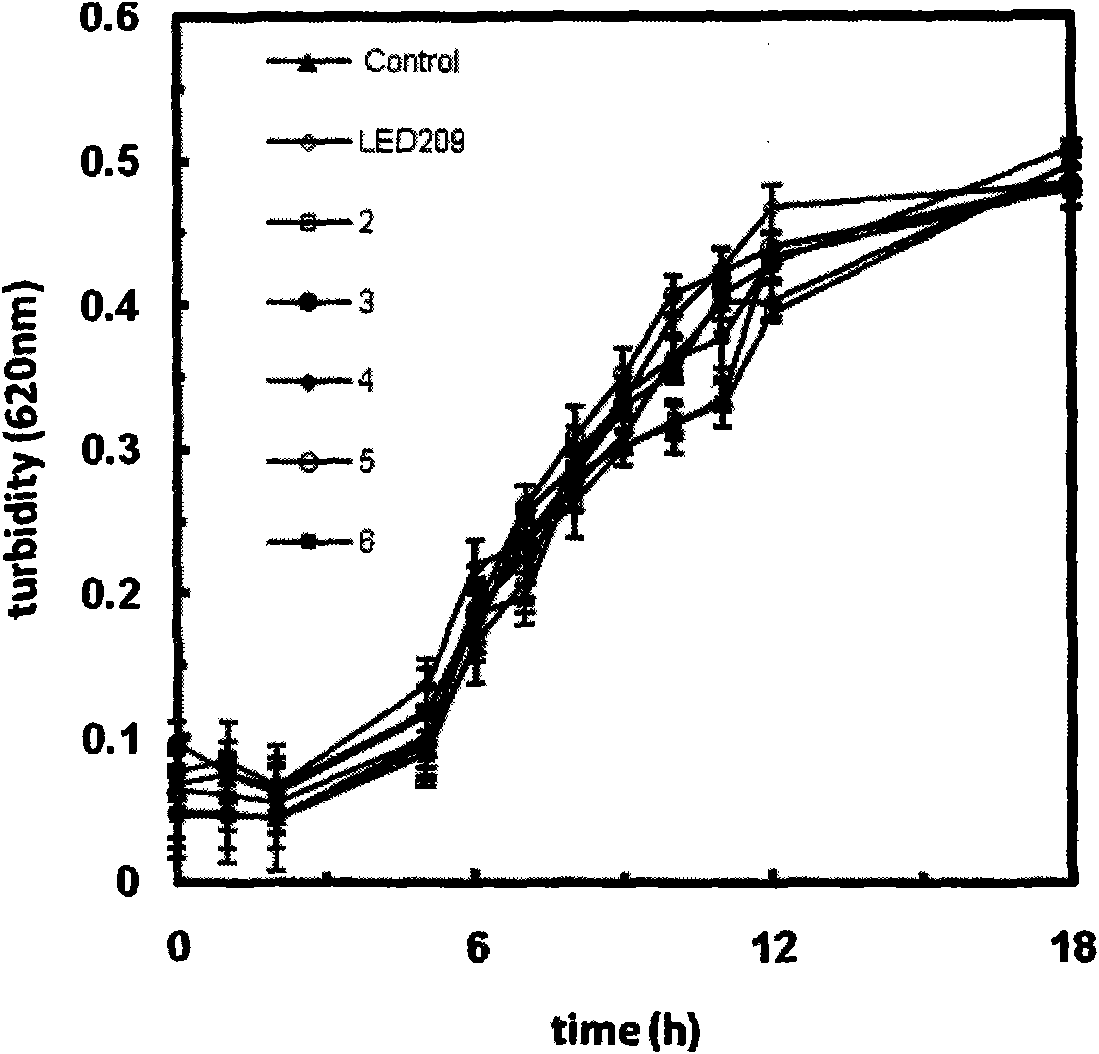
Synthetic method of QseC ligand derivatives with role of inhibiting bacterial virulence
A technology for inhibiting bacteria and derivatives, applied in antibacterial drugs, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high toxicity of compounds, poor water solubility, and limitations in clinical application, and achieve the effect of good reproducibility and simplified operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1 Preparation of N-(4-(N-phenylsulfamoyl) phenyl) acetamide
[0050] Add p-acetamidobenzenesulfonyl chloride (55g, 236mmol) in batches to a solution of sodium acetate (48.4g, 590mmol) and p-phenylenediamine (22mL, 200mmol) in ethanol (300mL) at 0°C, and stir overnight at room temperature The reactant was poured into ice water (1.5 L) and stirred vigorously for 1 h, and the precipitated white solid was collected by filtration, washed with ice water, dried in vacuo, and recrystallized from hot ethanol to obtain a white solid N-(4-(N-phenylsulfamoyl ) phenyl) acetamide (38 g, 60%);
Embodiment 2
[0051] Example 2 Preparation of 4-aminobenzenesulfonylanilide
[0052] Add anhydrous hydrochloric acid (6N, 40mL) to a solution of ethanol (80mL) in N-(4-(N-phenylsulfamoyl)phenyl)acetamide (20g, 55mmol) under stirring, heat to reflux for 3h, and decompress The reaction mixture was evaporated to dryness, the residue was dissolved in water, the pH value of the solution was adjusted to 8-9 with 1N ammonia water, stirred for 1 h, the precipitated white solid was collected by filtration, washed with ice water, dried in vacuum, recrystallized from hot ethanol to obtain a white solid 4 - Sulfonanilide (10 g, 65%).
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Preparation of N-phenyl-4-(3-phenylthioureido)benzenesulfonamide (i.e. compound 1)
[0054] Triethylamine (0.07 mL, 0.5 mmol) and phenylisothiocyanate (Ph-NCS, 2.1 mL, 11 mmol) were added to a solution of 4-aminobenzenesulfonanilide (2.48 g, 10 mmol) in dry acetone (30 mL) respectively , heated to reflux for 24 h, removed volatile substances in vacuum, and separated by flash silica gel column chromatography (n-hexane: acetone = 4: 1) to obtain white solid N-phenyl-4-(3-phenylthioureido)benzenesulfonate amides.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com